Physics Test 2
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Electric potential
defined as potential energy per unit charge: V=U/q. The unit of potential energy is the volt (v): 1 V =J/C
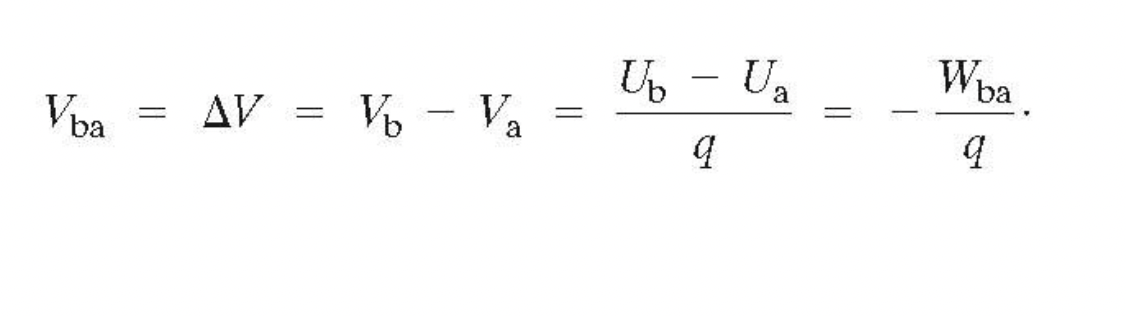
Only changes in potential can be measured, allowing for the assignment of ( V = 0 ) at any point.
Batteries and generators supply a constant potential difference
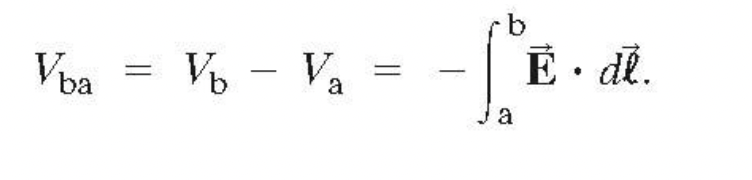
The general relationship between a conservative force and potential difference
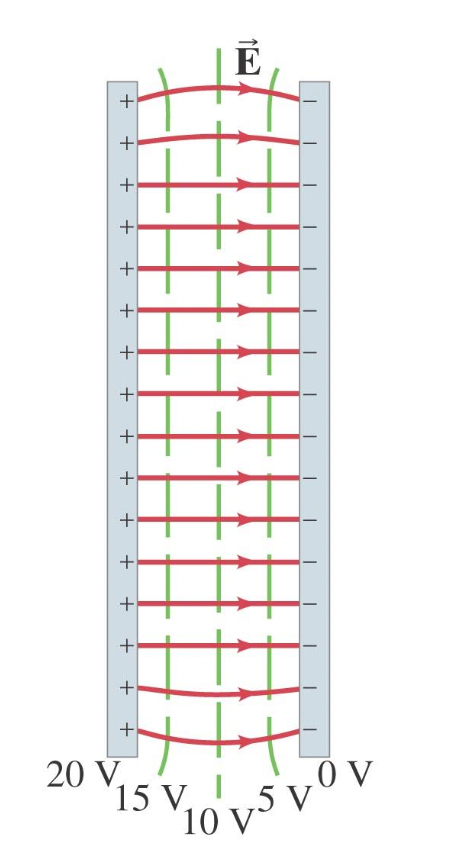
The simplest case is a uniform field: V=-Ed
Electric potential due to point charges
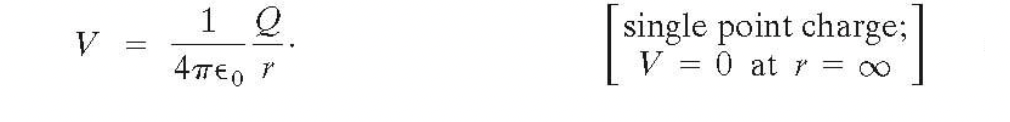
Potential due to any charge distribution
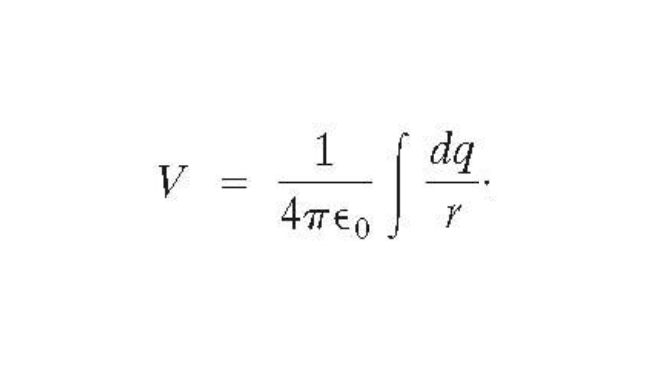
Equipotential Surfaces
a line or surface over which it is constant. The surface of a conductor is an equipotential. Electric field lines are always perpendicular to them
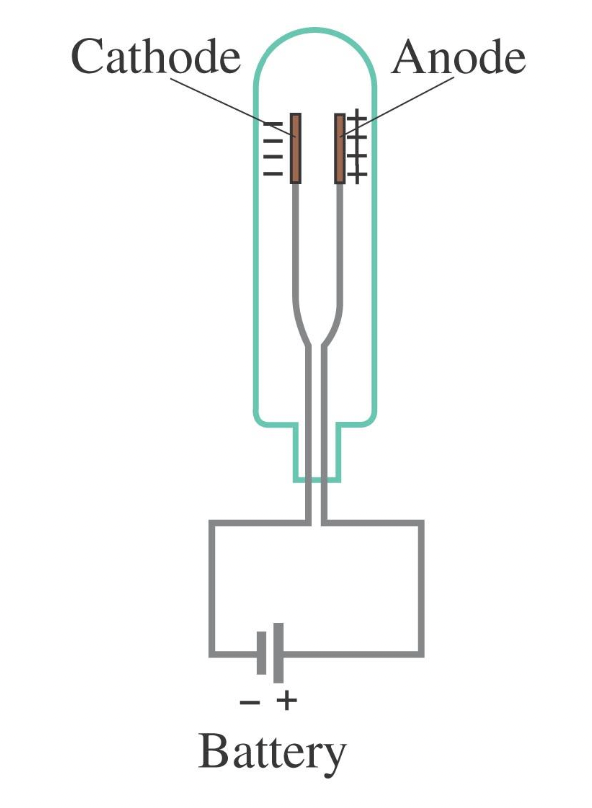
Cathode Ray tube
A cathode ray tube (CRT) uses a heated wire cathode to emit electrons, which are directed towards an anode by a voltage source.
The path of electrons can be manipulated using electric or magnetic fields.
CRTs are used in traditional televisions and computer monitors, while oscilloscopes display electrical signals by deflecting the electron beam.
A positive charge moves in a direction opposite to that of an electric field. What happens to the energy associated with the charge?
The electric potential energy of the charge increases, and the kinetic energy decreases
A negative charge moves in a direction opposite to that of an electric field. What happens to the energy associated with the charge?
The electric potential energy of the charge decreases, and the kinetic energy increases.
The electric potential at a certain distance from a point charge can be represented by V. What is the value of the electric potential at twice the distance from the point charge?
At twice the distance, the electric potential is V/2.
The electric potential at a certain location from a point charge can be represented by V. What is the value of the electric potential at the same location if the strength of the charge is tripled?
If you triple the value of the charge, the electric potential is 3V.
