Female Reproductive System
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
uterus
A hollow muscular organ in the pelvic cavity of the female, in which the embryo is nourished and develops before birth
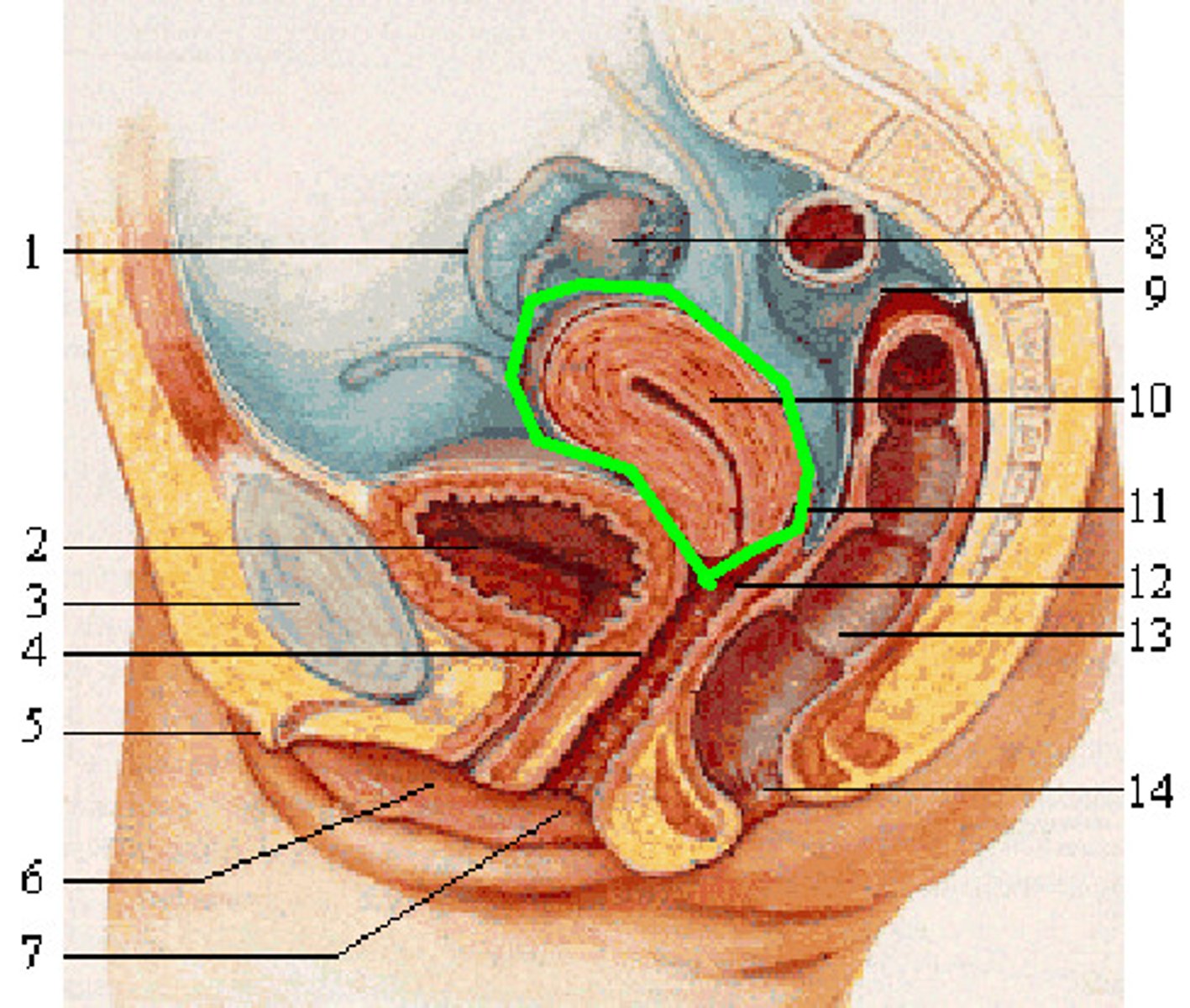
myometrium
muscle layer of the uterus - super thick so it can stretch as the baby grows; also so that it is strong enough to push out the baby.
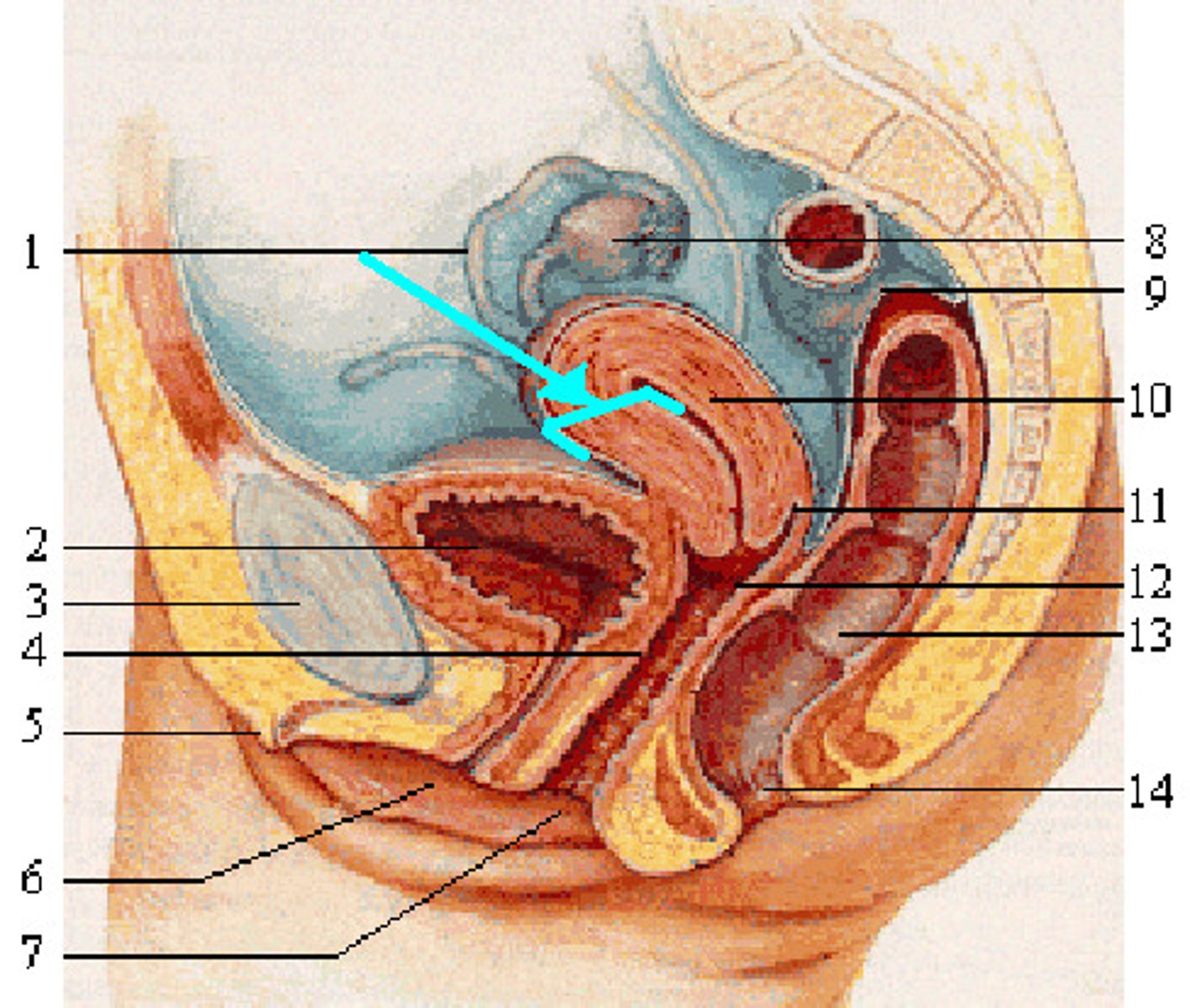
endometrium
The inner lining of the uterus, which is richly supplied with blood vessels. Estrogen and progesterone work together to cause it to thicken so that it can nourish an implanted embryo.
Menses - sloughing of this lining every month.
