ACA BST
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
What are the four key components of a mission statement?
Purpose, Values, Policies, Strategy
What is the definition of strategy?
Long-term direction and scope to achieve a competitive advantage through the configuration of resources to meet the needs of the markets and fulfil stakeholder expectations.
What makes planning strategic?
Longer term, considers whole organisation, considers resources and external environment, considers all stakeholders, looks at gaining a sustainable competitive advantage
Rational approach to strategic planning
formal and systematic, identify goals and select strategies to achieve them
Merits of strategic planning
Provides a framework.
Encourages long-term
planning.
Goal congruence.
Considers the needs of stakeholders.
Optimised use of resources.
Considers changes in the business environment. Monitors progress
Demerits of strategic planning
Lack of evidence to prove that it leads to success. Businesses may need to be more dynamic and react to problems as they occur.
Formal planning reduces initiative and innovative thinking.
Political infighting can disrupt the process
What are emergent strategies (aka bottom up approach)?
Behaviours adopted that have a strategic impact, emerge over time in response to the environment
Suitability of the emergent approach
Dynamic environments and require quick decision making
Have flexible, decentralised structures, managers can make decisions
Different grades of strategy (Mintzberg)
Intended strategy - conscious decision
Deliberate strategy - put into practice
Realised strategy - resultant energy
Unrealised strategy - strategy not implemented
Emergent strategies - develop over time
Resource-based (inside-out) strategic advantage
focus on developing internal competencies and resources that are hard to imitate and find or create markets to exploit these strengths
Risks of resource-based strategic advantage
may fail to react to long-term industry trends,
may find their resources and competencies are no longer valued by the customer
Positioning (outside-in) strategic advantage
analyse the external environment to identify customer needs and adapting to meet those needs
Risk of positioning strategic advantage
forced to constantly evolve and develop new competencies as customer's needs are ever changing
Influences on planning horizons
Nature of ownership - quick returns vs long term provision
Capital structure - banks may expect returns over a long period of time
Nature of industry - high level of capita; expect returns generated over a long period of time
Nature of Business Environment - dynamic industry, may be better to plan short term and react to current market
Nature of Management - need time and skill to master long-term planning
What is a mission statement?
Brief statement set out in general terms which doesn't include a timeframe or commercial terms, written to internal and external stakeholders.
Rational approach - mission at the start point of strategy formulation
Advantages of a mission statement
Help resolve stakeholder conflict
Set the direction of the organisation and so help formulate strategy
Help communicate the values and direction of the organisation to stakeholders
Criticisms of mission statements
Often full of meaningless terms, give staff little idea of what to aim at
Often ignored by managers
Often considered to be just a PR exercise
Objectives should be SMART
Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, Time-bound
Objectives of profit-making entities
Primary - maximise shareholder wealth
Secondary - e.g. customer satisfaction, social responsibility, innovation, meaningful employment
Objectives of not-for-profit entities
Primary - maximise benefit to target stakeholder
Secondary - e.g. investing in staff, minimal impact on the local environment, economy, efficiency, effectiveness
Issues with the objectives of NFPs
Often have multiple objectives to consider
Difficult to measure as success is typically non-financial
Stakeholder conflicts more difficult to resolve as they usually have a wide range of influential stakeholders
Financial constraints may limit the amount that they can achieve
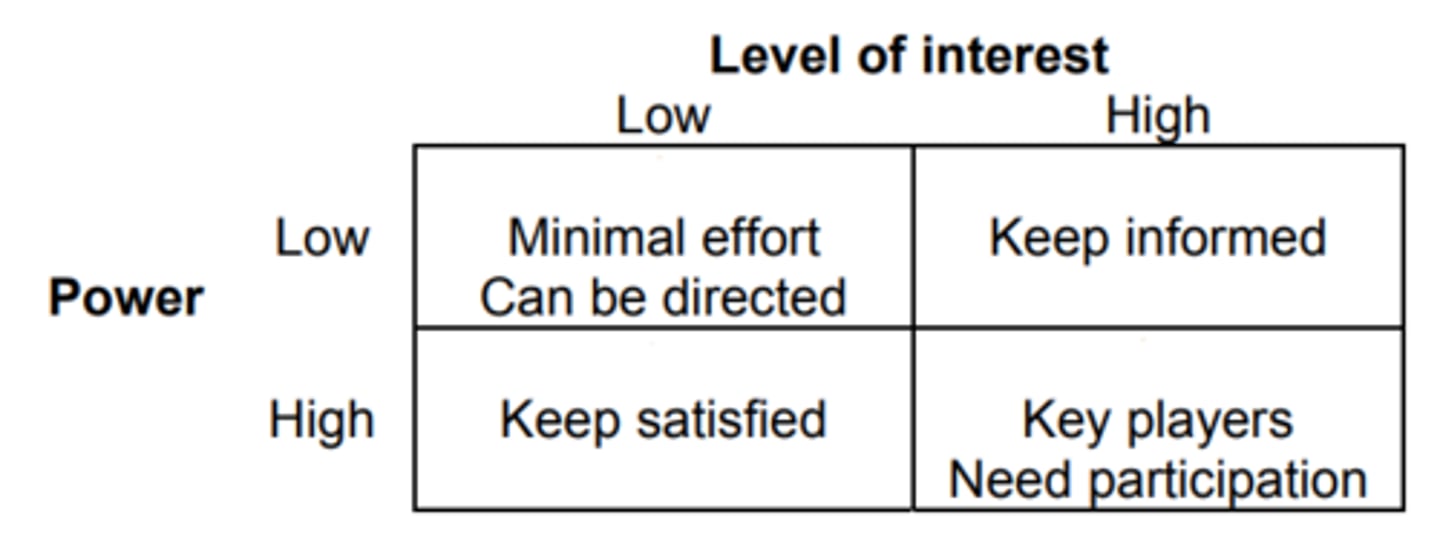
Mendelow's Matrix for stakeholder mapping
Interest - Power
L-L - minimal effort directed
L-H - keep satisfied
H-L - keep informed
H-H - key player needs participation
What is a stakeholder?
Any group or individual with an interest in what the organisation does
What are the 3 business environments?
