Clinical Medicine of the GI System, pt.2 : Other Manifestations of the GI Tract Disease
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
dysphagia
difficulty swallowing
what is the differential diagnosis for solid food dysphagia?
-stricture
-ring
-web
-cancer
What are solid food dysphagia often due to?
obstructive lesions
What are solid and liquid dysphagias usually due to?
due to esophageal motility disorders
What is the differential diagnosis for solid and liquid dysphagia?
-scleroderma
-achalasia
-EGJ outflow obstruction
-distal esophageal spasm
-hypercontractile esoohagus
What is the workup for dysphagia?
-barium swallow
-endoscopy
-motility study via manometry
esophageal stricture
-consequence of GERD or other insult
-dysphagia to solids
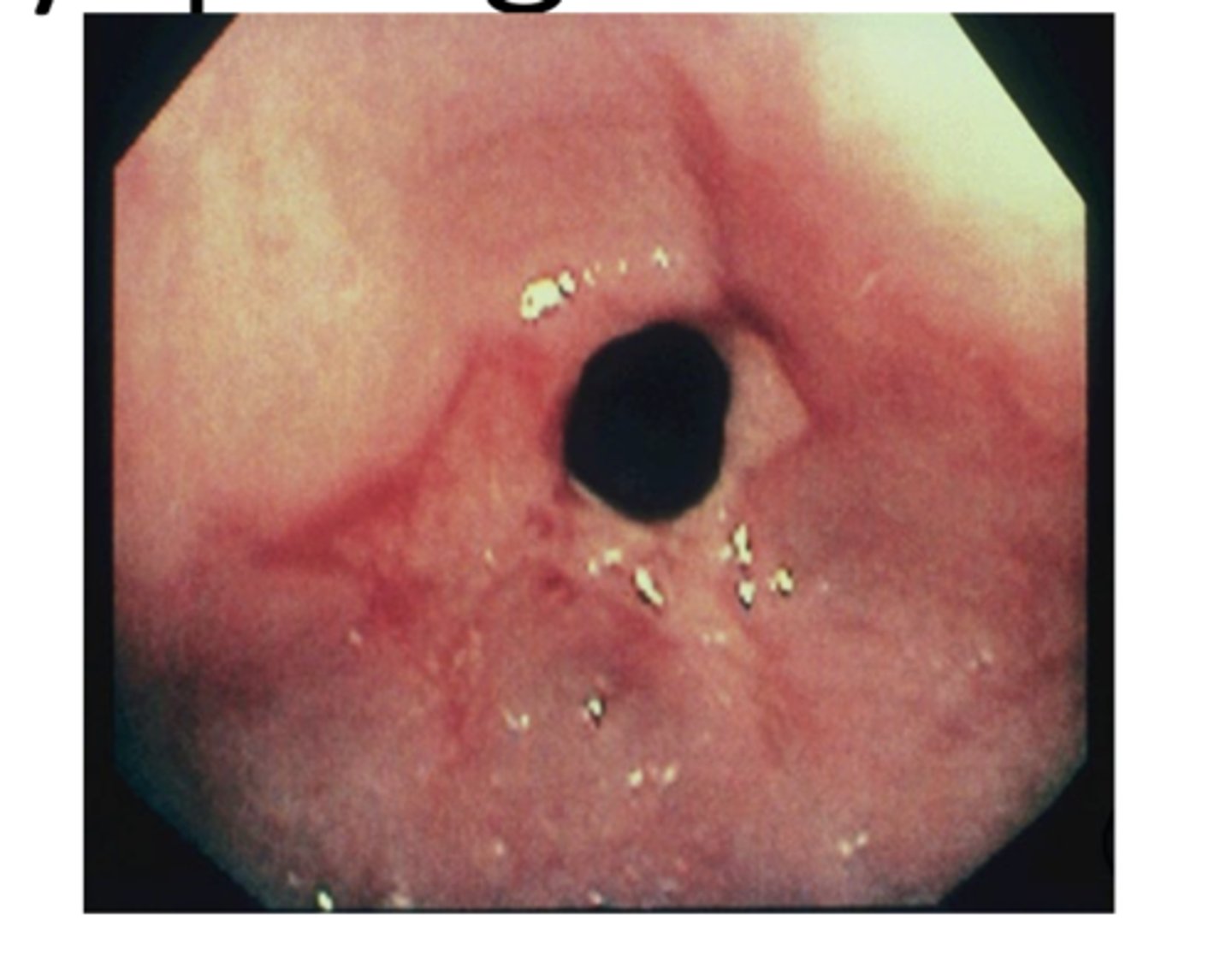
esophageal stricture will cause dysphagia to solids or liquids?
solids
esophageal web
proximal membrane formation
*occurs in
-iron deficiency anemia
-plummer-vinson syndrome
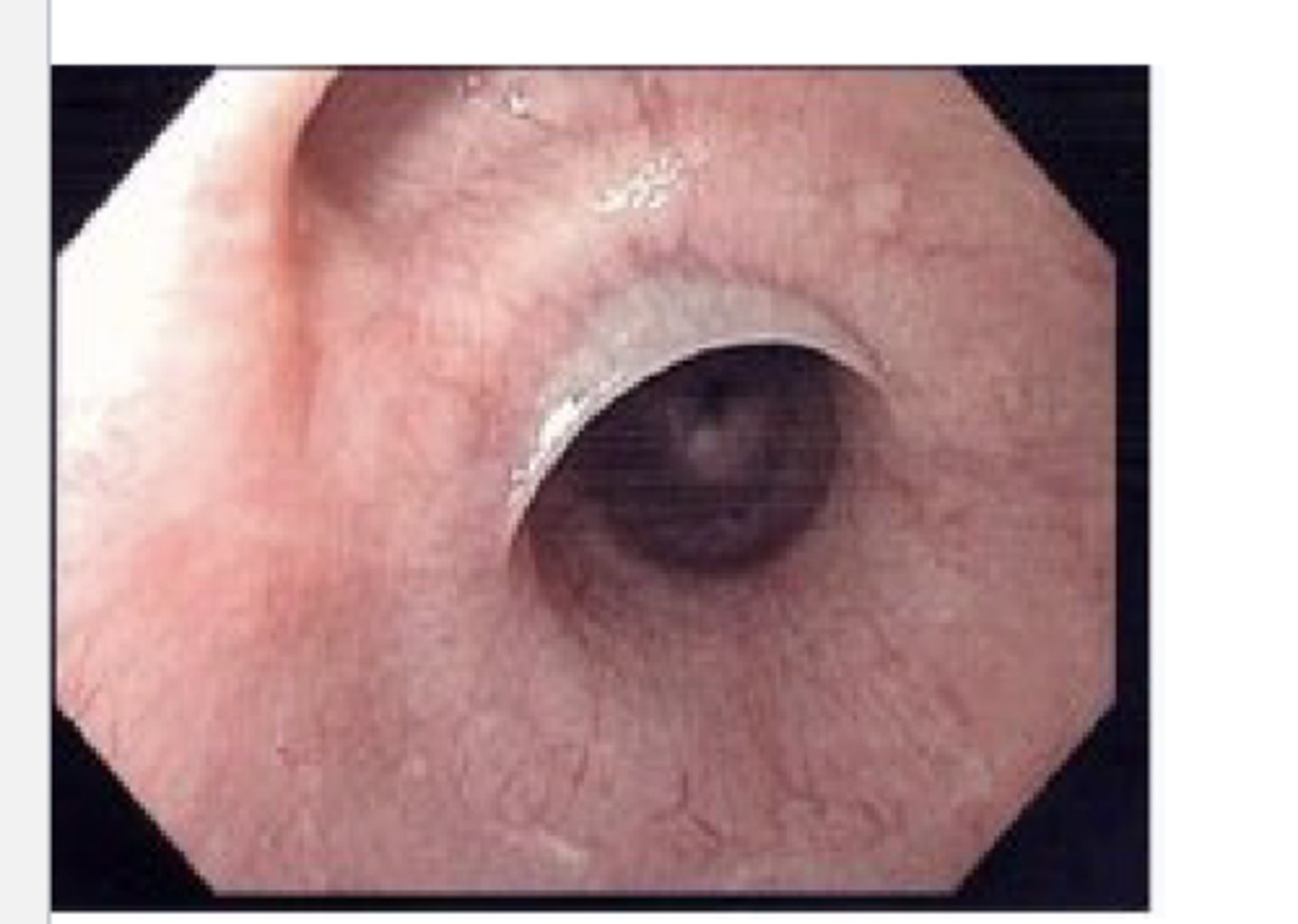
esophageal webs cause dysphagia to solids or liquids?
