Protein synthesis HT: Cell level systems: Biology: GCSE (9:1)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
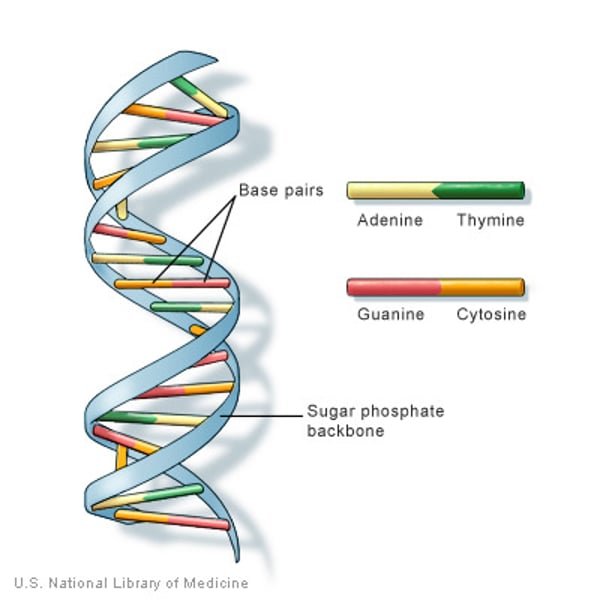
DNA
Chemical molecules found in every living organism that hold instructions for growth and development
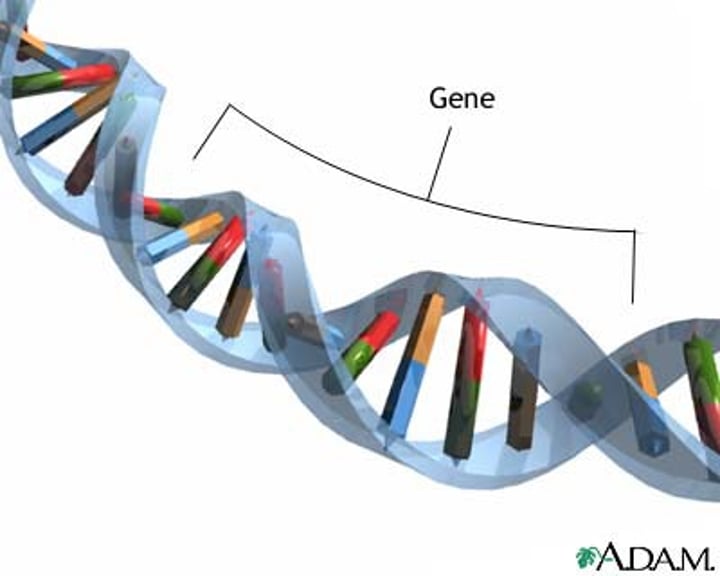
Gene
A small section of DNA that controls a specific characteristic by coding for a specific protein
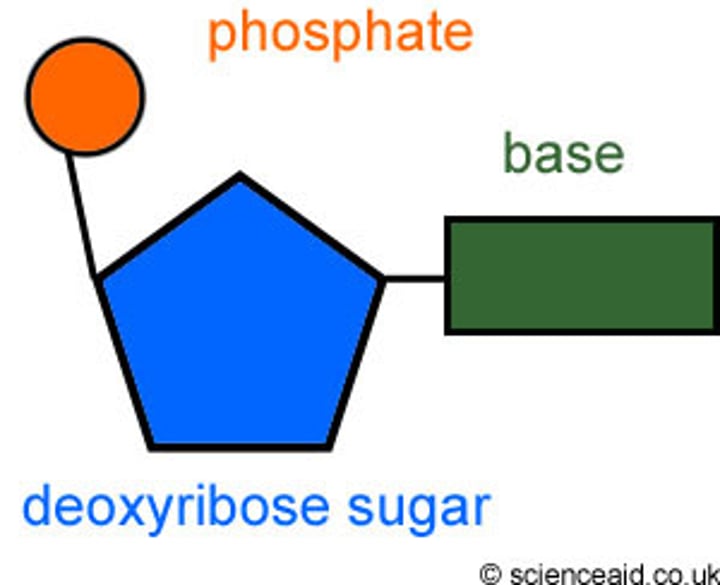
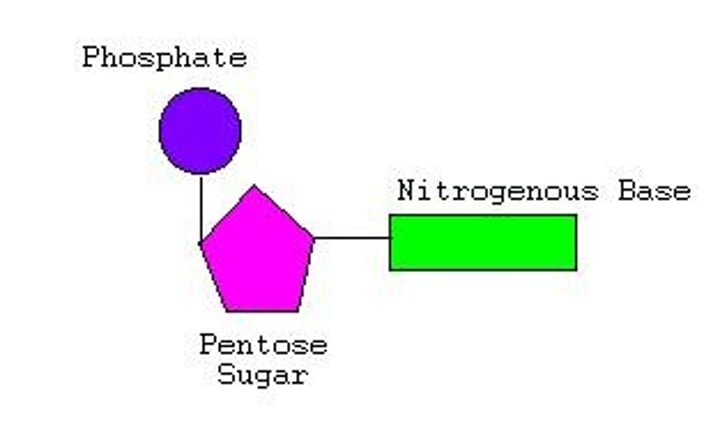
Nucleotide
A small structural unit of DNA, composed of a common sugar and phosphate group with one of four different bases attached to the sugar
Bases
