Ch 8 Intelligence and Creativity
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Fluid Intelligence
The ability to use your mind actively to solve new problems without applying prior knowledge.
Crystallized Intelligence
the use of knowledge acquired through schooling and other life experiences, long term knowledge gathered from life up until now.
Stanford Binet Intelligence Scale (Psychometric approach)
Forerunner of the IQ test used to calculate a child’s mental age, forms normal distribution
Intelligence quotient (IQ)
IQ = MentalAge/ChronologicalAge × 100
Wechsler Scales (Normed assessment)
For all ages, yields a verbal IQ score based on items measuring vocabulary, general knowledge, arithmetic reasoning and performance iq score based on problem solving. 100 as a score is defined as average, forms normal distribution.
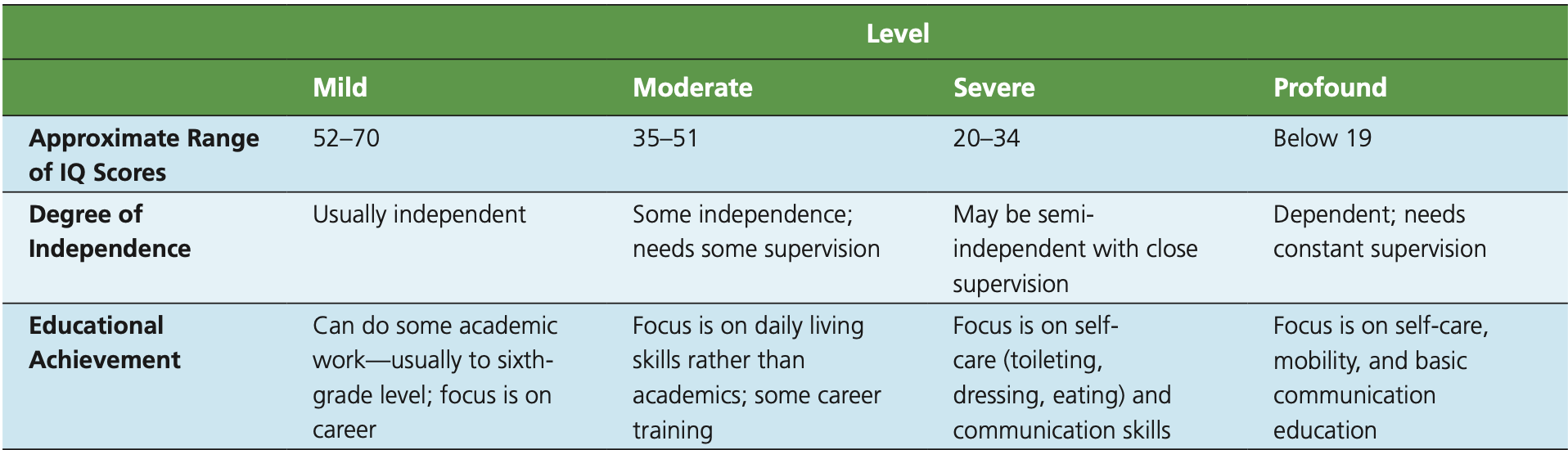
Intellectual disability
Significantly below- average intellectual functioning, 70 or below on an IQ test, deficits in self care and social skills before 18 yrs
Giftedness
IQ score of 130 or higher or they show special abilities in areas valued in society, such as mathematics, the performing and visual arts, leadership.