Internal Environment -> Industry -> Macro
To analyse: industry - 5 forces
macro - PESTEL
Macro Environment
Consists of external factors that effect the overall environment that the business operates in
Industry Environment
Consists of external factors affecting the competitiveness of the industry that the business operates in
Internal Environment (Internal Capabilities)
Consists of the organisation's own internal resources and capabilities
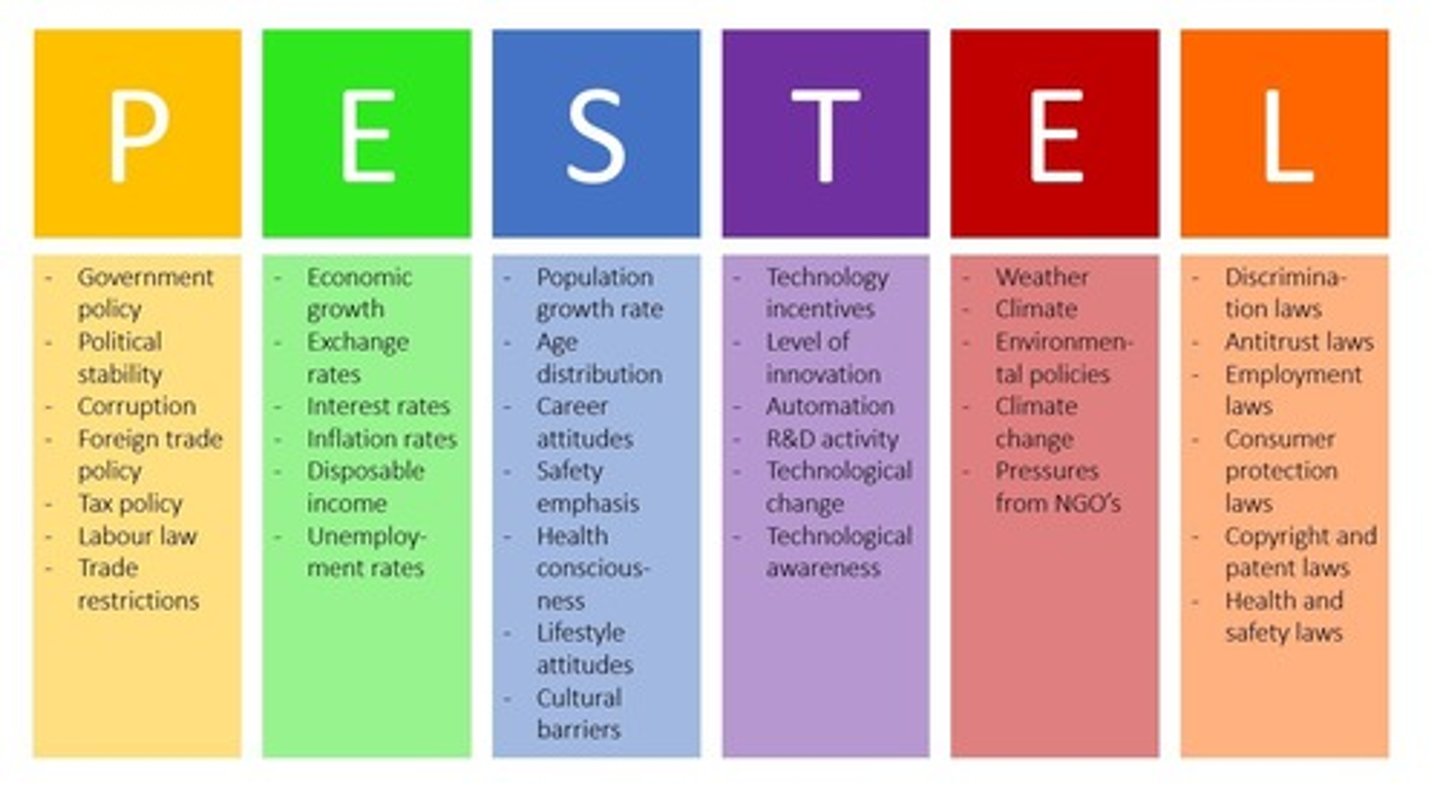
PESTEL Analysis
Political
Economic
Social
Technological
Ecological
Legal
Scenario Planning
Concerns the development of pictures of potential futures for the purpose of managerial learning and the development of strategic responses
Porter's Diamond
4 key determinants of national competitive advantage
Demand conditions
Strategy, structure and rivalry
Related and supporting industry
Factor Conditions
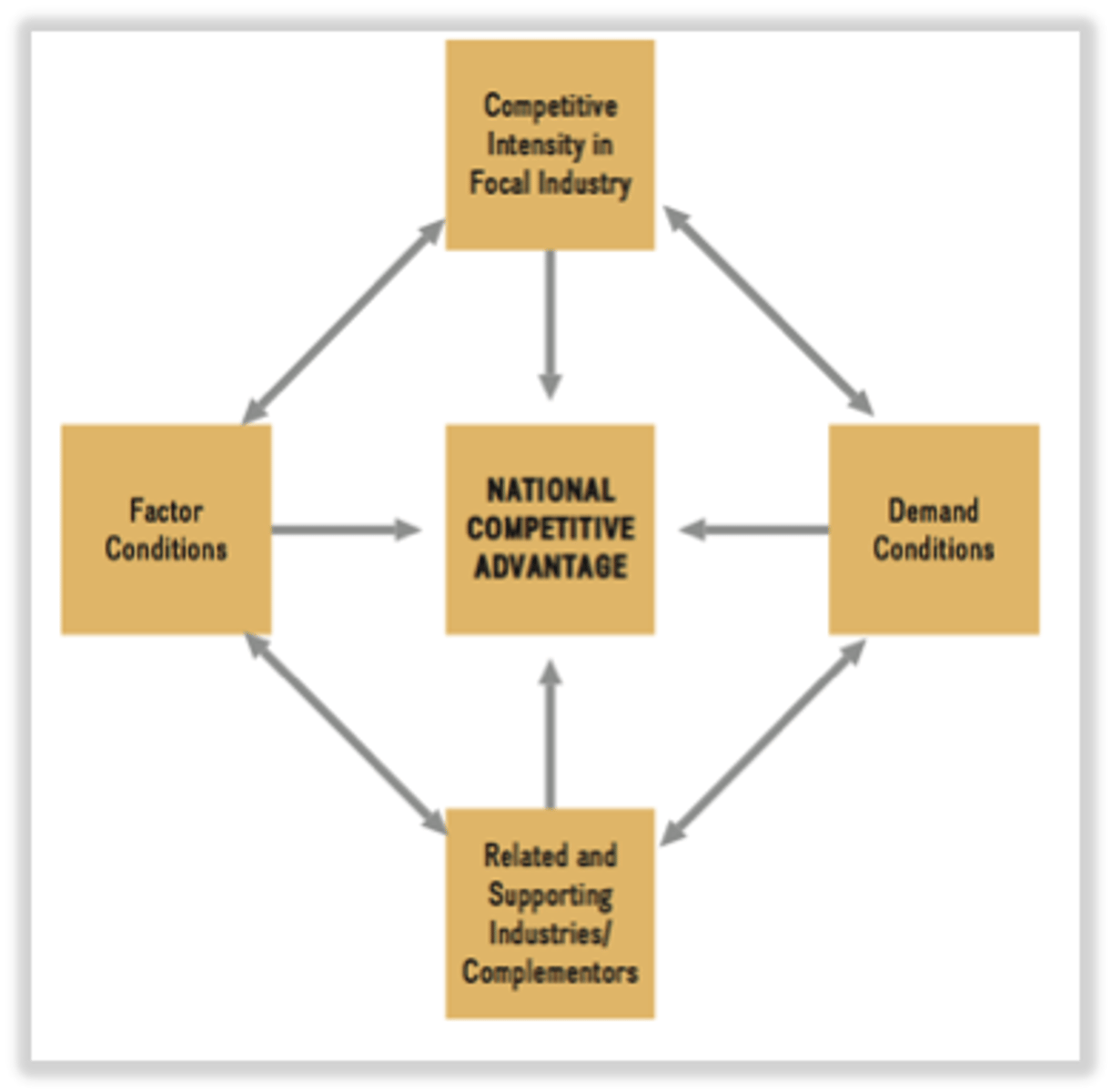
Porter's Diamond - Factor Conditions
Supply side
availability of the factors of production e.g. HR physical resources, infrastructure, capital, knowledge
Porter's Diamond - Demand Conditions
demanding local consumers force firms to become more innovative
trend setting local consumers help local producers to anticipate future global trends
Porter's diamond - Related and Supporting Industries
proximity leads to:
easy access to components, with reduced lead times and carriage costs
encourages knowledge sharing which increases innovation
Porter's Diamond - Strategy, Structure and Rivalry
Strong domestic rivalry forces local firms to become more efficient to survive