A specific organic section of a nucleotide that contains nitrogen, there are four different types of bases in a DNA polymer
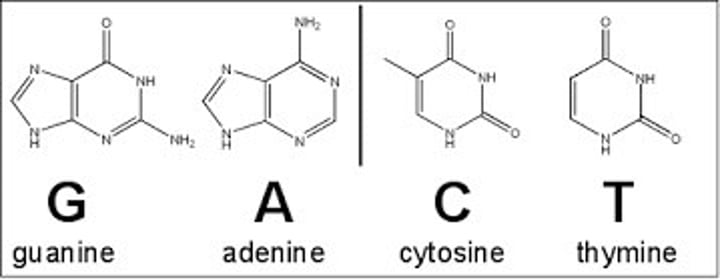
C, G, A and T
The letters that represent the four different types of bases found on a strand of DNA
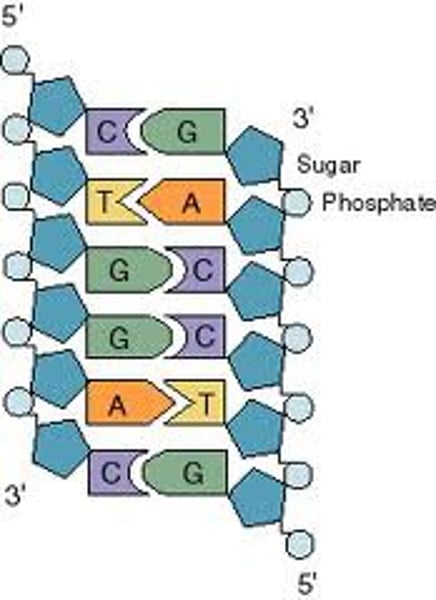
Repeating nucleotides
The DNA polymer is made up of repeating nucleotide units with different arrangements of the bases C, G, A and T
C
A base that is complementary to G, it will not pair up with A or T on the complementary strand
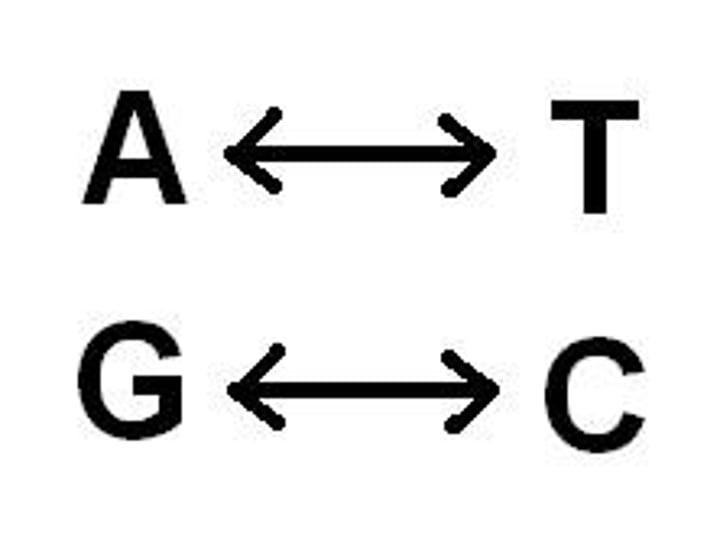
A
A base that is complementary to T, it will not pair up with a C or G on the complementary strand