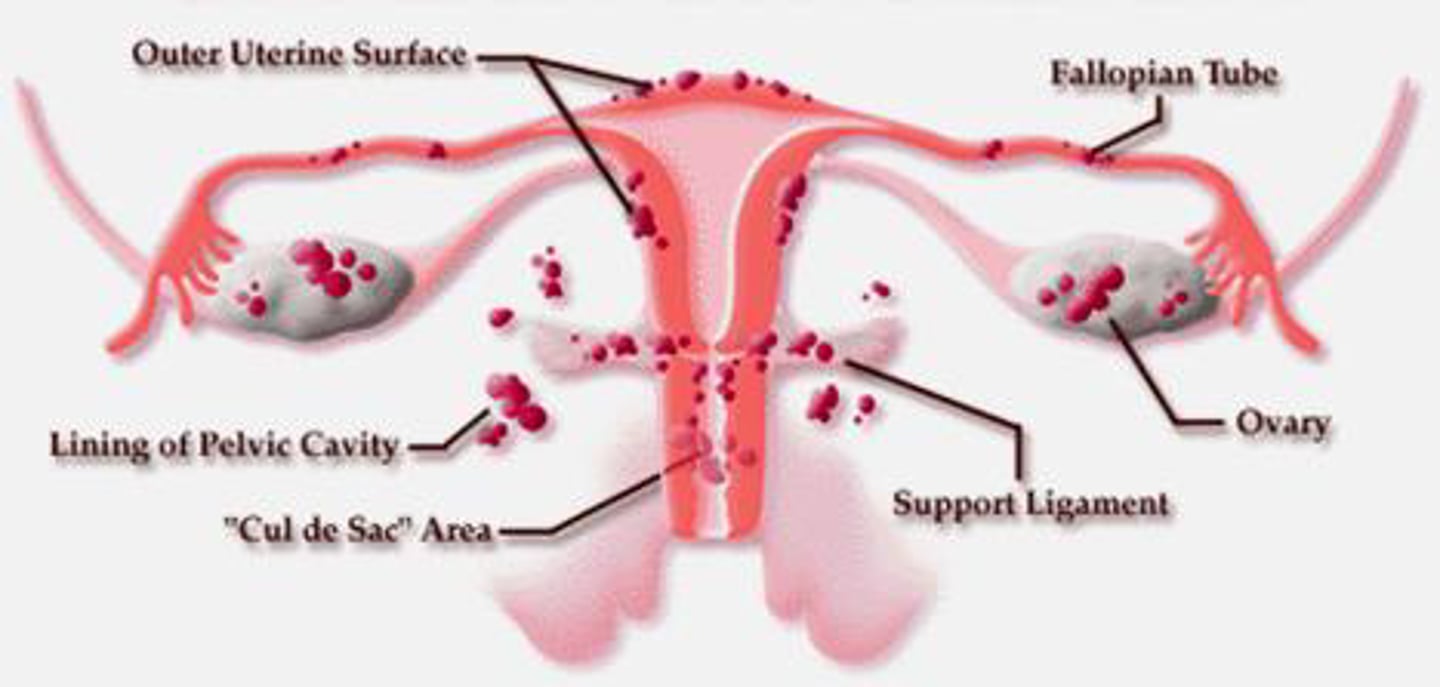
endometriosis
a condition in which patches of endometrial tissue escape the uterus and become attached to other structures in the pelvic cavity - particularly the ovaries, outside of the uterus or outside the fallopian tubes.
fallopian tube (oviduct)
lined w/cilia which propels egg forward; fertilization happens here
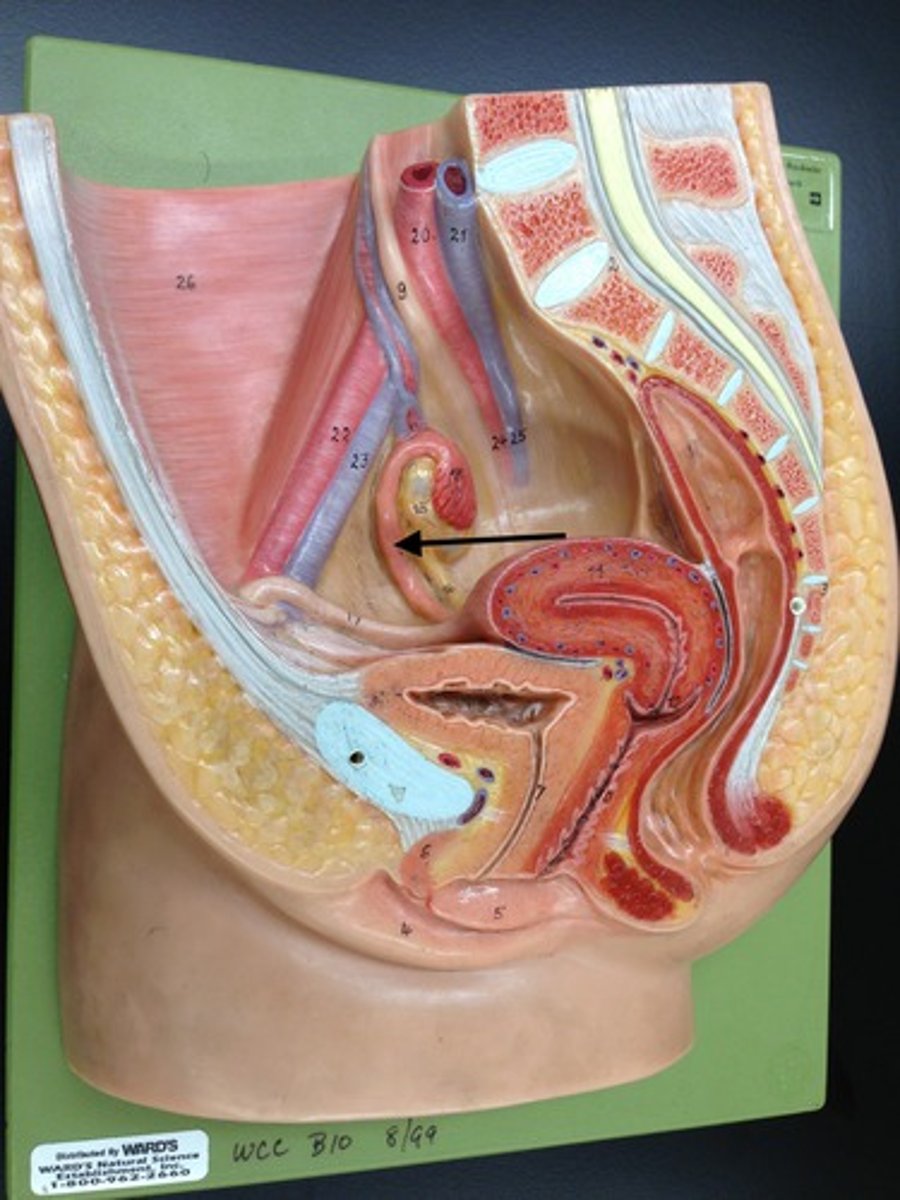
Ovaries
female gonads - produce estrogen and progesterone for development of the egg and corpus luteum. Controlled by FSH and LH from the pituitary gland.
