AAPC CPB Chapter 10 Review
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What is the first step in working a denied claim?
a. Resubmit the claim
b. Contact the carrier
c. Appeal the claim
d. Determine and understand why the claim was denied
d. Determine and understand why the claim was denied
The first step in working a denied claim is to understand why the claim has denied. Insurance carriers will use different denial codes on the remittance advice.
Which of the following is a statement sent to the patient from the insurance carrier explaining services paid for on their behalf?
a. Remittance Advice
b. Patient Statement
c. Explanation of Benefits
d. Patient Ledger
c. Explanation of Benefits
An Explanation of Benefits (EOB) is a statement sent by an insurance carrier to the covered individuals explaining what medical treatments and/or services were paid ro denied on their behalf.
Which are the two main types of Bankruptcy seen by medical practices and facilities?
a. Chapters 7 & 13
b. Chapters 11 & 13
c. Chapters 12 & 15
d. Chapters 7 & 15
a. Chapters 7 & 13
There are two main chapters of bankruptcy seen in medical practices and facilities:Chapter 7—Liquidation.
Chapter 13—Adjustment of Debts of an Individual with Regular Income.
Can a patient be refused treatment due to ability to pay for service?
a. No, a patient can never be refused treatment.
b. Yes, a provider can refuse to see any patient for any reason.
c. Yes, a provider can refuse to see a patient if it is not an emergency situation.
d. Yes, if a patient owes more than $5,000.
c. Yes, a provider can refuse to see a patient if it is not an emergency situation.
According to the Federal Emergency Medical Treatment and Active Labor Act (EMTALA), 42 U.S.C. § 1395, which is a separate section of the more comprehensive 1985 Consolidated Omnibus Reconciliation Act (COBRA), mandates minimum standards for emergency care. A patient cannot be refused treatment for emergency care; however, a physician can refuse patients for non-emergency, routine care.
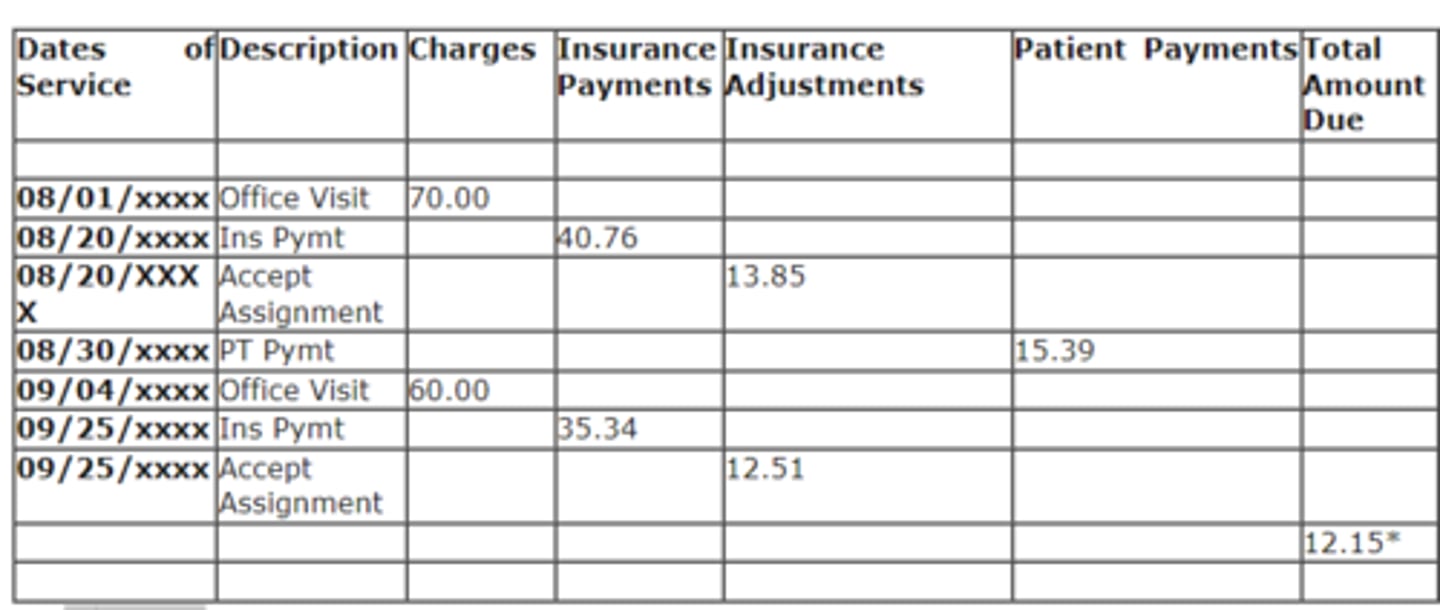
Based on this statement how much was the accept assignment write off amount for the two dates of service?
a. $130.00
b. $76.10
c. $26.36
d. $27.54
c. $26.36
Based off of the statement above the accept assignment write-off's are $13.85 and $12.51 which total $26.36.
