NSW Prelim EES Mod 1-4
1/167
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
168 Terms
accretion
A process in which masses in a protoplanetary disc attract particles by gravitational attraction
outgassing
The release of gases that were dissolved, trapped, frozen or absorbed in some material. For example, when a volcano erupts, releasing trapped gasses
seismic
_______________ waves (earthquake waves) produced by sudden Earth movements
primary
_________________ waves are the fastest seismic waves. They are compression waves that can pass through solids and liquids.
secondary
_________________ waves are the 2nd fastest seismic waves. They are transverse waves that cannot pass through liquids.
meteorites
A lump of rock or metal from space that reaches the surface of the earth without being completely vaporised
crust
A thin, hard outer coating, such as the hard outer surface of the earth
oceanic
_______________________ crust is thin crust made of basalt and other rocks higher density rocks
density
Mass per unit volume of a substance
gravity
The force of attraction between two masses
continental
_______________________ crust is thick crust made of granite and other rocks lower density rocks
mantle
A layer in the earth between the crust and the core and made of rock that is nearly solid but allows slow movements of the crust
outer core
The layer of the earth composed of liquid iron and nickel that lies below its mantle.
inner core
The solid central part of the Earth
lithosphere
Rigid crust and upper mantle of the earth
asthenosphere
That part of the upper mantle beneath the rigid lithosphere that is plastic enough for rock flow to occur
geologic time
The huge period of time over which Earth's rocks have formed
uniformitarianism
The idea that geological processes have occurred in the same regular manner and intensity throughout geological time
unconformity
A boundary between two rock strata of different ages, indicating that erosion occurred before the upper layer was deposited
radiation
The process of giving off radiant energy in the form of waves or particles
radioactive
The giving off of alpha particles, beta particles and gamma waves as an isotope forms a new isotope is called _______________________ decay
half-life
The time it takes for half a sample of radioactive atoms to decay
isotope
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
mineral
A crystalline solid with a definite composition that occurs in the rocks of the earth's crust
mafic
Dark coloured igneous rocks due to high concentrations of ferromagnesian minerals are called __________________ rocks
felsic
Light coloured igneous rocks with relatively large amounts of feldspars and quartz are called __________________ rocks
hardness
A measure of how easily a mineral can be scratched
streak
The color of the powder of a mineral
lustre
Description of how light reflects off the surface of a mineral
specific
The mass of a mineral divided by its volume is called its density or ________________ gravity
cleavage
The tendency of a mineral to break along flat surfaces
Moh's
A set of minerals used as standards for testing mineral hardness is ______________ hardness scale
rock
Made from a mixture of minerals
igneous
A type of rock that forms from the cooling of molten rock at or below the surface.
texture
The size of minerals in an igneous rock or a soil is called ___________________
sedimentary
Rocks formed from sediments compacted and cemented together
strata
The layers within sedimentary rocks
superposition
The law of _________________________states that the top rock layer and its fossils are youngest and the bottom are oldest.
clastic
Rocks formed from the weathered and eroded pieces of other rocks are called _______________ sedimentary rocks
precipitation
Chemical sedimentary rocks are formed by
chemical ______________________ or biological activity
organic
material derived from living organisms
inorganic
Not formed from living things or the remains of living things
metamorphic
___________________________ rocks form when other rocks are subjected to heat and/or pressure
contact
Rocks altered by heat from nearby magma are called _________________ metamorphic rocks
regional
Rocks altered primarily by pressure over a large area are called _________________ metamorphic rocks
foliations
Metamorphic minerals that are flaky (aligned in parallel structures) are called _______________________
