Geologic Time, Radioactive Decay, and Stratigraphy Principles
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
What is absolute time?
A process that happens at a known date.
What is the difference between relative and absolute time?
Relative time places events in order without exact dates, while absolute time provides specific dates using methods like radiometric dating.
What are isotopes?
Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
How does absolute dating work?
It uses known decay rates of radioactive isotopes to determine the actual age of a geologic event.
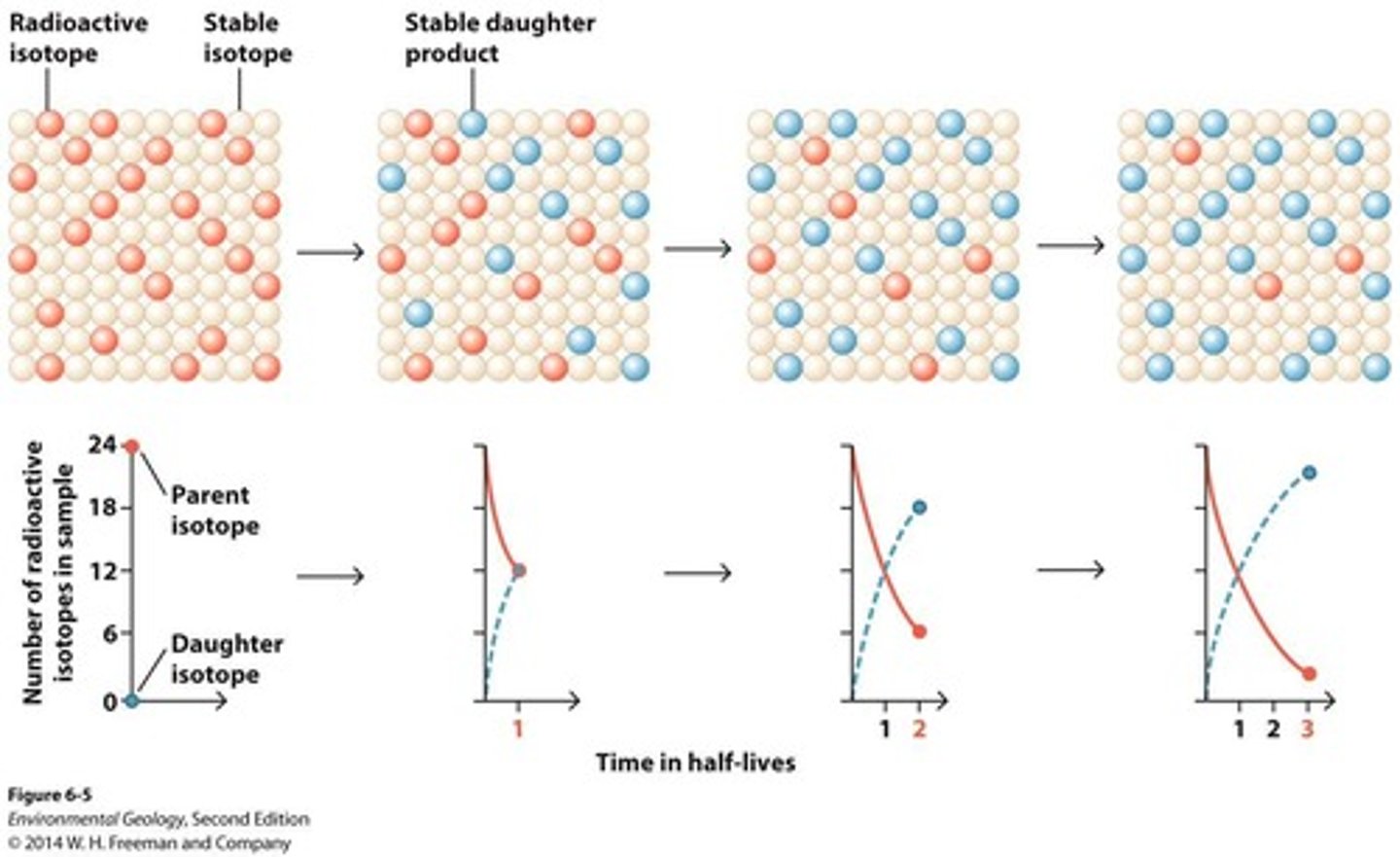
What are parent and daughter isotopes?