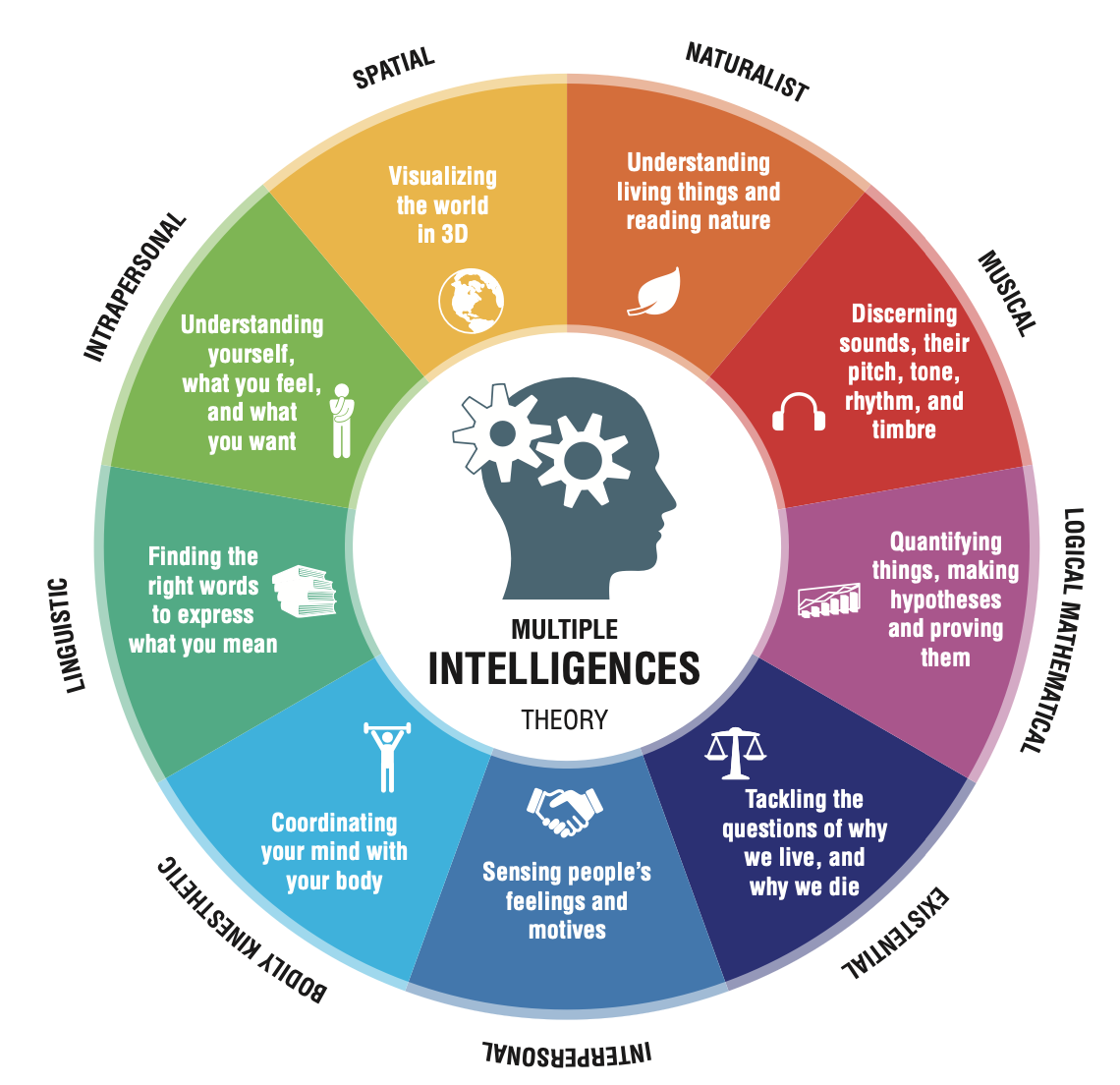
Gardner’s theory of multiple intelligences
There are many intelligences, most of which have been ignored by the developers of standardized intelligence tests, intelligence should be determined by measuring the strengths and weaknesses of ppl by assessing 8 or 9 intellectual abilities
Cattel-Horn-Carroll (CHC )Theory
Intelligence is a hierarchal structure, general abilities influence how well people do on a range of tasks
Limits of psychometric approach
emotional intelligence is not covered, artistic giftedness not included
Savant Syndrome
The phenomenon in which extraordinary talent in a particular area is displayed by a person otherwise intellectually challenged
Prodigies
Children who display ability levels comparable to adult professionals
Steinberg’s Triarchic Theory of Intelligence
○ Establish and achieve reasonable goals
○ Optimize your strengths and minimize weaknesses
○ Adapt to the environment
○ Use all three components of intelligence:
Practical → street smarts, used to solve problems in everyday life
Creative → to deal w novel problems, creating and inventing
Analytic → Critical thinking, planning evaluating
Creativity
the ability to produce novel/unique responses appropriate in context and valued by other creating products both original and meaningful
Why can’t iq tests be used to measure creativity?