horizon
Any layer within the soil
climate
The average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time
topography
refers to the shape and elevation of land in a region
leaching
removal of dissolved materials from soil by water moving downwards
pH
Scale for measuring the strength of different acids and bases
stratigraphy
the study of rock layers and the sequence of events they reflect
anticline
a fold formed by upfolding or arching of
rock layers
syncline
A fold in rock that bends downward to form a V shape
dyke
An igneous intrusion across rock layers
sill
An igneous intrusion between rock layers
inclusion
A body or particle of different composition embedded within igneous rock
correlation
Matching the ages of rocks and fossils from separate locations
relative
____________________ dating is describing how old something is by comparing it to something else
absolute
____________________ dating is describing how old something is in years
index
_________________ fossils are useful for dating the strata in which they are found.
resources
Materials found in the earth that people need and value
renewable
Resources that can be replaced at the same rate at which they are consumed
non-renewable
Resources that cannot be replaced once they are consumed
reserve
The known quantity of a resource that can be economically recovered
deposit
A natural concentration of minerals in the earth's crust is a mineral ___________________
ore
A rock containing a high enough concentration of a useful mineral to make it economic to mine
mining
the act of extracting ores or coal etc from the earth
hydrothermal
________________________ mineral deposits form in association with magma and water
segregation
Magmatic ___________________ is when minerals crystallize and sink to the bottom of a cooling magma chamber, with different minerals deposited at different temperatures
hot spot
A mantle plume where rising magma can reach the surface, especially away from the edge of crustal plates
pegmatite
A coarse-grained igneous rock with interlocking crystals often rich in feldspars, micas and quartz
vein
a narrow deposit of a mineral that is sharply different from the surrounding rock
evaporites
Minerals precipitated from the water in closed lakes or seas as they dry up
fossil fuels
Any fuels that formed from the decayed remains of ancient plants and animals
coal
A solid fossil fuel formed underground from buried, decomposed plant material.
seam
A layer of coal usually thick enough to be profitably mined
coal seam gas
A form of natural gas (mainly methane) extracted from coal beds
rock core
A vertical, cylindrical-shaped boring used to determine composition and stratification of rocks underground.
geophysical
The scientific study of the physical characteristics of the Earth uses _____________________________ techniques
remote sensing
processes that collect data from the Earth at a distance
drilling
the act of boring a hole in the earth in the hope of producing resources
overburden
Layer of soil and rock overlying a mineral deposit
open pit
Mine in which ore is exposed at the surface in a large excavation.
fracking
Pumping of high pressure water to break rocks and release natural gas
plate tectonics
theory that Earth's surface is made of huge sections that move with respect to each other
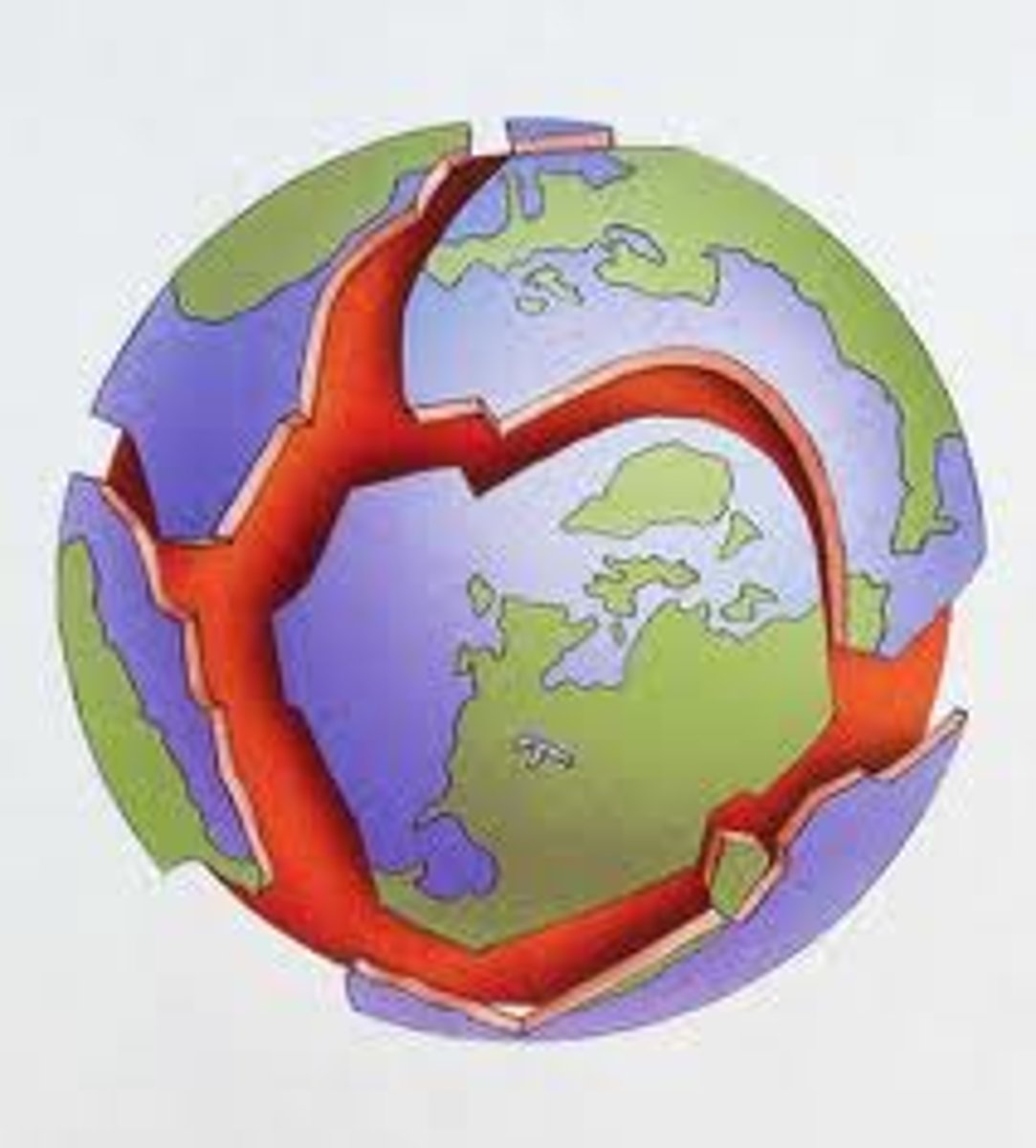

plates
The sections that the lithosphere are broken into.

