Renal Physiology: Nephrons, Urine Concentration, and ADH
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
Cortical Nephrons
85% of nephrons located in cortex.
Juxtamedullary Nephrons
15% of nephrons with long loops.
Nephron Loops
Deeply invade medulla, crucial for urine concentration.
ADH
Hormone increasing water channels in collecting ducts.
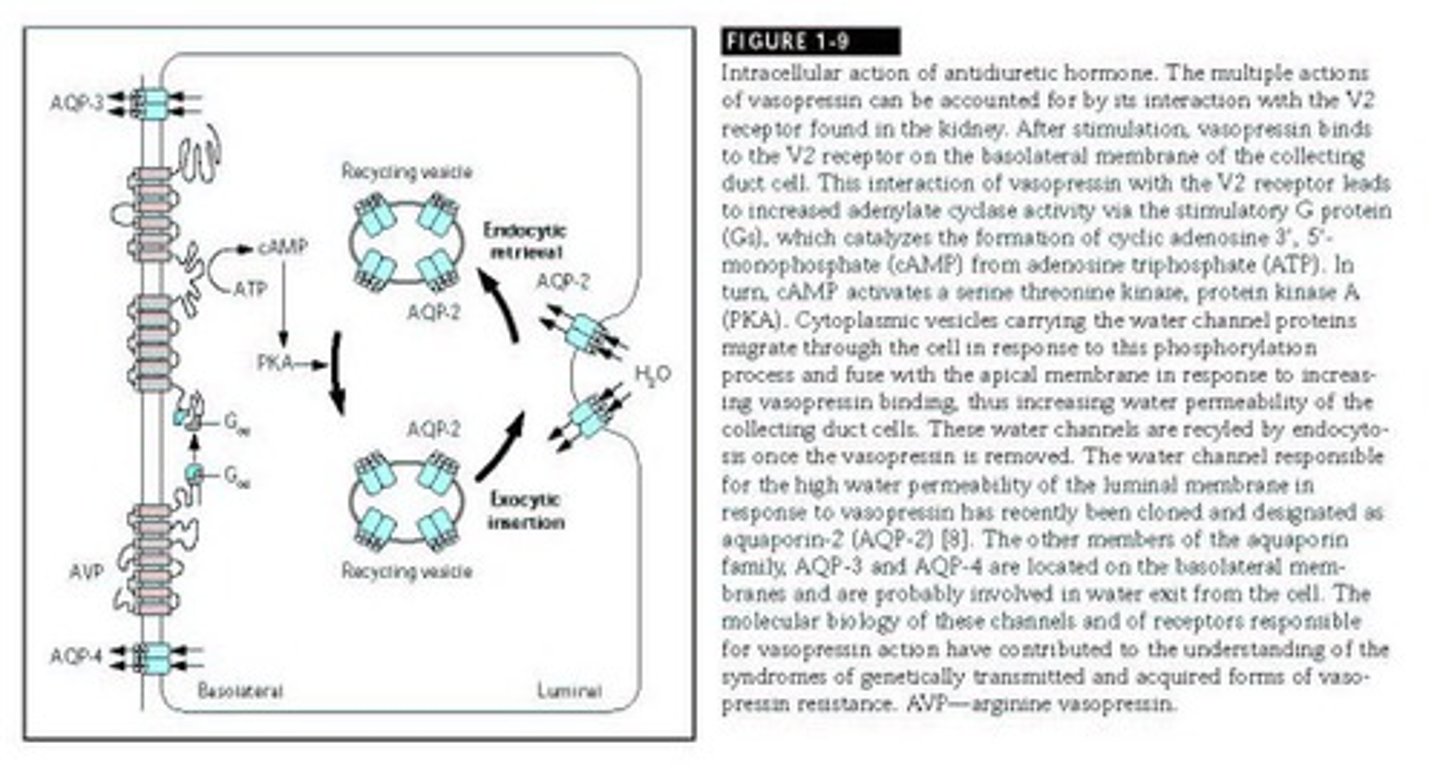
Collecting Ducts
Extend into medulla, affecting urine osmolarity.