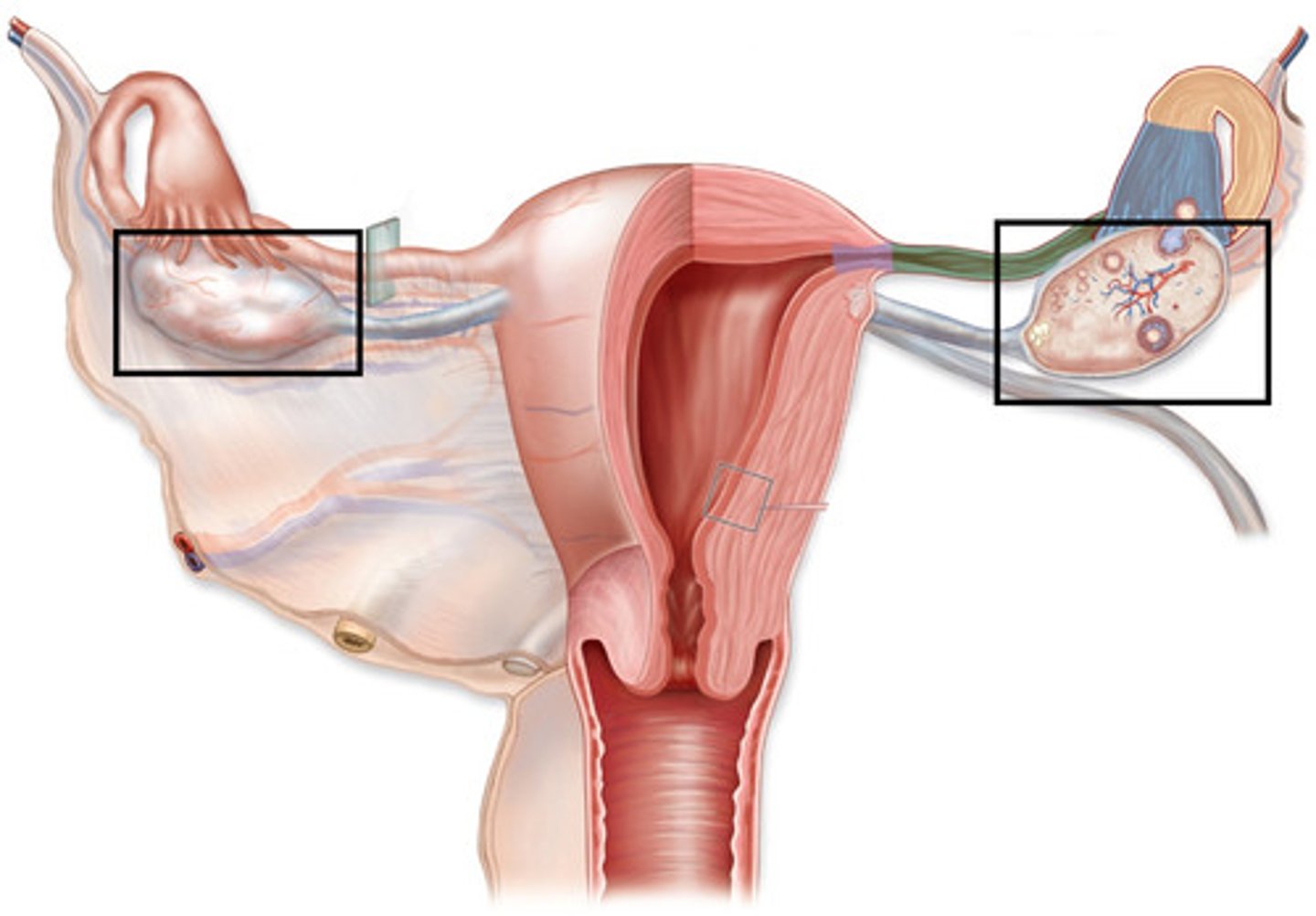
Fimbriae
Fingerlike projection of the uterin (fallopian) tubes that drape over the ovary.
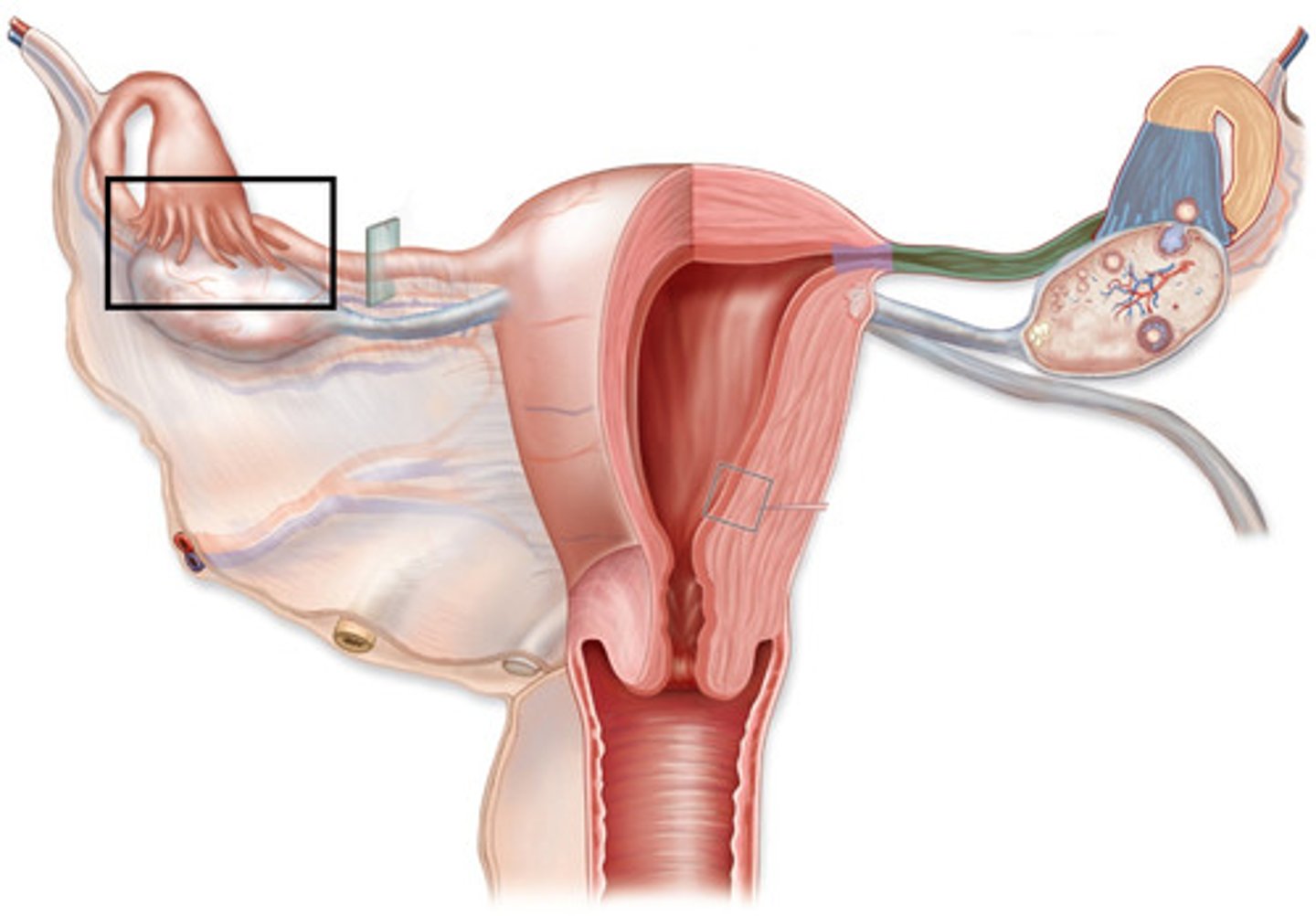
pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
An infection of the fallopian tubes and the surrounding tissues of the pelvis. Increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