Which federal act states that third-party debt collectors are prohibited from employing deceptive or abusive conduct in the collection of the debt?
a. Fair Credit and Charge Card Disclosure Act
b. Truth in Lending Act
c. Fair Credit Reporting Act
d. Fair Debt Collection Practices Act
d. Fair Debt Collection Practices Act
Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (FDCPA) states that third-party debt collectors are prohibited from employing deceptive or abusive conduct in the collection of consumer debts incurred for personal, family, or household purposes.
Which denial is when the patient is covered under another insurance?
a. Coordination of benefits
b. Timely filing
c. Incorrect information
d. Non-covered service
a. Coordination of benefits
Coordination of Benefits—If a patient is covered under more than one insurance plan one plan will be primary and the other is secondary.
Which is the best way to handle a denial for incorrect information?
a. Do nothing and resubmit the claim
b. Review the information, make sure it's correct and if it matches resubmit the claim
c. Contact the insurance company and the patient to figure out where the error is and get it corrected
d. Bill the patient and let them figure out what's wrong
c. Contact the insurance company and the patient to figure out where the error is and get it corrected
When a denial for incorrect information is received it is important to review the information to see if an error was made. If the information submitted matches the information that you have then there is a problem somewhere. Contact the insurance payer and/or the patient for updated information.
What is a lower level of care denial?
a. Service coded at a higher level than documentation supports
b. Care provided on an inpatient basis is typically provided on an outpatient basis
c. Outpatient procedure could have been done in the provider's office
d. Both b and c
d. Both b and c
"Lower level of care" is a denial that applies when the following occurs:
Care provided on an inpatient basis is typically provided on an outpatient basis
Outpatient procedure could have been done in the provider's office
Skilled nursing care could have been performed by a home health agency
Which of the following is the highest level of the appeals process of Medicare?
a. Reconsideration
b. Judicial Review
c. Appeals Council
d. Administrative Law Judge
b. Judicial Review
The final level of appeal for Medicare is to request a Judicial Review in Federal District Court. The threshold for review in federal district court is updated annually. A request must be made within 60 days of receipt of the Medicare Appeals Council's decision.
Using the information in the 2023_MBT_CPB_PA_Student_Ch10_Case 1.pdf, answer questions 1 and 2.
Based on the remittance advice and the payment policy provided, what action is required for this claim?
a. The claim was paid correctly. Minor surgeries are not paid when performed with an E/M.
b. The claim was paid correctly. The diagnosis does not support both an E/M code and a procedure.
c. The claim did not pay correctly. The E/M service should be paid at 100% and the surgical procedure should be discounted.
d. The claim did not pay correctly. The E/M service should be paid at 50% and the surgical procedure should be paid at 100%.
c. The claim did not pay correctly. The E/M service should be paid at 100% and the surgical procedure should be discounted.
Because the E/M value is greater than the procedure, the E/M code should be paid at 100% and the surgical procedure should be paid at 50%.
What is the appropriate action to take to address this denial?
a. Post the denial reason, write off the amount of the surgical procedure as inclusive, and write off the balance as the patient balance is too small to send a statement.
b. Post the denial reason and send a statement to the patient for the surgical procedure.
c. Post the denial reason, write off the amount of the surgical procedure as inclusive, and send a statement to the patient if the copayment was not collected.
d. Submit an appeal with the medical record, the health plan policy, and a copy of the claim.
d. Submit an appeal with the medical record, the health plan policy, and a copy of the claim.
According to the AAPC Health Plan Payment Policy, the E/M should be paid at 100% and the procedure should be paid at 50%. An appeal should be sent to the insurance carrier including the medical record to show the procedure was separately identifiable from the E/M code along with the health plan's policy
Use the information in the 2023_MBT_CPB_PA_Student_Ch10_Case 2.pdf to answer questions 3 and 4.
Review the remittance in Case 2, should this claim be appealed?
a. No; timely filing has past.
b. Yes; the second and third procedures on the claim were underpaid.
c. Yes; the third procedure on the claim was underpaid.
d. No; the second and third procedures had the multiple procedure reduction properly applied.
c. Yes; the third procedure on the claim was underpaid.
The multiple procedure discount was properly applied to the second procedure, but not properly applied to the third procedure. When multiple procedures are performed during the same session, the first procedure is reimbursed according to AAPC Health Plan 's payment policy, the second procedure is reimbursed at 50% of the allowed amount because of the multiple procedure discount. Even though the third procedure was performed during the same session, it is independent from the other procedures as identified by the ICD-10-CM code and modifier 59. The third procedure is to be reimbursed according to AAPC Health Plan 's payment policy with no reduction.
Use the information in the 2023_MBT_CPB_PA_Student_Ch10_Case 2.pdf to answer the following question.
How is the multiple surgery reduction applied when four procedures are performed with no modifier 59?
a. The allowed amount for all the procedures is added together and the total is paid at 150%.
b. The allowed amount for all the procedures is added together and the total is paid at 50%.
c. The procedure with the highest allowed amount is paid at 100% and the additional line items are paid at 50%.
d. The procedure with the highest allowed amount is paid at 100%, the next highest allowed amount is paid at 50%, and all other line items are paid at 25%.
d. The procedure with the highest allowed amount is paid at 100%, the next highest allowed amount is paid at 50%, and all other line items are paid at 25%.