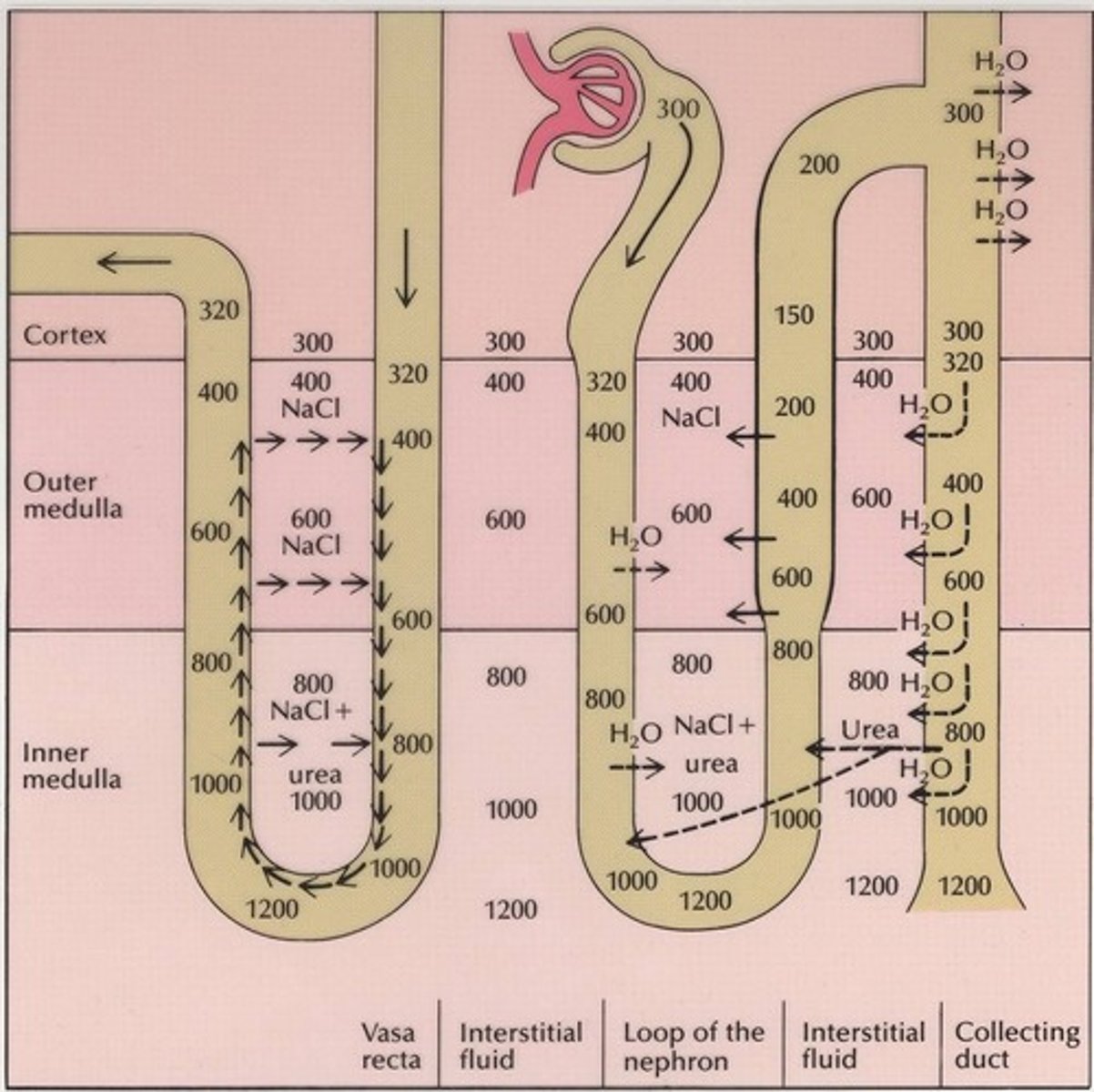
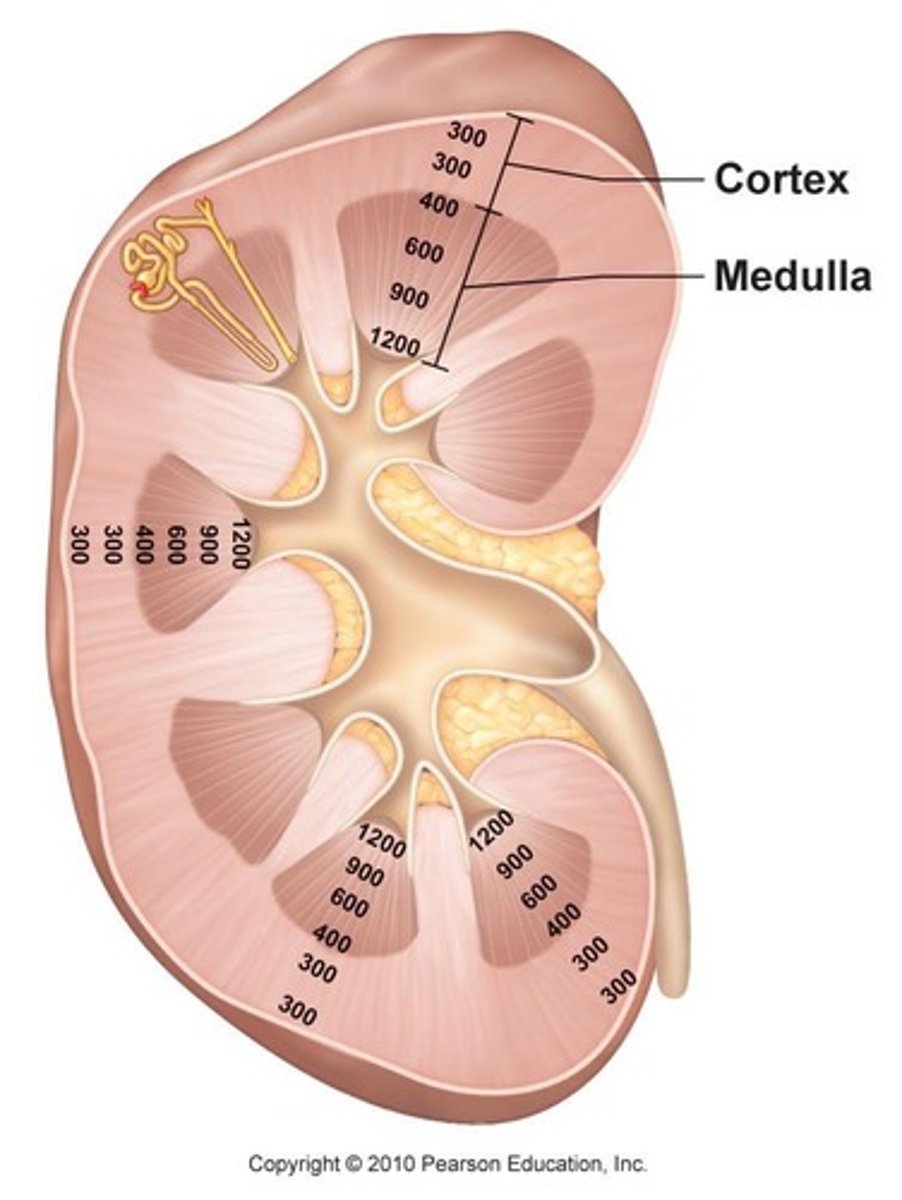
Osmolarity
Concentration of solutes in urine, up to 1200 mOsm/L.
