6.1 Digestion
5.0(1)Studied by 26 people
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:07 AM on 5/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
1
New cards
Which organs are in the alimentary canal
esophagus, stomach, small and large intestine
2
New cards
Which organs are the accessory organs
salivary glands, pancreas, liver, gall bladder
3
New cards
Distinguish between alimentary canal organs and accessory organs
Alimentary canal: food actually passes through these
\
Accessory organs: aid in digestion but do not transfer food
\
Accessory organs: aid in digestion but do not transfer food
4
New cards
Describe the structure and function of the esophagus
structure: hollow tube connecting the oral cavity to the stomach, separated from the trachea by the epiglottis
\
function: food mixed with saliva and moved in a bolus via peristalsis
\
function: food mixed with saliva and moved in a bolus via peristalsis
5
New cards
Describe the structure and function of the stomach
structure: lined by gastric pits that release digestive juices which create acidic environment (pH less than 2)
\
function: temporary storage tank where food is mixed by churning, protein digestion begins
\
function: temporary storage tank where food is mixed by churning, protein digestion begins
6
New cards
Describe the structure and function of the small intestine
structure: long, highly folded tube consisting of three sections (duodenum, jejunum, ileum)
\
function: usable food substances (nutrients) absorbed here
\
function: usable food substances (nutrients) absorbed here
7
New cards
Describe the structure and function of the large intestine
structure: final section of the alimentary canal, consists of ascending, transverse, descending, sigmodial colon, rectum
\
function: water and dissolved minerals (ions) absorbed here
\
function: water and dissolved minerals (ions) absorbed here
8
New cards
Describe the structure and function of the salivary glands
structure: includes the parotid gland, submandibular gland, sublingual gland
\
function: releases saliva to moisten food, contains enzymes to initiate starch breakdown
\
function: releases saliva to moisten food, contains enzymes to initiate starch breakdown
9
New cards
Describe the function of the pancreas
produces a broad spectrum of enzymes that are released into the small intestine via the duodenum, secrets hormones (insulin and glucagon) to regulate blood sugar concentration
10
New cards
Describe the function of the liver