According to the multiple procedure discount identified, the procedure with the highest allowed amount is paid at 100%, the next procedure with the highest allowed amount is paid at 50%, the third procedure with the highest allowed amount is paid at 25%, and the fourth procedure with the highest allowed amount is paid at 25%. If there are more than four procedures performed, each one after four will also be paid at 25% of the allowed amount.
Review the remittance advice and NCCI table provided above. The documentation has been sent to the coding department and the coding department verified that documentation does not support the addition of a modifier. Should the claim be appealed?
a. No, 92250 is inclusive to 92134. This claim is processed correctly.
b. Yes, both procedures should be paid at 100%.
c. Yes, the first procedure should be paid at 100% and the second at 50%.
d. No, because claims denied due to NCCI edits cannot be appealed.
a. No, 92250 is inclusive to 92134. This claim is processed correctly.
92250 is the column two code; therefore, according to the NCCI edits provided, 92134 is paid and 92250 is denied correctly.
The office policy for claims follow-up is to prioritize the insurance accounts past 90 days by highest outstanding balance. Based on the A/R report provided, which payer type and aging category would be one of the top priorities on which to focus collection efforts to have the biggest positive impact on revenue?
a. Self pay, 181-210 days
b. HMO, 121-150 days
c. Medicaid, 181-210 days
d. Medicare Advantage, 91-120 days
a. Self pay, 181-210 days
Focusing collection efforts on the insurance category with the highest outstanding balance will have the highest impact on revenue for the office.
Which of the following are best practices to reduce A/R?
I. Verify patient insurance for every encounter.
II. Submit clean claims electronically.
III. Check status reports daily for suspended claims by the clearinghouse.
IV. Refund negative balances.
V. Post contractual adjustments when the claim is transmitted.
VI. Write off the balance when a denial is received.
VII. Rebill all claims if payment is not received within 30 days.
a. I, II, and III
b. I, II, III, IV, and V
c. I, II, III, IV, and VII
d. All of the options are correct.
a. I, II, and III
Best practices to reduce A/R include verifying patient insurance at every encounter which will allow submitting clean claims electronically, and checking status reports daily to identify suspended claims by the clearinghouse. Identifying suspended claims will allow the correction and resubmission of claims while they're still in current status.
Case 5 is a sample aging report containing accounts with an outstanding balance. The office policy is to follow up on the oldest accounts first. Following the office policy, which statement below is true?
a. Follow up with Bradley Browne's HMO insurance because his account has the largest outstanding balance. It appears that Bradley paid his copayment, but the HMO insurance hasn't paid their portion.
b. Follow up with Breanna Browne since she is a self-pay account with an outstanding balance.
c. Follow up with Aetna on Chandler Brown's outstanding balance. Even though his account has the smallest balance, his account is the oldest and that's following office policy.
d. Follow up with Medicaid on Alicia Browne. Medicaid has a timely filing deadline and if they haven't received her claim, it will be important to resubmit it.
c. Follow up with Aetna on Chandler Brown's outstanding balance. Even though his account has the smallest balance, his account is the oldest and that's following office policy.
An employee must be compliant and follow office policy. The first step is to identify Chandler Brown as having the oldest outstanding account balance. Since there isn't a payment on his account, the second step is to place a phone call to Aetna to make sure the claim has been received, and then to identify why it hasn't been paid.
Tracking insurance claims submitted to third-party payers is the responsibility of the insurance biller. From the list below, which is the most important activity that a biller can do to ensure that claims are processed and paid in a timely manner?
a. Keep a paper or electronic copy of each claim submitted.
b. Document information in the practice management system about claims submitted.
c. Review the remittance advice to be sure the claim was processed correctly, and that accurate payment was received.
d. All the above activities are equally important.
d. All the above activities are equally important.
It is important that the medical biller be organized. Printing an aging report around the same time each month using the practice management software, and following up on accounts with an outstanding balance is vital for the financial status of the medical practice. Most accounts with an outstanding balance will have a shared responsibility between the insurance carrier and the responsible party on the patient's account. The older an account becomes the more difficult it may become to get it resolved.
Case 6 is a sample aging report containing accounts with an outstanding balance. The office policy is to follow up on the oldest accounts. Following the office policy, which statement below is true?
a. Follow up with Stephanie Taylor. This is a self-pay account and this one has the largest outstanding balance.
b. Follow up with Aetna. This account shows a payment was made but the balance continues to be outstanding.
c. Follow up with Medicare on Dee Taylor's outstanding balance. Even though her account has the smallest balance, her account is the oldest.
d. Follow up with Humana on Albert Taylor.
c. Follow up with Medicare on Dee Taylor's outstanding balance. Even though her account has the smallest balance, her account is the oldest.
An employee must be compliant and follow office policy. The first step is to identify Dee Taylor as having the oldest outstanding account balance. The second step is to place a phone call to Medicare and identify if an additional payment is pending.