solids
What are come symptoms/complications of Plummer-Vinson Syndrome?
-anemia
-hand abnormalities
-risk for cancer
-esophageal webs --> solid food dysphagia
What kind of dysphagia does a esophageal schatzki ring cause?
dysphagia to large solids
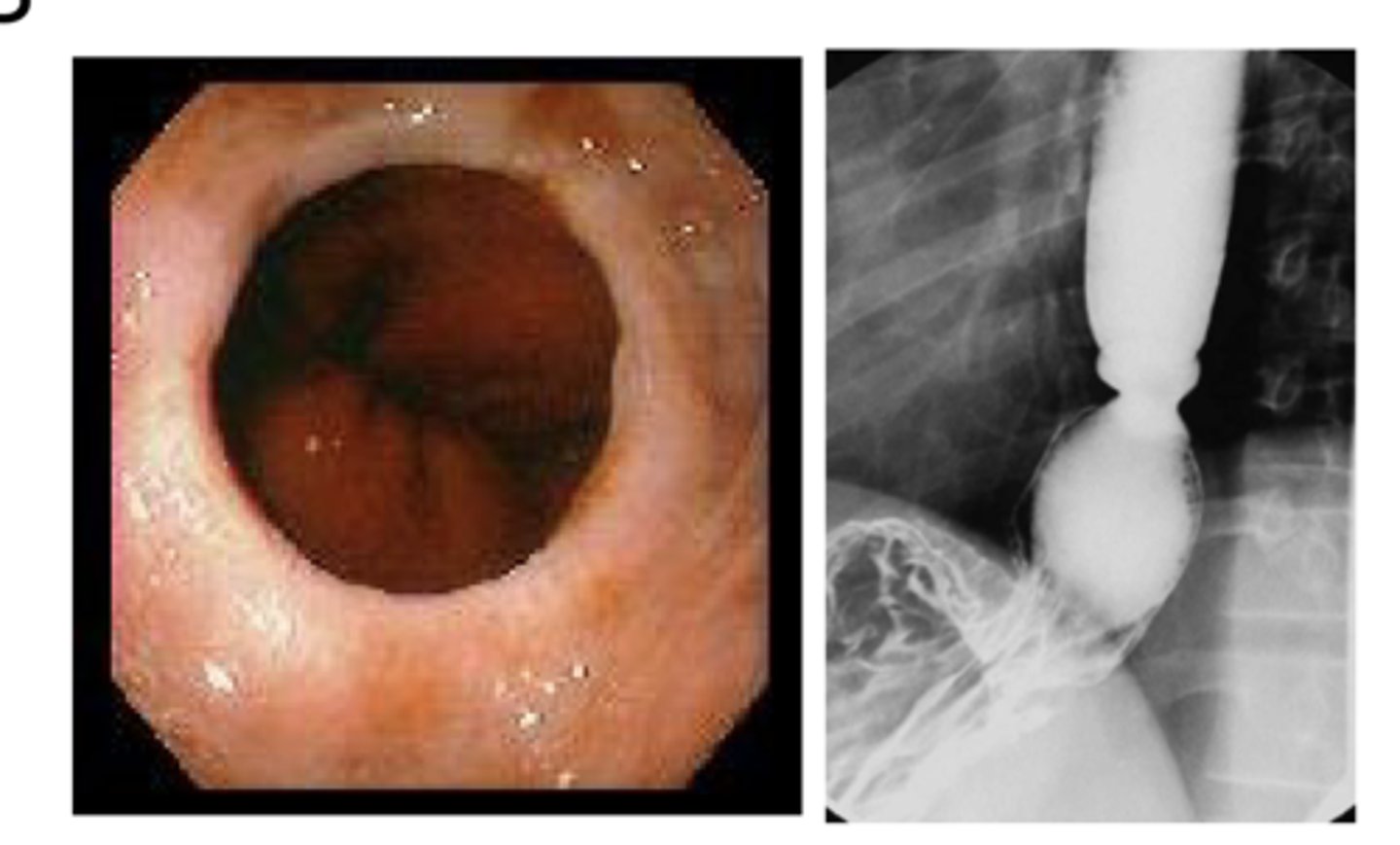
How does esophageal cancer look on endoscopy?