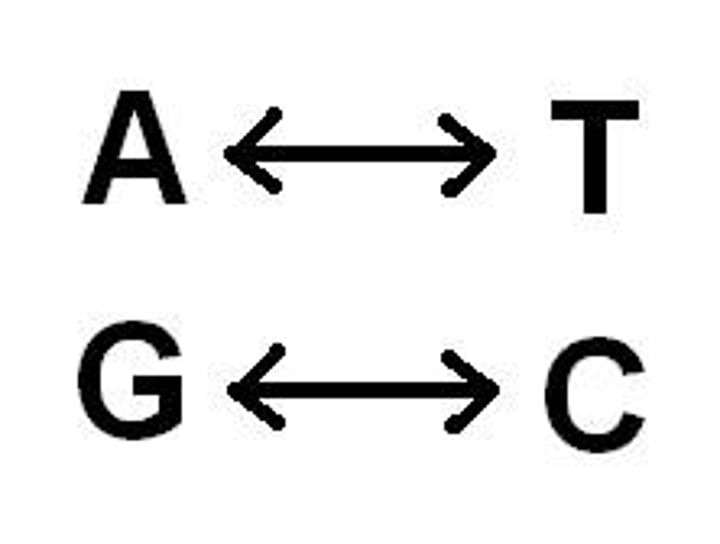
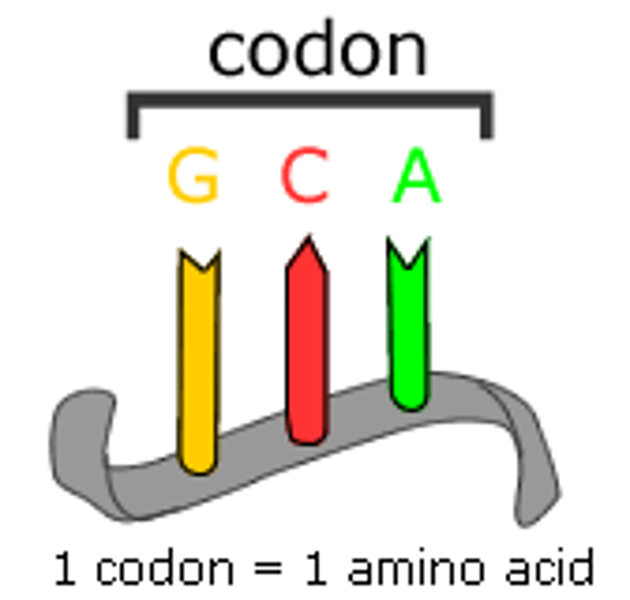
Triplet code
The genetic code for an amino acid also called a codon or simply a triplet, this arrangement of three bases leads to the formation of one specific amino acid
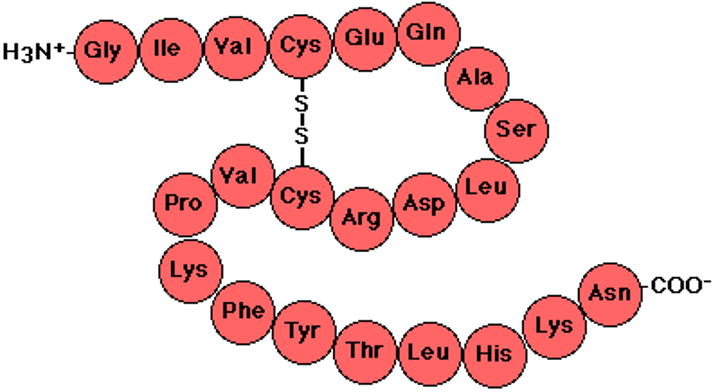
Amino acids
The building blocks of proteins, the sequence of amino acids determines the shape and function of the overall protein

Proteins
Building blocks of cells and tissues, made up by a specific order of amino acids which in turn is coded for by a specific sequence of DNA