The strategies or structures that have become prevalent in a particular nation may give advantages in particular industries
What is an industry?
Group of organisations supplying a market offering similar products using similar technologies to provide customer benefits
Industry Life Cycle
Introduction
Growth
Shakeout
Maturity
Decline
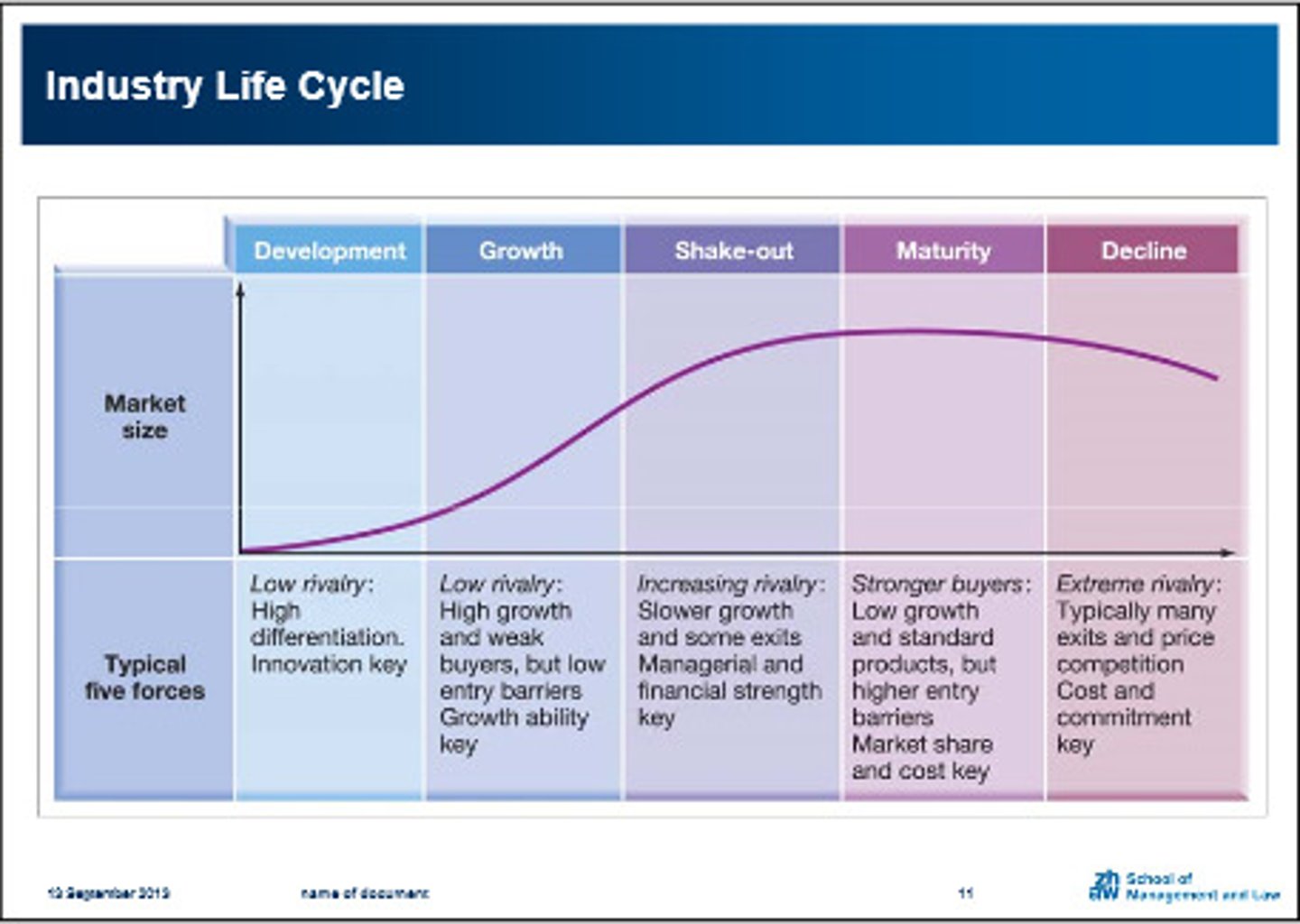
Key stages of industry life cycle - introduction
new product or service invented
can be significant first mover advantage for the first firms in the market (reputation and experience)
Key stages of industry life cycle - growth
rapid growth
market becomes attractive to new entrants
competitive rivalry is relatively low as firms are experiencing growth without having to increase market share
Key stages of industry life cycle - shakeout
market growth begins to slow
weaker players are forced to leave the industry or merge with another company
Key stages of industry life cycle - maturity
stable period of low growth
competition intensifies and smaller competitors (who lack scale economies) are shook-out of the industry
Key stages of industry life cycle - decline
sales volumes start to fall as demand declines
firms leave the industry and eventually it ceases to exist
Porter's Five Forces
Determine the level of competition and therefore profitability of the industry
Threat of new entrants
Bargaining power of customers
Bargaining power of suppliers
Threat of substitutes
Competitive rivalry
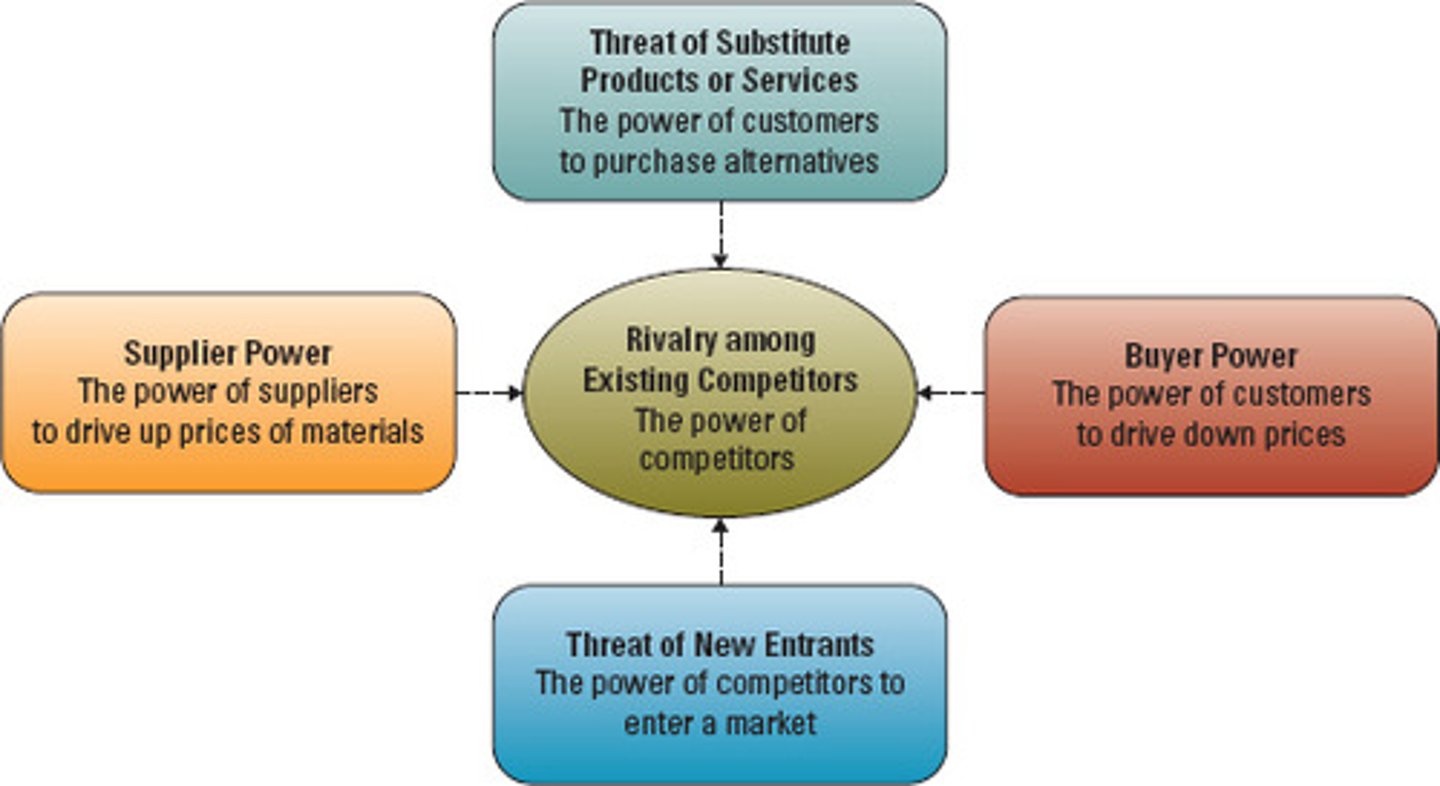
Porter's 5 Forces - threat of new entrants
Market Attractiveness:
high industry growth, high profit margins, few existing competitors, easy customer switching
Barriers to entry:
economies of scale, brand loyalty, capital requirements, access to distribution, patents, government subsidies
Porter's 5 Forces - competitive rivalry
Higher if there are:
large number of existing competitors
high levels of fixed costs
low industry growth
low switching costs
high exit barriers
high strategic importance
Porter's 5 Forces - threat of substitutes
Availability of substitutes:
from different industries e.g. rail vs bus
from sub-industries e.g. CD vs MP3
Increased likelihood:
price of substitute is low
relative performance of the substitute is comparable
customers can switch easily
Porter's 5 Forces - power of customers
Higher if there are:
small numbers of large customers
large number of competitors
low levels of product differentiation
low switching costs
the customers own profitability is low
high degree of price transparency in the market
Porter's 5 Forces - power of suppliers
Bargaining power will be increased if:
few large suppliers
supplier's products are differentiated
high switching costs for the customers
the supplier has other buyers they can sell to instead
Different types of suppliers:
providers of raw materials
service providers and outsourced services
employees and hire workers
What are critical success factors (CSFs)?
a small number of key goals vital to the success of the organisation
What product features are valued by customers and where must the organisation excel? What resources and competencies will enable them to achieve its CSFs?