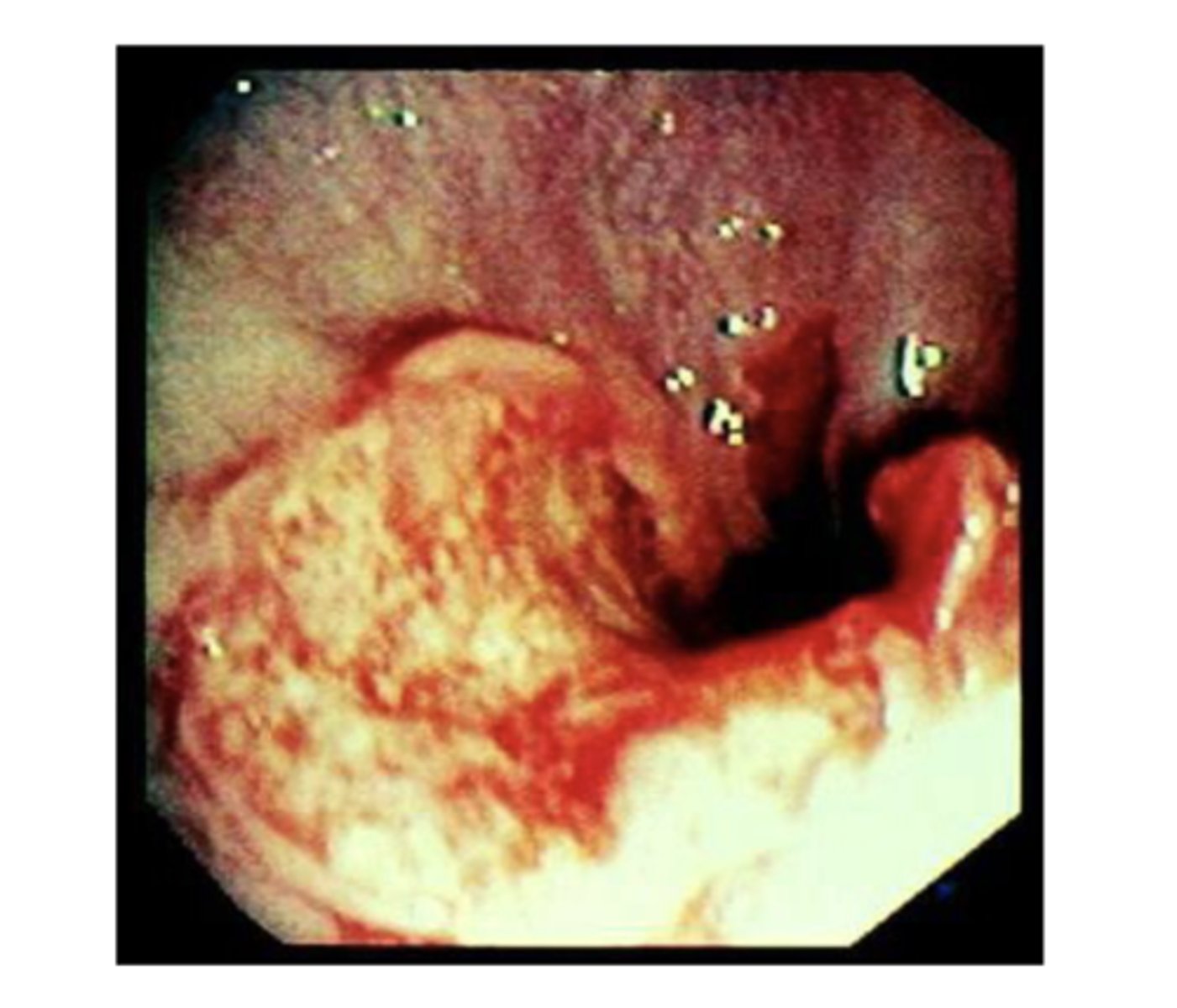
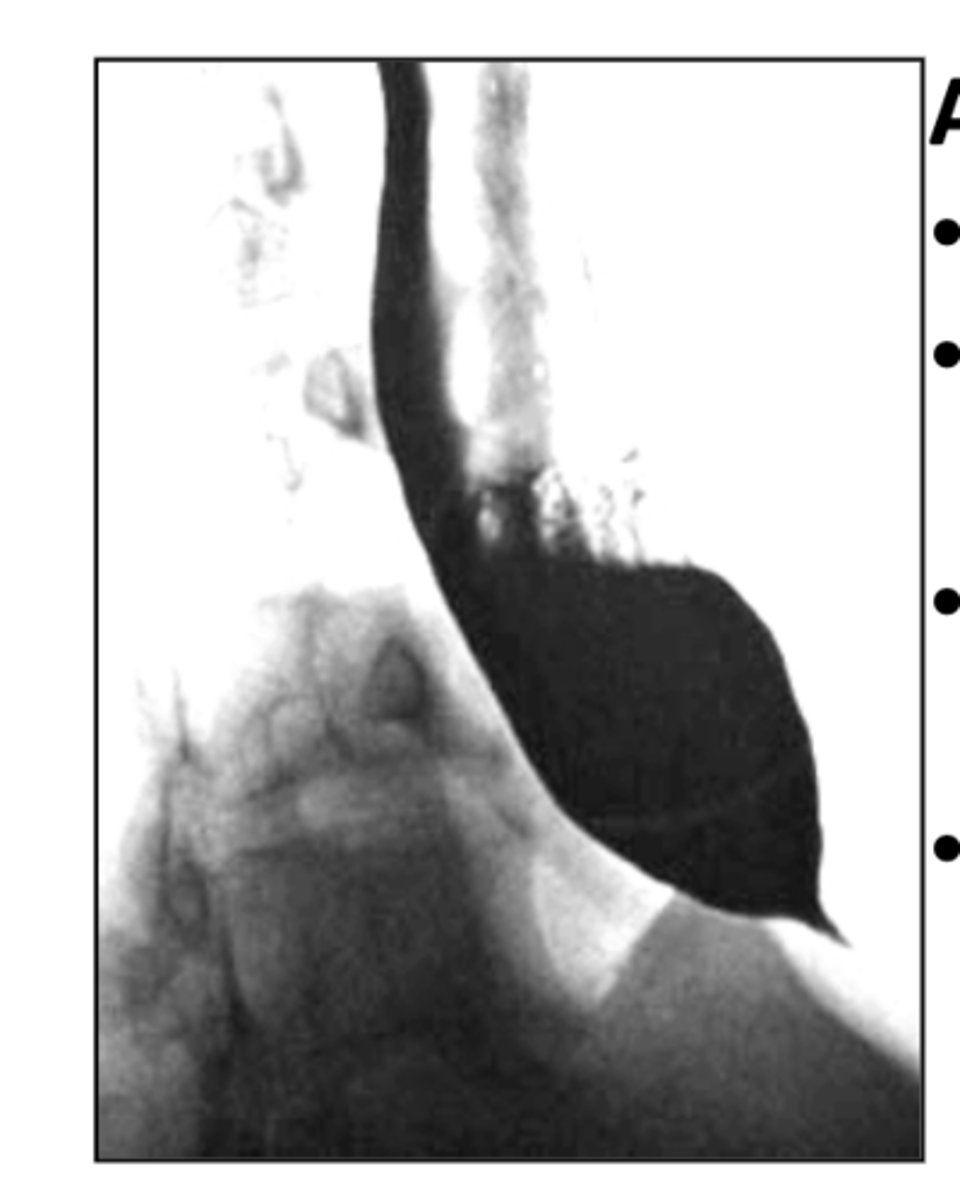
Achalasia
esophageal motility disorder due to distal stricture caused by absent ganglion cells (birds beak appearance on barium swallow)
*causes dysphagia to solids & liquids
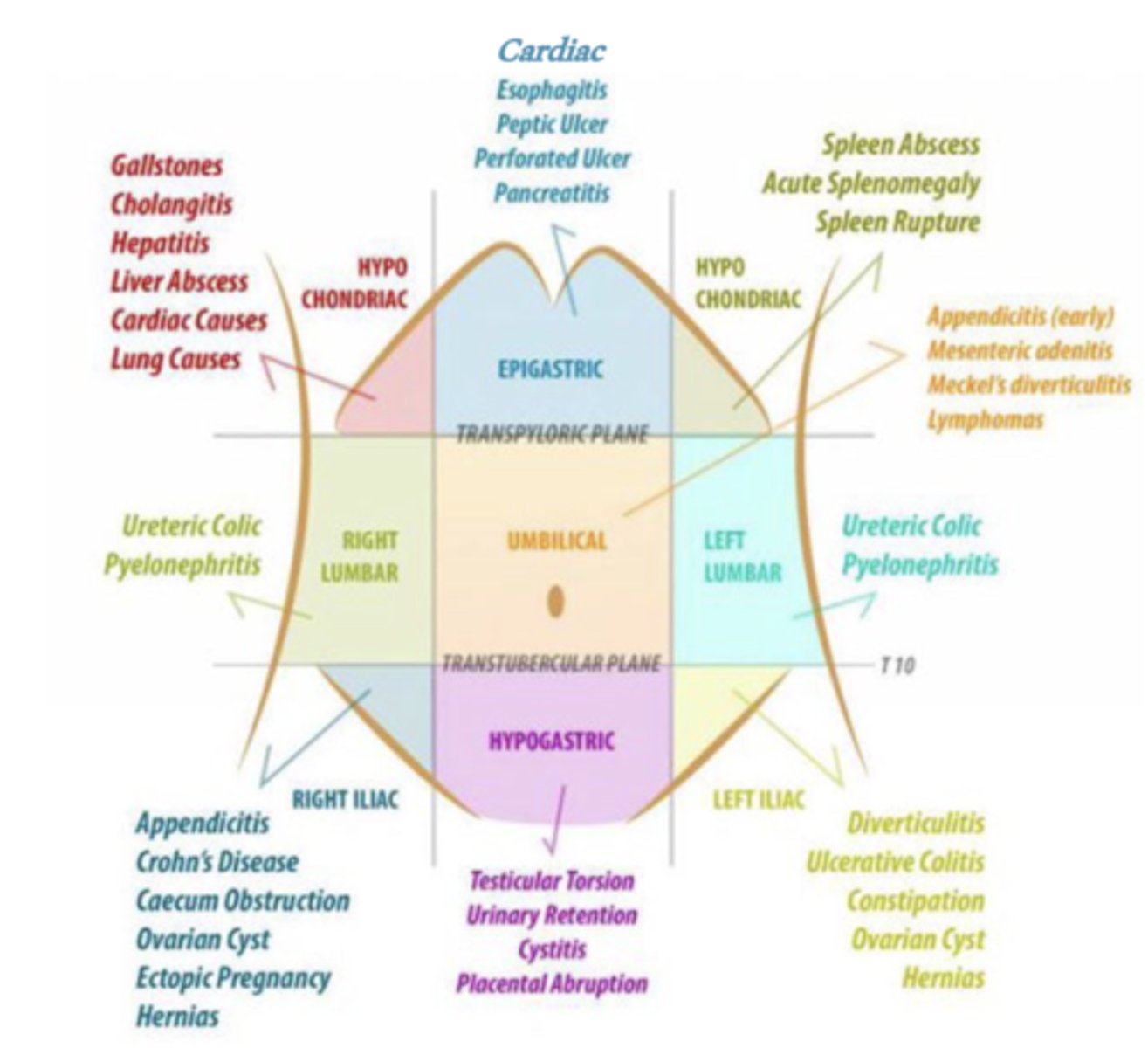
What is the diagnostic differential for epigastric pain?