palaeoclimate
A climate existing at a particular time in the geological past.
magnetic reversal
When Earth's magnetic field changes polarity from normal to reversed.
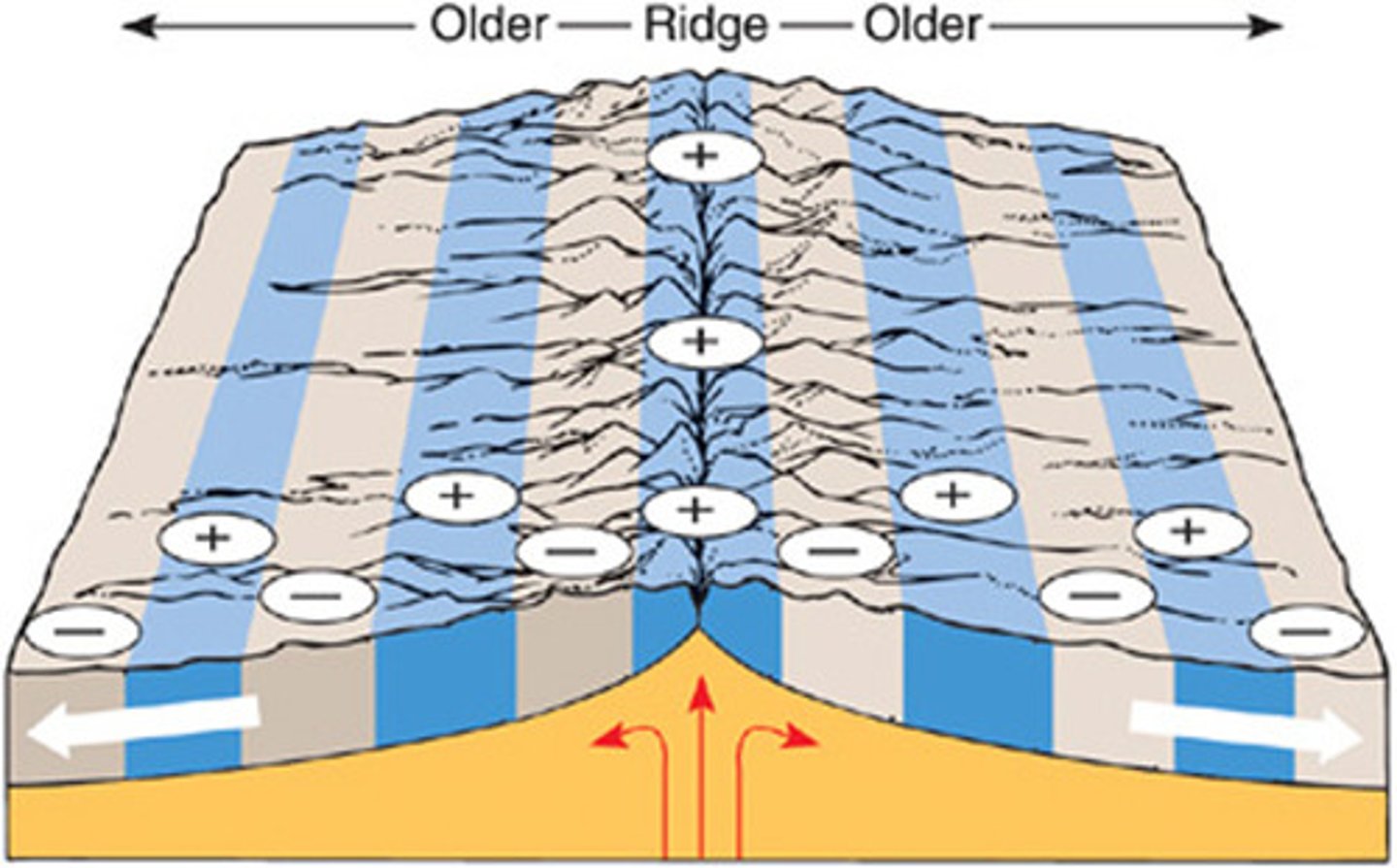
mid-oceanic ridge
An underwater mountain range formed when tectonic plates diverge and magma rises.