What are threshold resources?
Basic resources needed by all firms in the market
What are unique resources?
Resources which are better than those of the competition and difficult to replicate, giving the firm a sustainable competitive advantage
9Ms Model
Checklist when performing a resource audit
Men (HR) - number, skills, potential etc
Machines - premises, location, capacity, age
Money - existing finance, access to future funding
Materials - relations with suppliers, access to inputs
Markets - existing customers, locals, distribution syst
Management - quality, skills, leadership style
Methods - activities and processes adopted
Management Information Systems - quality to assist in marketing, production, R&D
Make-up - attitudes, culture, structure
Human Capital
considers the collective attributes of an organisation's HR E.g. capabilities, creativity, skills and knowledge of the workforce and how these combine to create economic value
Programmes to enhance the value of the workforce
Education and training
Allowing creativity
Infrastructure
Recognising the intellectual property
Motivation
Competition
Participation in activities
Flexible workplace arrangements
Home working
Improvements in technology e.g. cloud computing
Core competencies
critical activities and processes which enable the the firm to meet the CSFs and therefore achieve a sustainable competitive advantage
Kay's Core Competencies Model
Reputation - reason customers are attracted
Competitive architecture - network of relationships - internal (employees), external (suppliers, customers, intermediaries), network (collaborating businesses)
Innovative ability - ability to develop new products and services
What is a value chain?
Identifies the relationships between the company's resources, activities and processes that link the business together and create a profit margin
Porter's Value Chain Analysis
value is measured by the difference between the cost of the activities and sales revenue created by sales to customers
non-value adding activities can be identified and reduced or eliminated
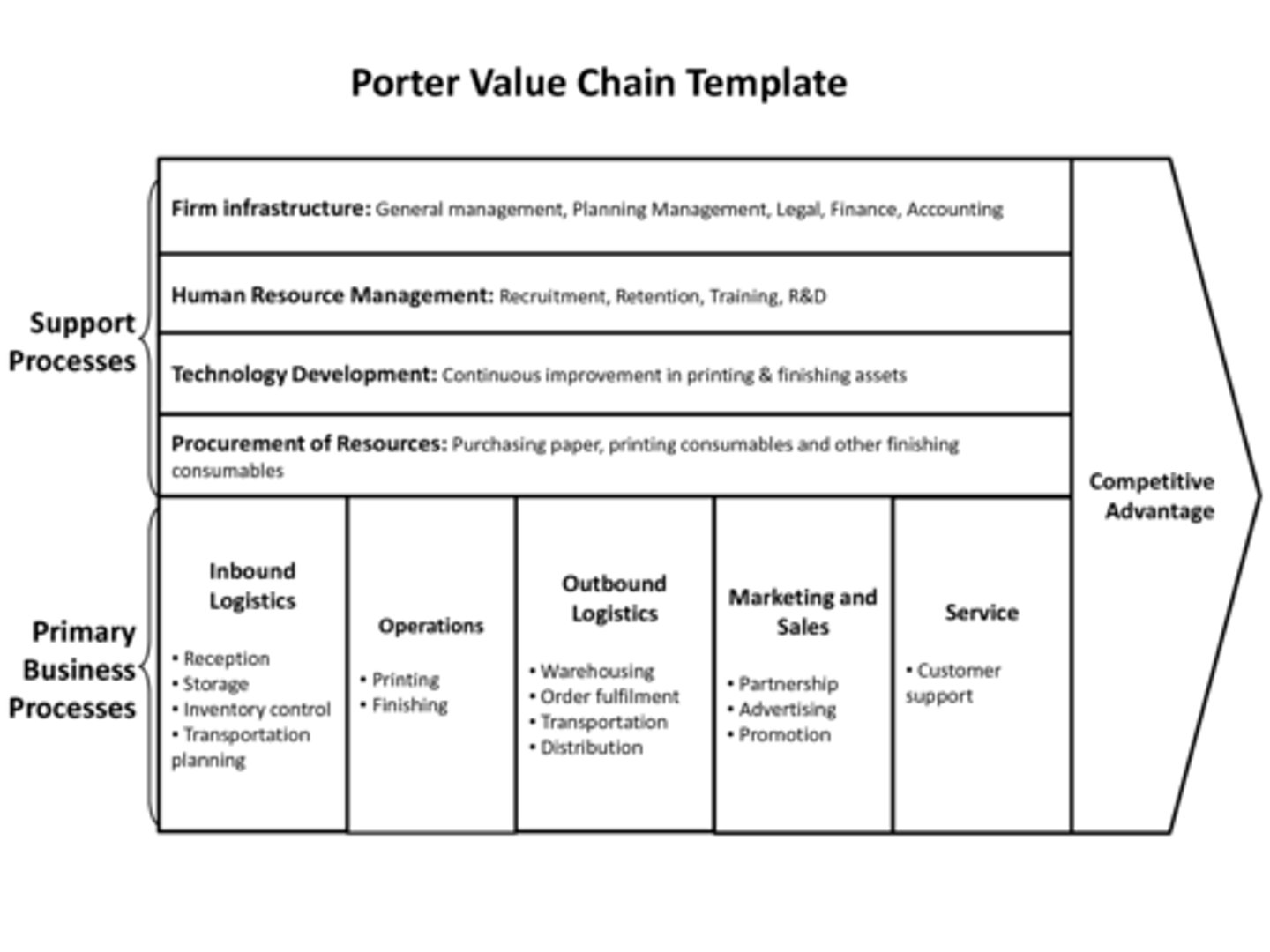
Performing a value chain analysis
1. Identify the generic strategy
Cost leadership - seeking to be the lowest cost producer in the industry - should seek cost advantages throughout the value chain
Differentiation - creating tangible and intangible product features that the customer is willing to pay more for - should seek quality advantages throughout the value chain