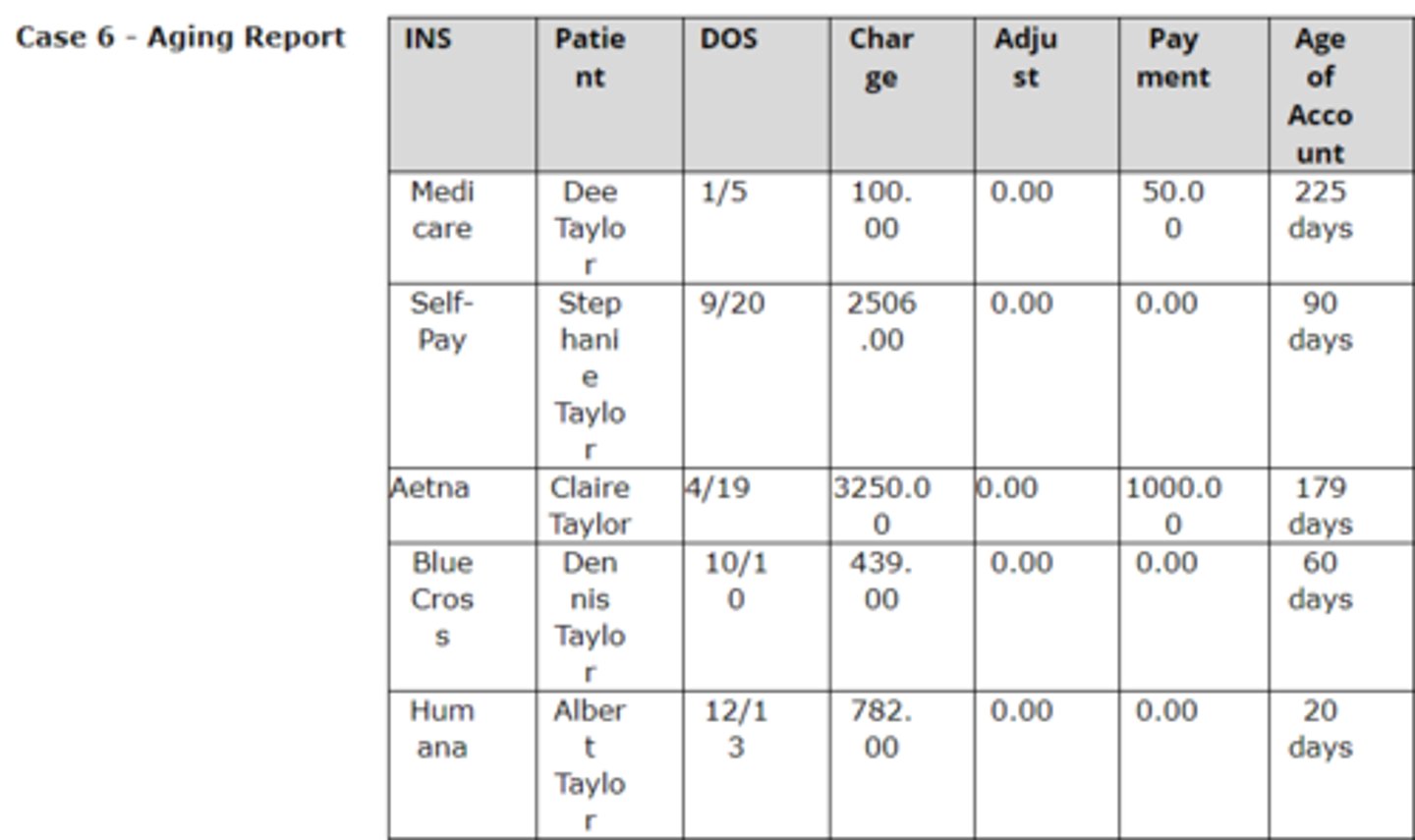
Case 7 is a sample aging report containing accounts with an outstanding balance. After many attempts to receive payment from BlueCross, the office has been unsuccessful. BlueCross continues to deny the claim. What is the first step the office should take in filing an appeal with Blue Cross?
a. Follow up with the patient (Robert Flores) asking if he has received anything in the mail regarding payment from BlueCross.
b. Write a letter to BlueCross asking for an explanation on payment.
c. Continue to wait in hopes that BlueCross will correct the issue.
d. Download the Claims Review Form and submit for review/appeal.
d. Download the Claims Review Form and submit for review/appeal.
Download the Claims Review Form, complete and send to BlueCross. The office can also follow up by phone.
Based on the remittance advice and the payment policy provided, what action is required for this claim?
a. The claim was paid correctly. Only one service can be paid for each visit.
b. The claim was paid correctly. The diagnosis does not support both an E/M code and a procedure.
c. The claim did not pay correctly. The E/M service should be paid at 100% and the radiological procedure should be discounted.
d. The claim did not pay correctly. The E/M service should be paid at 50% and the radiological procedure should be paid at 100%.
c. The claim did not pay correctly. The E/M service should be paid at 100% and the radiological procedure should be discounted.
Because the E/M value is greater than the procedure, the E/M code should be paid at 100% and the radiological procedure should be paid at 50%.