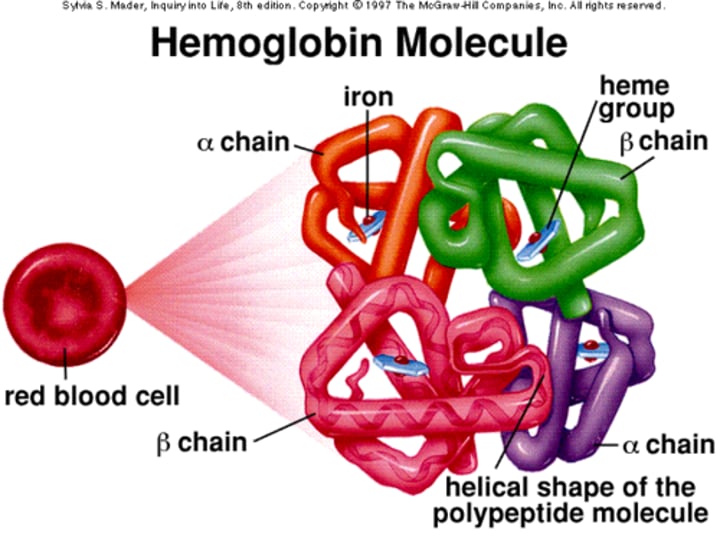
Applications of proteins
Cell formation, enzymes, antibodies, haemoglobin, hormones, muscles, collagen in bones and connective tissue
Protein synthesis
Each gene is made up of many triplets that code for a particular sequence of amino acids, which overall makes up a specific protein
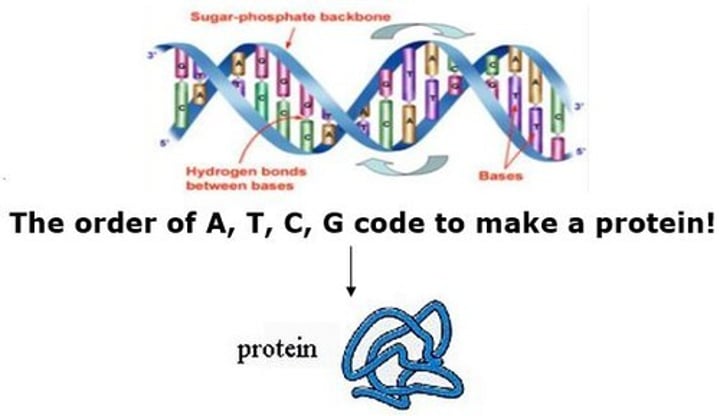
First stage of protein synthesis
Known as transcription, a single strand of DNA is unzipped from the double helix by enzymes and copied by a messenger molecule called mRNA
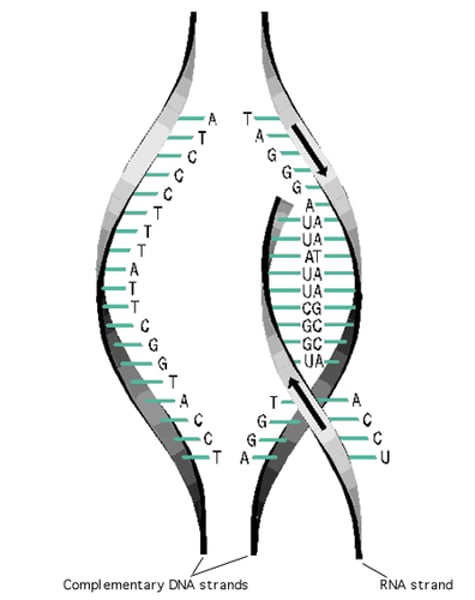
mRNA