Wegener
Alfred ____________________ proposed the continental drift theory
continental drift
Wegener's hypothesis that the continents slowly moved over Earth's surface
Holmes
Arthur ___________________ was the geologist who first proposed that convection currents in the mantle where driving plate movements
Hess
Harry ______________ pioneered early sea floor mapping and proposed sea floor spreading
convergent
A _________________ boundary occurs when two tectonic plates collide into each other.
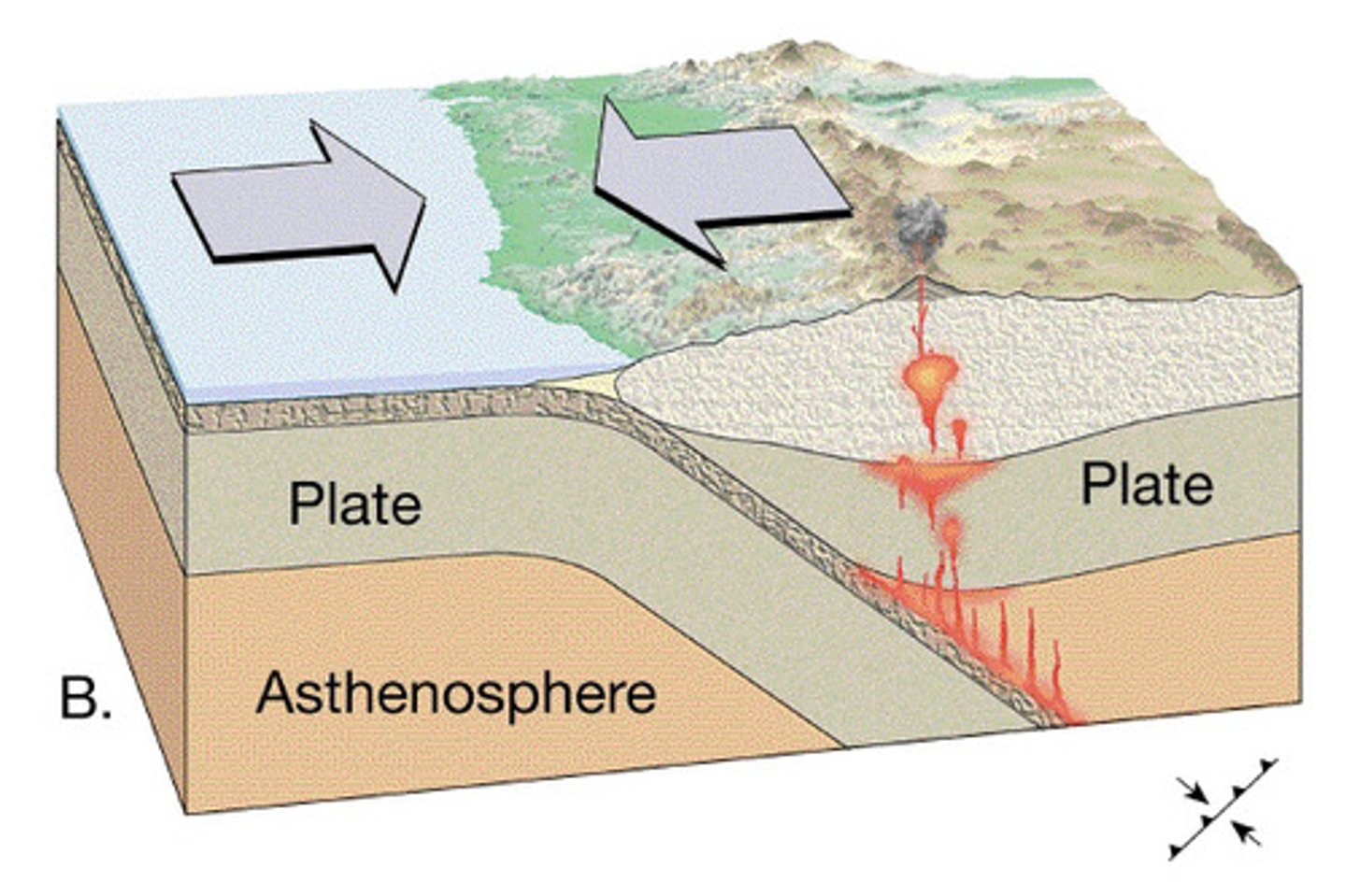
