Field Parasitology Exam 2
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
what class is considered a traditional group containing free-living flatworms; marine, freshwater and terrestrial
Class Turbellaria
what class is a Monophyletic group containing most of the parasitic flatworms
Superclass Neodermata
what class has direct life cycles and is primarily ectoparasitic on the gills of fish
Class Monogenea
What class has a subclass digenea, has parasitic flukes and has at least two hosts one is a mollusk?
Class Trematoda
What class has tapewoms?
Class cestoidea
no body cavity
body is filled with ______
This describes what kind of organisms?
Acoelomate organisms
body is filled with parenchyma
What type of symmetry do flatworms have?
bilateral symmetry
The outer covering in parasitic platyhelmihtes is called?
tegument
What type of digestive system do flatworms have?
incomplete digestive system
Flatworms do excretion by __________ (aka _____ cells/ bulbs)
protonephridia (aka flame cells/bulbs)
How could you best describe the nervous system of flatworms?
ladder type arrangement (in most)
most parasitic platyhelminths are __________ aka hermaphroditic
Monoecious
flukes can be defined as:
parasites of all classes of vertebrates
in the subclass Digenea of trematoda sexual reproduction occurs in a ___________ in the definitive host
vertebrate
in the subclass Digenea of trematoda their first intermediate host is almost always a _______
mollusk (snail, clams)
the _________ is the outer covering and is typically _______ in nature
tegument, syncytial
what does the complex muscle system of trematodes allow them to do? the muscle tissue can be described as _______
complex movement and smooth
Trematoda reproduction can be described as ________
monoecious
Life cycles of trematodes include sexual reproduction in vert. host and asexual in molluscan host, asexual reproduction =
polyembryony- multiple embryos from the same zygote (egg)
Life cycles of trematodes include sexual reproduction in vert. host and asexual in molluscan host, sexual reproduction =
sexual reproduction produces the egg
most trematode eggs have an ________ at one end, and it is used for?
operculum, it is used as an escape hatch
what stimulates hatching of the trematodes eggs?
light, osmotic pressure, etc.
What is the difference between the redia and sporocyst stages?
the sporocyst has does NOT have a mouth and the redia does have a mouth
the miracidium stage is typically found where? and has a retractable ______ ________ that penetrates the snail?
the miracidium is typically found in water and has a retractable apical papilla
in the snail the miracidium becomes a ________, which lacks what?
sporocyst, which lacks a mouth and digestive system
the intramolluscan stages often occupy the ______ and ___________ (digestive gland) of snail
gonad and hepatopancreas
who is active, ingest snail tissue (has mouth, pharynx, short gut), can ingest sporocysts
redia
what stage leaves the redia or sporocyst and snail, is free-swimming and short-lived, most have a tail, often must find the next host in the life cycle
cercariae
what types of glands do cercariae have?
penetration
mucous production for adhering to host
cyst production
what stage is this?
encysted quiescent (resting) stage
may be in, or on a host on some substrate (vegetation, rocks, etc.)
Encystment
metacercaria
what stage matures to adult in definitive (vert) host?
adult fluke
what happens in the vertebrate host?
cercaria penetrates definitive host or metacercaria is ingested —> excystation may be triggered by host cues —> migrate to cite of infection (liver, lungs, bladder, circulatory system) —> develop —> sexual maturity (adult)
what stage is an intermediate stage between cercaria and metacercaria?
mesocercaria
different environments = different challenges such as?
osmolarity, temperature, PH
who are facultative anaerobes?
adult flukes
phylum mollusca includes who?
snails, octopuses, squid, clams, scallops, oysters and chitons
mollusks are _________ meaning they have a body cavity
eucoelomate
mollusks body plan are typically all covered with?
covered with a mantle typically secretes the shell
what does gastropoda mean?
stomach foot
who is the largest group of mollusks?
class gastropoda
gastropod shells can either be _____ or ______ because they exhibit chirality
sinistral (opening to the left) or dextral (opening to the right)
there are 2 gastropoda systematics, what are they?
pulmonata and prosbranchia
this describes what gastropoda systematic
name refers to gills located in body cavity
contains most freshwater, marine and land snails
possess shell aperture with calcareous or horny operculum
mostly dioecious
includes freshwater viviparidae
Prosobranchia
this describes what gastropoda systematic?
mostly freshwater and terrestrial
no gills
no operculum (mostly)
monoecious
freshwater taxa include: planorbidae, lymnaeidae, physidae
Class Bivalvia includes?