Plasma Osmolarity
Normal level around 300 mOsm/L; affects ADH secretion.
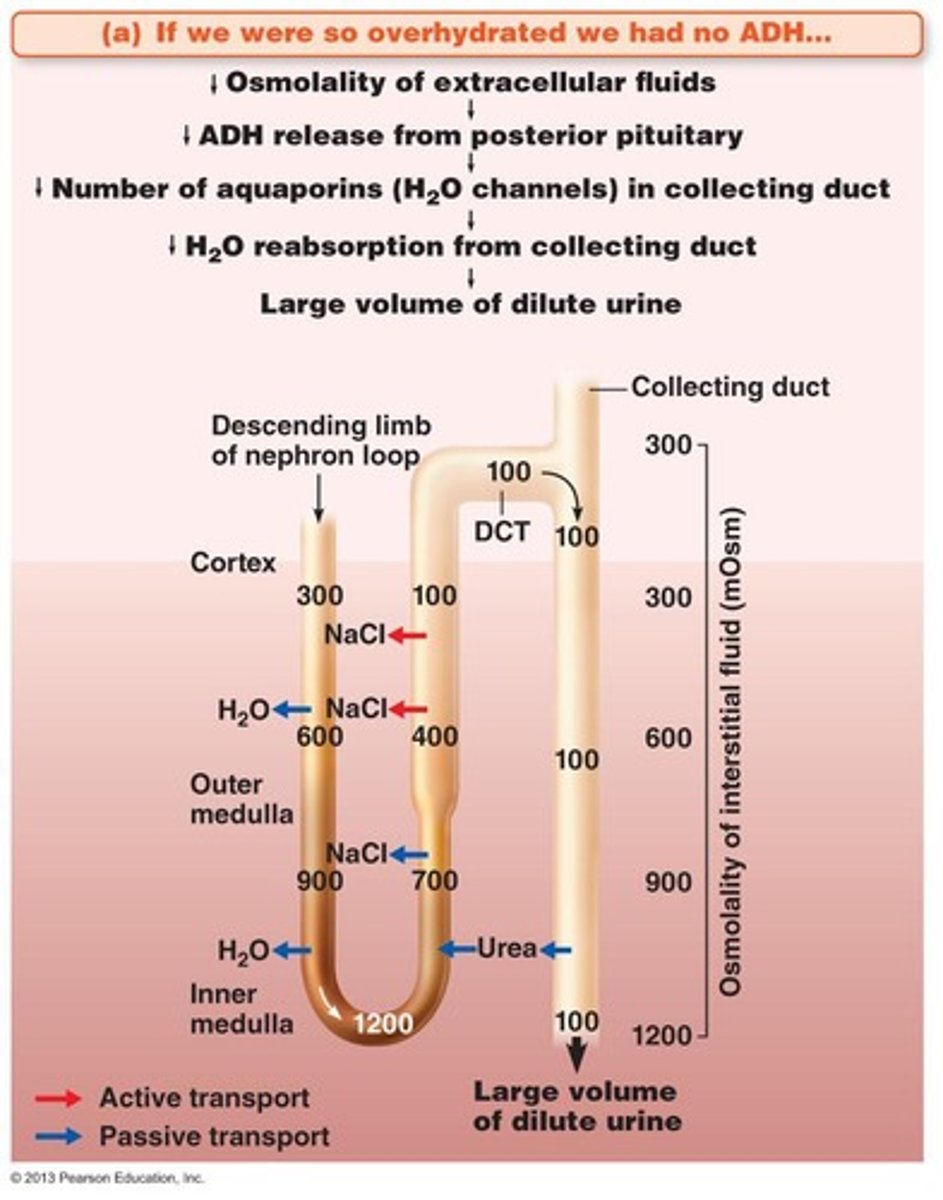
Dilute Urine
Produced when ADH is absent, osmolarity as low as 100 mOsm/L.
Urea Recycling
Process enhancing medullary osmotic gradient for urine concentration.