takes raw materials absorbed by small intestine and uses it for key chemicals; responsible for detoxification, storage, metabolism, bile production, hemoglobin breakdown
11
New cards
Describe the function of the gall bladder
stores bile produced by the liver because bile salts are used to emulsify fats, bile is released into th small intestine via the common bile duct
12
New cards
Know how to draw and label a diagram of the digestive system
13
New cards
List the processes of mechanical digestion
chewing (mouth), churning (stomach), segmentation (small intestine)
14
New cards
Describe the movement of food during chewing
* grinding action of the teeth breaks down food
* tongue pushes food to back of the throat
* food travels down esophagus as a bolus
* epiglottis prevents the bolus from entering the trachea
* uvula prevents the bolus from entering the nasal cavity
* tongue pushes food to back of the throat
* food travels down esophagus as a bolus
* epiglottis prevents the bolus from entering the trachea
* uvula prevents the bolus from entering the nasal cavity
15
New cards
Describe the movement of food during churning
* stomach lining has muscles that squeeze and mix the food with strong digestive juices
* food is digested within the stomach for hours
* food turns into a creamy paste called chyme
* chyme enters the small intestine through the duodenum for absorption
* food is digested within the stomach for hours
* food turns into a creamy paste called chyme
* chyme enters the small intestine through the duodenum for absorption
16
New cards
Describe peristalsis
a movement of the esophagus, stomach, and gut
* continuous segments of longitudinal move rhythmically contracting and relaxing
* food is moved unidirectionally from mouth to anus
* continuous segments of longitudinal move rhythmically contracting and relaxing
* food is moved unidirectionally from mouth to anus
17
New cards
Describe segmentation
occurs in the intestines
* contraction and relaxation of non-adjacent segments of circular smooth muscle
* moves chyme in both directions to allow for greater mixing of food with digestive juices
* bidirectional propulsion can slow overall movement
* contraction and relaxation of non-adjacent segments of circular smooth muscle
* moves chyme in both directions to allow for greater mixing of food with digestive juices
* bidirectional propulsion can slow overall movement
18
New cards
Describe how stomach acids aid in chemical digestion
* stomach has gastric glands to release digestive acids and create a low pH
