C3, C4, and CAM plants
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
25/10/24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
C3 plants
located in generally cool, moist environment
wheat
soybean
oat
barley
sunflower
Alfalfa
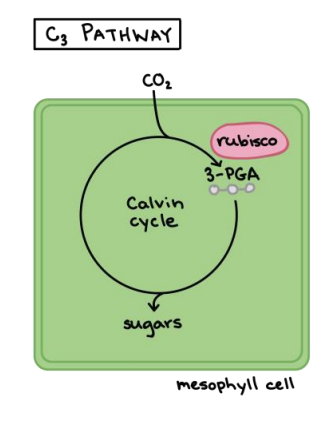
why are C3 plants called C3 plants
first organic product in calvin cycle is 3-PGA
3-PGA has 3 carbons
it follows the C3 pathway
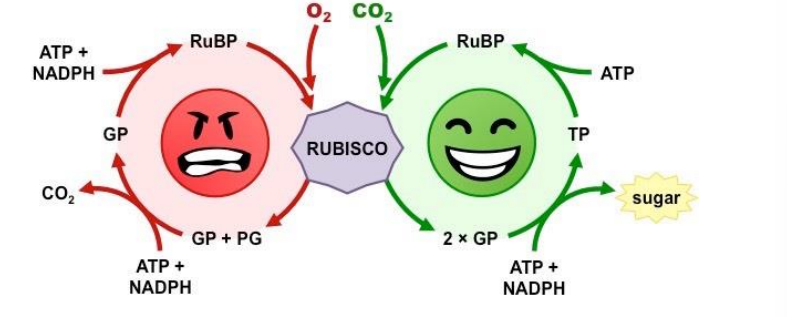
photorespiration
occurs when stomata closes and gas cannot move in and out of plant
common in hot and dry weather
CO2 is not low or not available
rubisco fixes oxygen to RuBP instead
does not produce ATP, NADPH, or G3P
plant is unable to make its own food
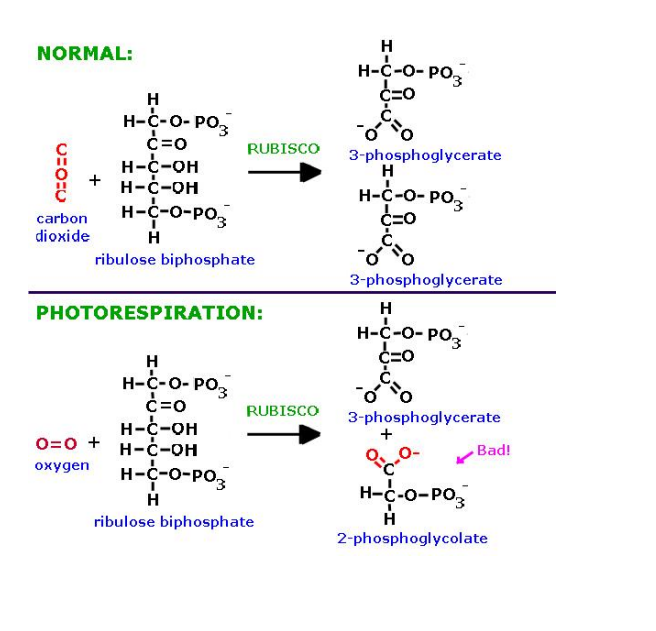
RuBP + O2 → 2-PG + 3-PGA
does rubisco only fix CO2
no, can fix other molecules, does not have a specific one
temperature and gas differences in calvin cycle and photorespiration
calvin cycle: low temperature, high CO2 to O2 ratio
photorespiration: high temperature, low CO2 to O2 ratio
why does the stomata close in a plant
especially in hot and dry environments
to prevent water loss
carbon fixation vs photorespiration main products
carbon fixation: CO2 + RuBP → two G3P
photorespiration: O2 + RuBP → phosphoglycolate + 3-phosphoglycerate
chemical difference between photorespiration and carbon fixation
lack of third carbon from CO2
leads to different molecule
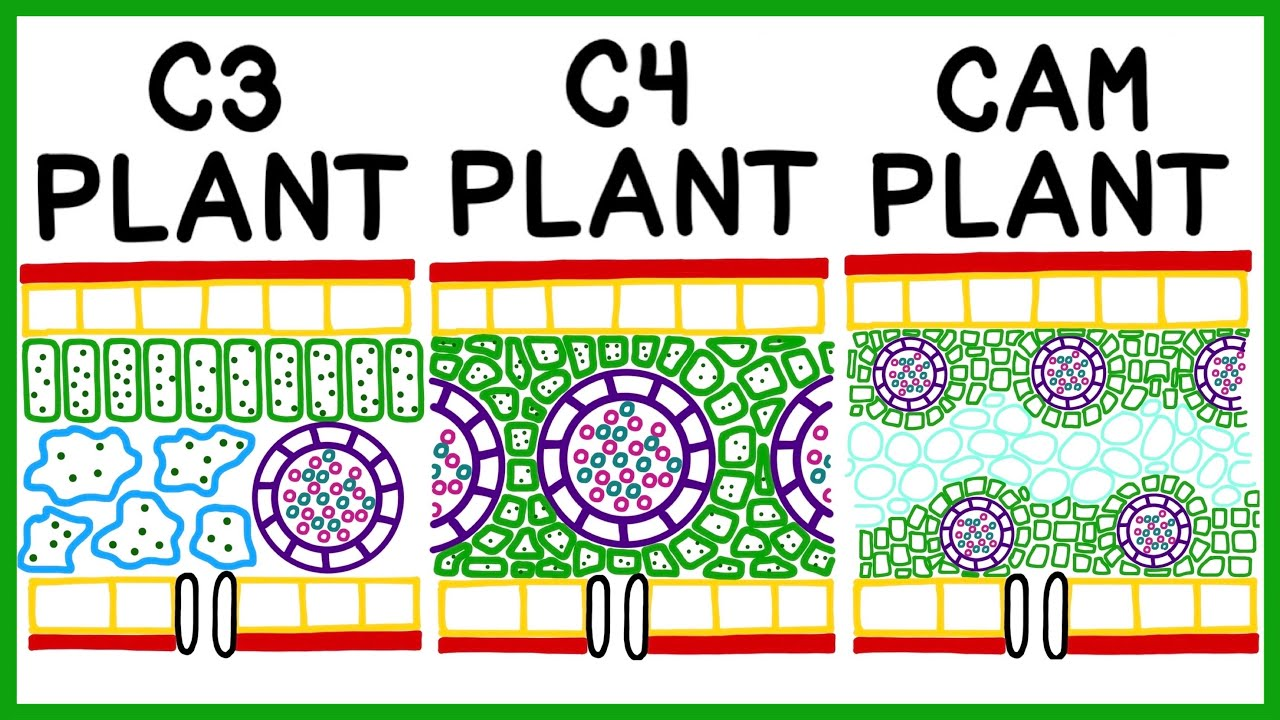
C4 plants
tropical grasses, corn, sugarcane
present in hot and dry environments
adapted to environment
not as efficient as C3 plants
has unique anatomy: bundle sheath and mesophyll cells
difference in anatomy of C3 vs. C4 plant
vascular bundle in center of C3 and C4 plant
C4 plant has tightly packed palisade mesophyll
bundle sheath surrounds vein/vascular bundle
allows for separation of photorespiration
CAM plants have large vacuoles to store CO2 until night
first product of photorespiration after carbon fixation gives a 4 carbon compund is
oxaloacetate
photosynthetic cells of C4 plant