Cost drivers
factors that cause costs to be incurred. Important for a cost leader who is trying to reduce costs
Value drivers
Potential sources of value. Important for differentiators who are trying to generate quality advantages in their value chain
Value chain analysis - Primary Activities
Inbound logistics - receiving, storing and distributing inputs of the products
Operations - transform inputs into final product
Outbound logistics - collecting, storing and distributing the final product
Marketing and Sales - informing, persuading and enabling to buy product
Service - after sales services e.g. installation, repair, training and customer service
Value chain analysis - Supporting activities
Procurement - processes for acquiring the various resource inputs to the primary activities
Technology development
HR management - recruiting, managing, training, developing and rewarding internally
Infrastructure - systems of planning; finance, QC, info management, structures and routines to sustain the culture of the organisation
Linkages in the value chain
Internally - two or more activities in the chain impact each other. 2 types:
co-ordination - consistent with each other and work together
optimisation - strength in one area can lead to committing fewer resources to another
Externally - internal should be consistent with customer's and supplier's chains
Strengthening the value chain
Outsourcing - external providing performing traditionally in-house activities
Automation - equipment to replace a process
Shared service centres - number of internal activities brought together into one site
Harmon's process-strategy matrix
Low importance low complexity - automate/outsource - processes are simple and straightforward
High importance and low complexity - automate - processes important to the organisation but simple to perform
Low importance and high complexity - outsource - processes add little value, but are too complex for automation
High importance and high complexity - improve - processes are a core competence and should be improved as much as possible

Product Life Cycle
application of life cycle theory to product or services
Development-Introduction-Growth-Maturity-Decline
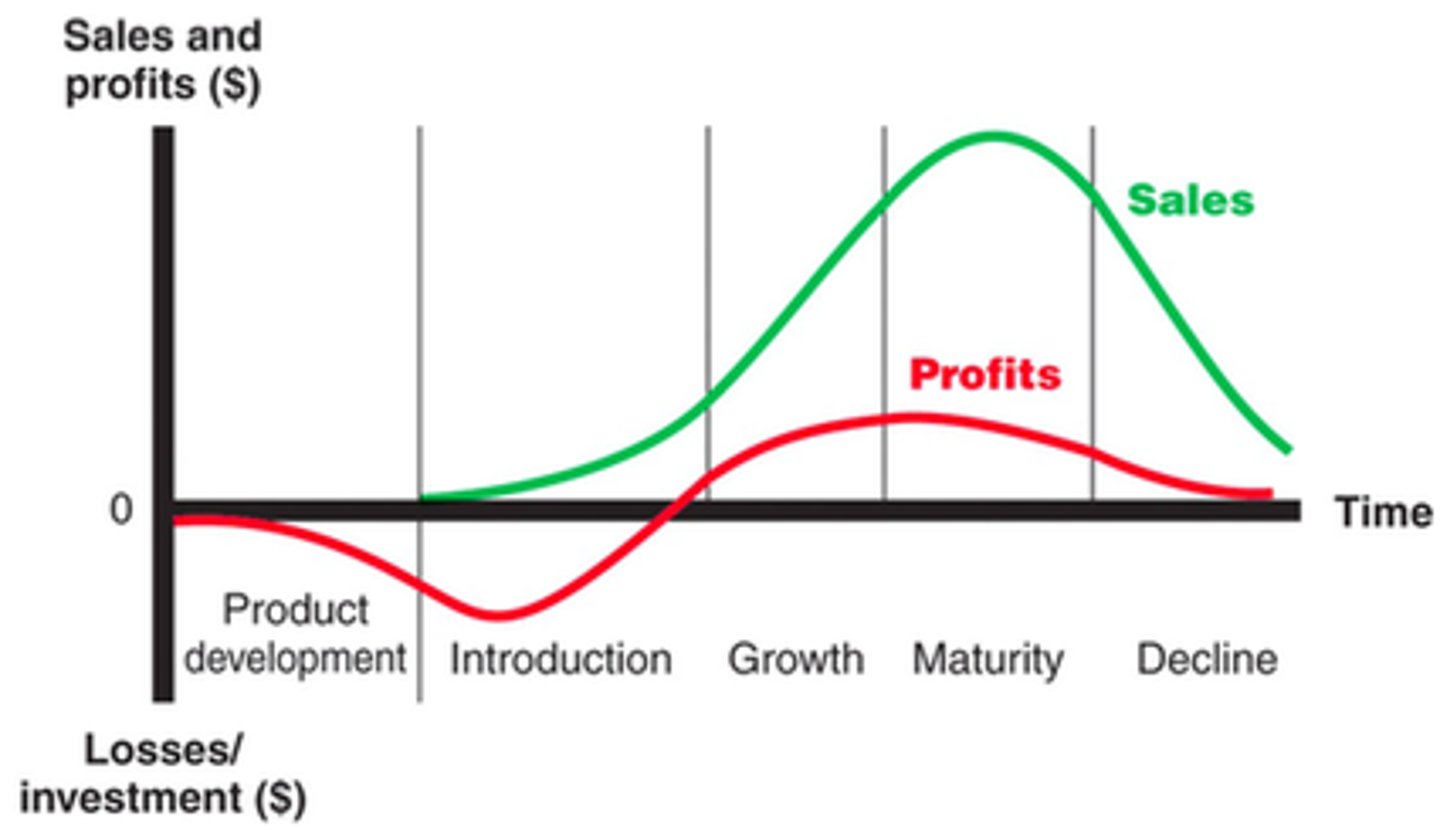
Stages of the product life cycle
Development - negative cashflows (investment in R&D and initial marketing), market research