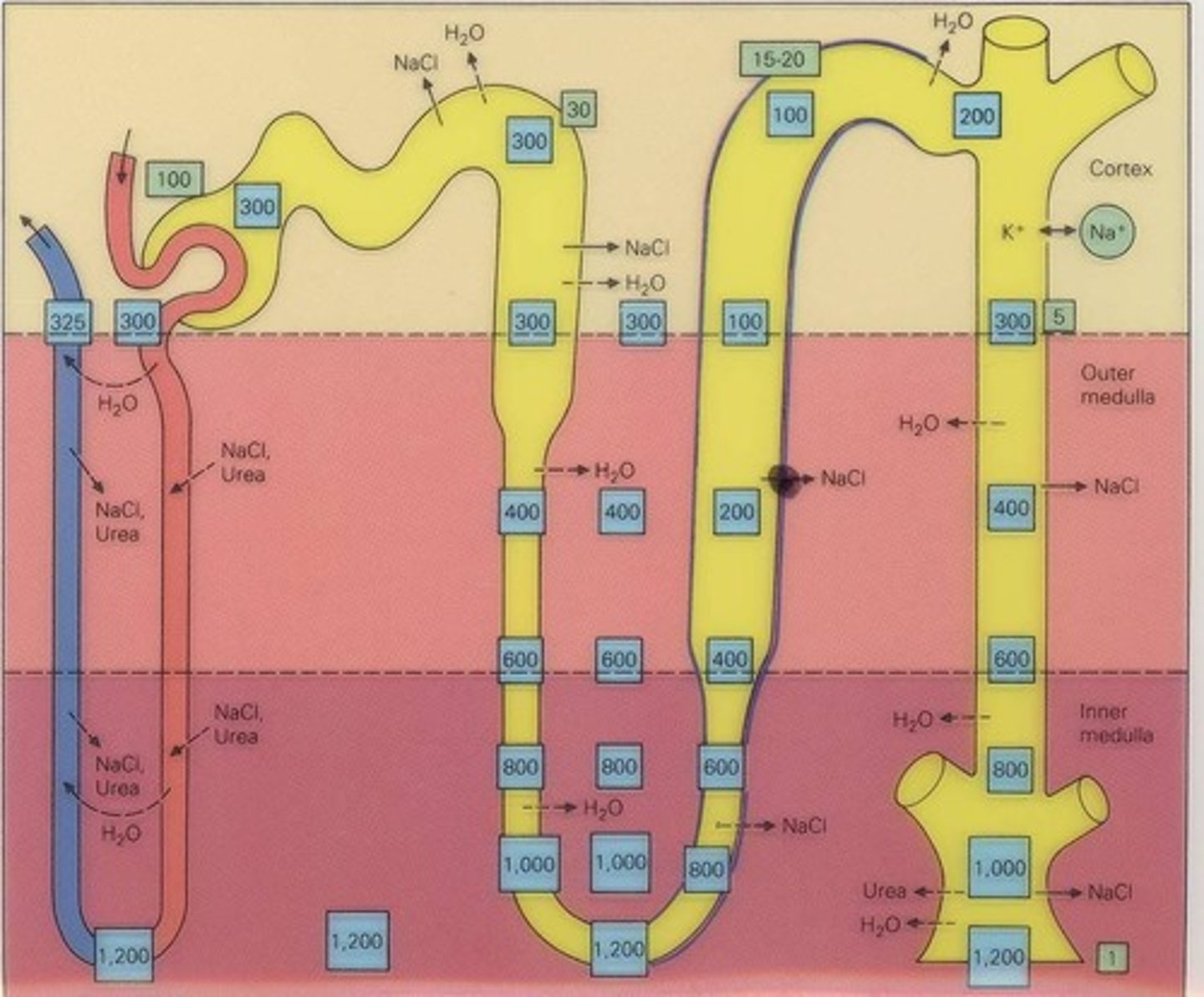
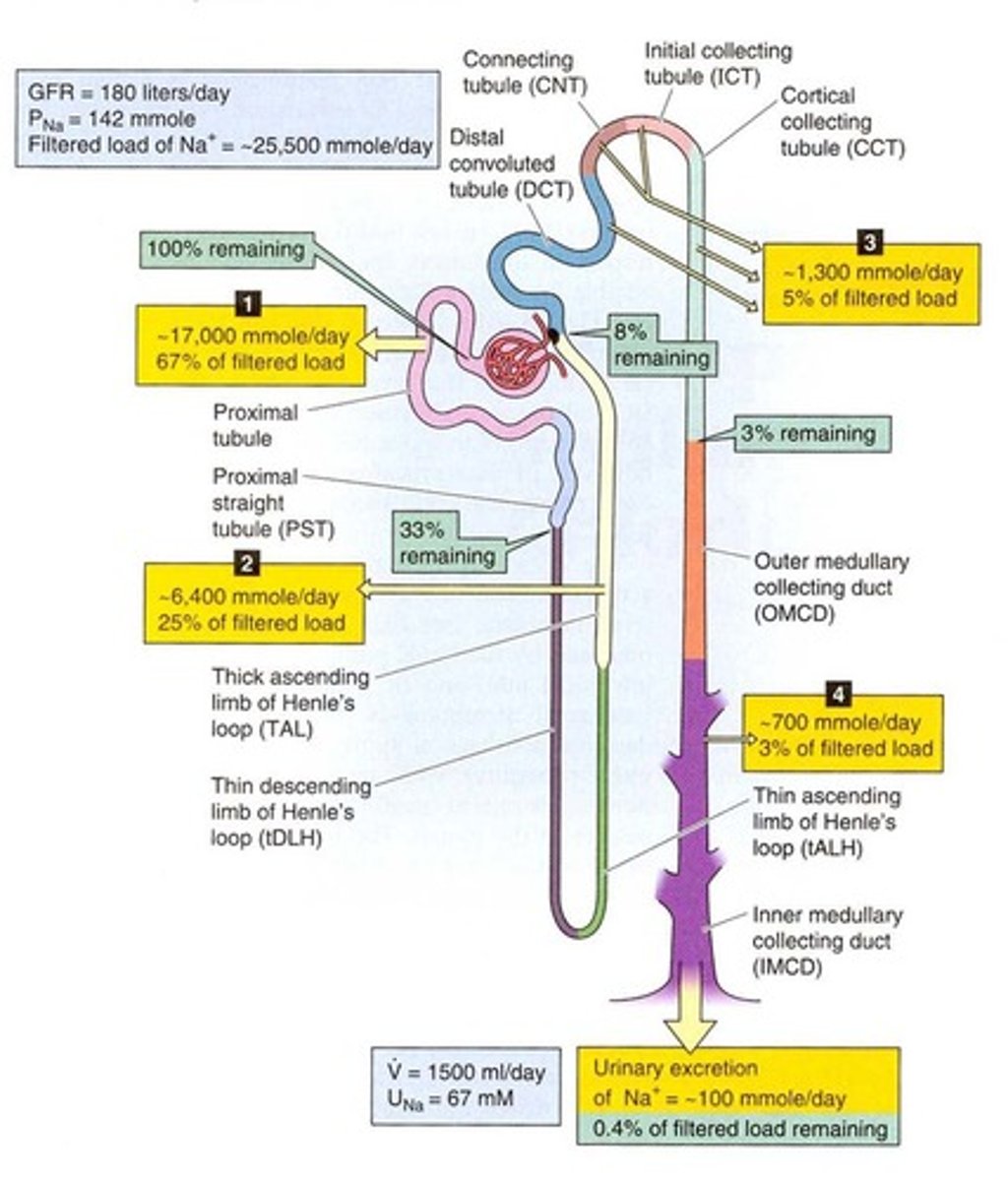
Proximal Tubule
Site for sodium and bicarbonate reabsorption.