Parent isotopes are unstable and decay into daughter products, which are stable isotopes formed from the decay.
What is radioactive decay?
The breakdown of a radioactive isotope, which emits energy and can be measured to determine age.
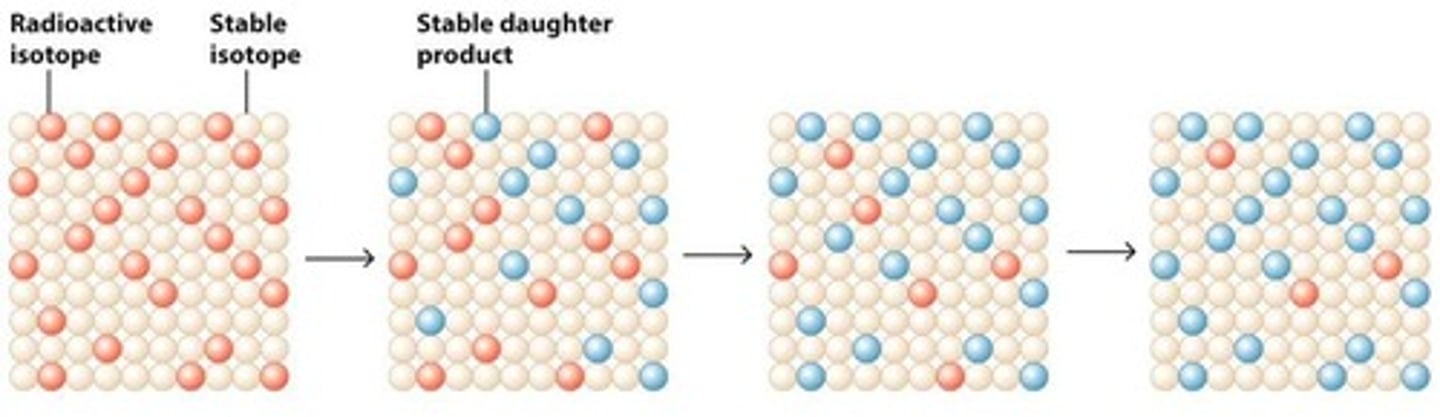
What is the half-life of a radioactive isotope?
The time taken for the radioactivity of a specified isotope to fall to half its original value.