* acidic environment denatures proteins and other macromolecules to help with digestion
* the stomach epithelium has a mucous membrane to prevent the acids from damaging the gastric lining
* pancreas releases alkaline compounds to neutralize the acids as they enter the intestine
* acidic environment denatures proteins and other macromolecules to help with digestion
* the stomach epithelium has a mucous membrane to prevent the acids from damaging the gastric lining
* pancreas releases alkaline compounds to neutralize the acids as they enter the intestine
19
New cards
Describe how bile aids in chemical digestion
* bile is stored and concentrated in the gall bladder
* bile has bile salts which interact with fat globules and divide them into small droplets (called emulsification)
* this increases total surface area available for enzyme activity by lipase
* bile has bile salts which interact with fat globules and divide them into small droplets (called emulsification)
* this increases total surface area available for enzyme activity by lipase
20
New cards
Describe how enzymes aid in chemical digestion
* speed up the rate of chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy
* allow digestive processes to occur at body temperatures and at sufficient speeds for survival
* Enzymes are specific for a substrate and so can allow digestion of certain molecules to occur independently in distinct locations
* allow digestive processes to occur at body temperatures and at sufficient speeds for survival
* Enzymes are specific for a substrate and so can allow digestion of certain molecules to occur independently in distinct locations
21
New cards
Describe carbohydrate digestion
* salivary glands release amylase in the mouth
* the pancreas also secretes amylase to continue carbohydrate digestion in the small intestine
* enzymes for disaccharide hydrolysis are immobilized on the epithelial lining of the small intestine
* humans can not digest cellulose
* the pancreas also secretes amylase to continue carbohydrate digestion in the small intestine
* enzymes for disaccharide hydrolysis are immobilized on the epithelial lining of the small intestine
* humans can not digest cellulose
22
New cards
Describe the digestion of proteins
* begins in the stomach with the release of proteases
* function optimally in acidic pH
* smaller polypeptide chains are broken down by endopeptidases (released by pancreas) in the small intestine
* work optimally in neutral environments