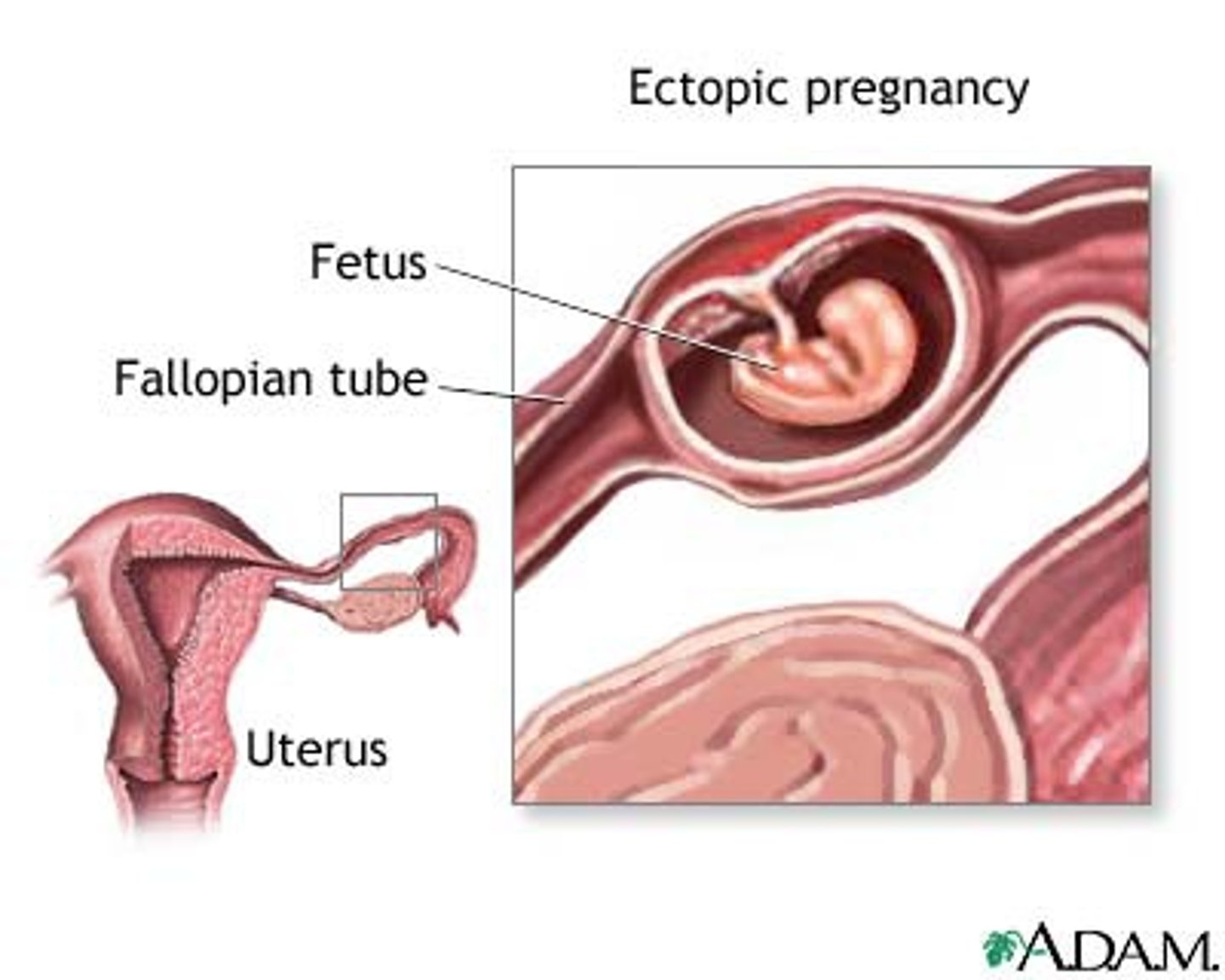
ectopic pregnancy
A pregnancy outside of the uterus, usually in a fallopian tube
ovarian cyst
a fluid filled sac in an ovary
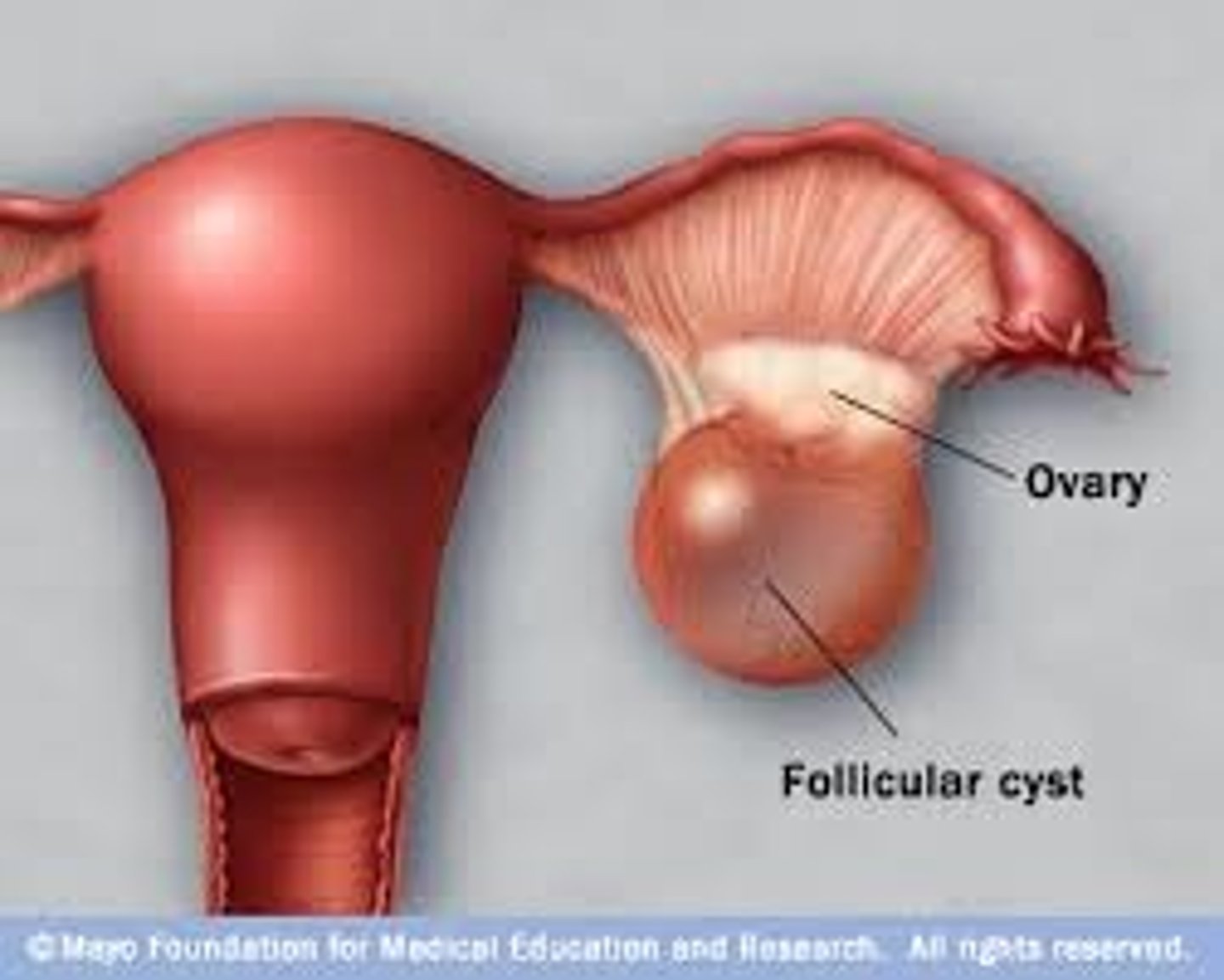
polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
endocrine disorder associated with chronic anovulation - caused by imbalance of reproductive hormones