What is the appropriate action to take to address this denial?
a. Post the denial reason and write off the amount of the injection procedure as inclusive.
b. Post the denial reason and send a statement to the patient for the injection procedure.
c. Post the denial reason, write off the amount of the injection procedure as inclusive, and send a statement to the patient if the copayment was not collected.
d. Appeal the denial.
d. Appeal the denial.
The claim was denied inclusive; however, according to the policy for modifier 25 and the bundling edits, the vaccine administration and vaccine should be payable. The denial should be appealed.
Based on the remittance advice and the payment policy provided, what action is required for this claim?
a. The claim was paid correctly. Only one service is paid per day.
b. The claim was paid correctly. The diagnosis does not support both an E/M code and a procedure.
c. The claim did not pay correctly. The E/M service should be paid at 100% when procedures are performed.
d. The claim did not pay correctly. The E/M service should be paid at 50% and the surgical procedure should be paid at 100%. Also, the diagnosis does not support both an E/M code and a procedure.
d. The claim did not pay correctly. The E/M service should be paid at 50% and the surgical procedure should be paid at 100%. Also, the diagnosis does not support both an E/M code and a procedure.
Based on the codes submitted, the EM should be paid at 50% when procedures are performed, and the procedure performed should be paid at 100%. Also, the diagnosis code Z23 (Encounter for immunization) does not support both the E/M code and the procedure code.
Review the following financial policy:Collections Policy:Invoices not paid within 60 days begin our collection process. Invoices not paid within 120 days are subject to patient dismissal and submission to our Collection Agency and notification to your insurance plan.
According to this policy, at what age is a balance owed by the patient considered a bad debt and sent to their collection agency?
a. 365 days
b. 120 days
c. 60 days
d. 30 days
b. 120 days
Rationale: Invoices not paid within 120 days are subject to patient dismissal and submission to our Collection Agency and notification to your insurance plan.
Which statement is TRUE regarding denials?
a. Denials for not timely filing cannot be appealed.
b. Denials should be reviewed to determine whether additional information is needed, if errors need to be corrected, or if the denial should be appealed.
c. Denials for lack of medical necessity cannot be appealed.
d. All denials should be written off in the practice management system. If appealed and paid, the balance can be reversed.
b. Denials should be reviewed to determine whether additional information is needed, if errors need to be corrected, or if the denial should be appealed.
Rationale: Denials or reimbursement problems should be worked as soon as they are received from the insurance carriers. Each denied claim should be reviewed to determine whether additional information is needed, if errors need to be corrected, or if the denial should be appealed. These denials will be identified when posting the payments, reviewing the remittance advices, and on aging reports.
What documents are needed for a successful appeal?
a. Copy of the medical record, a letter detailing why the claim should be paid, and a statement from the patient.
b. Copy of the RA, copy of the medical record, copy of the original claim, and a letter detailing why the claim should be paid.
c. Copy of the RA, encounter form, medical record, and a letter detailing why the claim should be paid.
d. The original RA, copy of the medical record, encounter form, and a statement from the patient.
b. Copy of the RA, copy of the medical record, copy of the original claim, and a letter detailing why the claim should be paid.
Rationale: The following documents are needed to successfully appeal a denied claim:· Copy of the remittance advice for the denied claim· Copy of the medical record (supporting documentation)· Copy of the original claim· Letter (or form specified by the insurance carrier) detailing why the claim should be paid
Review the following Accounts Receivable Policy:1-Insurance balances will be referred to internal follow-up staff for follow-up at 45 days post initial claim. The collection services department becomes responsible for all balances as soon as the charge is entered. 2-After 45 days, internal follow-up staff will work the largest balances first.
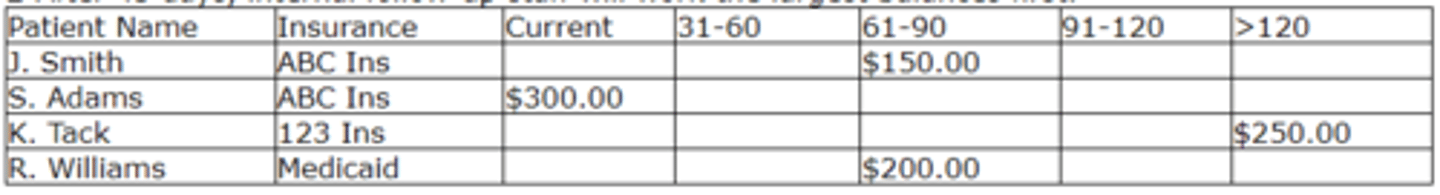
According to the above policy, which account should be worked first?
a. R. Williams
b. J. Smith
c. S. Adams
d. K. Tack
d. K. Tack
Rationale: The policy indicates insurance balances should be worked after 45 days, starting with the largest balances first. In this case, K. Tack has the largest balance that is over 45 days.