* function optimally in acidic pH
* smaller polypeptide chains are broken down by endopeptidases (released by pancreas) in the small intestine
* work optimally in neutral environments
23
New cards
Describe the breakdown of lipids
* occurs in the lipids with the release of bile from the gall bladder that enables the emulsification of fat globules
* smaller fat droplets are digested by lipases from the pancreas
* smaller fat droplets are digested by lipases from the pancreas
24
New cards
Describe the breakdown of nucleic acids
* pancreas releases nucleases to digest nucleic acids into smaller nucleosides
25
New cards
List the four main tissue layers of the small intestine
serosa, muscle layer, submucosa, mucosa
26
New cards
State the structure of the serosa layer of the small intestine
protective outer covering composed of a layer of cells reinforced by fibrous connective tissue
27
New cards
State the structure of the muscle layer of the small intestine
outer layer of longitudinal muscle (peristalsis) and inner layer of circular muscle (segmentation)
28
New cards
State the structure of the submuscosa layer of the small intestine
composed of connective tissue that separate the muscle layer from the innermost mucosa
29
New cards
State the structure of the mucosa layer of the small intestine
a highly folded inner layer which absorbs material through the surface epithelium from the intestinal lumen
30
New cards
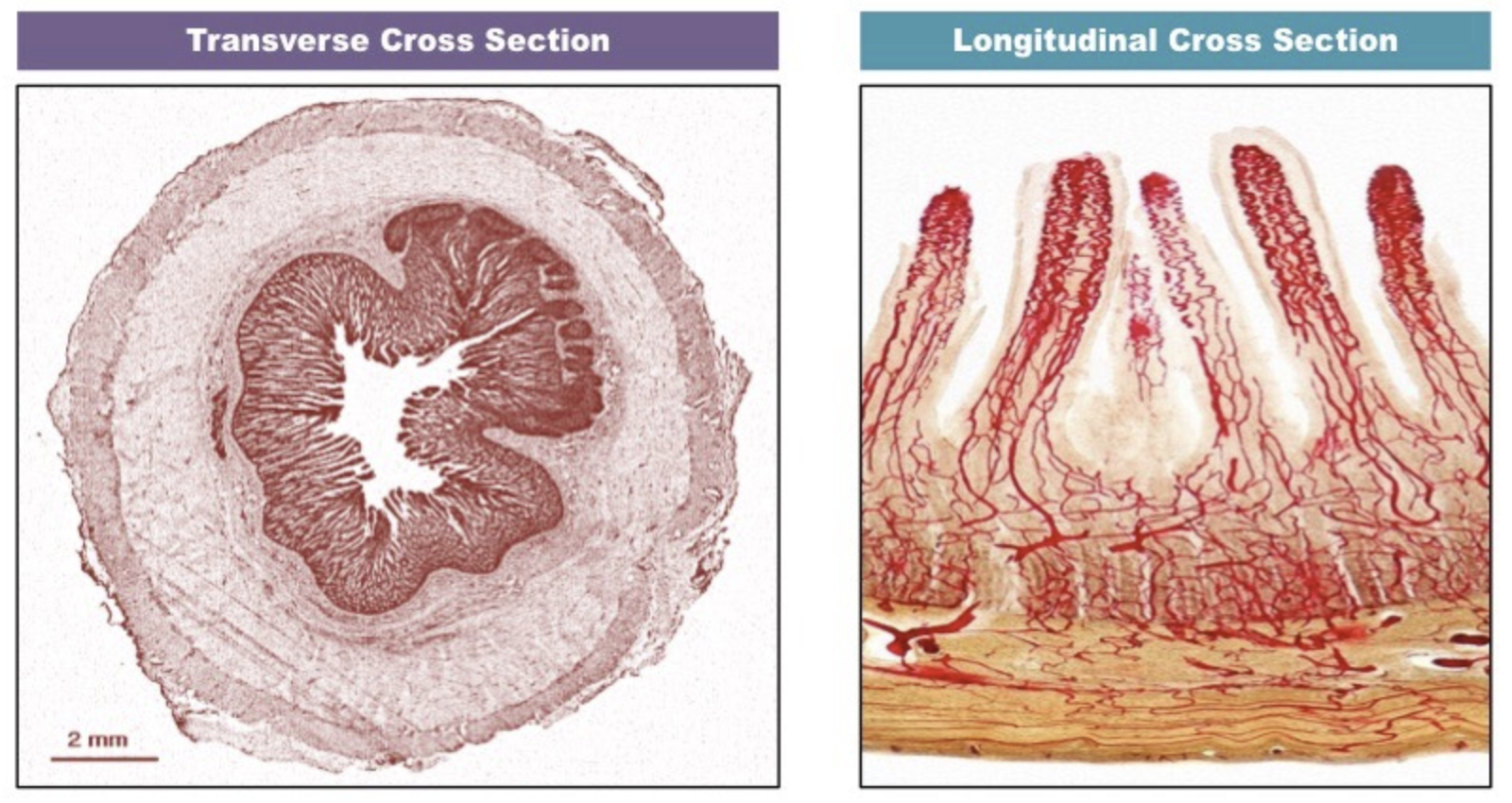
Label the cross section of the small intestine tissue
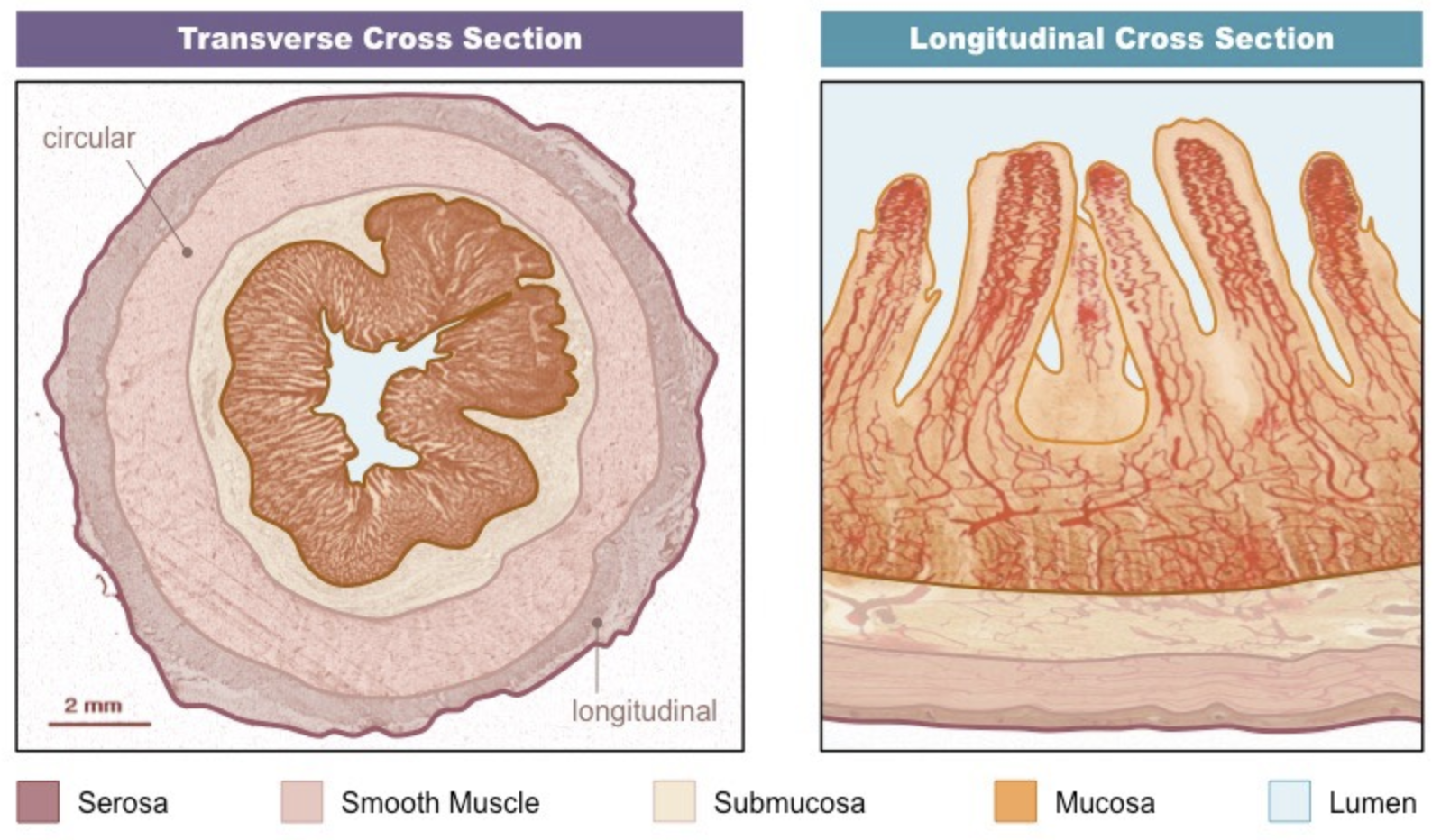
31
New cards
List the features of intestinal villi
Microvilli
* ruffling of epithelial membrane increases surface area further
Rich Blood Supply
* dense capillary network rapidly transports absorbed products
Single Layer Epithelium
* minimizes diffusion distance between lumen and blood
Lacteals
* absorbs lipids from the intestine into the lymphatic system
Intestinal glands
* exocrine pits release digestive juices
Membrane proteins
* facilitates the transport of digested materials into epithelial cells
* ruffling of epithelial membrane increases surface area further
Rich Blood Supply
* dense capillary network rapidly transports absorbed products
Single Layer Epithelium
* minimizes diffusion distance between lumen and blood
Lacteals
* absorbs lipids from the intestine into the lymphatic system
Intestinal glands
* exocrine pits release digestive juices
Membrane proteins
* facilitates the transport of digested materials into epithelial cells
32
New cards