HCO3- Reabsorption
Occurs in proximal tubule and collecting duct.
Loop of Henle
Structure involved in urine concentration and dilution.
Thin Descending Limb
Permeable to water, impermeable to salts.
Thin Ascending Limb
Impermeable to water, allows salt reabsorption.
Thick Ascending Limb
Active salt reabsorption, impermeable to water.
Distal Convoluted Duct
Further regulates sodium and water reabsorption.
Cortical Collecting Duct
Final site for sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion.
Outer Medullary Collecting Duct
Involved in final urine concentration adjustments.
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Hormonal system regulating blood pressure and fluid balance.
Glucose Transport
Mechanism for reabsorbing glucose in kidneys.
Micturition Reflex
Neural control of bladder emptying.
H+ Secretion
Proximal tubule & collecting duct adjust H+ levels.
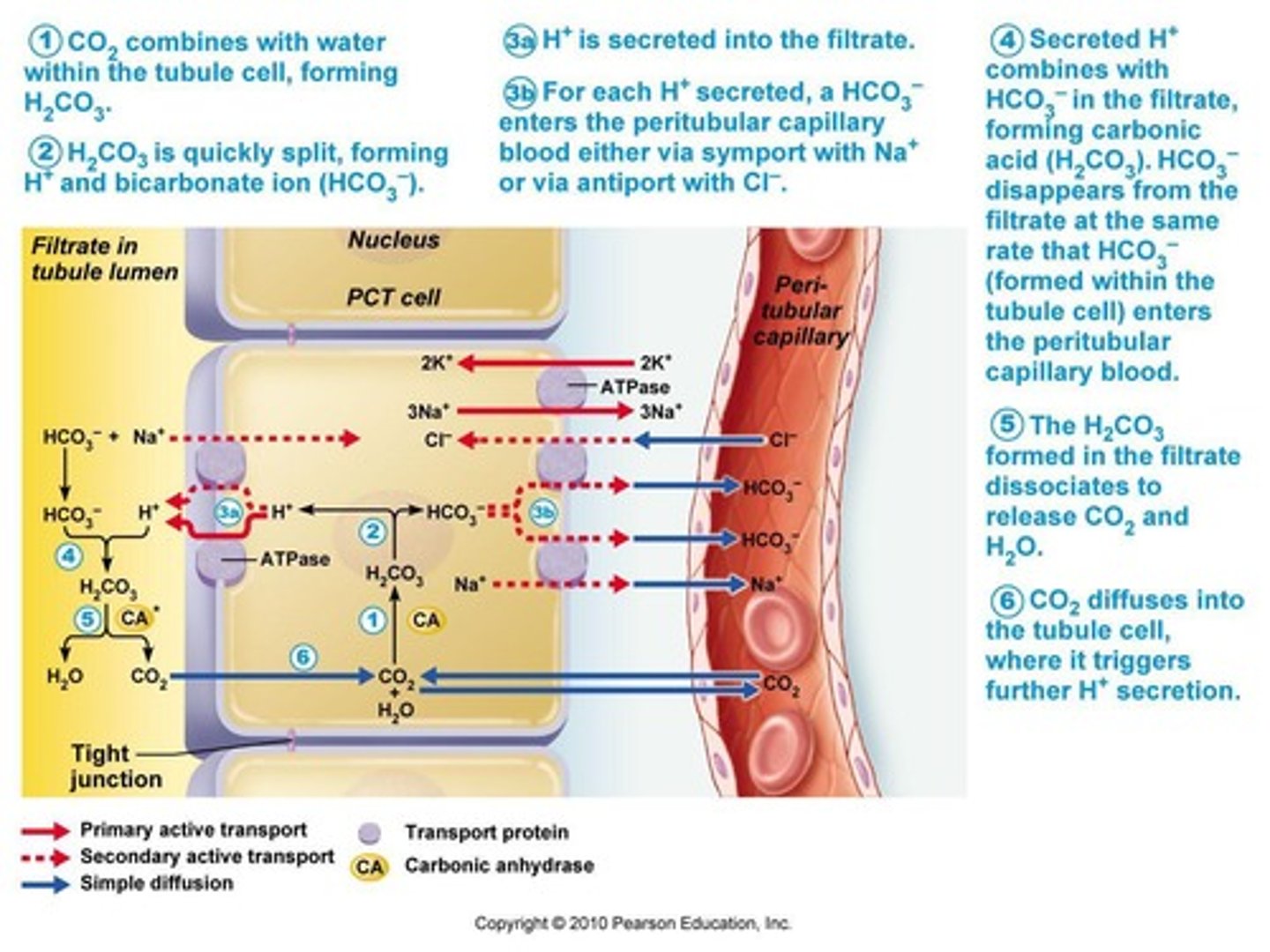
Carbonic Acid
Source of secreted H+ in renal tubules.