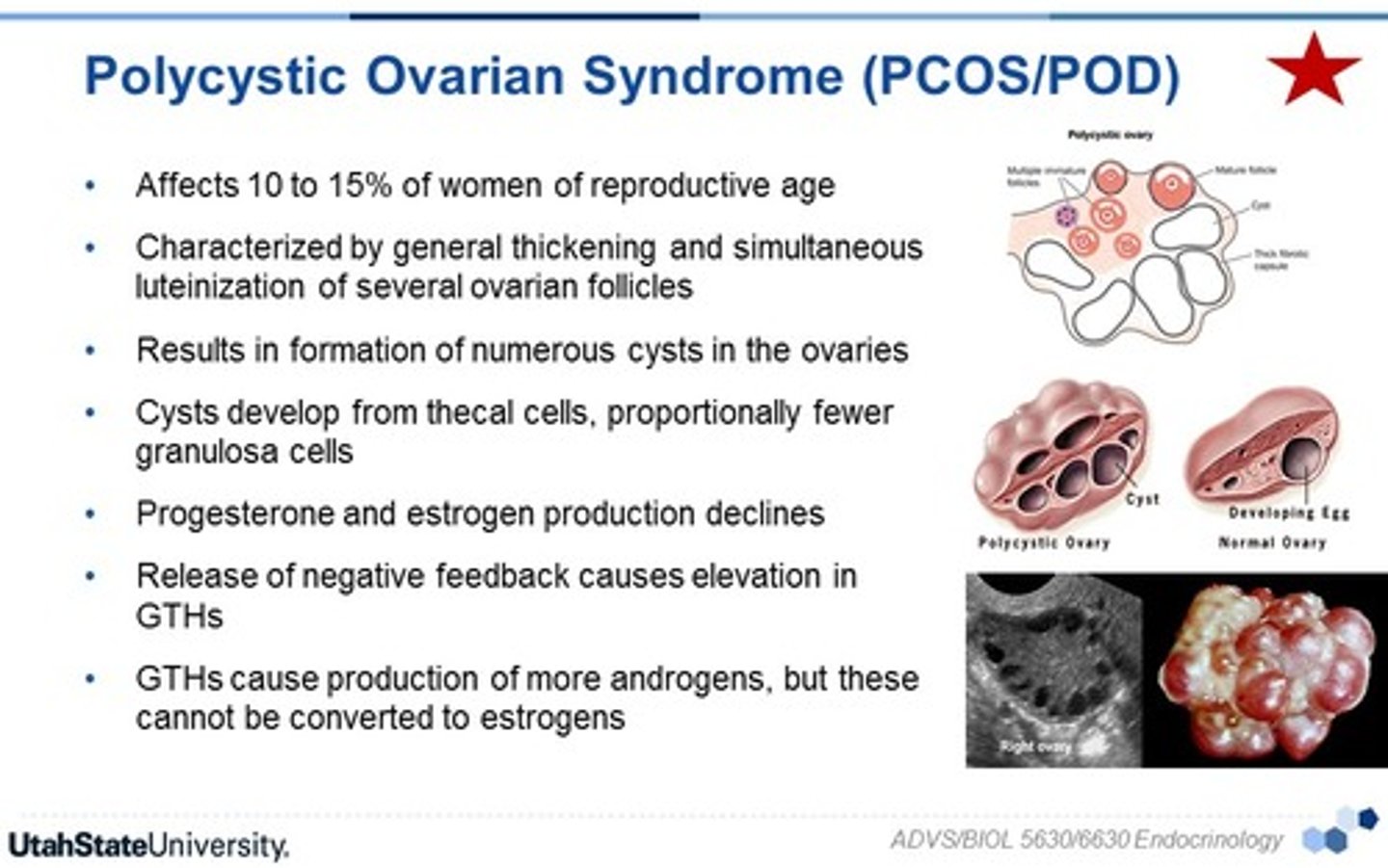
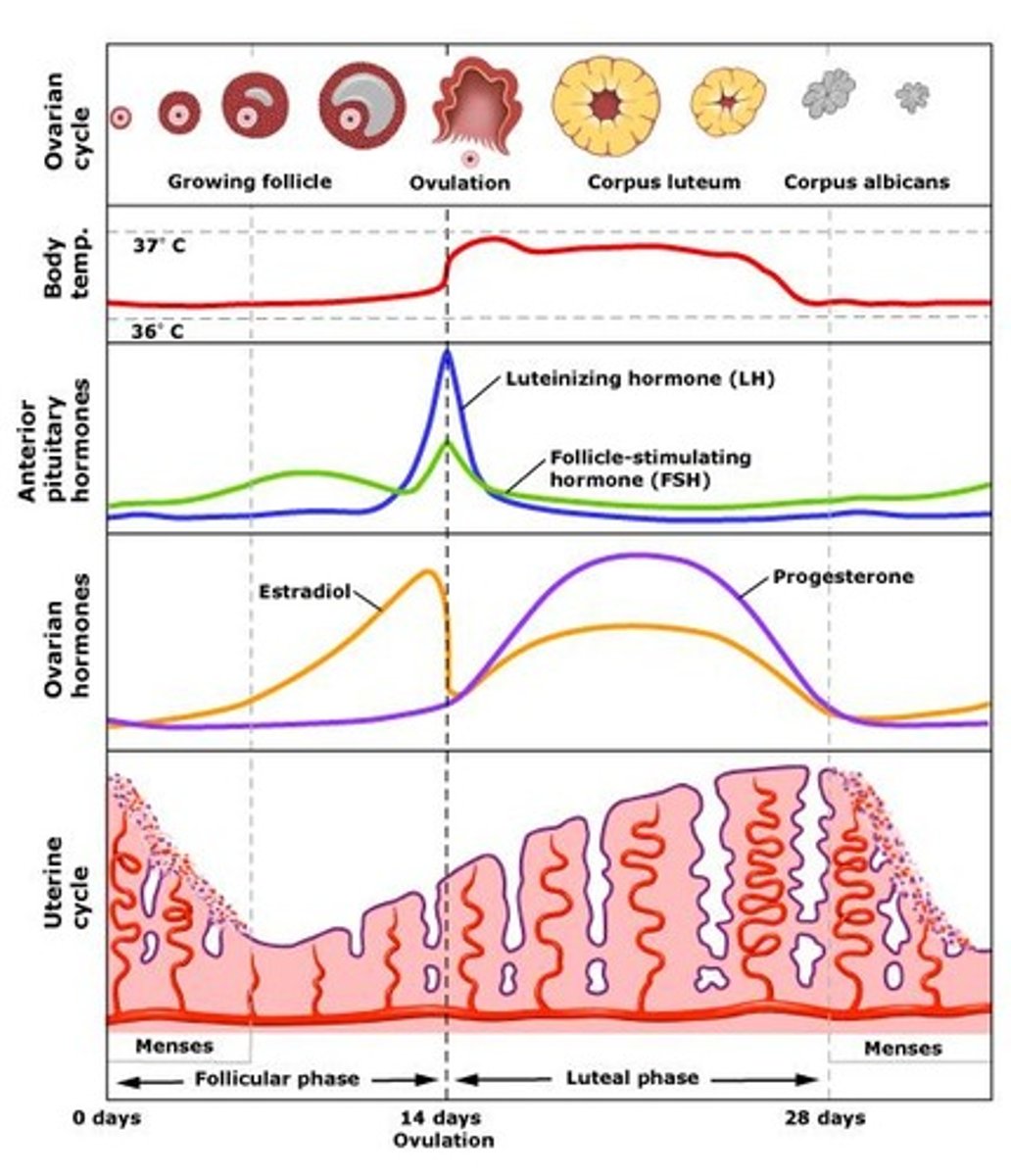
Signs of ovulation
A spike in LH causes ovulation - cervical mucus thickens (to increase likelihood sperm survive and get inside the uterus)
*body temp raises for the entire last 2 weeks of the ovarian cycle.