-cardiac--> inferior MI
-esophagitis
-peptic ulcer disease
-perforated ulcer
-pncreatitis
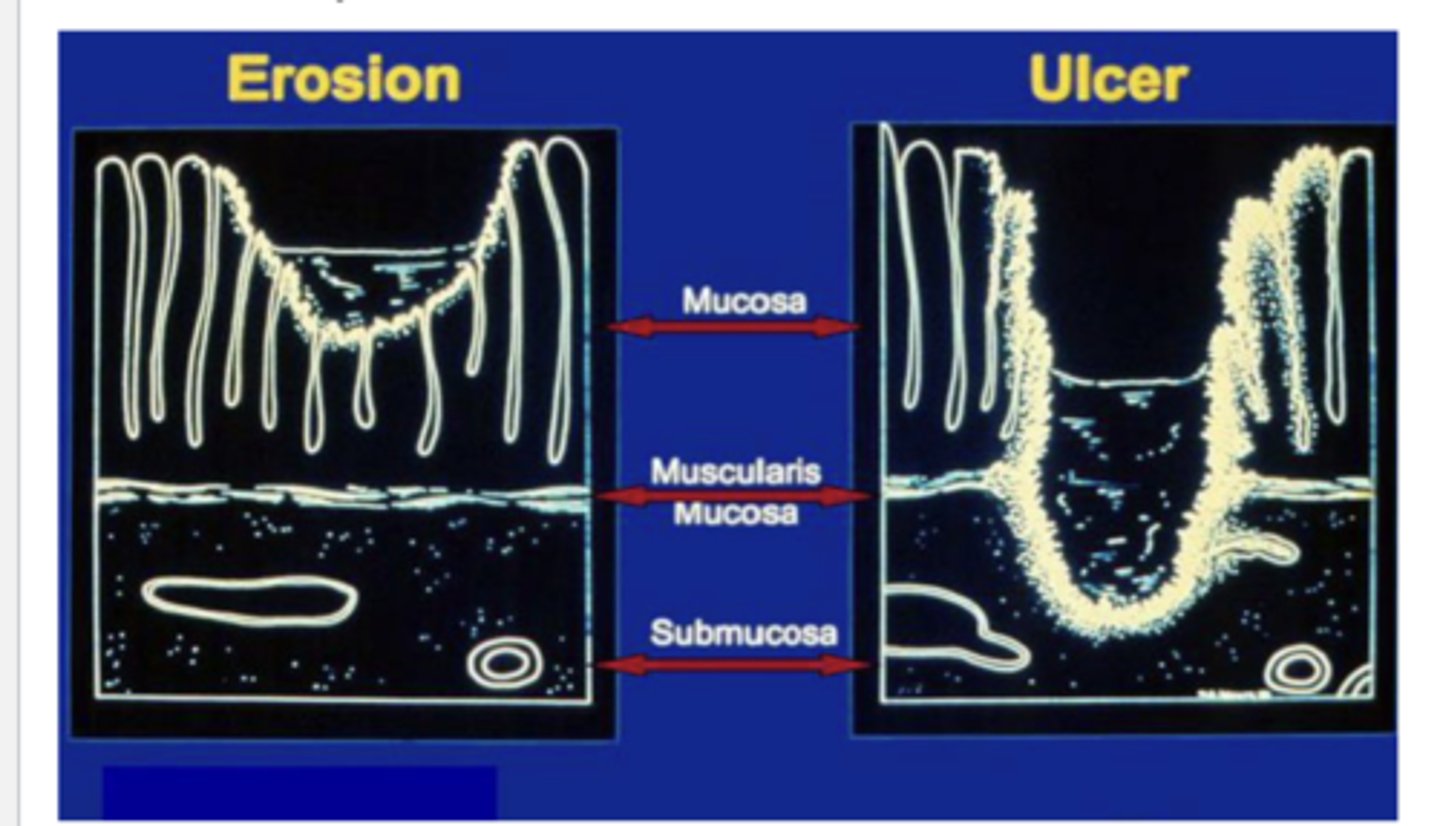
What is peptic ulcer disease?
injury to the lining of the stomach/duodenum that penetrates through the muscularis mucosa of stomach/duodenum
What are the symptoms of peptic ulcer disease?
