Atomic structure, interatomic bonding & atomic arrangements
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What forms an atom?
Nucleus & orbiting electrons
What forms the nucleus?
Protons & neutrons
What are the charges of subatomic particles?
Electrons: -1.602 × 10^-19 C
Protons: +1.602 × 10^-19 C
Neutrons: neutral
The mass of an electron to a proton (or neutron) is like the mass of:
a penny to a bowling ball
what are the three types of primary atomic bonding?
Ionic, covalent, and metallic
What are Ionic bonds?
Transfer of electrons
Strong attractive force (coulombic) between ions
non-directional
What is non-directional bonding?
attraction is uniform in all directions
ex. like a magnet in the middle of a room, no matter where you stand around it the force is the same
What are the properties of materials with ionic bonds?
high melting point
hard and brittle
electrical/thermal insulators when solid
conductive when dissolved in water (aqueous)
soluble in polar solvents
What are covalent bonds?
sharing of electrons
small differences in electronegativity of atoms (so one atom can’t pull electron away)
varying bonding energies ( not all equally strong)
what are the properties of materials with covalent bonds?
varying melting temperatures
varying mechanical properties
typically electrical insulators, but some are conductive
can be solid, liquid or gas
What are metallic bonds?
free electrons shared by atoms
what are the properties of materials with metallic bonds?
good conductors
can be strong or weak
mostly ductile
What are secondary (Van der Waals) bonds?
weak bonds
formed by dipoles (uneven electron distribution
intermolecular
What is bonding energy?
amount of energy needed to separate two bonded ions
What does high bonding energy mean for melting points?
High melting points. The higher the bonding energy the harder it is to break bonds.
What is short range order?
Atoms are arranged in a pattern near each other, but that pattern doesn’t last very far
ex. People standing in a crowd
What is long range order?
Atoms are arranged in a repeating, regular pattern that goes on and on over a large area.
ex. Soldiers lined up
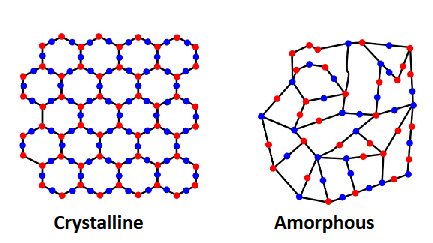
Are amorphous materials short range or long range order?
only short-range order
Amorphous materials vs. Polycrystalline materials
Amorphous: short-order, disordered
Polycrystalline: made of many small crystals, ordered
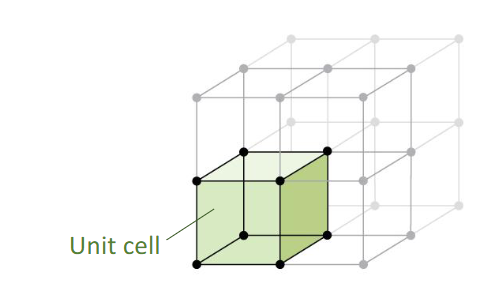
Describe crystal structure
Lattice: divides space into segments
Unit cell: individual segment that makes up the lattice, retains the characteristics of the entire lattice
What is the atomic packing factor?
how much space in the unit cell is actually occupied by atoms
What is allotropy?
same element, different strucutres
applies to elements only (one atom)
same element can exist in different crystal structures depending on conditions (temperature or pressure)
ex. carbon → diamond (3D tetrahedral structure) vs graphite (layered structure)
What is Polymorphism?
same compound, different structures
applied to compounds (more than one type of atom)
same compound can exist in different crystal structures
ex. Silicon dioxide (SiO2) can exist as quartz, cristobalite, or tridymite
What is X-ray Diffraction?
technique used to look at the atomic arrangement of atoms in a crystal by measuring how X-rays scatter when they hit a crystal
Why can X-rays be used to study crystals?
X-rays have similar wavelengths to the distance between atoms, so when they hit a crystal, they scatter in patterns that reveal atomic spacing
How do atoms in a crystal affect X-ray scattering?
Atoms scatter X-rays because of their electrons.
More electron → stronger scattering
arrangement of atoms determined constructive or destructive interference
What is constructive and destructive interference in XRD?
Constructive: waves align → add → bright spot
Destructive: waves oppose → cancel → dark spot
pattern depends on atomic plane spacing and X-ray wavelength
How does crystal structure affect X-ray diffraction intensity?
Type of atoms: more electrons → stronger scattering
Number of atoms in a place: more atoms → stronger peak
Spacing of planes: determines diffraction angles
Wave interference: constructive = strong, destructive = weak
What is Bragg’s Law
describes the angle at which a beam of x-rays of a particular wavelength diffracts
Primary chemical bonds found in solids are ionic, metallic, and Van der Waals bonds. True or False?
False.
The primary chemical bonds found in solids are ionic, covalent, and metallic
What is the smallest repeating unit in a crystalline material?
a unit cell