Biodegradable Polymers
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
polymers
covalently bound, repeating unis of smaller molecules
polymers properties
viscosity, hardness, toughness, and flammability
natural protein polymers
polypeptides, collagen
natural sugar polymer
polysaccharides, glycosaminoglycans, cellulose
nucleic acid polymer
dna, rna
synthetic polymers
polyethylene glycol, polyester, polyanhydride, polyurethane
natural polymers
hyaluronic acid, dermatan sulfate, chondrotitin 6-sulfate, keratan sulfate, heparan sulfate, heparin
pet; pete; recycling 1
plastic water and soda bottles
hdpe (high density polyethylene); 2
laundry/dish detergent containers
vinyl or pvc; 3
pipes, shower curtains
ldpe (low density polyethylene); 4
grocery and sandwich bag
pp (polypropylene); 5
tupperware, syrup bottles, yogurt cups
ps (polystyrene); 6
coffee cups, disposable cutlery
low density pe mw
1000-2000
high-density pe mw
10,000-100,000
ultra high mw pe
2-6 million
mn =
sum(xi) Mi
mw
sum(wi) Mi
pdi
mw/mn
polymer breaks down into smaller units
with hydrolysis and enzyme action
smaller units themselves can be
metabolized; excreted
plga breaks down into
lactic acid and glycolic acid
bioeliminable
non-degradable, water soluble, kidney excretable
peg attach to protein, hydrophobic drug
to make water soluble, shield dug, increase circulation
permanent/retrievable polymers
non-degradable, non-excretable
permanent polymers
polyethylene and non-poylmers like metals
biodegradable polymers usage
need of material is temporary, time-dependent, no follow-up surgery, avoid chronic inflammation, cell-mediated healing
polymers
monomer → residue, repeating unit
M =
nM0; chain length/degree of polymerization
when chain length/dp = n+m
M = nMn0 + mMm0
types of copolymers
homopolymer, random, graft, alternating, block
copolymers vary
mechanical strength, hydrophobicicty, functional groups, degradation, crystallinity
polymer skeletal structure
linear, branched, network
applications of structural polymer
sutures, artificial heart
polymer delivery
plga microspheres and pbae nanoparticles
polymer tissue engineering
polymeric scaffolds, nanofibers
doxil
polyethylene glycol
gliadel wafer
polyanhydrides
biodegradable suture
plga
pacemaker?
polyurethanes
degradation mechanism
oxidation, microorganism
hydrolysis susceptible bonds
esters, anhydrides, carbonates, amides
poylmer bond stability
polyanhydrides least, polyamides most
cleavage of crosslinks
between water soluble polymer chain
transformation/cleavage of side chains
leading to the formation of polar or charged groups
cleavage of backbone linkages
between polymer repeat units
surface erosion
erosion of outer surface only
inner layers do not see water
until outer layers are eroded
surface erosion exhibits
zero order release when surface area doesn’t change substantially
surface erosion looks like
a bar of soap
bulk erosion
erosion throughout the volume of the material simultaneously
entire mass
encounters water
results in bursts of release
once polymers degrade into small sized oligomers
parameters that affect erosion
water diffusion, hydrophobicity, steric effects, bonds/forces that maintain structure, length scale, density, mcirostructure, environemtal conditions
rate of degradation
1/M = 1/M0 + kefft
M/M0
e^-kefft
degradation products are catalytic and don’t diffuse away
degradation will be autocatalytic
driving force of erosion
degradation of polymer bonds
poisson kinetics
t reaction = 1/k * ln n
t reaction
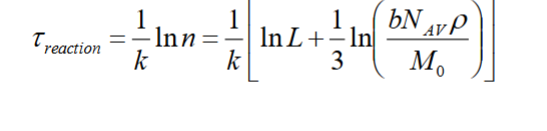
t diffusion
L²/D
t diffusion
pi * L² / ($D)
L ~
sqrt(Dt)
erosion number