Introduction - continued cash outflow (high marketing>initial sales), initial demand (will determine pricing policy)
Growth - new competition (quality improvements to compete), economies of scale (emerge through mass production)
Maturity - critical mass (leads to cost efficiencies), positive cashflows (max sales, min marketing)
Decline - heavy price discounting (utilise spare capacity and cover overheads), brand loyalty (may be key to retain customers)
Too many products in one phase can cause problems e.g. cash flows
BCG Matrix
Help decide where to allocate resources
Market attractiveness - measured by market growth
Competitive strength - measured by relative market share RMS = sales/largest competitor's sales
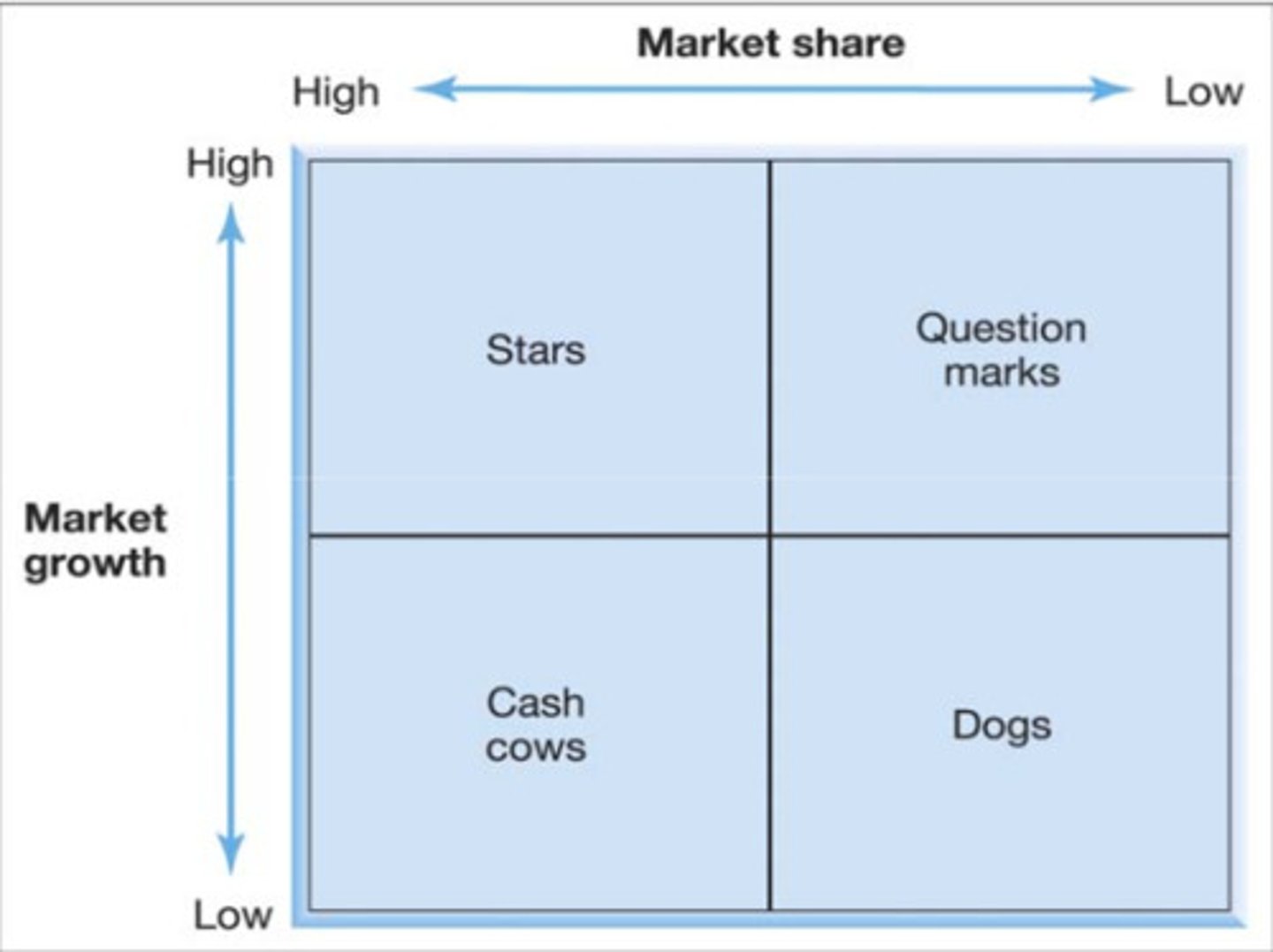
BCG Matrix - Problem Child
Definition - attractive market but don't have the market share to be competitive
Implications - lack of economies of scale limit cash flow
Decisions - should the company invest further to gain market share?
BCG Matrix - Star
Definition - Dominant position in an attractive market
Implications - high threat of new entrants requires the company to continue to invest to defend market share
Decisions - consolidate current position or invest further to seek additional growth?
BCG Matrix - Cash Cow
Definition - dominant position in a low growth market
Implications - competitors will decide not to attack out market share as the market does not warrant the investment, large positive cash flows can be achieved
Decisions - 'milk the cow' and enjoy cash flows accepting market share may fall
BCG Matrix - Dog
Definition - low share of an unattractive market
Implications - product may lack economies of scale but the market is not attractive enough to seek growth
Decisions - when should the company 'put the dog down' and divest from this product?
SWOT Analysis
Internal and external analysis used to perform a corporate appraisal to evaluate the strategic position of the organisation
Strategic Impact of SWOT analysis
can strength match opportunities?
address weaknesses before pursuing opportunities
sufficient strengths to minimise threats?
can weaknesses be converted into strengths?
can threats be converted into opportunities?
gap analysis
comparison between entity's ultimate objective and the expected performance from projects
Why does the gap exist?
Strategies to close the gap?