Electrochemical Balance
Na+ reabsorbed for each H+ secreted.
Phosphate Buffer System
Weak base HPO4^2- regulates pH in kidneys.
Type A Intercalated Cells
Secrete H+ and generate new HCO3-.
NH4+ Excretion
Generated from glutamine metabolism in PCT.
Bicarbonate Ion Excretion
Occurs via type B intercalated cells.
Renin-Angiotensin System
Pathway for aldosterone secretion regulation.
Aldosterone Secretion
Triggered by high K+ or low Na+ levels.
Addison's Disease
Adrenal insufficiency leading to low aldosterone.
Hypoaldosteronism
Condition of insufficient aldosterone production.
Hypovolemia
Low blood volume risk in Addison's patients.
Hyperkalemia
High potassium levels due to aldosterone absence.
Adrenocortical Tumor
Excess aldosterone causing low ECF potassium.
Principal Cell
Cell type involved in Na+ and K+ handling.
Furosemide
Diuretic affecting Na+ reabsorption in kidneys.
Thiazides
Diuretics that inhibit Na+ reabsorption.
Ouabain
Inhibitor of Na+/K+ ATPase pump.
Barium
Blocks potassium channels affecting renal function.
HCO3-/Cl- Antiport
Mechanism for bicarbonate reabsorption in kidneys.
Micturition
Process of urination or voiding urine.
Detrusor Muscle
Muscle that contracts to expel urine.
Internal Urethral Sphincter
Muscle controlled by ANS to retain urine.
External Urethral Sphincter
Muscle controlled by somatic nervous system.
Micturition Reflex
Involuntary urination response triggered by bladder distension.
Stretch Receptors
Sensors activated by bladder distension during micturition.
Parasympathetic Neurons
Nerve fibers stimulating detrusor contraction.
Urinary Incontinence
Inability to control urination, often due to muscle weakness.
Stress Incontinence
Urine leakage due to increased abdominal pressure.
Overflow Incontinence
Urine dribbles when bladder is overfilled.
Urinary Retention
Inability to expel urine from the bladder.
Fluid Compartments
Different areas of body where fluids are distributed.
Intracellular Fluid (ICF)
Fluid within cells, primarily composed of water.
Extracellular Fluid (ECF)
Fluid outside cells, includes interstitial and blood plasma.
Water Balance
Equilibrium between water intake and output.
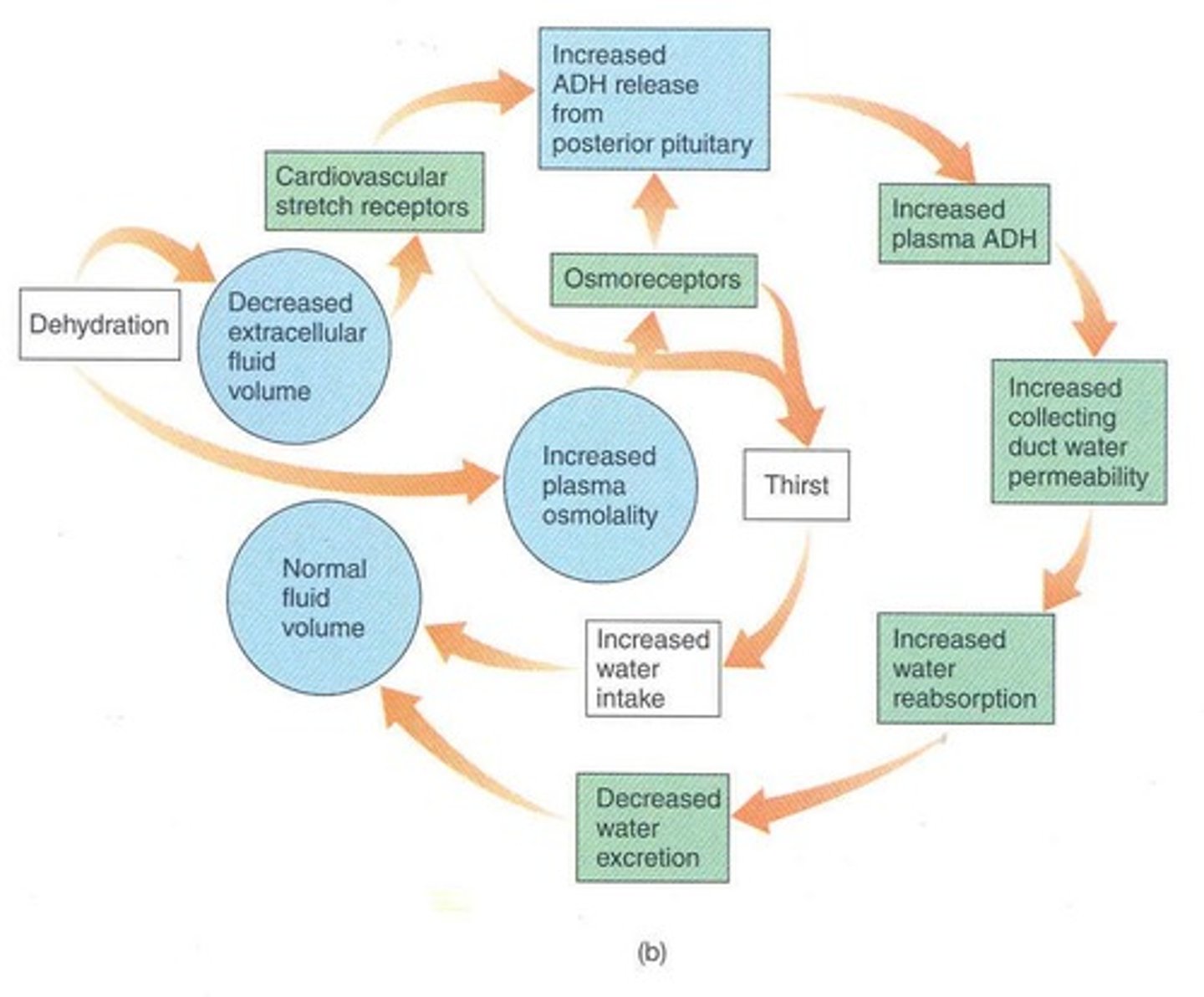
Thirst Mechanism
Physiological response to dehydration signaling need for water.