List the structural features of villus epithelium
tight junctions, microvilli, mitochondria, pinocytotic vesicles
33
New cards
Describe the function of the tight junctions of the epithelial lining of villi
* Occluding associations between the plasma membrane of two adjacent cells, creating an impermeable barrier
* They keep digestive fluids separated from tissues and maintain a concentration gradient by ensuring one-way movement
* They keep digestive fluids separated from tissues and maintain a concentration gradient by ensuring one-way movement
34
New cards
Describe the function of the microvilli of the epithelial lining of villi
* Microvilli borders significantly increase surface area of the plasma membrane (>100×), allowing for more absorption to occur
* The membrane will be embedded with immobilised digestive enzymes and channel proteins to assist in material uptake
* The membrane will be embedded with immobilised digestive enzymes and channel proteins to assist in material uptake
35
New cards
Describe the function of the mitochondria of the epithelial lining of villi
* Epithelial cells of intestinal villi will possess large numbers of mitochondria to provide ATP for active transport mechanisms
* ATP may be required for primary active transport (against gradient), secondary active transport (co-transport) or pinocytosis
* ATP may be required for primary active transport (against gradient), secondary active transport (co-transport) or pinocytosis
36
New cards
Describe the function of the pinocytotic vesicles of the epithelium lining of villi
* Pinocytosis (‘cell-drinking’) is the non-specific uptake of fluids and dissolved solutes (a quick way to translocate in bulk)
* These materials will be ingested via the breaking and reforming of the membrane and hence contained within a vesicle
* These materials will be ingested via the breaking and reforming of the membrane and hence contained within a vesicle
37
New cards
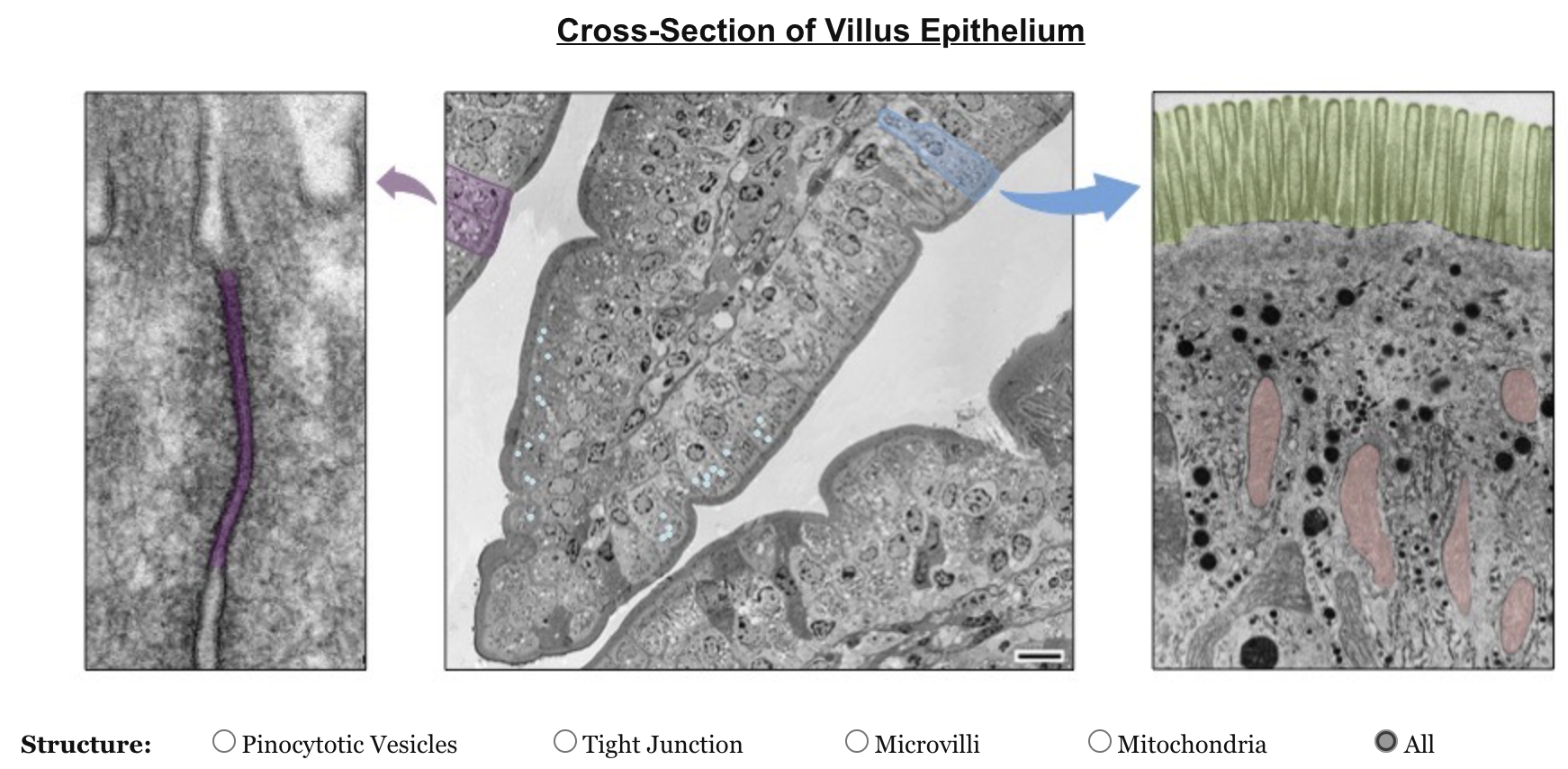
Label the following structures
purple: tight junction
blue: pinocytotic vesicles
green: microvilli
red: mitochondria
blue: pinocytotic vesicles
green: microvilli
red: mitochondria
38
New cards
Describe how secondary active transport enables digestion in the small intestine
* transport protein couples the active translocation of one molecule with the passive movement of another (co transport)
* glucose and amino acids are co transported across the epithelial membrane by the active transport of sodium ions