Review the following payment policy:
Payment arrangements are acceptable under the following terms:
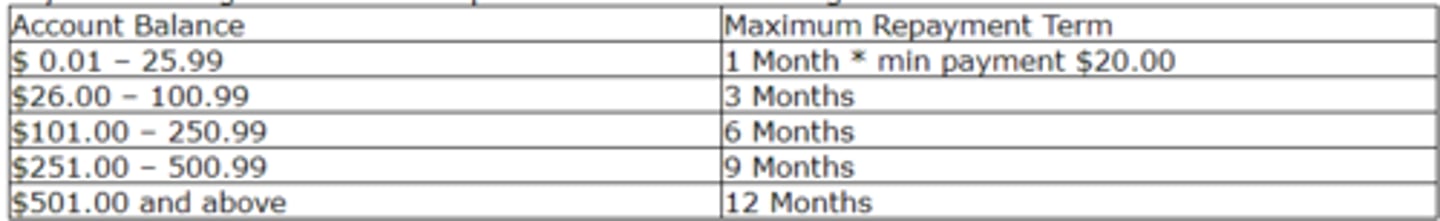
What is the monthly payment a patient will need to make for a total patient balance of $150.00?
a. $75.00
b. $100.00
c. $20.00
d. $25.00
d. $25.00
Rationale: According to the policy, a patient with a balance of $101.00 - $250.99 will have six months to repay the balance. $150.00 divided by 6 equals $25.00/month.
Which statement is TRUE about a patient's insurance?
a. Verification of coverage should happen once per year.
b. Once you have a patient's insurance information it is up to the patient to let you know when it changes.
c. Insurance coverage can only change at the beginning of a year and it is good for the remainder of the year.
d. Verification of coverage should happen at each visit.
d. Verification of coverage should happen at each visit.
Rationale: The patient's insurance coverage should be verified each time a patient is seen. The patient may present an insurance card, but that does not mean that they are insured. Changes in coverage are common. A patient may change insurance plans or the copayments and deductibles may change. Prior to treatment, the insurance carrier should be contacted to verify coverage and the amount to be collected from the patient.
Which Chapter of the U.S. Bankruptcy Code combines the debt of the debtor and reduces the monthly payments allowing a potential for a provider to receive a portion of what is owed?
a. Chapter 7
b. Chapter 9
c. Chapter 11
d. Chapter 13
d. Chapter 13
Rationale: Chapter 13 - Adjustment of Debts of an Individual with Regular Income. The debts owed by the debtor are combined and the monthly payment is potentially reduced for the debtor. Under this filing, a provider or facility has the potential to receive a portion of the debt owed. Instructions for filing a claim against the bankruptcy are found on the back of the bankruptcy notice.
A claim has been denied as not medically necessary by Medicare. The biller has checked the patient's medical record and the patient's insurance policy. No ABN was signed. What is the next action the biller should take?
I. Write-off the charge
II. Check with the provider to appeal the claim
III. Transfer the charge to the patient's account
a. I or II
b. I
c. II or III
d. III
a. I or II
Rationale: Medicare has determined, based on information (procedure and diagnosis code(s)) submitted on the claim, that the procedure was not medically necessary. When a claim is denied due to lack of medical necessity, if the information was reported correctly, the provider can either appeal the claim or write off the amount. If the patient has signed an ABN prior to the procedure, the balance may be transferred to patient responsibility.
What steps should be taken when a medical office receives notice that a patient has filed bankruptcy?
a. Obtain the case number, verify the case filing, verify the provider is listed as a creditor, and stop all collection efforts for balances filed under the bankruptcy.
b. Stop all collection efforts and dismiss the patient from the practice.
c. Dismiss the patient from the practice and send any outstanding balances to a collection agency.
d. Obtain the case number and write-off all patient and insurance balances on the patient's account.
a. Obtain the case number, verify the case filing, verify the provider is listed as a creditor, and stop all collection efforts for balances filed under the bankruptcy.
Rationale: When a medical provider or facility receives notice that a patient has filed for bankruptcy, the following steps should be taken:· If notice is received from the patient, ask for the case number. If a notice is received from the bankruptcy court, the case number will be on the notice.· Verify the case filing with the bankruptcy court.· Verify the medical provider or facility is listed as a creditor.For providers listed as a creditor, stop all collection efforts on balances incurred prior to the filing of bankruptcy. The provider or facility may continue to collect balances due from the insurance carriers.
Review the following Accounts Receivable Management Policy:1-Insurance claims will be created daily for manual and electronic filing. This should ensure that all insurance claims are submitted within two days of charge entry.2-Guarantor statements will be created weekly to ensure timely initial billing of personal balances. Patients will receive one statement per month for personal balances. Each charge on which there is an unpaid personal balance will be billed a minimum of three times.3-Insurance balances will be referred to internal follow-up staff for follow-up at 45 days post initial claim, and personal balances will be referred at the time the patient becomes responsible for payment. The collection services department becomes responsible for all balances as soon as the charge is entered.4-Personal balances will be eligible for referral to an outside collection agency after three statements have been sent.
Based on this policy, when does follow-up of insurance balances begin?
a. 45 days post initial claim.
b. After three claims have been sent.
c. Within two days of charge entry.
d. 60 days post initial claim.
a. 45 days post initial claim.
Rationale: According to this policy, insurance balances will be referred to internal follow-up staff for follow-up at 45 days post initial claim.