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Hormone regulating water retention in kidneys.
Sodium Balance
Regulation of sodium levels in the body.
Aldosterone
Hormone influencing sodium reabsorption in kidneys.
Body Water Content
Percentage of water in the human body.
Total Body Water
Average water content in adults, ~40 L.
Adipose Tissue Hydration
Least hydrated tissue type in the body.
Osmotic Pressure
Pressure from solutes causing water movement.
Hydrostatic Pressure
Pressure exerted by fluids in compartments.
ECF Osmolality
Concentration of solutes in extracellular fluid.
Thirst Mechanism
Physiological drive to consume water.
Hypothalamic Thirst Center
Brain region regulating thirst sensation.
Osmoreceptors
Cells detecting changes in plasma osmolality.
Metabolic Water
Water produced during cellular metabolism.
Water Intake
Total water consumed, ~2500 ml/day.
Water Output
Total water excreted, mainly via urine.
Dehydration
Loss of water from extracellular fluid.
Hypotonic Hydration
Excess water intake causing cellular swelling.
Hyponatremia
Low sodium concentration in blood.
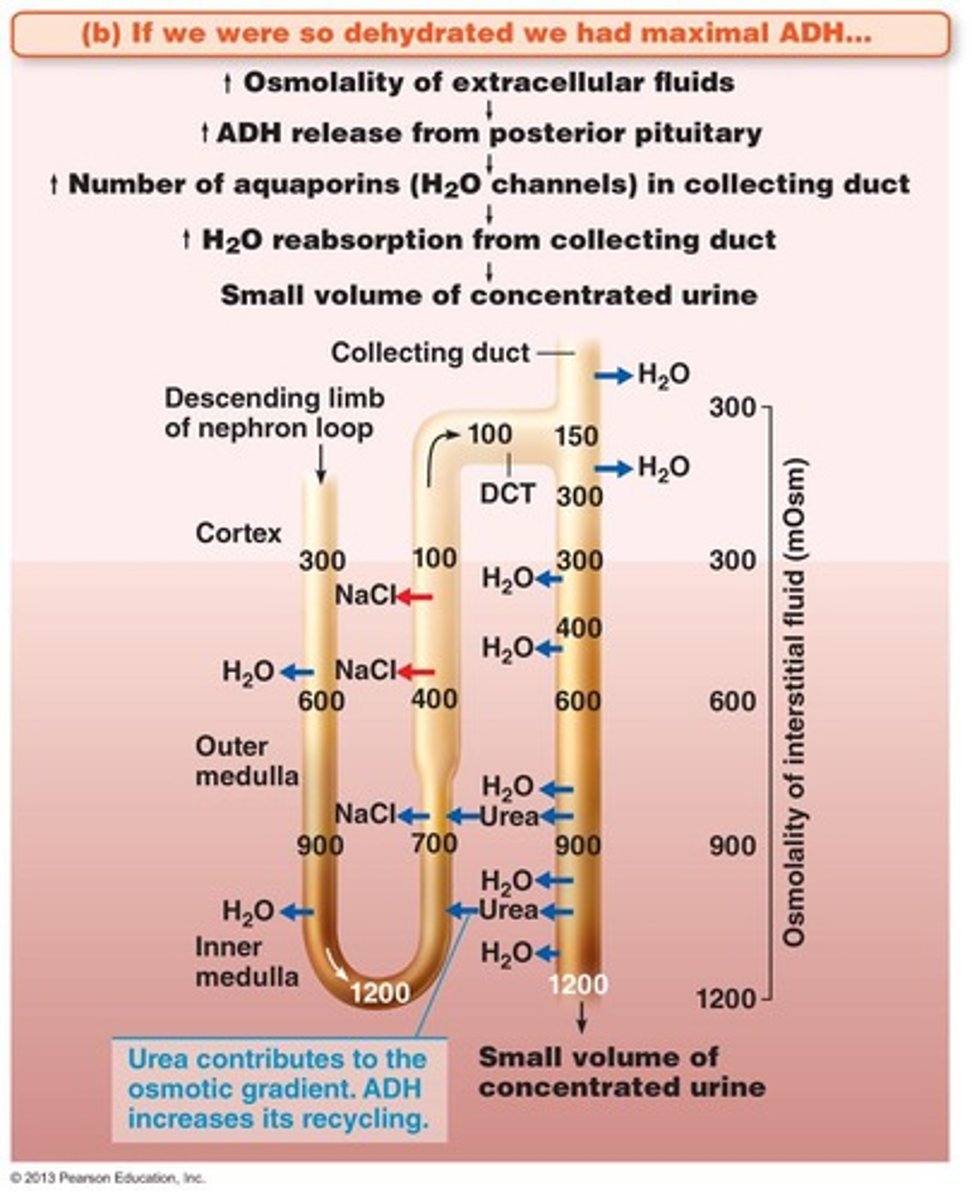
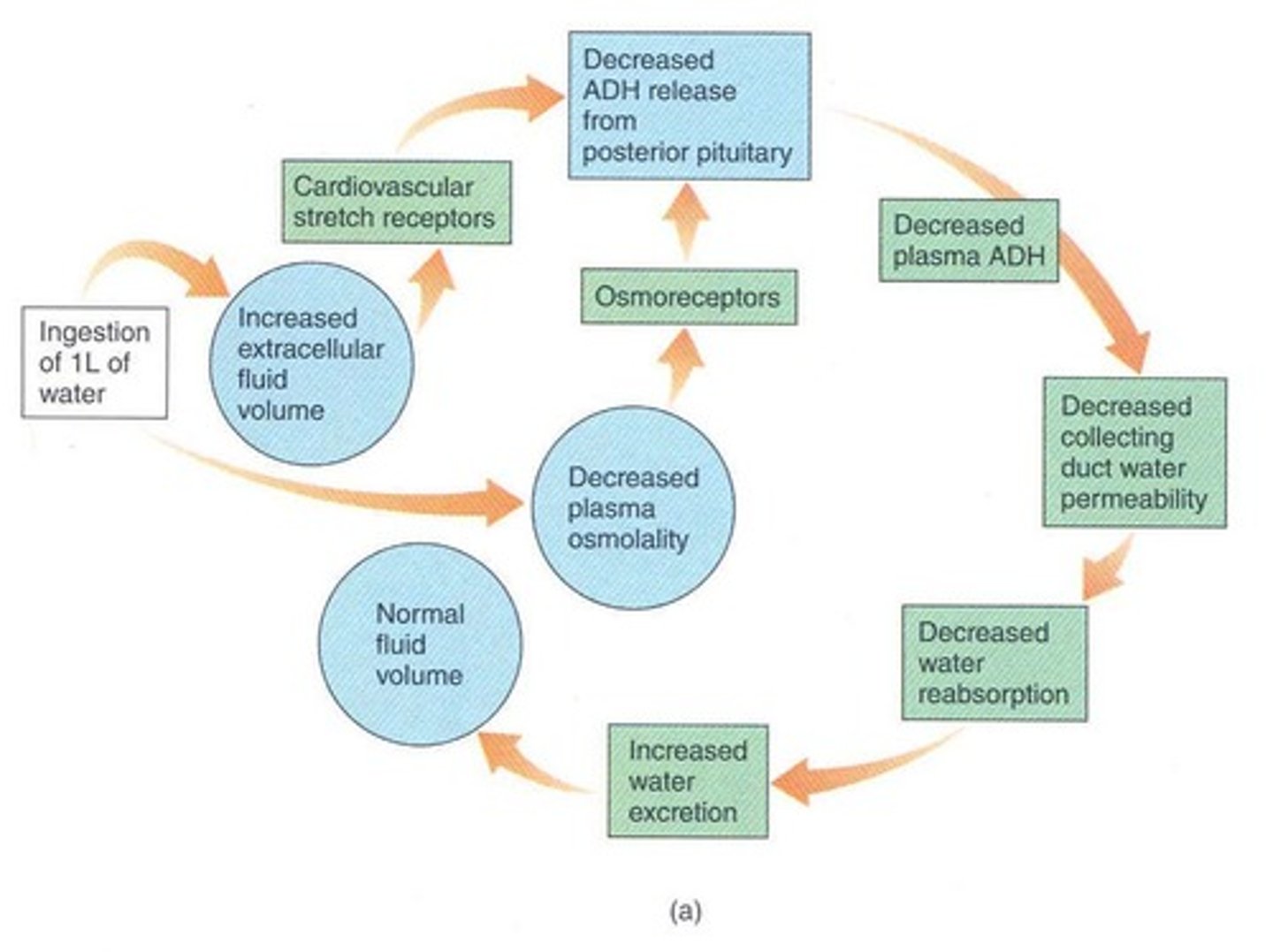
ADH Release
Hormone release in response to high osmolality.
Oliguria
Production of abnormally small urine amounts.
Cerebral Edema
Swelling of brain cells due to excess water.
Edema
Abnormal fluid accumulation in body tissues.
Pitting Edema