Capacitor
nontouching conductors carrying equal and opposite charge
Capacitance
Q=CV. The unit of capacitance is the farad (F)
Determination of capacitance
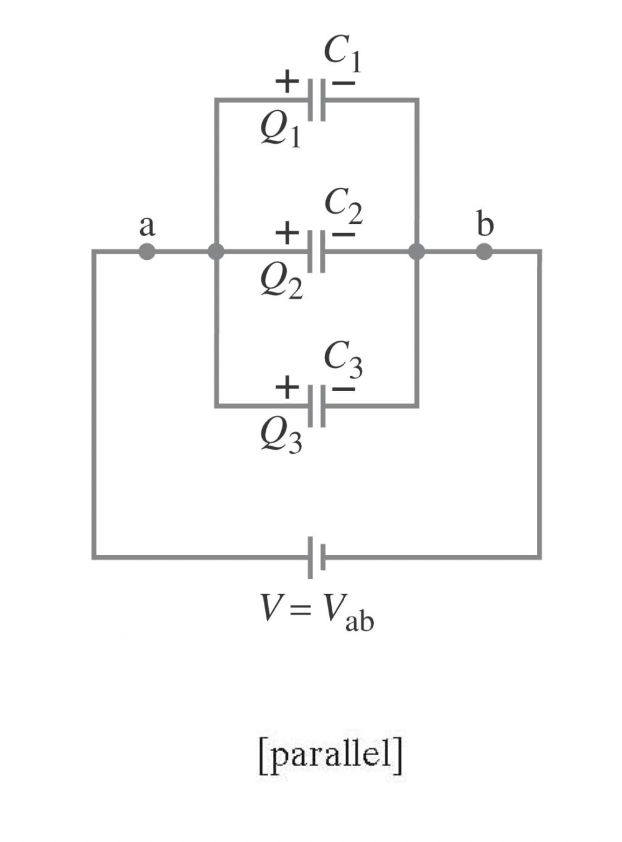
Capacitors in Parallel
have the same voltage across each one. The equivalent capacitor is the one that stroes the same charge when connected tot he same battery
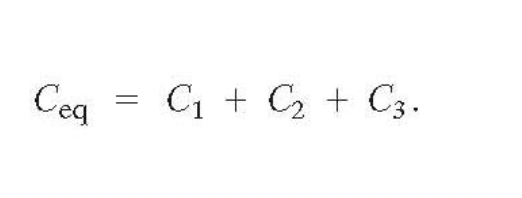
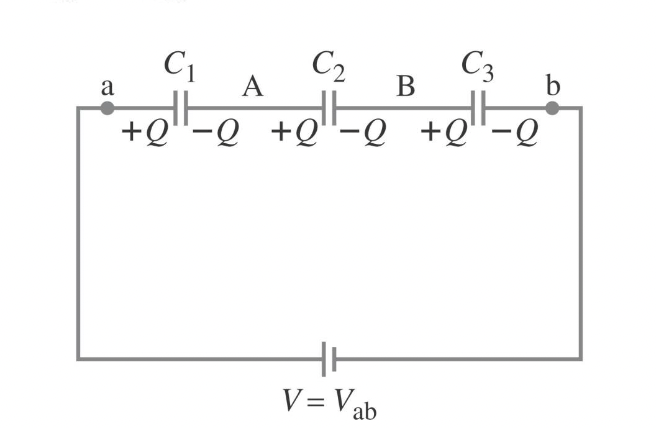
Capacitors in Series
have the same charge. The equivalent cpacitor has the same charge across the total voltage drop
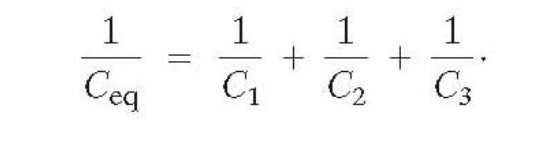
Electric Energy storage
A charged capacitor stores electric energy, the energy stored is equal to the work done to charge the capacitor
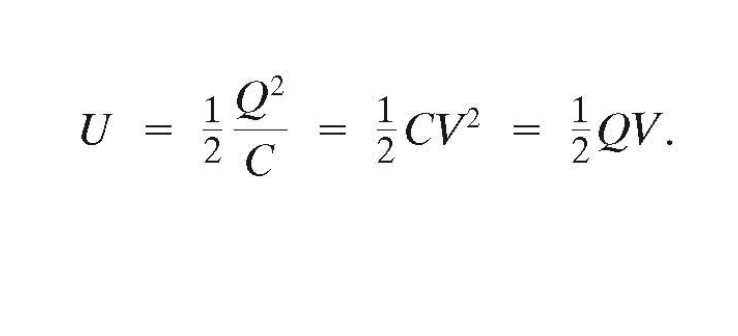
Energy density
*Note: sudden discharge of electric energy can be harmful since capacitors can retain their charge indefinitely even when disconnected
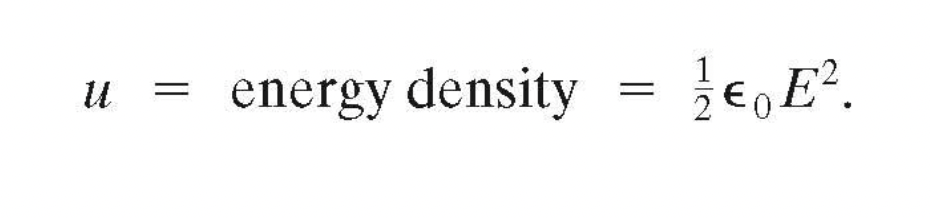
Dielectric
an insulator. The dielectric constant (K) gives ratio of the total field to the external field. Dielectric strength is the maximum field a dielectric can experience without breaking down.