-epigastric pain --> gnawing pain
-symptoms vary with location & etiologies
-symptoms similar to GERD
What are the major causes of peptic ulcer disease?
-H.pylori
-NSAIDs
-ischemia
-smoking
-alcohol
What are other etiologies for peptic ulcer disease?
-physiologic stress
-gastrin hypersecretion
-lymphoma
-crohn's disease
how is peptic ulcer disease diagnosed?
-clinical
-H.pylori testing
-endoscopy
How is peptic ulcer disease treated?
-stop aspirin/NSAIDs
-treat for H.pylori
-acid suppression --> usually PPI
-address other contributing factors
-follow-up 4-6 weeks to monitor healing & rule out complications or malignant gastric ulcer
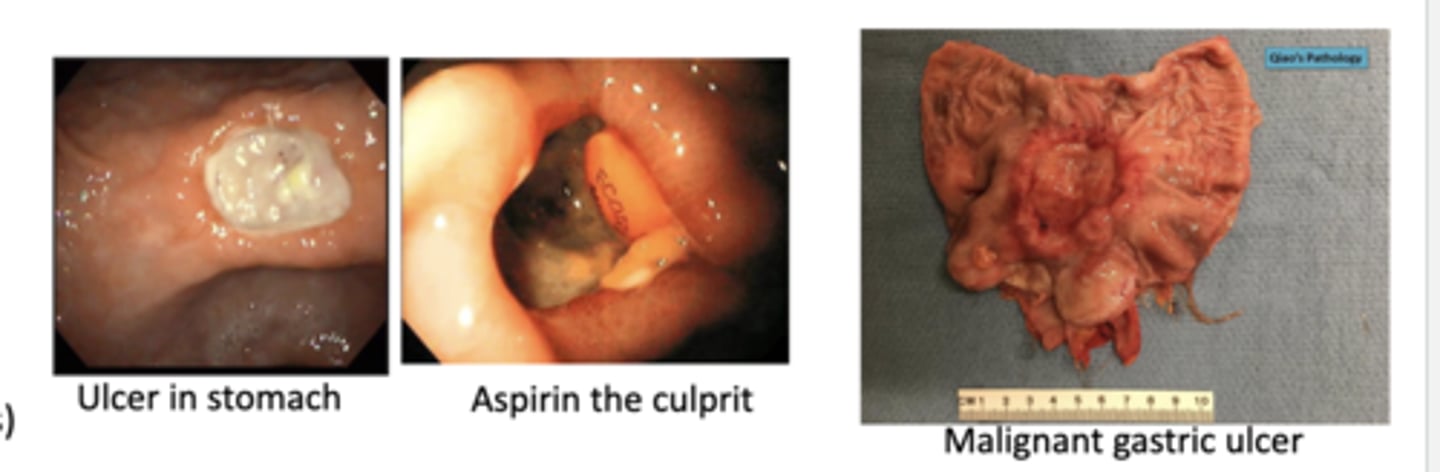
What's the difference between the benign ulcers and malignant ulcers?
-benign --> have defined borders
-malignant ulcers--> undefined borders
what are the complications of peptic ulcer disease?
-bleeding
-perforation
-obstruction
How does perforation of a peptic ulcer present?
-acute abdominal pain
-hypotension
-air under the diaphragm
*requires emergency surgery
True or False: Peptic ulcer disease has a high recurrence rate
True
*H. pylori treatment reduces recurrence rate
what are the differential diagnoses for upper GI bleeding?
-peptic ulcer disease
-varices --> esophageal & gastric
-arteriovenous malformations
-mallory weiss esophageal tears
-esophagitis
-malignancy
What are signs of chronic/slow upper GI bleeding?
-dark tarry stools--> due to partially digested blood
-signs of iron deficiency anemia
What are signs of acute/severe upper GI bleeding?
-bright blood per rectum if significant hemorrhage
-hypotension if significant hemorrhage
True or False: Insults to the pancreas can lead to activation of enzyme and auto-digestion of tissue
True
what are the symptoms of acute pancreatitis?
-epigastric pain --> dull & steady & then becoming severe, radiating to the back
-nausea & vomiting
-fever
-tachycardia
-jaundice (less common)
Describe the epigastric pain associated with acute pancreatitis?
dull & steady & then becoming severe radiating to the back
Describe the epigastric pain associated with peptic ulcer disease?
gnawing
what are the complications of acute pancreatitis?
-fatal if untreated (15%)
-multiorgan system failure (1st wk)
-sepsis & complications (2nd wk)
How does acute pancreatitis affect the pancreas?
-tissue destruction
-inflammation
-hemorrhage
-activation of enzymes & autodigestion of tissue
what are the most common causes of acute pancreatitis?
-alcohol
-gallstones
*80% of cases in the US
How acute pancreatitis diagnosed?
need 2 out of 3
-clinical presentation
-elevated lipase & amylase --> levels don't indicate severity
-imaging--> CT scan
what causes acute pancreatitis?
-alcohol
-gallstones
-abdominal trauma
-medications
-infections
-tumors
-genetic/anatomical variants
-high triglyceride levels
-high Ca2+
-scorpion bites
How is acute pancreatitis treated?
-bowel rest --> nothing by mouth
-resuscitation --> IV fluids
-monitor patient labs & vitals closely
What are the complications of acute pancreatitis?
-death
-hemorrhage
-chronic pancreatitis
Which pancreatitis leads to irreversible changes?
chronic pancreatitis
what are the symptoms of chronic pancreatitis?
-asymptomatic until severe tissue lost
-epigastric abdominal pain --> may be intermittent, may radiate to back
-weight loss
-diarrhea (steatorrhea)
Describe the epigastric pain associated with chronic pancreatitis?
-may be intermittent
-may radiate to back
what are the causes of chronic pancreatitis?
-80% alcohol
-metabolic
-hereditary
-other
How is chronic pancreatitis diagnosed?