Which act protects information collected by the consumer reporting agencies?
a. Fair Credit Reporting Act
b. Fair Debt Collection Practices Act
c. Truth in Lending Act
d. Equal Credit Opportunity Act
a. Fair Credit Reporting Act
Rationale: Fair Credit Reporting Act - protects information collected by the consumer reporting agencies such as the credit bureaus, medical information companies, and tenant screening services. Organizations that provide information to consumer reporting agencies also have specific legal obligations including the duty to investigate disputed information.
When a provider wants to give a discount on services to a patient, which option is acceptable?
a. The provider can waive the co-payment at his discretion.
b. The provider cannot discount the charge under any circumstance.
c. The provider can accept insurance only payments and write-off all patient balances.
d. The provider must discount the charge prior to billing the insurance carrier.
d. The provider must discount the charge prior to billing the insurance carrier.
Rationale: A provider who practices routine write-offs of co-payments and deductibles is at risk of violating insurance carrier contracts or federal and state laws. When a patient covered by insurance is offered a discount at the time of service, often referred to as a prompt payment discount, the insurance carrier must also be offered the same discount.
How often should the patient's insurance coverage be verified?
a. once a month
b. once a year
c. at the initial visit and when the insurance coverage changes
d. every visit
d. every visit
Rationale: The patient's insurance coverage should be verified every time a patient is seen. The patient may present an insurance card, but that does not mean that they are insured. Changes in coverage are common. A patient may change insurance plans or the copayments and deductibles may change. Prior to treatment, the insurance carrier should be contacted to verify coverage and the amount to be collected from the patient. This can be done through phone calls, the insurance carrier's website, or through the clearinghouse.
Review the following financial policy:Financial Policy:You are responsible for paying all co-payments at the time of service. Co-payments, co-insurance, deductibles, and non-covered services cannot be waived by our office, as it is a requirement placed on you by your insurance carrier. Failure to pay your portion of services rendered will be reported to your insurance carrier and could result in termination of your insurance plan.Non-covered Services: The following services are considered "Non-Covered Services" by most insurance carriers. The fees listed below must be paid at the time of service.· Forms Completion: Disability Form, Insurance Form, Travel Form, Release from Work Form, Prior Authorization, and other forms are not required by most insurance plans or employers. If you require a physician to complete one of these forms, there will be a $25 charge in addition to your office visit charge.
· Paper Medical Records: We will provide to you, upon written request, a paper copy of your medical record. We charge a base fee of $20.00.
· Late Fees: Invoices not paid within 60 days will result in a $5 per month late fee.
· Co-payment Collection Fee: If we must bill you for your co-payment, you may be required to pay a $20 Co-payment Collection fee.
When must a co-payment be collected by the office for the patient to avoid a penalty?
a. Before the appointment is scheduled.
b. After receiving a statement.
c. After the insurance is billed.
d. At the time of service.
d. At the time of service.
Rationale: The policy states "You are responsible for paying all co-payments at the time service." Co-payments should be collected by the front office staff during patient registration. It is more difficult to collect payment after the patient has received treatment. Many times, patients will leave the office without paying or state they forgot their checkbook or debit card at home. When this happens, the practice has the added cost of sending an invoice to the patient to collect the money that should have been collected up front.
What should be included in a financial policy?
I. Explain that patient balances are due at the time services are provided.
II. List insurance carriers the providers are contracted with.
III. List insurance carriers the providers are not contracted with.
IV. List the practice's policy when seeing patients who are out-of-network.
V. List the patients on the Medicaid roster.
a. II, IV, V
b. I, II, IV
c. I, III, V
d. I, III, IV
b. I, II, IV
Rationale: The financial policy should explain that the total cost of the visit, copayments, co-insurance, and/or deductibles are required to be paid at the time of service. The policy should also list the insurance plans that are accepted, and the practice's policy for patients with out-of-network insurance plans.
A provider removes a skin lesion in an ASC and receives a denial from the insurance carrier that states "Lower level of care could have been provided." What steps should the biller take?
a. Check with the provider and write an appeal to the insurance carrier explaining why the service was not an inpatient service.
b. Write-off the charge.
c. Check with the provider and write an appeal to the insurance carrier explaining why the service was provided in the ASC.
d. Submit the CMS-1500 claim form with a different place of service code.
c. Check with the provider and write an appeal to the insurance carrier explaining why the service was provided in the ASC.
Rationale: "Lower level of care could have been provided" is a denial that applies when the following occurs:o Care provided on an inpatient basis that is typically provided on an outpatient basiso Outpatient procedure that could have been done in the provider's officeo Skilled nursing facility care that could have been provided by a home health agencyWhen this type of denial occurs an appeal letter should be written to the insurance carrier explaining the reason why the higher level of care was required. Along with the appeal letter the documentation from the patient's medical record that supports the level of care provided should also be submitted.
When should patient invoices (statements) be sent to the patient?
a. At the end of the year.
b. At the end of the month.
c. As soon as the patient is seen.
d. As soon as the RA is posted and a balance is transferred to the patient's account.
d. As soon as the RA is posted and a balance is transferred to the patient's account.