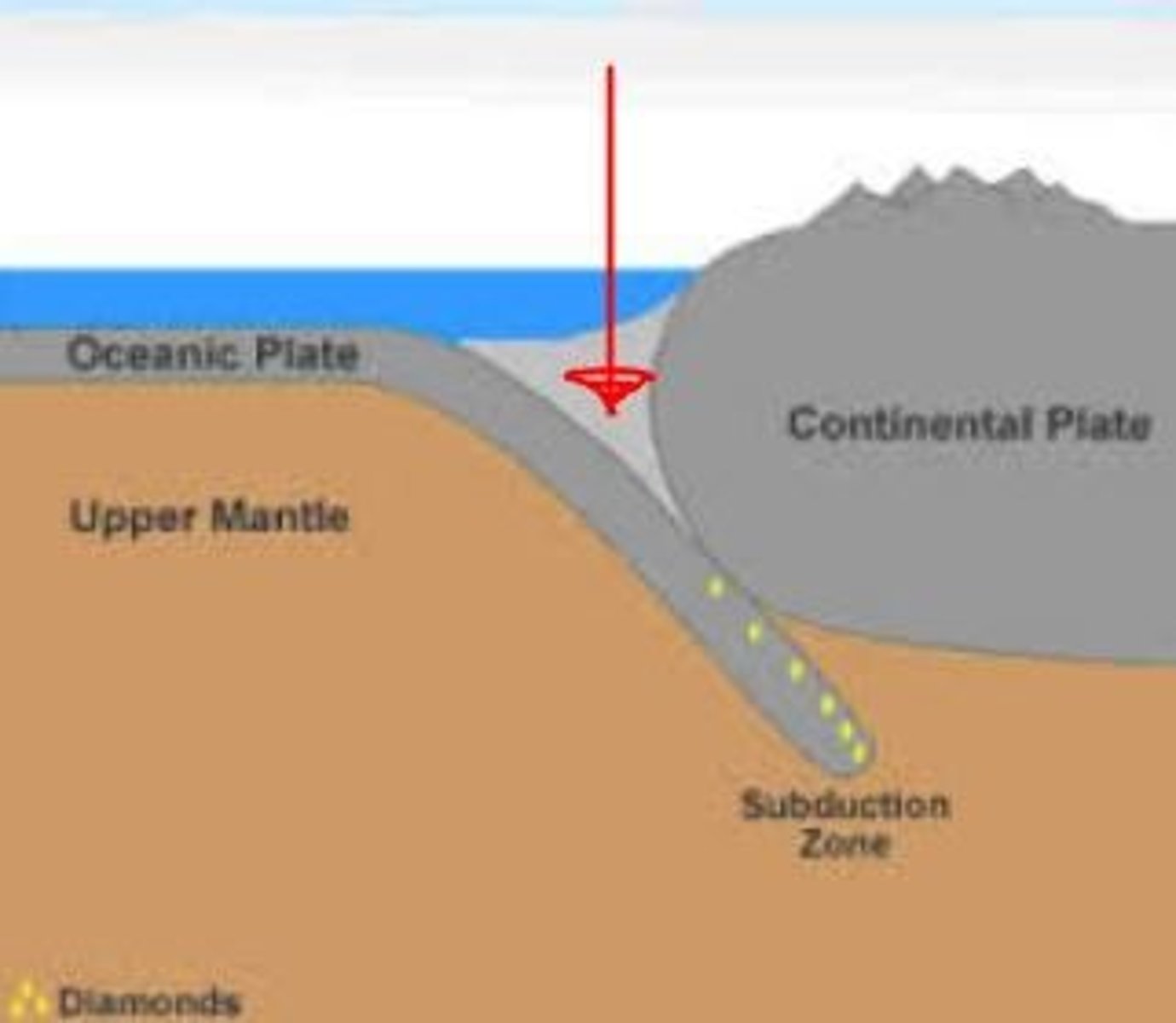
subduction
process in which two plates collide and the denser ocean plate descends below the other
trench
extremely deep areas in the ocean that are created by a subducting plate
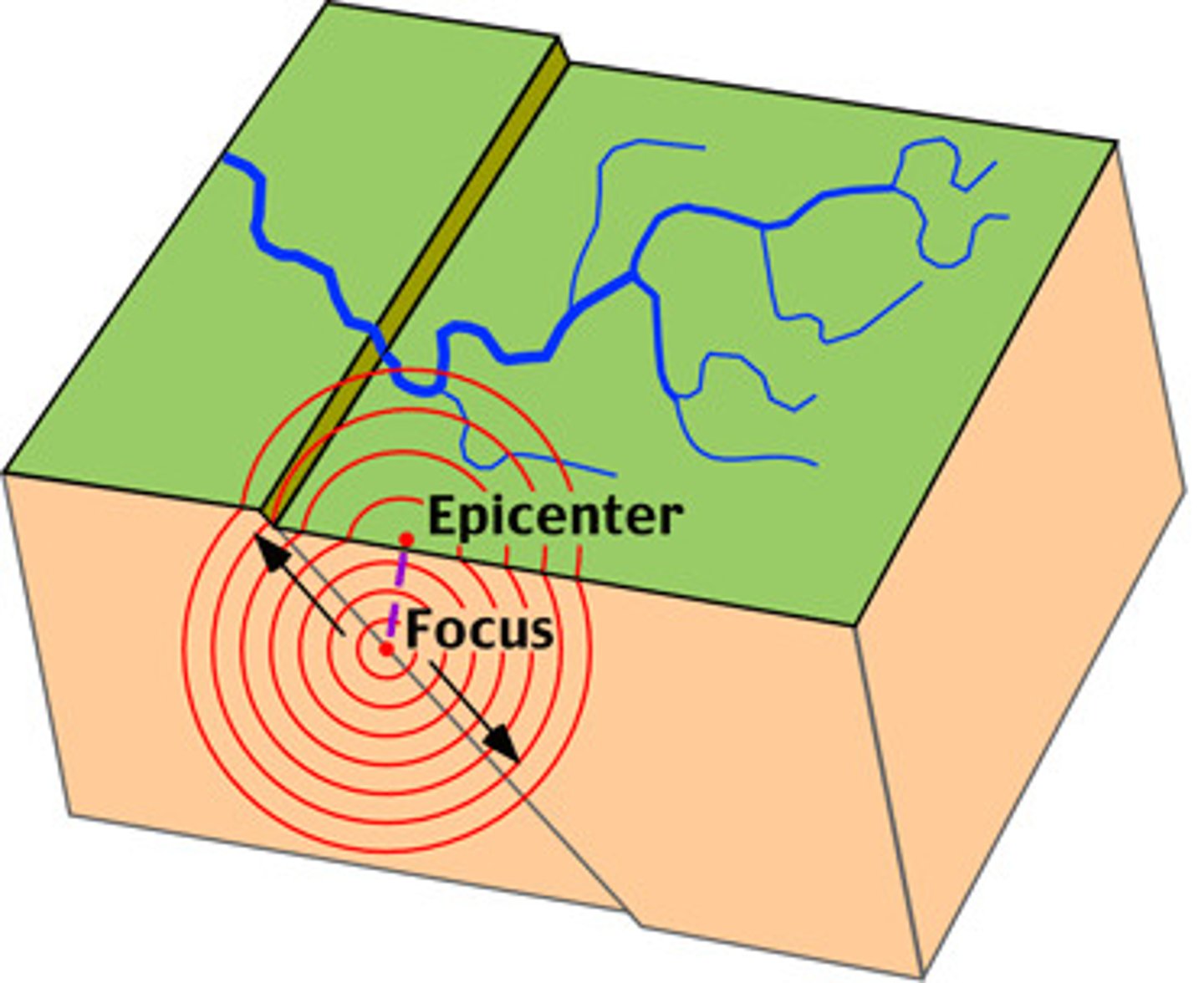
earthquake