-imagining --> X-ray, CT scan, ERCP
-labs may be normal
Describe the pathology of chronic pancreatitis?
atrophy, fibrosis, calcification, chronic inflammatory infiltrate of the pancreas
*varies with early & late stage
How is chronic pancreatitis treated?
-pain management
-nutritional supplementation
-alcohol cessation
-endoscopy/surgery if obstructive
What are the complications of chronic pancreatitis?
-malnutrition from pancreatic insufficiency--> maldigestion
-diabetes --> islet cell destruction
-pancreatic cancer
True or False: There is an association between periodontal disease and the progression of pancreatic cancer.
True
How is diarrhea diagnosed?
-is it acute or chronic?
-history of present illness--> what are the characteristics of the diarrhea
-patient history --> recent travel, etc?
-are their other symptoms?
-risk factors?
Brown poop is ___________________.
healthy poop
What is black poop usually due to?
-foods
-medications
-bleeding ulcers
Green poop is often due to?
-eating green veggies
-iron supplements
What is yellow poop usually due to?
could be a sign of blockage in the bile duct
What can cause watery poop?
-secretory diarrhea --> secretion of electrolytes into lumen (makes water follow) due to altered mucosal transport or secretory dysfunction (ex: vibrio cholera)
-osmotic diarrhea--> something in lumen is drawing water out of body (ex: lactose intolerance)
secretory diarrhea
secretion of electrolytes into lumen (makes water follow) due to altered mucosal transport or secretory dysfunction
*causes watery stool
ex: vibrio cholera
osmotic diarrhea
something in lumen is drawing water out of body
*causes watery stool
ex: lactose intolerance
What causes steatorrhea?
-malabsorption--> damage to or loss of absorptive ability
>ex: celiac disease
-maldigestion --> loss of digestive function
>ex: pancreatic insufficiency
steatorrhea
fatty stool
What kind of stool is produced by vibrio cholera?
watery
What kind of stool is produced by lactose intolerance?
watery
What kind of stool is produced by celiac disease?
fatty stool ==> due to malabsorption from damage to or loss of absorptive ability
what kind of stool is produced in pancreatic insufficiency?
fatty stool ==> due to loss of digestive function due to lack of enzymes (leads to diarrhea & malnutrition)
stool that has blood or pus accompanied by elevated white blood cell count is called ___________________.
inflammatory/exudative diarrhea
What kind of stool is produced by pseudomembranous colitis?
inflammatory/exudative diarrhea
What kind of stool is produced by irritable bowel syndrome?
diarrhea secondary to altered bowel motility
What are some common causes of secretory diarrhea?
-vibrio cholera
-neuroendocrine tumors (VIPoma)
-non-osmotic laxatives (senna)
-microscopic colitis
How does vibrio cholera cause secretory diarrhea?
cholera toxin ultimately upregulates cAMP--> opens Cl- channels --> water follows electrolytes --> severe life threatening diarrhea
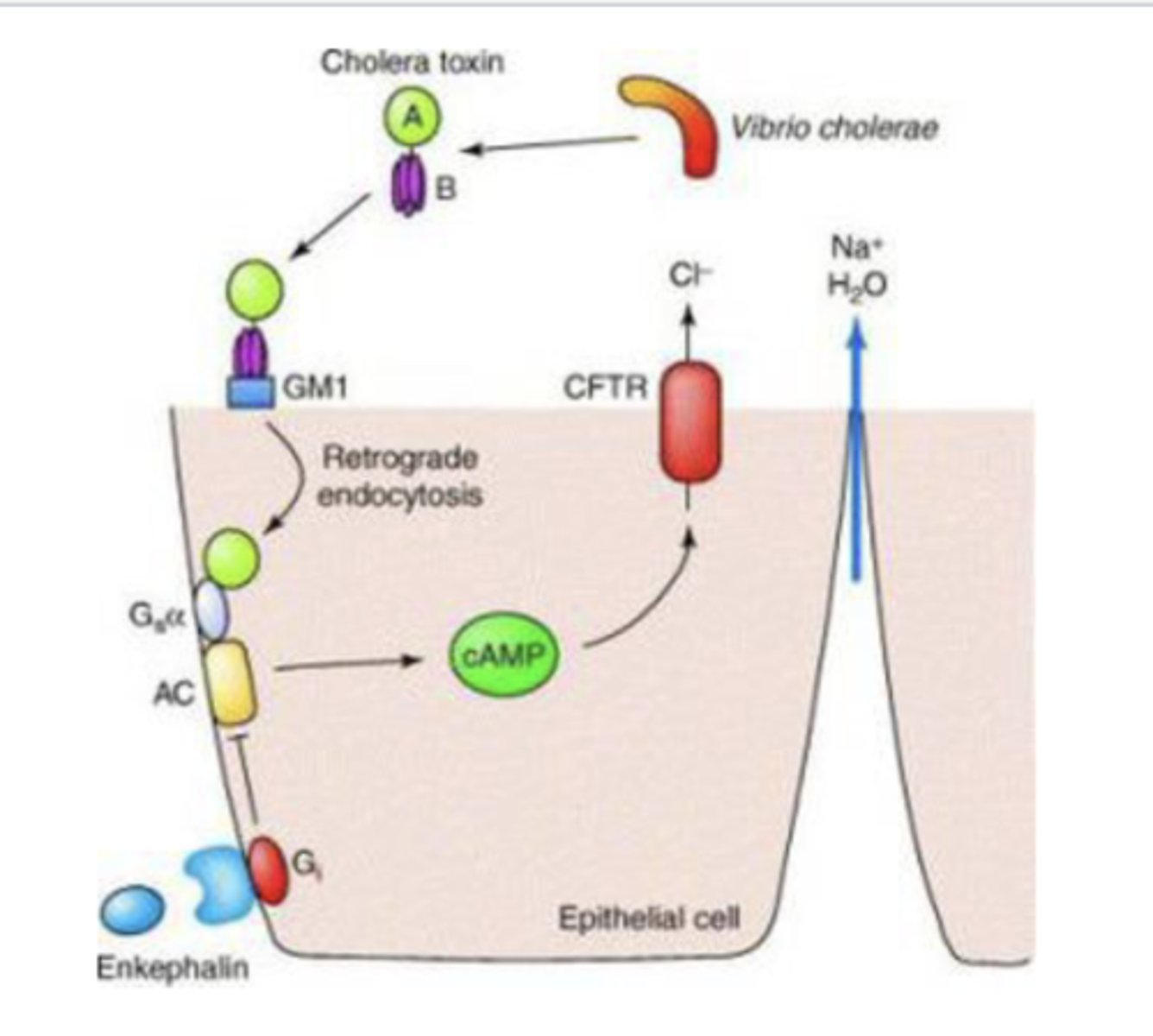
Treatment for Vibrio Cholera
fluids, esp oral electrolytes & glucose
what are some common causes of osmotic diarrhea?
-lactose intolerance
-carbohydrate malabsorption
-osmotic laxatives
-sugar alcohols --> mannitol, sorbitol (often in sugarless gum)
What are the symptoms of lactose intolerance?