mesophyll cell: tightly backs around bundle sheath
bundle sheath: surrounds vein
how does C4 carbon fixation work?
PEP fixes CO2 in mesophyll cells
forms oxaloacetate
forms malate
also forms pyruvate
CO2 leaves pyruvate by decarboxylation for calvin cycle
pyruvate forms atp
forms PEP
CAM plants
located in desserts, hot and dry weather
succulents, agave, aloe vera, cacti, pineapple
same anatomy as C4 plant
fixes Carbon only at night to organic molecules
Usually opens stomata for day and closes at night to avoid water loss
materials held in mesophyll cells until night
separates anatomy and time of reaction
fixation in each type of plant
C3 plant: regular CO2 fixation to RuBP
C4 plant: uses PEP to fix CO2 to RuBP
CAM: uses PEP to fix CO2 to RuBP only at night time
PEP
enzyme used in C4 carbon fixation
only fixes CO2 and not O2
helps plants limit photorespiration
CAM plants are best for
water conservation, loses least water out of CAM, C3 and C4
how do C3 plants lose water?
photorespiration
Which type of plant (C3 , C4 , or CAM) would you expect to grow most efficiently in each environment? Explain your reasoning. A hot, wet tropical environment
C4 plants as they are adapted to hot environments and do not prioritize water conservation like CAM plants
Which type of plant (C3 , C4 , or CAM) would you expect to grow most efficiently in each environment? Explain your reasoning. Environment extremely hot days but cool night
CAM Plants as they conserve water best and can thrive in extremely hot environments by completing the calvin cycle at night
Which type of plant (C3 , C4 , or CAM) would you expect to grow most efficiently in each environment? Explain your reasoning. – Cool, damp environment
C3 plants as they are native and used to this environment
Which type of plant (C3 , C4 , or CAM) would you expect to grow most efficiently in each environment? Explain your reasoning.– Moderate climate but nutrient poor soil
C3 plant as C4 and CAM as especially adapted to certain hotter environmemts