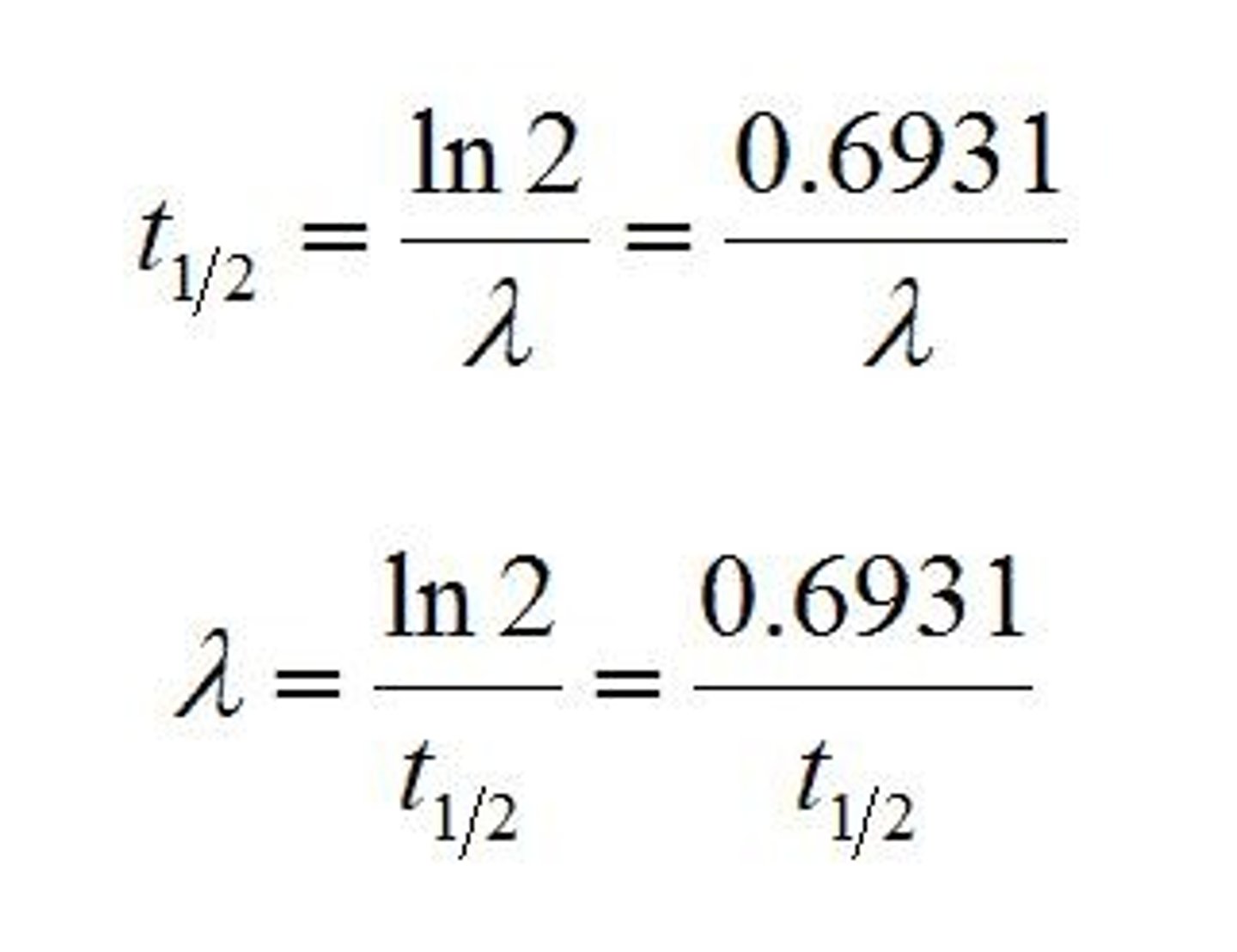
What factors influence the rate of radioactive decay?
The amount of radioactive material present and the half-life of the radioactive material.
What is the decay constant (λ)?
It determines the rate of decay and is the fraction of the number of atoms that decay in a unit of time.
What is the ratio of parent to daughter isotopes after one half-life?