-bloating
-flatulence
-abdominal cramps
-nausea
-diarrhea
*only occurs 30 min to 2h after ingestion
what are some common causes of steatorrhea?
-celiac disease
-gastric bypass
-medications --> ex: Orlistat (inhbits fat absorption)
-bacterial overgrowth in small bowel
-pancreatic insufficiency
-amyloidosis
Medications like Orlistat inhibits fat absorption. How does this affect the stool?
fatty stool
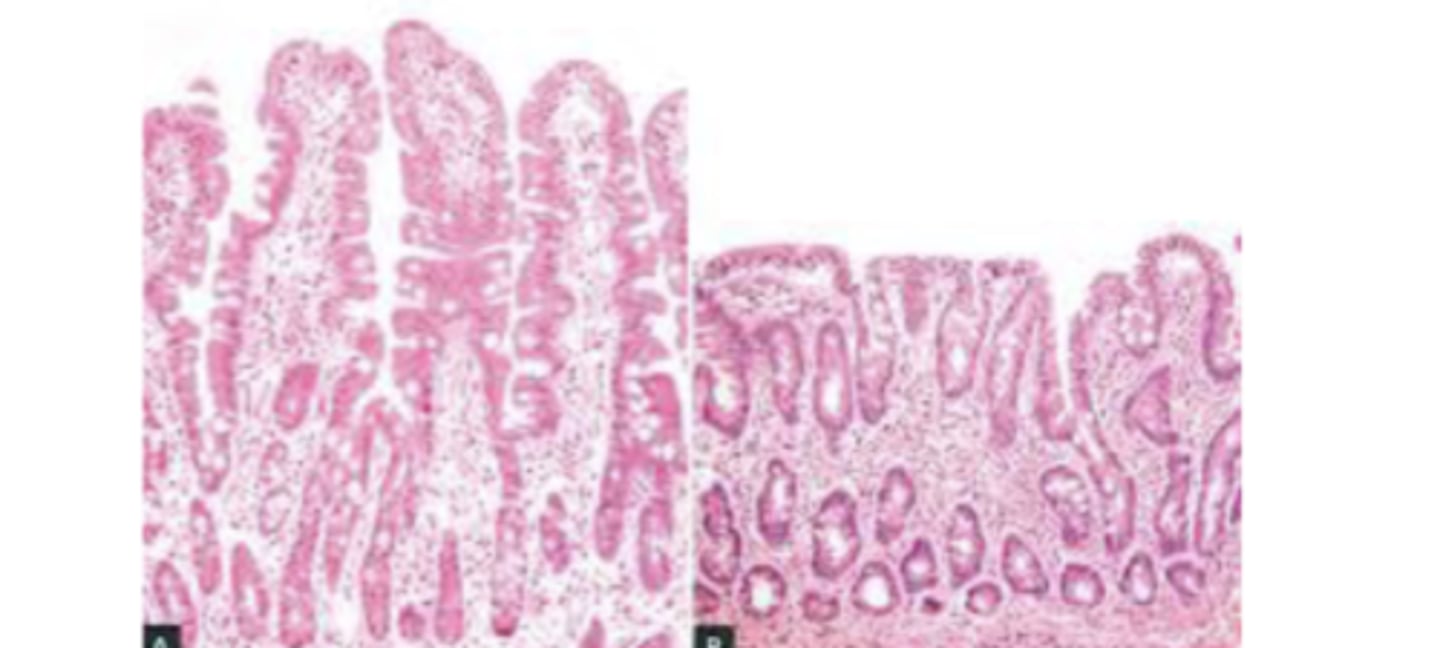
What is celiac disease?
gluten sensitive enteropathy; immune-mediated reaction against gluten
*blunting of villi & loss of surface area
What are some common causes of inflammatory or exudative diarrhea?
pseudomembranous colitis
-altered GI flora after use of broad spectrum antibiotics (ex: clindamycin)
-C. difficile (most common cause)
What is the most common cause of inflammatory or exudative diarrhea?
C. difficile infection
What are common causes of Pseudomembranous colitis?
-altered GI flora after use of broad spectrum antibiotics--> clindamycin
-C. difficile
How is pseudomembranous colitis diagnosed?
stool culture for C. difficile
How is C. Difficile Colitis treatment and prevention?
-primary prevention = hand washing
-contact precautions
-avoid unnecessary antibiotics
-supportive treatment
avoid anti-motility treatment
-IV or PO Flagyl, PO Vancomycin, other
What are the complications of C. Difficile Colitis?
-relapse --> may be a role for probiotics & fecal transplant
-toxic megacolon
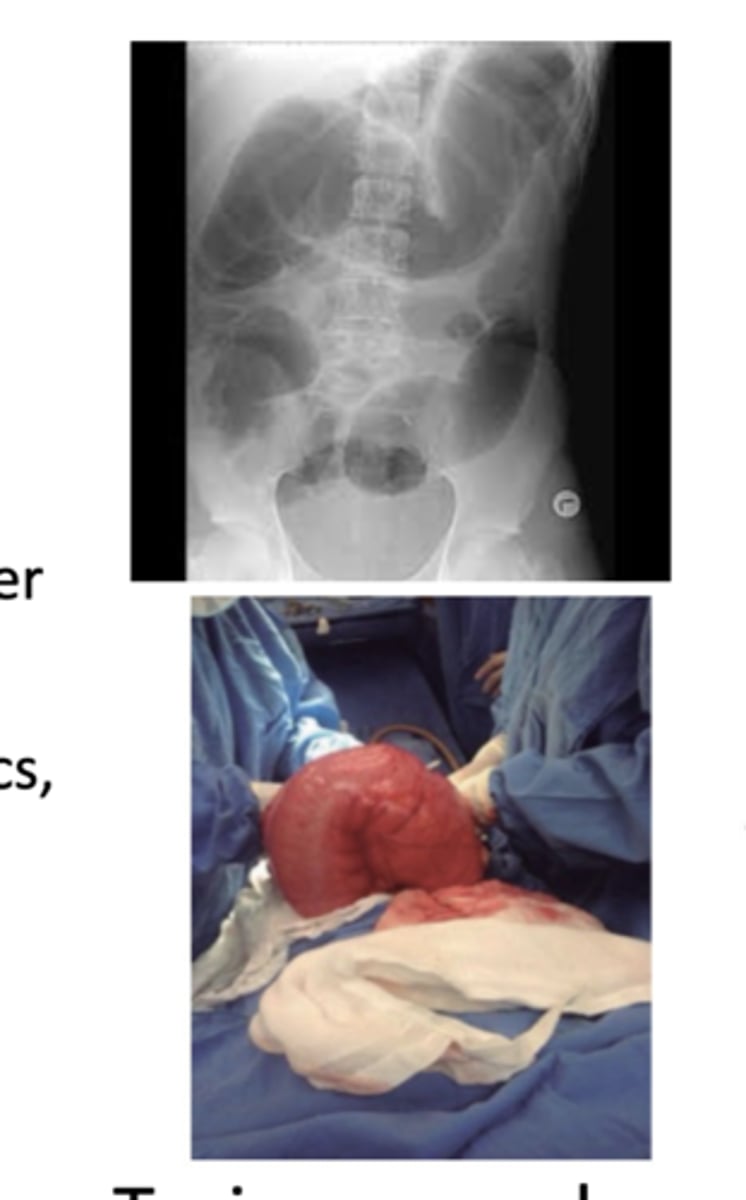
What are some differential diagnoses for inflammatory or exudative diarrhea?