* glucose and amino acids are co transported across the epithelial membrane by the active transport of sodium ions
39
New cards
Describe how facilitated diffusion enables digestion in the small intestine
* channel proteins often located near membrane-bound enzymes to create a localized concentration gradient
* certain monosaccharides like fructose, vitamins, some minerals transported by facilitated diffusion
* certain monosaccharides like fructose, vitamins, some minerals transported by facilitated diffusion
40
New cards
Describe how osmosis aids in digestion
absorption of water and dissolved ions occurs in small and large intestine
41
New cards
Describe how simple diffusion aids in digestion i
hydrophobic materials (lipids) pass through the hydrophobic portion of the membrane
* after absorption, the lipids pass first into the lacteals instead of being transported via blood
* after absorption, the lipids pass first into the lacteals instead of being transported via blood
42
New cards
Describe how pinocytosis aids in digestion
allows materials to be ingested en masse, hence takes less time than membrane protein transport
43
New cards
Explain why starch digestion only occurs in the mouth and the intestines
amylase is optimal in neutral pH
44
New cards
Describe how amylase breaks down starch
* digests amylose into maltose subunits (a disaccharide) and amylopectin into branched chains called dextrins
* maltose and dextrins are digested by enzymes like maltase which are fixed to the epithelial lining of the small intestine
* results in the formation of glucose monomers which can be used to produce ATP or stored as glycogen
* maltose and dextrins are digested by enzymes like maltase which are fixed to the epithelial lining of the small intestine
* results in the formation of glucose monomers which can be used to produce ATP or stored as glycogen
45
New cards
Describe the two functions of the pancreas in breaking down starch
* produces amylase which is released from the exocrine glands into the intestinal tract
* produces insulin and glucagon which are released from endocrine glands into the blood
* insulin lowers blood glucose levels by increasing glycogen synthesis
* glucagon increases blood glucose levels by limiting synthesis and storage of glycogen
* produces insulin and glucagon which are released from endocrine glands into the blood
* insulin lowers blood glucose levels by increasing glycogen synthesis
* glucagon increases blood glucose levels by limiting synthesis and storage of glycogen