1:1
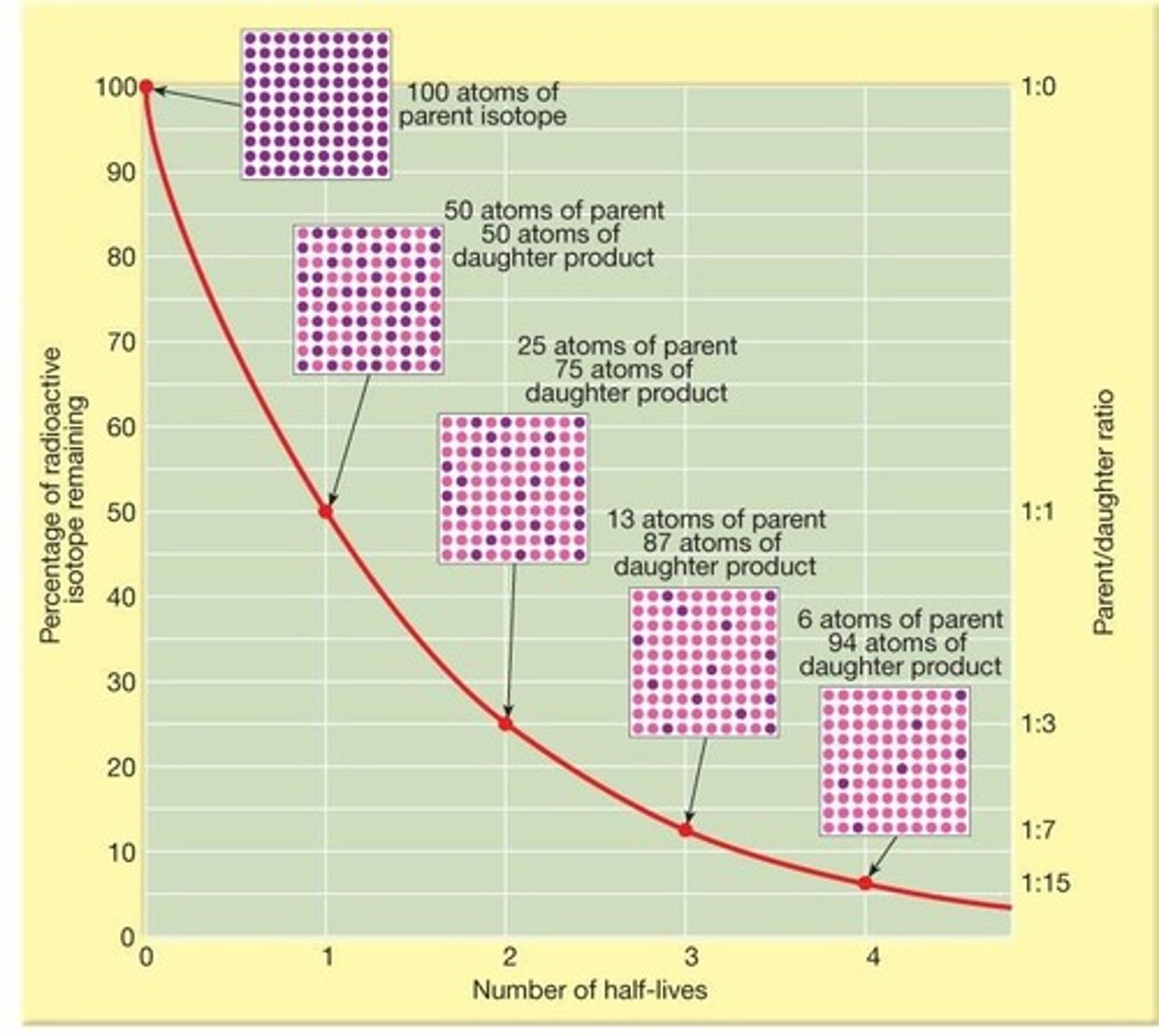
What is the ratio of parent to daughter isotopes after two half-lives?
1:3
What is the half-life of carbon-14?
5730 years.
How can the age of a sample be estimated using carbon-14?
By measuring the remaining percentage of carbon-14 and comparing it to its half-life.
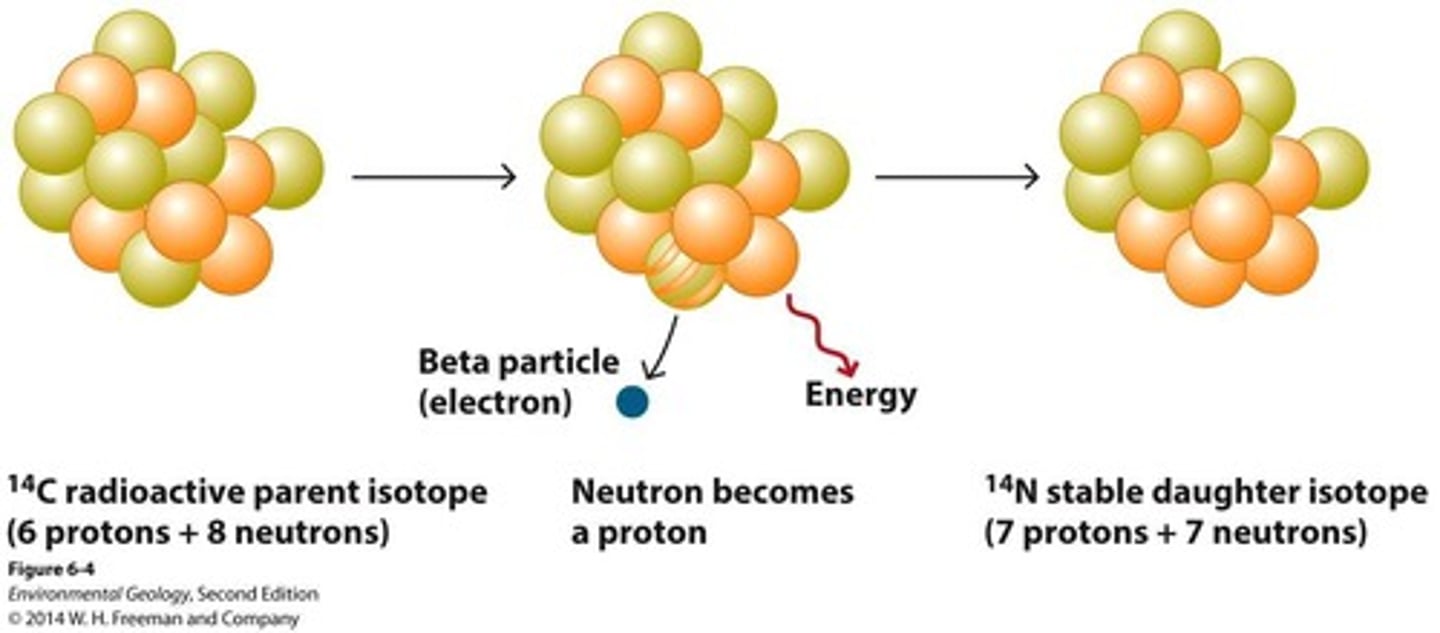
What happens to radioactive elements over time?