-inflammatory bowel disease --> crohn's /ulcerative colitis
-diverticulitis
-invasive infectious disease
>bacterial --> tuberculosis, yersinia
>parasites --> entamoeba (travel history key)
>ulcerating viral infections --> CMV, HSV
-neoplasia--> colon cancer, lymphoma
-radiation colitis
What are the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome?
-abdominal pain
-disturbed defection--> diarrheas ans/or constipation
-bloating
-improves with fasting
-pertinent negatives --> no clear structural or biochemical abnormalities
What is the most common GI condition?
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
What is the possible pathophysiology of IBS?
-altered motility
-neurohumoral receptors --> serotonin signaling
-visceral hypersensitivity
-post-infectious
-altered colon flora
-psychosocial
What are possible treatments for IBS?
-diet modification
-behavorial psycotherapeutic treatments
-medications
>antispasmodic & antidiarrheal agents
>promotility agents
>antidepressants
What will a patient with IBS present with during a physical exam?
-abnormal abdominal exam
-fever
-positive fecal occult blood
What can you expect to see in a patient's history who was diagnosed with IBS?
-family history of cancer or inflammatory bowel disease
-weight loss
-onset in older patient
-nocturnal awakening due to symptoms
What do you expect to see in the labs of a patient diagnosed with IBS?
-low hemoglobin/hematocrit
-high white blood cell count
-high ESR (sedimentation rate) --> non-specific sign of inflammation
-abnormal chemistries
yet no clear structural or biochemical abnormalities (pertinent negatives)
What are the 2 main types of colon polyps?
-hyperplastic--> nonmalignant potential
-adenomatous polyp --> neoplastic, pre-maglinant
How does a adenomatous polyp progress to cancer?
get larger --> severe dysplasia (precancerous polyp) --> adenocarcinoma --> invasive cancer
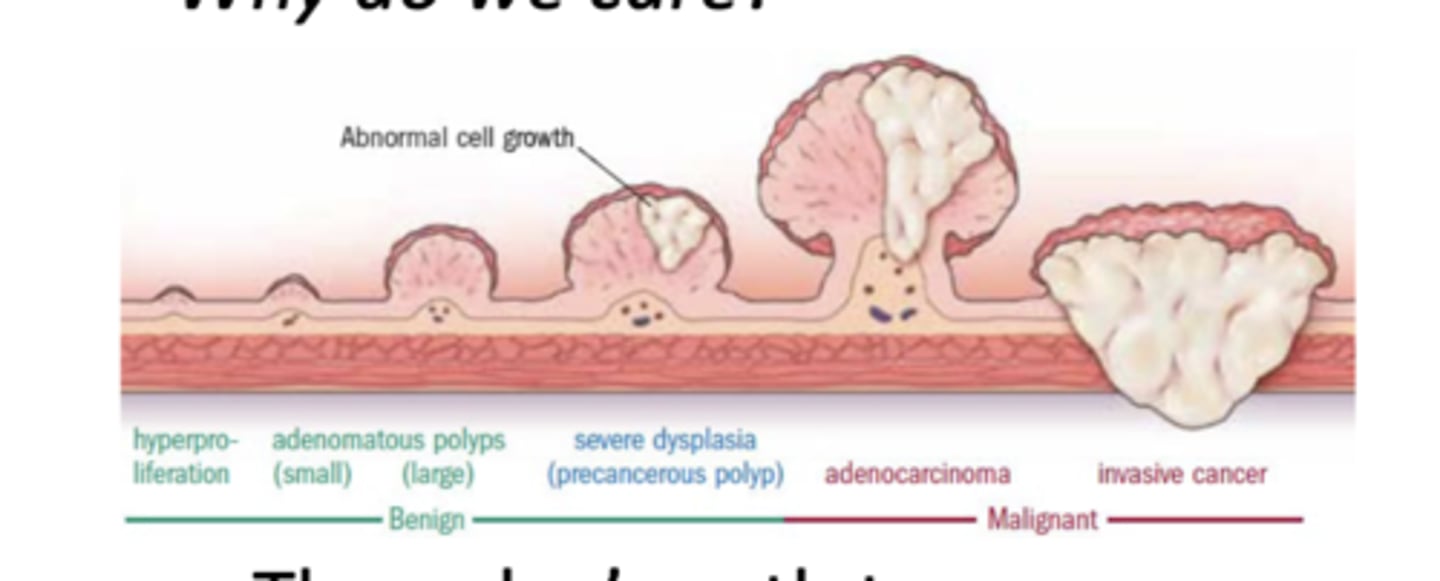
what is the 5 year survival rate of colon cancer?
66%
What is the 2nd leading cause of cancer-related deaths?
colon cancer
At what age range does the incidence of colon cancer increase?
40 - 50 years old
What are the risk factors for colon cancer?
-age
-family history
-IBD
-diabetes
-obesity
-alcohol
-smoking
-radiation to the pelvis
What are the cancer syndromes associated with colon cancer?
-peutz-jeghers
-familiar adenomatous polyposis (FAP)
-gardner disease (subset FAP)
-herediatray non-polyposis colorectal cancer (HPNCC- Lynch Syndrome)
What is the recommended frequency of colon cancer screening for average risk adults?
starting at the age of 45, repeat every 10 yrs.
Who are patients at high risk for colon cancer screening?
-family history of colon cancer before age 60
-polyposis syndromes
-IBD
-history of radiation to abdomen/pelvis
what are the screening methods for colon cancer?
-hemoccult testing --> fecal test for occult blood
-flexible sigmoidoscopy--> only examines the left colon
-air contrast barium enema
-colonoscopy --> examines the entire colon; cancer prevented by removal of polyps (gold standard)
-cologuard --> home stool test that detects mutations to help with early diagnosis
-virtual colonoscopy/CT colonoscopy --> quick CT that's non-invasive; F/U scope if lesons found
What is the gold standard of colon cancer screening?
colonoscopy
-examines the entire colon
-cancer can be prevented by removal of polyps
-current gold standard
What are the tests for blood loss and anemia used when these issues are due to GI Tract Disease?
-hematocrit
-hemoglobin
-red cell indices
-serum iron/ferritin if indicated
-fecal occult blood test
What are the tests for infection or inflammation used when these issues are due to GI tract disease?
-WBC count--> can get a differential of specific cell types
-ESR --> erythrocyte sedimentation "sed" rate
-CRP--> nonspecific