Vibrations produced when rocks break along a fault
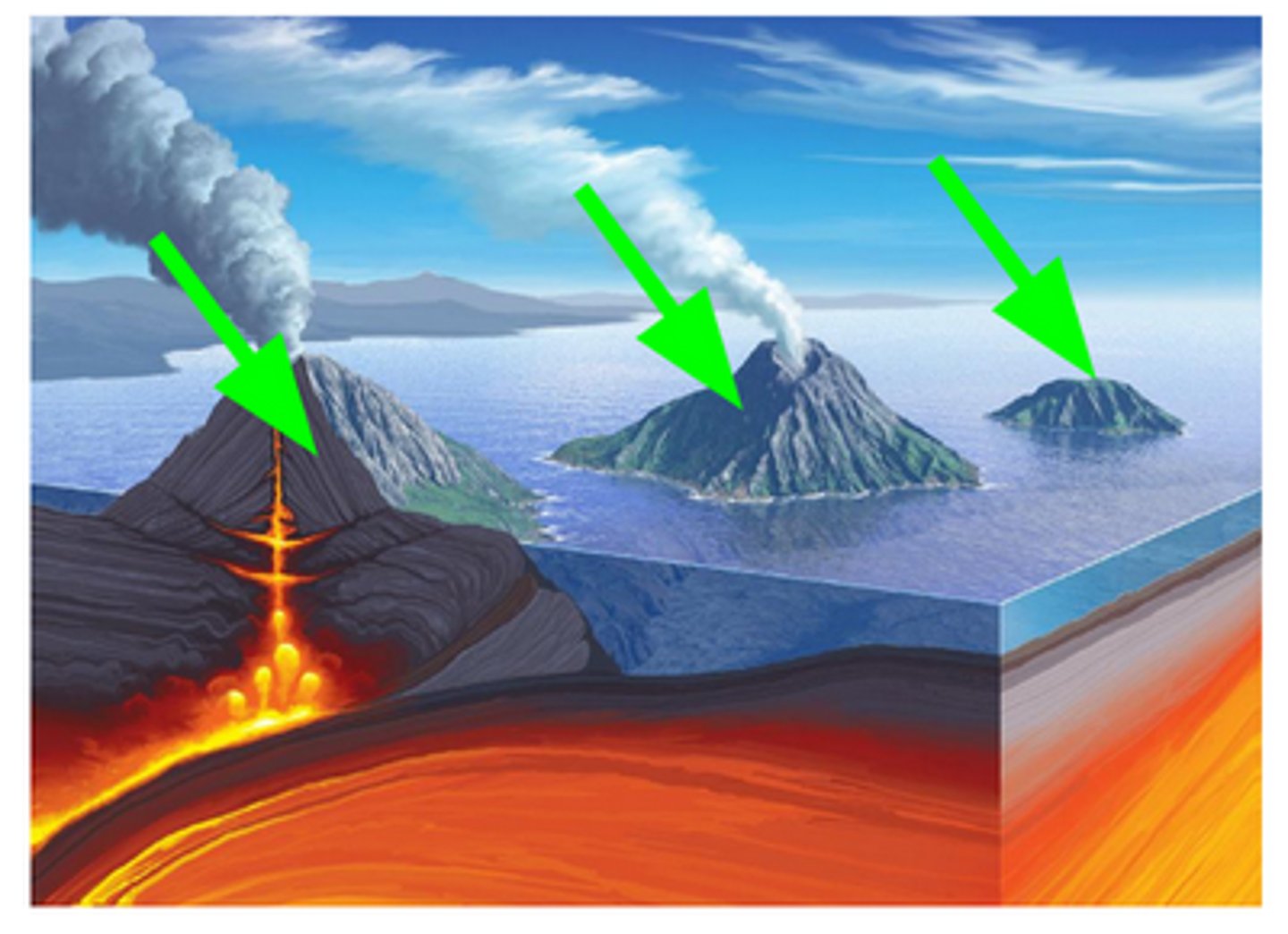
island arc
a chain of volcanic islands formed at an ocean-ocean convergent boundary

focus
The point beneath Earth's surface where rock breaks under stress and causes an earthquake