Molecular description of dielectrics
when in an external electric field molecules become oriented in a way that reduces the external field

Capacitance of parallel plate capacitor w/ dielectric

Consider two capacitors with unequal capacitance connected in parallel to a battery. Which of the following statements are true?
The voltage across each of the capacitors is the same.
The sum of the charge stored on each capacitor is equal to the charge supplied by the battery.
The equivalent capacitance of the combination is greater than the capacitance of either of the capacitors.
Consider two capacitors with unequal capacitance connected in series to a battery. Which of the following statements are true?
The charge stored on each of the capacitors is the same.
The algebraic sum of the voltages across the two capacitors is equal to the voltage supplied by the battery.
The equivalent capacitance of the combination of the two capacitors is less than the capacitance of either of the capacitors.
Which of the following statements are true?
The capacitance of a capacitor depends upon its structure. |
The electric field between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor is uniform. |
A capacitor is a device that stores electric potential energy and electric charge. |
Which of the following will increase the capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor?
Decreasing the separation between the plates will increase the capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor.
Increasing the area of the plates will increase the capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor.
The plates of a parallel-plate capacitor are maintained with a constant voltage by a battery as they are pulled apart. How is the strength of the electric field affected during this process?
The strength of the electric field decreases during this process.
The plates of a parallel-plate capacitor are maintained with a constant voltage by a battery as they are pushed together, without touching. How is the amount of charge on the plates affected during this process?
The amount of charge on the plates increases during this process.
The voltage applied across a given parallel-plate capacitor is doubled. How is the energy stored in the capacitor affected?
The energy stored in the capacitor quadruples its original value.
A parallel-plate capacitor connected to a battery becomes fully charged. After the capacitor from the battery is disconnected, the separation between the plates of the capacitor is doubled in such a way that no charge leaks off. How is the energy stored in the capacitor affected?
The energy stored in the capacitor doubles its original value.
Which of the following statements are true?
The insertion of a dielectric material between the two conductors in a capacitor allows a higher voltage to be applied to the capacitor. |
The insertion of a dielectric material between the two conductors in a capacitor allows the plates of the capacitor to be placed closer together without touching. |
If a dielectric material, such as Teflon®, is placed between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor without altering the structure of the capacitor, how is the capacitance affected?
The capacitance increases because of the insertion of the Teflon®.
A dielectric material, such as Teflon®, is placed between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor without altering the structure of the capacitor. The charge on the capacitor is held fixed. How is the voltage across the plates of the capacitor affected?
The voltage decreases because of the insertion of the Teflon®. The electric field decreases.
Current flows through a resistor
From high potential to low potential
Which of the following will increase the resistance of a wire?
Increasing the length of the wire will increase the resistance of the wire.
Increasing the resistivity of the material the wire is composed of will increase the resistance of the wire.Decreasing the cross-sectional area of the wire will increase the resistance of the wire.