Rationale: Patient invoices should be sent as soon as the remittance advice has been posted. The sooner the invoice is received by the patient, the sooner it is likely to be paid. Patient invoices should detail the date of service, services provided, insurance reimbursement received, payments collected at the time of service, and the reason why the patient balance is due.
When accepting debit cards in a medical practice, which act requires the office to disclose specific information before completing a transaction?
a. Fair Credit Billing Act
b. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
c. Equal Credit Opportunity Act
d. Electronic Funds Transfer Act
d. Electronic Funds Transfer Act
Rationale: When allowing payments via a debit card, the office must also be familiar with the Electronic Funds Transfer Act. This act requires the office or facility to disclose specific information before completing a transaction.
Which statement is TRUE regarding the Prompt Payment Act?
a. Federal agencies are not required to respond to all clean claims within 30 days of receipt.
b. Patient balances are dismissed if a statement is not sent to the patient within 30 days.
c. Federal agencies are required to pay clean claims within 30 days of receipt.
d. Patients are required to pay patient balances within 30 days.
c. Federal agencies are required to pay clean claims within 30 days of receipt.
Rationale: The Prompt Payment Act is a federal law that ensures that federal agencies pay their bills within 30 days of receipt and acceptance of material and/or services.
When a patient files Chapter 7 under the U.S. Bankruptcy Code, which statement is TRUE?
a. The patient's debt is reorganized and paid at a discounted rate.
b. Most medical debt is discharged, the provider will write-off amounts owed.
c. The patient's debt is adjusted.
d. The provider is required to refund the patient any balances paid.
b. Most medical debt is discharged, the provider will write-off amounts owed.
Rationale: Chapter 7 - Liquidation. The person's assets are sold and the payment is made to debtors. In the case of Chapter 7 under the U.S. Bankruptcy Code, most medical debt is discharged. In this case, the provider will write-off the amount owed by the patient.
A claim was resubmitted to AAPC Insurance Company through a clearinghouse 60 days after the date of service and the claim was denied. AAPC Insurance Plan has a 60 day timely filing limit. The biller checked the claim status system and determined AAPC Insurance Plan did not receive the claim. What action should the biller take?
a. Transfer the balance to patient responsibility.
b. Write-off the balance since the claim was not received within Medicare's timely filing deadline.
c. Check with the provider.
d. Check the clearinghouse's report and appeal the denial with proof of claims submission.
d. Check the clearinghouse's report and appeal the denial with proof of claims submission.
Rationale: If a claim is submitted after the filing deadline, the claim is denied. This type of denial can be appealed if you have documentation that supports the claim was originally filed within the timely filing deadline. When a claim is denied because it was not filed timely, and there is no documentation for an appeal, the balance must be written off by the participating provider and cannot be billed to the patient.
Which statement is TRUE regarding patient balances?
a. The financial policy of the practice cannot include information about write-offs for patient balances.
b. Small balances for which processing costs exceed potential collections may be automatically written-off according to the financial policy of the practice.
c. Writing off any patient balance is considered waiving co-payments and puts the practice at risk for violating state and federal regulations.
d. Best practices is to write-off any patient balance under $50.00.
b. Small balances for which processing costs exceed potential collections may be automatically written-off according to the financial policy of the practice.
Rationale: The financial policy should address handling of past due accounts. A practice may automatically write off small patient balances for which processing costs exceed potential collections.
What are some potential errors that can happen during patient registration?
I. Invalid address
II. Invalid ICD-10-CM code(s)
III. Invalid CPT® code(s)
IV. Invalid insurance information
V. Invalid phone number
a. I, IV, V
b. I, II, III
c. I-V
d. II, III
a. I, IV, V
Rationale: The patient registration process is one of the most important steps when it comes to accounts receivable. Accurate information must be obtained initially to avoid costly errors later. Claims can be denied by the insurance carrier if the correct information is not collected. A patient statement cannot be paid if it is not delivered to the patient. An incorrect address can result in postal returns. CPT® and ICD-10-CM codes are not entered during the registration process.
Once a credit balance for an insurance carrier has been identified, what action should the biller take?
a. Post an adjustment to zero balance the account.
b. Research to determine if it is a true overpayment, then submit a refund to the patient for the overpayment.
c. Make a note in the practice management system and let the insurance carrier identify it.
d. Research to determine if it is a true overpayment, then submit a refund to the insurance carrier for the overpayment.
d. Research to determine if it is a true overpayment, then submit a refund to the insurance carrier for the overpayment.
Rationale: When it is determined that an insurance carrier has overpaid for a service, or paid a service in error, the amount of the overpayment must be refunded to the insurance carrier as soon as discovered and verified. Failure to refund an overpayment to an insurance carrier violates the False Claims Act.
Which Act prohibits third-party debt collectors from calling debtors at odd hours?
a. Fair Credit Reporting Act
b. Truth in Lending Act
c. Equal Credit Opportunity Act
d. Fair Debt Collection Practices Act
d. Fair Debt Collection Practices Act
Rationale: The Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (FDCPA) states that third-party debt collectors are prohibited from employing deceptive or abusive conduct in the collection of consumer debts incurred for personal, family, or household purposes.