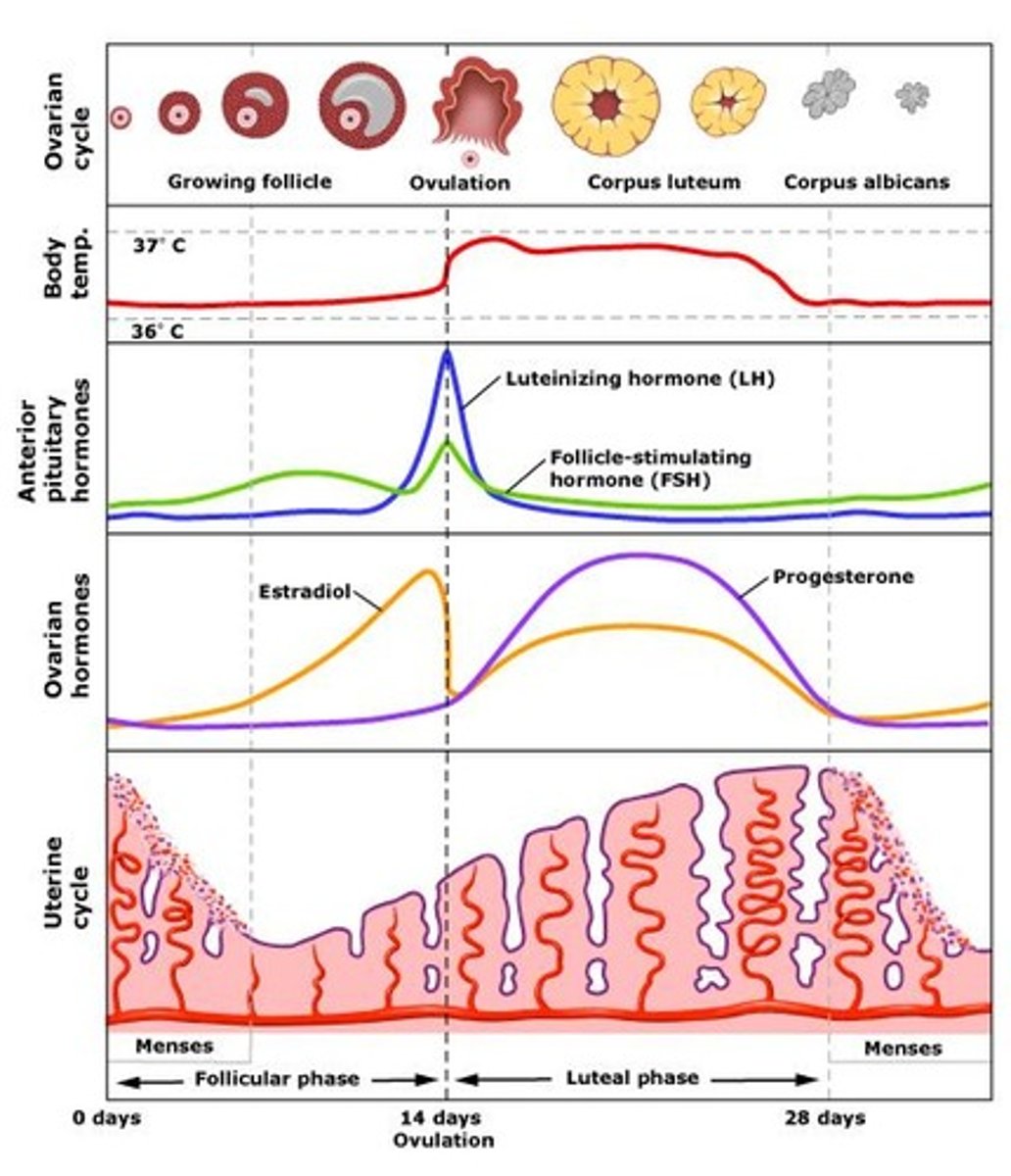
role of the corpus luteum
Produces progesterone after egg is ovulated. Continues production for 2 weeks, unless fertilization continues, in which case it keeps producing progesterone throughout the first trimester of pregnancy (while the placenta is developing)
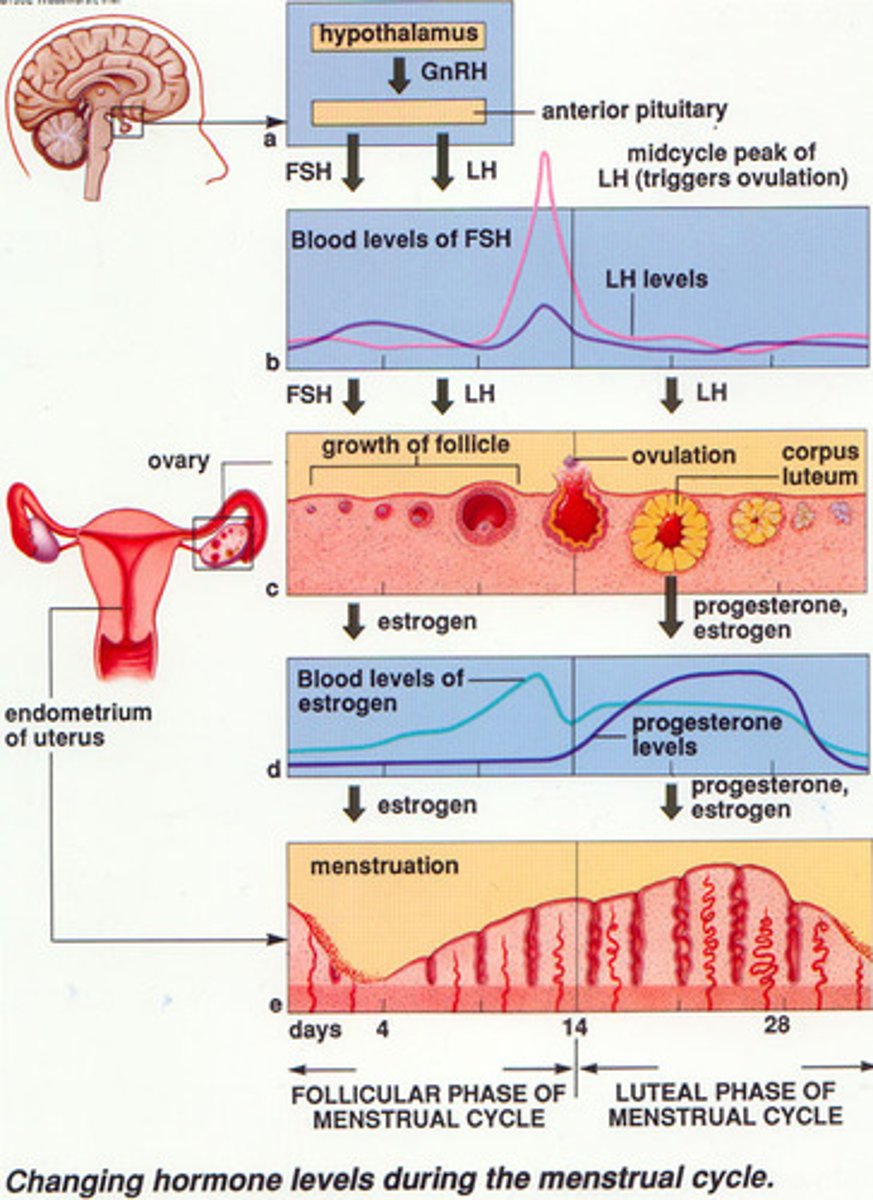
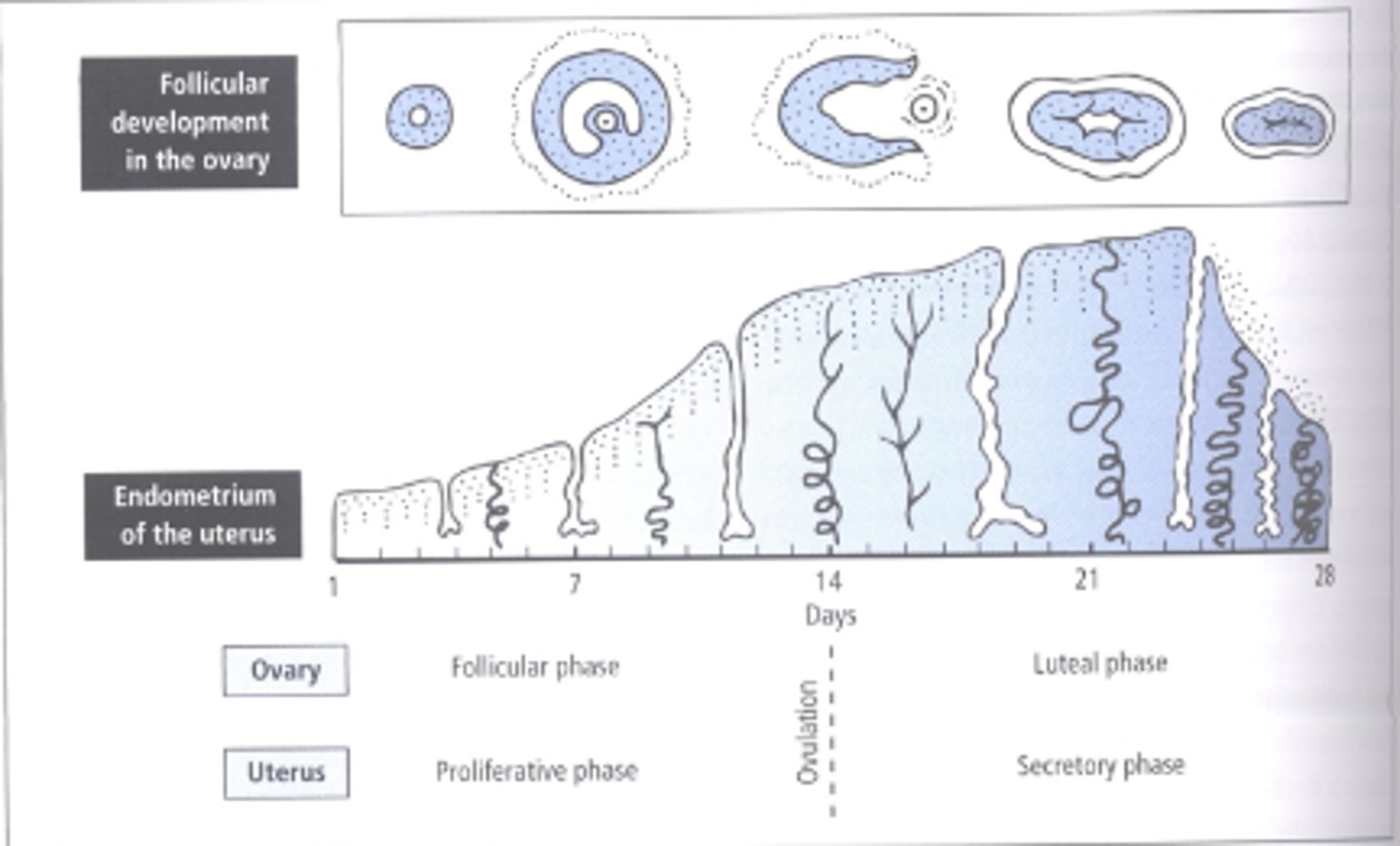
ovarian cycle
The 28 days of the menstrual cycle as they apply to events in the ovary. The ovarian cycle has three subphases: the follicular phase, ovulation, and the luteal phase.