Swelling caused by fluid leakage from vessels.
Insensible Water Loss
Unnoticeable water loss through skin and lungs.
Electrolyte Loss
Loss of ions essential for body function.
Fluid Homeostasis
Balance of fluid intake and output.
Inhibitory Feedback Signals
Body signals that reduce thirst sensation.
Interstitium
Space between cells where fluid accumulates.
Interstitial Fluid Accumulation
Excess fluid in interstitial space causing tissue swelling.
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Hormone regulating water reabsorption in kidneys.
ADH Release Effects
Increased ADH leads to concentrated urine.
Decreased ADH Effects
Leads to dilute urine and reduced body fluid.
Hypothalamic Osmoreceptors
Senses ECF solute concentration to regulate ADH.
Central Diabetes Insipidus
Inadequate ADH release causing dilute urine production.
Polyuria
Excretion of large volumes of dilute urine.
Exogenous ADH Infusion
Corrects Central Diabetes Insipidus symptoms.
Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH (SIADH)
Excess ADH causing water retention and hypoosmotic fluids.
Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus (NDI)
Decreased AQP-2 expression leads to dilute urine.
Pyelitis
Infection of renal pelvis and calyces.
Pyelonephritis
Infection/inflammation of the entire kidney.
Dysuria
Painful urination often associated with infections.
Urethritis
Inflammation of the urethra.
Cystitis
Inflammation of the bladder.