Also called messenger RNA or a messenger molecule, an mRNA strand is a copy of a single DNA strand that is small enough to leave the nucleus
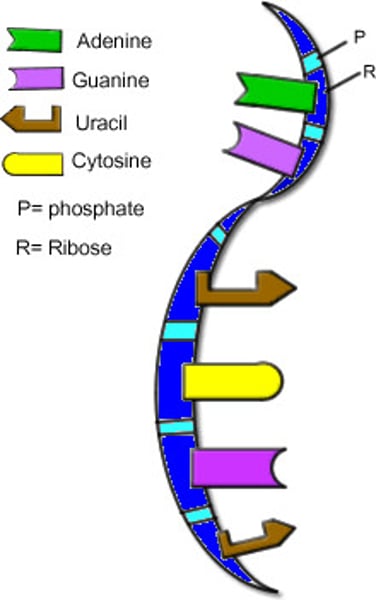
mRNA structure
mRNA has a slightly different structure than DNA, it is single-stranded and has a base called U instead of T
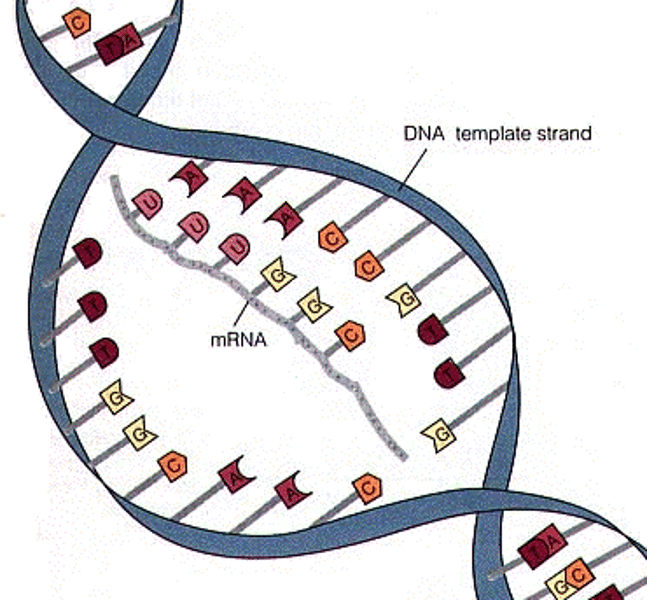
Second stage of protein synthesis
Known as translation, an mRNA molecule moves to a ribosome in the cytoplasm and is translated into amino acids by carrier molecules
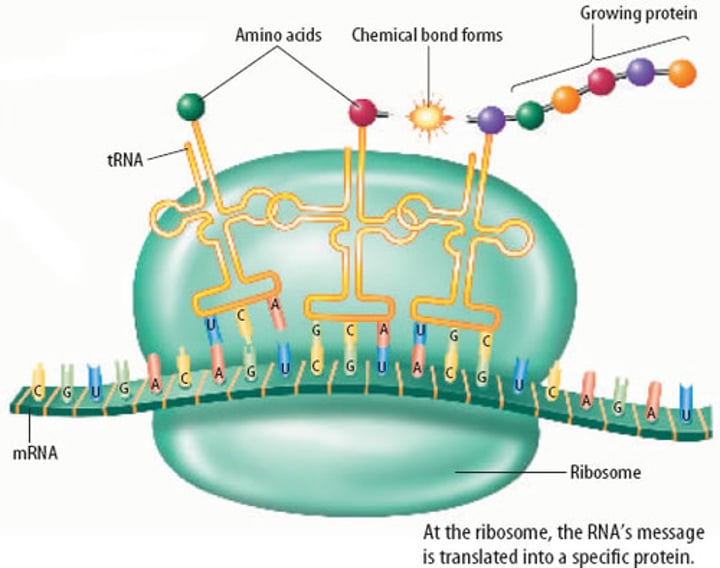
Ribosome
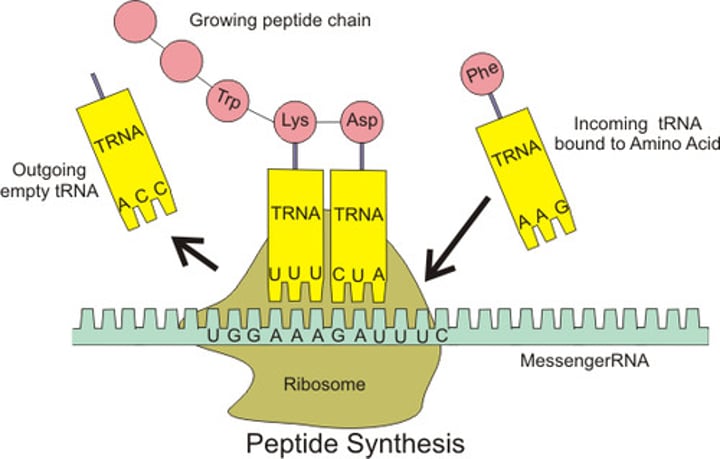
The site of protein synthesis, where carrier molecules called tRNA bring specific amino acids to form a chain according to the sequence of mRNA