They decay and change into different elements.
Are all elements radioactive?
No, only certain elements are radioactive and useful for geologic dating.
What is the significance of radiometric dating?
It provides a reliable means to calculate the ages of rocks and minerals containing radioactive isotopes.
What is the process of radioactivity?
Some atomic nuclei spontaneously break apart and emit energy.
What is the importance of knowing the decay rates of isotopes?
It allows scientists to date geological events accurately.
What is a decay curve?
A graphical representation showing the decrease in the amount of a radioactive substance over time.
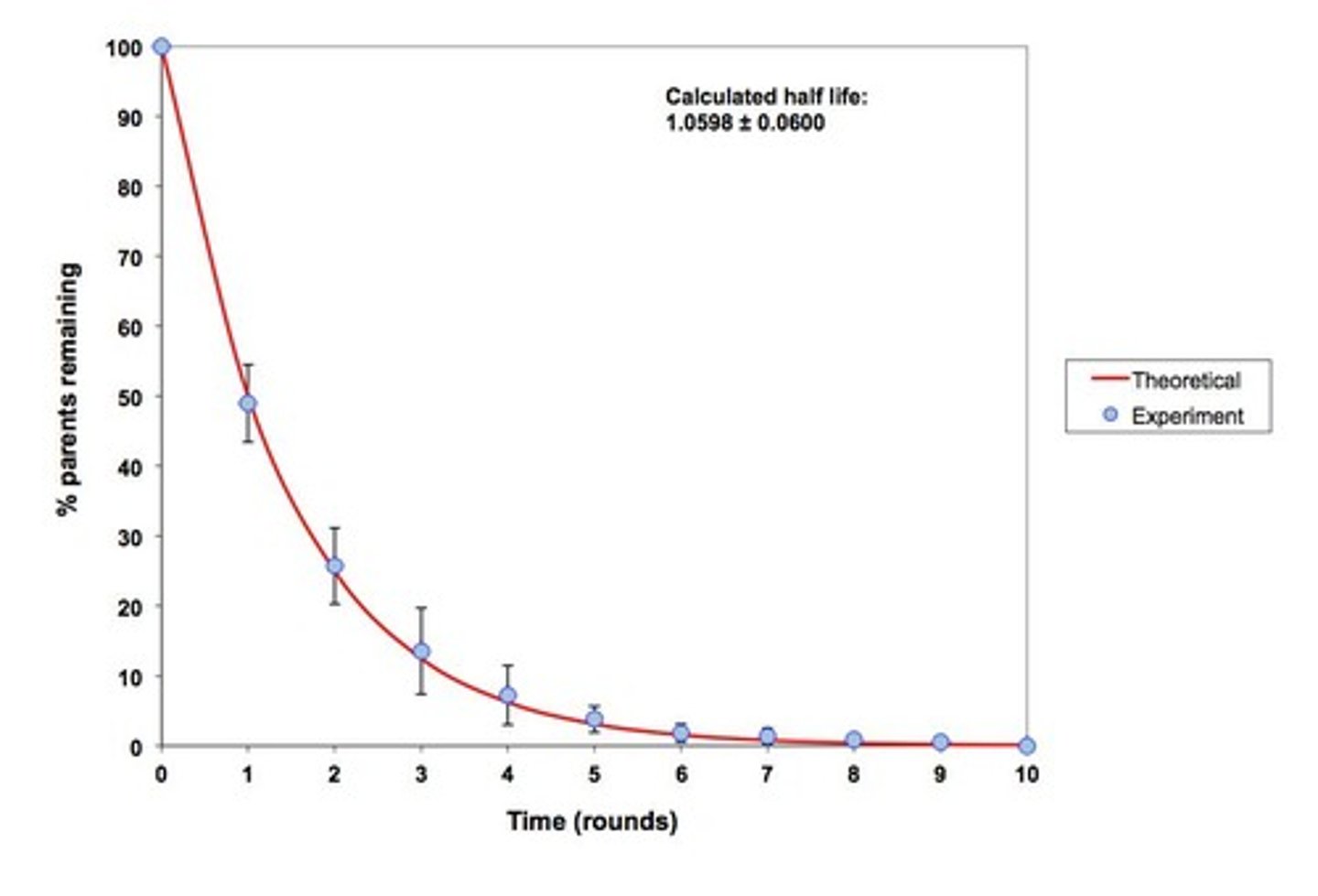
What is the role of the parent isotope in radiometric dating?
It is the original unstable isotope that decays into stable daughter isotopes.
What are the five major reservoirs of Earth?
Atmosphere, Hydrosphere, Biosphere, Pedosphere, Geosphere.
What is the Atmosphere?
A mixture of gases (N2, O2, Ar, CO2, H2O vapour) that surrounds the Earth.
What does the Hydrosphere encompass?
All of Earth's water, including oceans, lakes, groundwater, snow, and ice.
Define the Biosphere.
All of Earth's organisms and any organic matter that has not decomposed.
What is the Pedosphere?
The layer of aggregated and decomposed rock debris at the surface of exposed landmasses.
What constitutes the Geosphere?
The solid Earth, including the lithosphere, mantle, and core.
What is the Anthroposphere?
The part of the environment made or modified by humans.
What are the four essential processes of life?
Metabolism, Growth, Reproduction, and Evolution.
What is Metabolism?
The sum of all chemical reactions by which energy is provided and used for life processes.
How is life classified?
At levels including atoms, molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms, populations, communities, ecosystems, biomes, and the biosphere.