Where does fertilization of an egg occur?
fallopian tubes
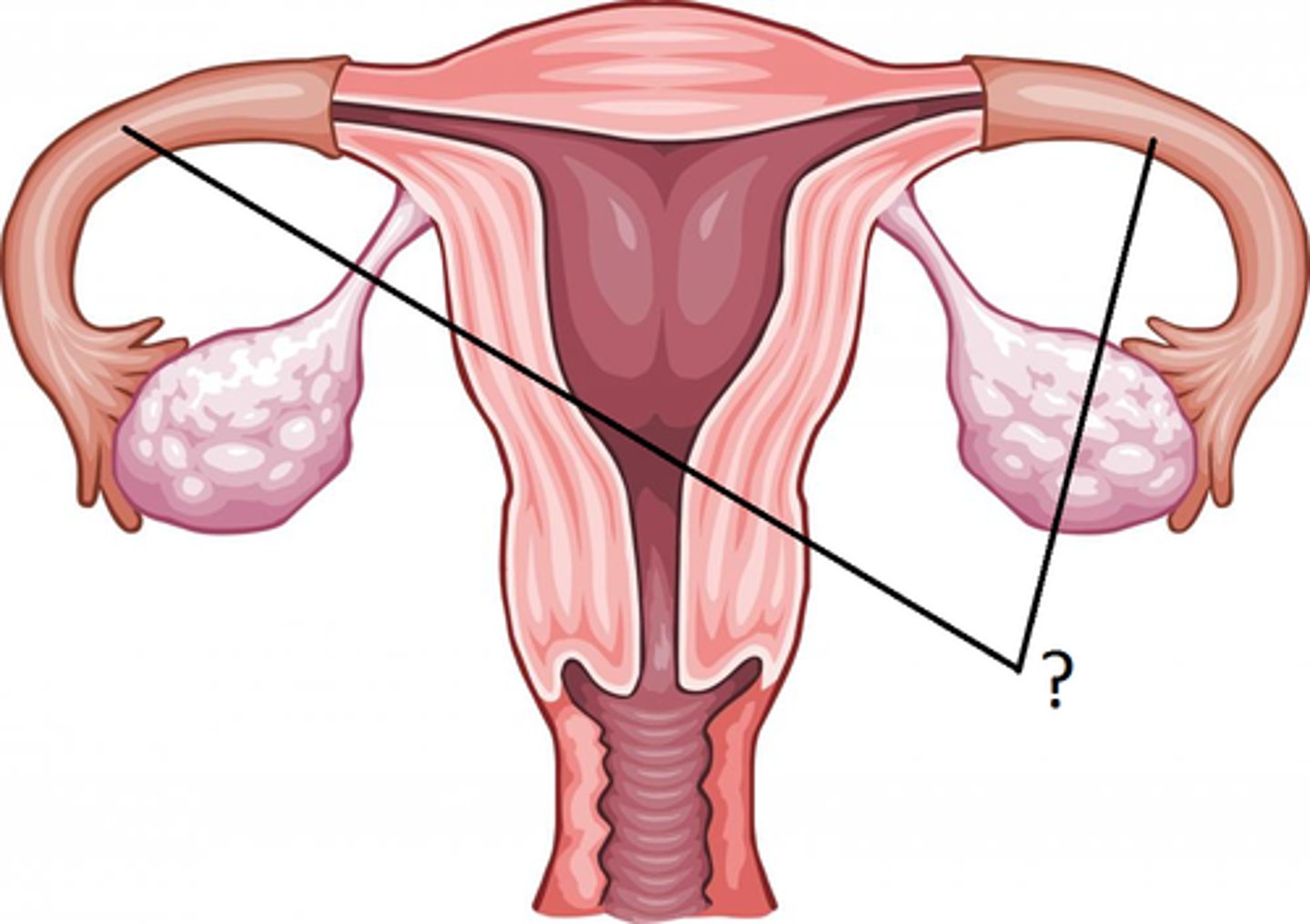
Where does implantation of a fertilized egg occur?
uterus
What hormone is "dominant" during the follicular phase?
estrogen - causes egg maturation
What hormone is "dominant" during the luteal phase?
progesterone - continued thickening of uterine lining
Why does menses occur?
Endometrium sloughs off in response to progesterone withdrawal
What hormone maintains the entire pregnancy?
progesterone
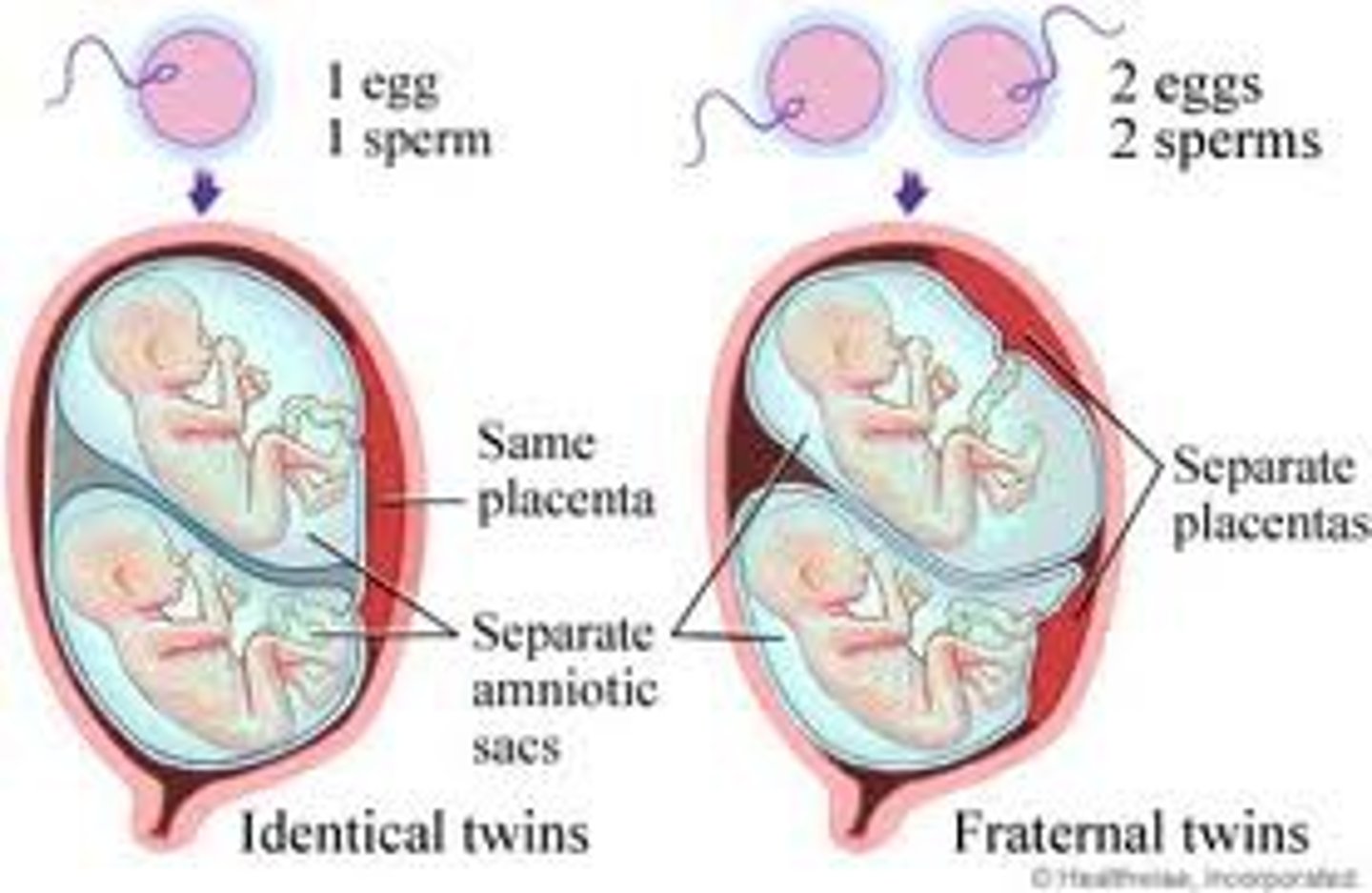
What causes fraternal twins?
two eggs are released at the same time and are both fertilized by separate sperm.
each implants and develops its own placenta, amnion, and chorion - they are genetically like siblings born at the same time.