Porter's Generic Strategies
To obtain a sustainable competitive advantage, generic strategy which best fits the organisation's environment (5 forces) and then organising value-adding activities (Value chain analysis) to support the chosen strategy
Cost leadership - lowest cost producer
Differentiation - tangible and intangible features customer willing to pay for
Focus - utilising either in a narrow profile of market segments (niching)
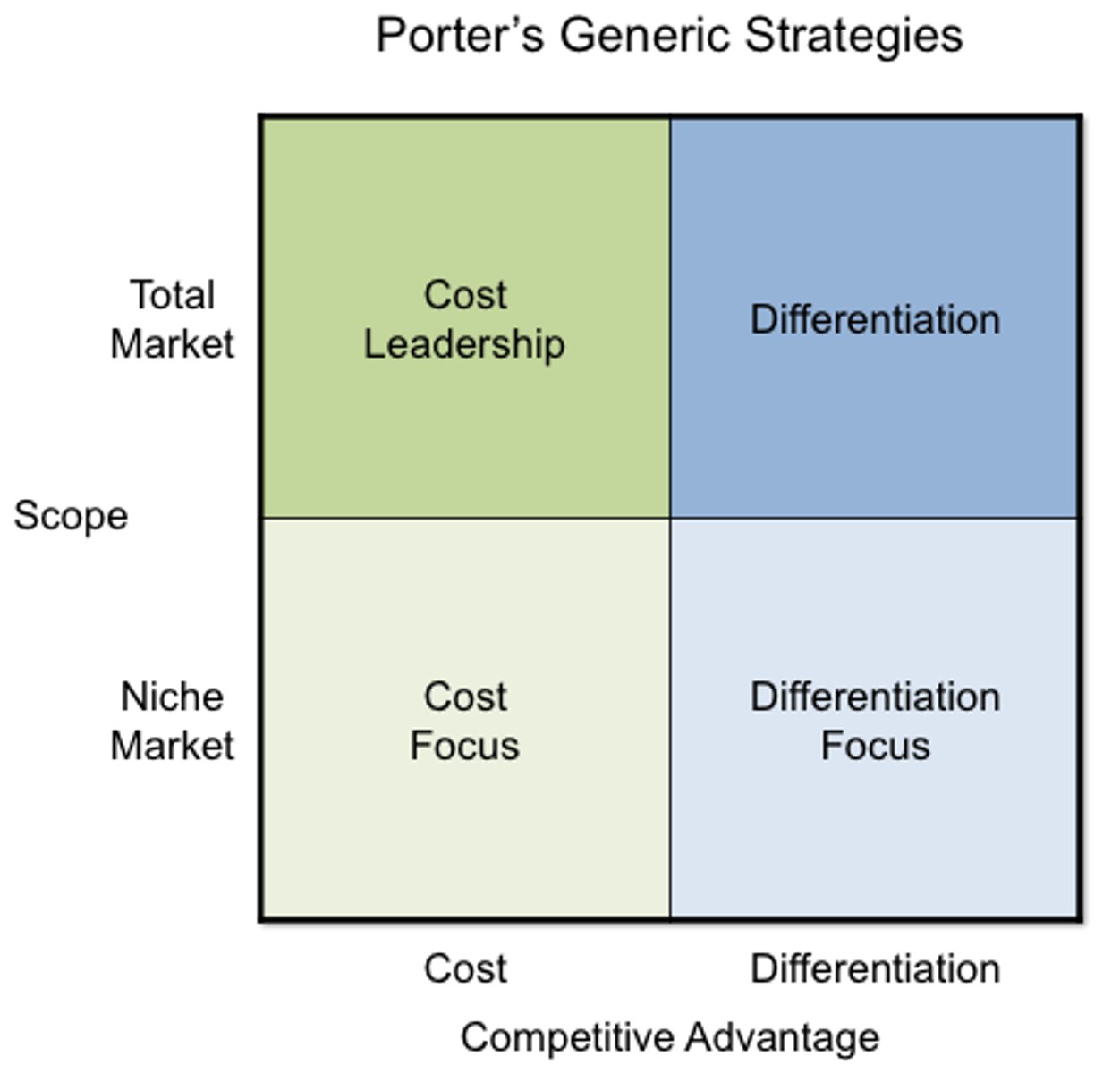
Porter's Generic Strategies - Cost leadership strategies
To achieve: economies of scale, seek cheaper sources of supply, reduced labour cost, use value chain to identify non-key activities
Potential benefits: can earn higher profits by charging same price as competitors, remain profitable in price war, economies of scale create barrier entires
Risks: only room for one cost leader, cost advantage may be lost because of inflation, movements in exchange rates, competitors using cheap overseas labour etc, customers may pay extra for better product
Porter's Generic Strategies - Differentiation Strategies
Based on product features (actual) or altering consumer perception
To achieve: strong branding, product innovation, quality, product performance
Potential benefits: products command a premium price so higher margins, fewer perceived substitutes due to uniqueness and brand loyalty - demand less price sensitive, less direct competition
Risks: cheap copies, being out-differentiated, customers unwilling to pay the extra, differentiating factors no longer valued by customer
Porter's Generic Strategies - Focus/Niche Strategy
Focus on segment of market rather than whole market
To achieve: identify segment of customers/consumers with similar needs, choose differentiation or cost-focus, develop products to meet the needs of the segment, develop a marketing strategy to specifically target chosen segment
Potential Benefits: smaller segment so smaller investment in marketing/production to develop competitive advantage, less competition, entry is cheaper and easier
Risk: if segment too small, difficult to achieve sufficient sales, if too large then large players may become interested
Ansoff's Matrix
Existing products, existing markets - market penetration (more sales of existing products to existing markets)
New products, existing markets - product development (developing new products for existing markets)
Existing products, new markets - market development (finding new markets for existing products)
New products, new markets - diversification (developing new products for new markets)

Ansoff's Matrix - Market Penetration
To achieve: competitive pricing, advertising or sales promotion, improving competitive advantage through adjustments in the value chain
Potential Implications: greater market strength and economies of scale, lack of diversification
Ansoff's Matrix - Product Development
To achieve: invest in R&D
Potential implication: the business should already have good knowledge of their customers, product failure may damage the brand
Ansoff's matrix - Market Development
To achieve: new geographical markets or market segments, using new distribution channels
Potential implications: market research may be needed to overcome lack of market knowledge, customer's awareness may need to be generated in the new market
Ansoff's Matrix - Diversification
seeks growth in new markets with new products
Related diversification (concentric)
Unrelated diversification (conglomerate)