What distinguishes Eukaryotic cells from Prokaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and specialized cell components, while Prokaryotic cells do not.
What are the six kingdoms of life?
Bacteria, Archaea, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia.
What is Net Primary Productivity (NPP)?
The amount of organic matter produced by autotrophs after accounting for respiration.
What is the role of Decomposers in an ecosystem?
They recycle nutrients, preventing waste accumulation and enabling nutrient cycling.
What is the First Law of Thermodynamics?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed.
What is the Second Law of Thermodynamics?
Energy is lost as heat with each transfer between trophic levels.
What is the difference between Gross Primary Production (GPP) and Net Primary Production (NPP)?
GPP is the total amount of carbohydrates produced by autotrophs, while NPP is GPP minus respiration.
What is Primary Production?
The production of carbohydrates by autotrophs in an ecosystem.
What are Trophic Levels?
Levels in an ecosystem that include Producers, Herbivores, Carnivores, and Decomposers.
What is Biomass in an ecosystem?
The total amount of organic matter present in an ecosystem, usually measured in mass or mass/unit area.
What is the purpose of the Earth Science Café?
To engage the public in Earth science topics through presentations and discussions.
What are the main soil horizons?
O (Organic), A (Alluviation), E (Eluviation), B (Clay Minerals), C (Parent Material), R (Bedrock).
What does the 'O' horizon in soil represent?
The Organic layer, consisting of loose material and organic matter.
What is the significance of the 'A' horizon in soil?
The Alluviation layer, which contains humus and decomposed plant material just under the O horizon.
What does the 'E' horizon indicate in soil profiles?
The Eluviation layer, characterized by sand and quartz where materials have been leached out.
What is found in the 'B' horizon of soil?