Clams, mussels, osyters, scallops
what class of mollusks does this describe:
no distinct head
shell divided into halves
no radula
some have eyes or sensory tentacles along outer edge
mantle cavity contains gills for feeding and has exchange
most are suspension (filter) feeders
mostly sessile
Class Bivalvia
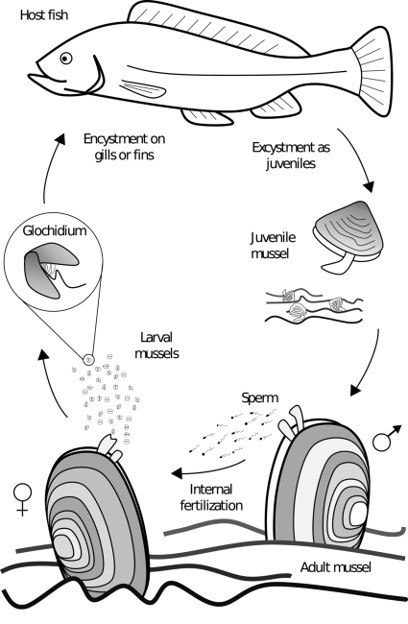
What lifecycle does this describe?
family Unionidae : freshwater mussels
what phylum has:
bilateral symmetry
is pseudocoelomate
has complete digestive system
most dioecious with sexual dimorphism
phylum Nematoda
papillae is a ______ receptor that is cephalic and caudal
touch
amphids are a __________ located on the head of nematodes
chemoreceptor
what sensory structure is similar to amphids but is located on the posterior end? (is also a chemoreceptor)
phasmids
what sensory structure is similar to papillae but is located near nerve ring?
Derids
Do nematodes have a complete digestive system?
yes
Most nematodes have what type of excretion?
secretory-excretory (SE)
Nematodes gonads are solid cords of ______- continuous with tubes for what 3 things?
Tissue, continuous with tubes for development, storage and ejection
What type of sexual dimorphism do nematodes exhibit?
females are larger
males often have curled posterior ends and sex structures at cloaca
How do male and female nematodes find each other?
Chemoreception, using pheromones and Thigmotaxis (touch)
Male nematodes reproduction system have accessory structurees called _______, that are used to hold vulva of female open while sperm is inserted
spicule
What are the 3 layers of the nematode egg?
vitelline (outer)
Chitinous (middle)
Lipid (inner)
in nematode dev. the number of cells remains constant through life is called?
Eutely
How many juvenile stage are there in nematodes? what happens between each juvenile stage?
J1-J4
molt cuticle between each
what is hypobiosis?
developmental arrest
Give the common name, order and family of who this description refers to:
name from curvature of anterior end
impt path of humans and domestic animals
male have distinct copulatory bursa
female has 2 eggs and produce thousands of eggs/day
buccal capsule- bears cutting plates or teeth
Hookworms
Order: strongylida
Family: ancylostomatidae
How do humans become infected with hookworms?
Upon contacting human skin (usually feet, hands or butt) penetrates and enter blood or lymph circ.
What is the name of the most common hookworms of domestic dogs?
A. caninum
Describe a cutaneous larva migrin (aka creeping eruption)
Occurs when sp. that normally develop in non-human hosts attempt to infect humans
What is the drug of choice for cutaneous larva migrins (creeping eruption)
Topical Thiabendazole
What is the order and family of trichuris trichiura?
Order: Trichurida
Family: Trichuridae
This morphology describes who?
adults thin except for posterior end
mouth w/o lips
small buccal capsule followed by a long esophagus
trichuris trichura
thing tube surrounded by unicellular glands is called?
stichocytes
gland cells + esophagus =
stichosome
do both male and female trichuris trichura have a single gonad?
yes
this is the pathology of who?
often infection is light and asymptomatic
heavy infection (>200 worms) may result in: anemia, dysentery, retardation of growth, finger and toe clubbing, retal prolapse, reduced cognitive func.
Trichuris trichura
______ _________ is large round worm of humans
ascaris lumbricoides
A. suum is the large round worms of who?
pigs
_____ ______ is a very common parasite of dogs and an important parasite of humans
toxicara canis
visceral larva migrins can be caused by a number of nematodes but ______ is the most common cause
Toxicara
These are symptoms of?
juv wonder into deep tissues and organs (nearly any organ may be infected)
causes a delayed type hypersensitivity reaction (sympt: fever, hepatomegaly, pulmonary probs)
liver is most common site
brain and CNS are also commonly infected
visceral larva migrins caused by Toxicara
why are small children most likely to ingest eggs of toxicara canis?
close association with dogs and puppies
How can Toxicara canis be disgnosed?
ELISA
Are there any treatment/ control methods for toxicara canis
No effective control treatment known and control= worming pets and careful handling of feces
_____ is common in domestic and other cats
T. cati
T. cati may cause _____ ______ ______ (sim to T. canis) what is an effective control method?
Visceral larva migrins
covering the sandbox
What is the name of the ascarid parasite of raccoons?
Baylisascaris proyonis
Can humans be infected by Baylisascaris procyonis?
yes, commonly migrates to the brain or eyes
What is the name of the parasite of marine mammals? (use fish as 2nd int. hosts)
Anisakis sp.
How are humans infected by anisakis sp? what does it cause?
humans infected by ingesting juv. in raw, salted, or pickled fish
causes anisakiasis
How can anisakiasis be controlled? and where (in the world) is it most commonly seen?
it can be controlled by freezing fish to kill the juvenile worms
most commonly seen in Japan (100s to 1000s cases per year)
What does the phylum name Acanthocephala mean?
Means thorny-headed worm
is the Phylum Acanthocephala pseudocoelomate?
yes
the _____________ sp can be found in adult turtle intestines
neoechinorhynchus sp
what are the 1st and 2nd intermediate host of the neoechinorhynchus sp?
1st int. host= ostracod
2nd int. = snails or fish