Chemical Systems and Equilibriums - Titrations and Buffers
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
titration set up
base in the burette, acid and indicator in erlenmeyer flask
titration
an analytical lab technique used to determine the concentration of a given solution (acid or base)
neutralization reaction is carried out quantitatively
titrant
solution of known concentration (solution in burette)
sample
solution of unknown concentration (solution in Erlenmeyer flask)
equivalence pt (or stoichiometric pt)
the point at which the reaction is complete (=same number of moles of hydronium and hydroxide)
indicator
substance that changes colour at (or near) the equivalence pt
endpoint
point in a titration where a sharp change in a measurable and characteristic property occurs (ie. colour change of acid-base indicator – record final volume and compare to the initial volume)
equipment in titration (6)
Burette
Burette Clamp
Erlenmeyer Flask
Volumetric Pipette
Beakers
Phenolphthalein
neutralization rxn
double displacement reaction between an acid and a base to produce a salt and water (solvent)
acidic and basic properties are destroyed
acid + base → salt + water
titration curve of a strong acid with a strong base
pH increases slowly at first and rapidly as it approaches the equivalence pt
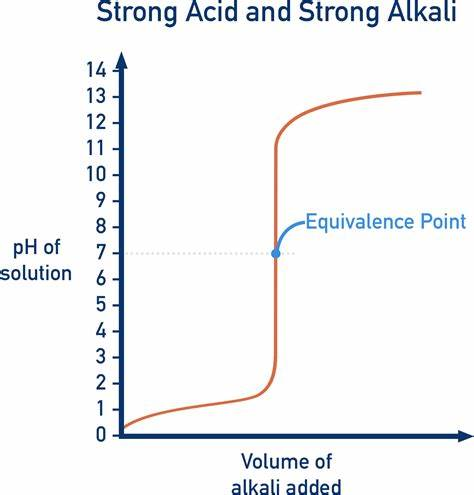
titration curve
a graph of the pH of an acid (or base) against the volume of an added base (or acid)
equivalence point is equal to the midpoint on the titration curve
titrations involding WEAK acids and STRONG bases
to calc concen of H+, we must consider WEAK ACID IONIZATION EQ
indicators are used to
pinpoint the neutralization pt of the rxn (ENDPT)
indicators are molecules that have a diff colour in acid than in does in base (basically according to the pH)
phenolphthalein
colourless in acid, pink in base (pH 8.2 to 10)
bromothymol blue
yellow in acid, blue in base (pH 6 to 7.6)
acid base indicators
a weak acid or base that has diff colours in the non-ionized and ionized forms
HIn(aq) ⇌ H+ (aq) + In- (aq)
Red Yellow
if acidic, the rxn shifts left to oppose it, therefore is red
if basic, rxn shifts right and therefore is yellow
buffer
a solution that contains a weak acid/conjugate base mixture or a weak base/conjugate acid mixture
what do buffers do
resists changes in pH when a moderate amount of an acid or a base is added to it
able to neutralize acids and bases without allowing the pH of the solution to change greatly
2 ways to make buffers
by using a weak acid and one of its salts; for example, by mixing acetic acid and sodium acetate
by using a weak base and one of its salts; for example, by mixing ammonia and ammonium chloride
buffers usually have ____ in them that act as a reservoir and help mainatin a relatively const pH
common ions; and therefore should be treated as a common ion problems
importance of buffers
Living organisms are very sensitive to pH changes as enzymes carry out their function optimally over a small pH range.
Any change in pH of more than 0.2 induced by poisoning or disease is life-threatening.
buffer capacity
amount of acid or base that can be added before considerable change occurs to the pH of the solution
what is buffer capacity dependent on
the concentration of the buffer components
concentrated buffer resists to changes more than a diluted buffer
if there was no buffer, the pH would
change by a significant factor instead of by a slight factor