Clay minerals and accumulated materials such as limonite and hematite.
What is the 'C' horizon in soil?
The Parent Material layer, consisting of regolith.
What does the 'R' horizon represent in soil profiles?
The Bedrock layer beneath the soil.
What mineral is commonly associated with yellow soil coloration?
Limonite (FeO(OH)).
What mineral is associated with red soil coloration?
Hematite (Fe2O3).
What are Spodosols?
Soils that develop under conifer cover, often acidic.
What are Mollisols known for?
They are considered the great soils of the world, typically fertile and rich in organic matter.
What characterizes Gelisols?
Soils found on permafrost, subject to cryoturbation.
What are Oxisols?
Tropical soils, previously called laterite, composed mainly of oxides with little clay.
What is the primary factor affecting soil profiles in different regions?
Climate, which influences vegetation and weathering processes.
What is the role of feldspar in the Earth's crust?
It is the most common mineral and plays a significant role in soil formation.
What happens to pyrite (FeS2) when it oxidizes?
It can produce limonite and then hematite.
Why are tropical regions vulnerable to logging and soil degradation?
Due to high biodiversity and rapid decomposition, which can lead to loss of soil nutrients and structure.
What is the significance of soil horizons in agriculture?
Different soil horizons affect water retention, nutrient availability, and overall soil fertility.
What is a hardpan in soil?
A hardened impervious layer, typically of clay, that impairs drainage and plant growth.
How does climate influence soil types?
Climate determines moisture levels, temperature, and vegetation, which all affect soil formation and characteristics.
What is the impact of soil erosion on agriculture?
It can lead to loss of fertile topsoil, reducing agricultural productivity.
What is the relationship between soil color and mineral content?
Soil color can indicate the presence of specific minerals, such as limonite for yellow and hematite for red.
What are Inceptisols?
Young, shallow soils that are in the early stages of profile development.
What is the role of organic material in soil health?
Organic material improves soil structure, water retention, and nutrient availability.
What is the low estimate of warming by 2100 according to IPCC AR5 2013?
1.5 °C
What is the high estimate of warming by 2100 according to IPCC AR5 2013?
4 - 5 °C
What will happen to the contract between wet and dry regions by 2100?
It will increase.
What is relative time in geology?
Ordering a sequence of events based on their natural change and evolution.
What is absolute time in geology?
Determining the actual age of a geologic event using known decay rates of radioactive isotopes.
What does relative age dating rely on?
The association of fossils with specific periods of geologic time.
What is the Rule of Horizontality?
Layers of sediment are originally deposited horizontally.
What is the Rule of Lateral Continuity?
Layers of sediment initially extend laterally in all directions.
What is the Rule of Superposition?
In undisturbed layers, the oldest layers are at the bottom and the youngest are at the top.
What is the Rule of Cross-Cutting Relationships?
If a geological feature cuts through another, it is younger than the feature it cuts.
What is the Rule of Inclusions?
If one rock body contains fragments of another, it must be younger than the fragments.
What are the three types of unconformities?
Disconformity, Angular Unconformity, Nonconformity.
Who is known as the 'Father of Stratigraphy'?
Nicholas Steno.
Who is known as the 'Father of Geology'?
James Hutton.
What concept did Charles Lyell present?
Uniformitarianism.
What does stratigraphy study?
The order and relative position of strata and their relationship to the geological time scale.
What is the significance of fossils in relative dating?
Fossils help indicate the age of sedimentary layers.
What is the importance of radioactive isotopes in absolute dating?
They allow for determining the actual age of geological events.

What is the process of measuring parent and daughter isotopes used for?
To determine the time of formation of a mineral or glass.
What is the purpose of relative age dating?
To establish the chronological order of geological events.
How can one identify an unconformity?
By examining the relationships between different rock layers.
What is the significance of Steno's Rules?
They provide foundational principles for understanding geological time and stratigraphy.
What happens during a disconformity?
There is a gap in the geological record where layers are missing.
What characterizes an angular unconformity?
It occurs when tilted or folded layers are overlain by younger, more horizontal layers.
What is a nonconformity in geology?
It occurs when sedimentary rocks are deposited on top of eroded igneous or metamorphic rocks.