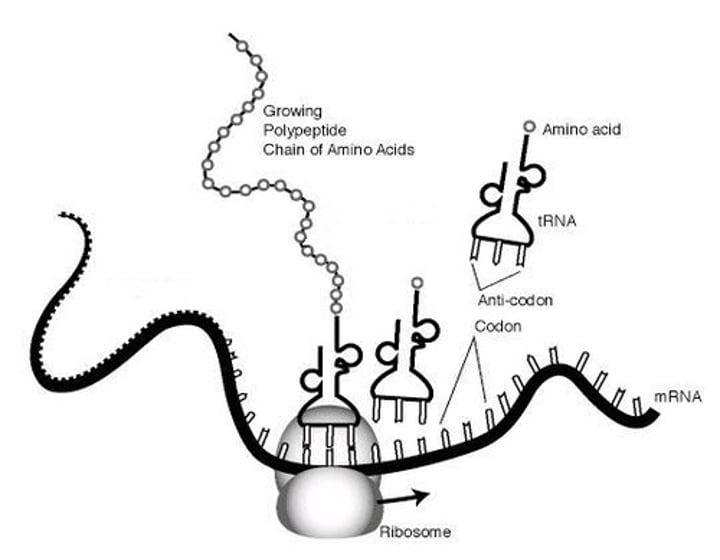
tRNA
Also called transfer RNA or a carrier molecule, each tRNA molecule reads a triplet of bases on the mRNA molecule and translates it into an amino acid
tRNA structure
Each tRNA is attached to an amino acid and contains three bases that are complementary to a triplet on the mRNA molecule
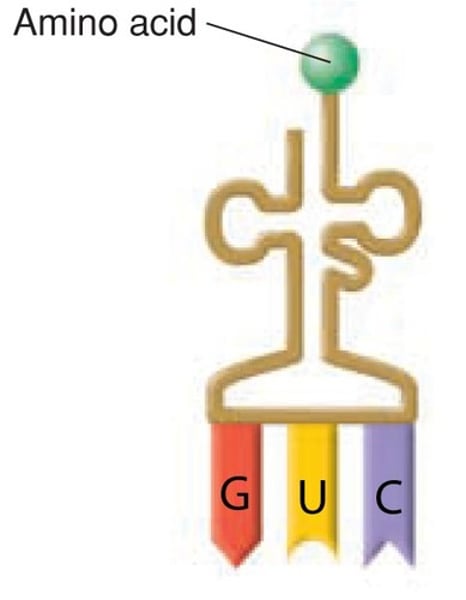
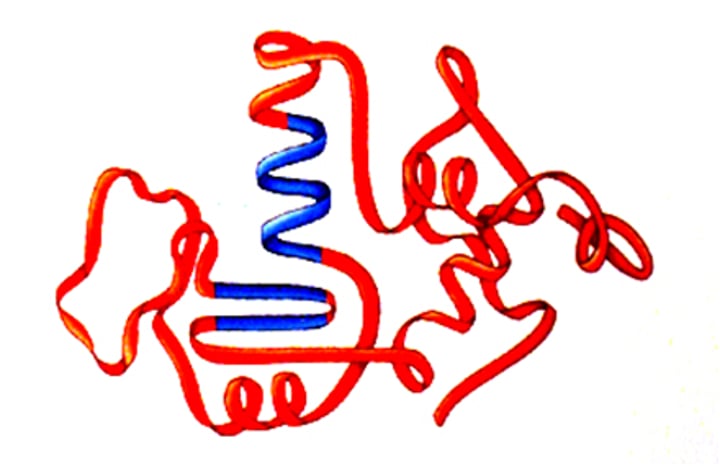
Protein chain
When a chain of amino acids is completed it folds up to form a specific shape, enabling proteins to do their jobs as enzymes, hormones or structural collagen