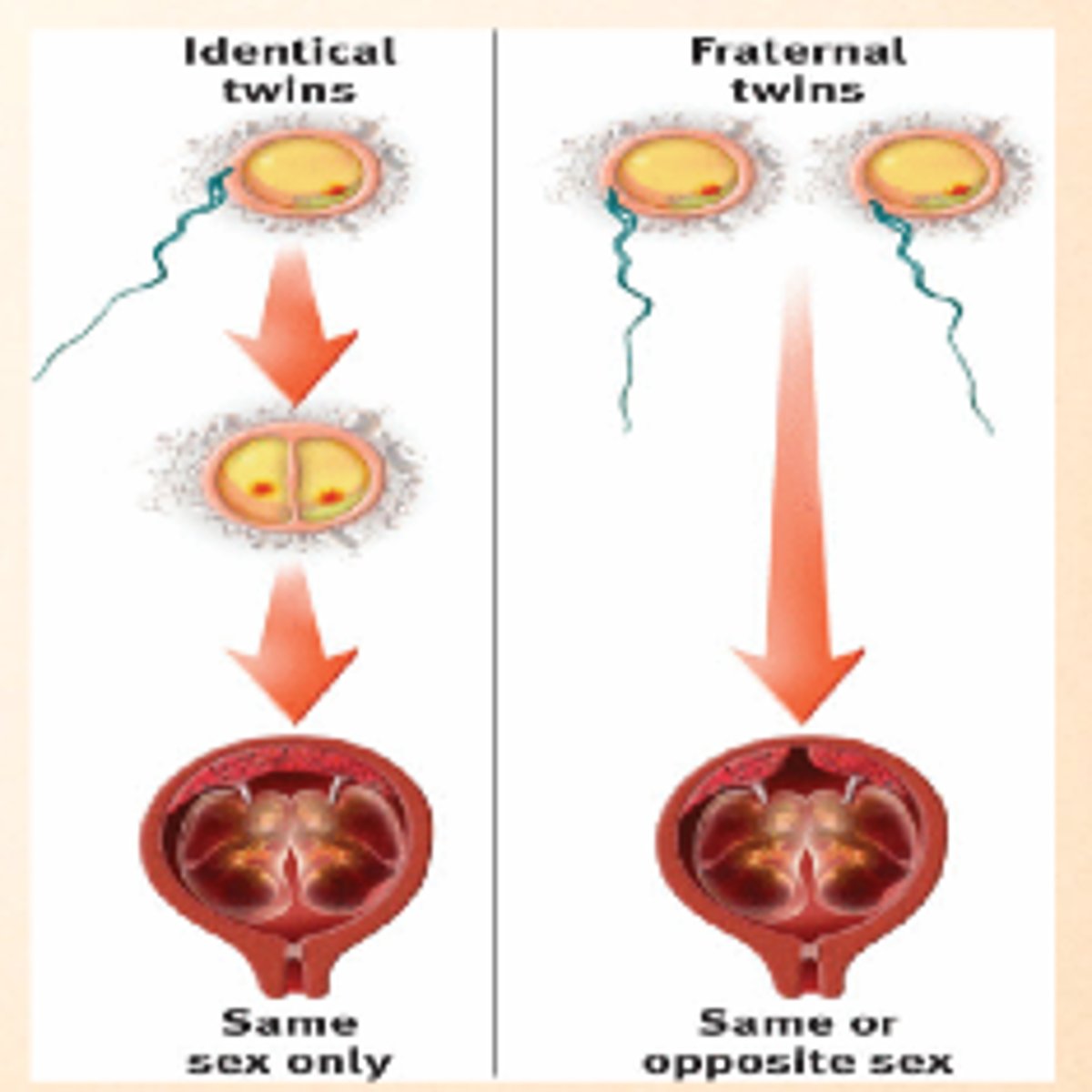
What causes identical twins?
a single zygote splits into two embryos
Note - it's important to realize that identical twins CAN have separate placentas! It all depends on when the egg "splits". The earlier the split, the more likely they'll share the same placenta and possibly even amniotic sac
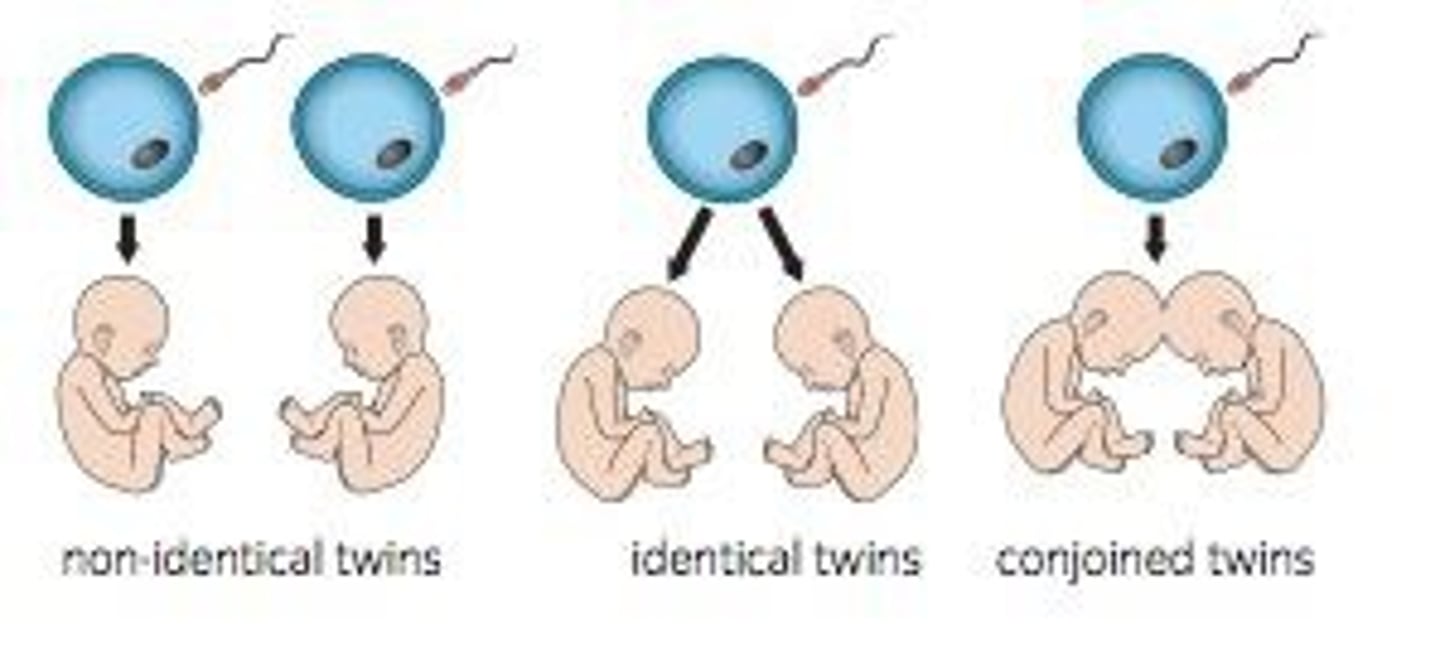
What causes conjoined twins?
A fertilized egg splits into identical twins but remains slightly attached, so some organs are shared.
vagina
A muscular, elastic passageway that extends from the uterus to the outside of the body - contracts during orgasm