Bc creativity uses divergent thinking, while iq tests use convergent thinking.
convergent thinking involves piecing together info to get to a correct answer whereas divergent thinking comes up with a variety of solutions that may not be a correct answer (preschool children display high levels of this)
Ideational fluency
number different and novel ideas someone can generate
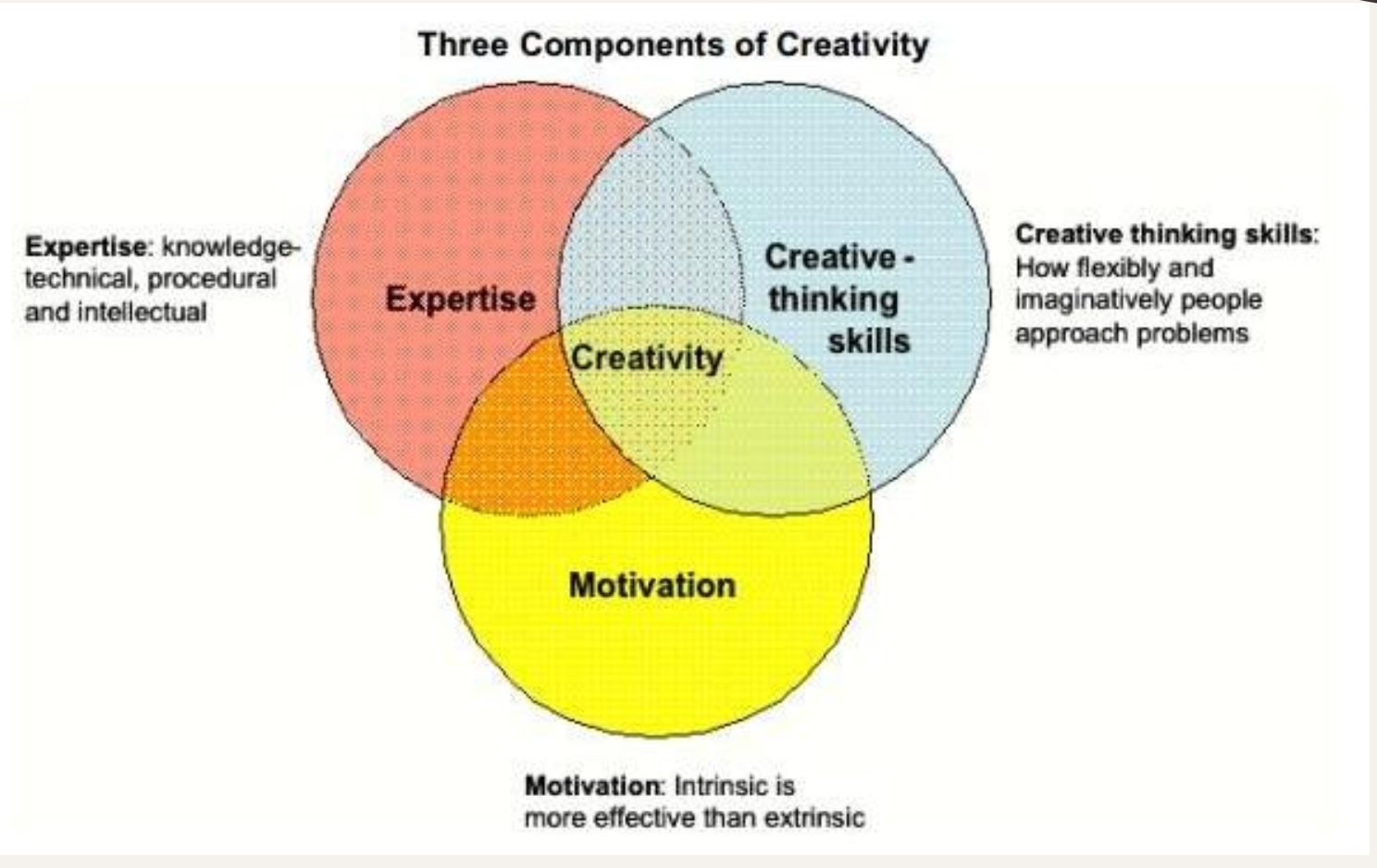
Componetial model of creativity
creativity is made up of expertise, creative thinking skills and motivation
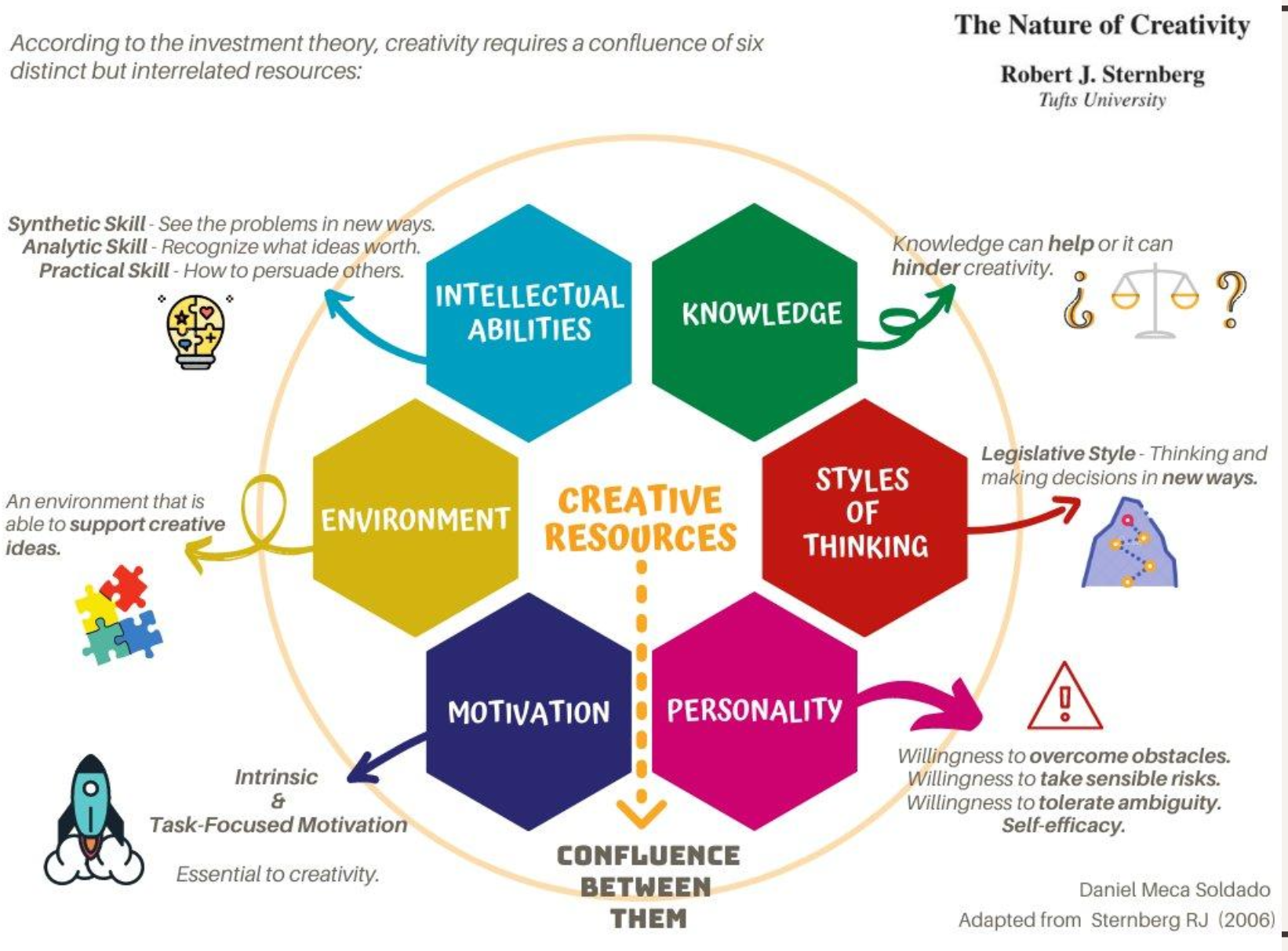
Sternberg’s investment theory
Creativity is a decision, ppl decide to be creative, making ideas that “defy the crowd” (buying low), then persuade many people (sell high)
creativity is affected by
Intellectual ability
environment
motivation
knowledge
styles of thinking
personality
Infant
How to measure intelligence?
Bayley scales (BSID)
Cognitive, language and motor scale
Test result compared to performance of a large norm group of infants and toddlers
Merrill Palmer Revised Scales of Development (MPR), assesses these idea domains
Cognitive
Language/communication
Motor (fine and gross)
Social emotional development
Self help/adaptive
Child
around age 4, iq has a fairly strong relationship with later iq.
iq scores are influenced by
Motivation
Testing procedures
Intelligence
children who live in unstable low ses environments fluctuate in iq the most, gainers of iq points gain more bc parents converse more with them, expose them to more vocab, and offer more encouragement. Drops are result of poverty, unsafe env, bad health care, lack of cognitive stimulation
Cumulative deficit hypothesis
impoverished environments inhibit
intellectual growth
Negative effects caused accumulate over time
Originality
Ability to produce original ideas, sharp decline starting in sixth grade
Adolescent
Intellectual growth continues rapid pace,
Flynn effect → Phenomenon over the 20th century: average IQ scores have increased in all countries studied, probably because:
■ Children today are better educated
■ Improved nutrition and living conditions
■ Increased familiarity with standardized testing
■ Healthier environment
Reverse Flynn effect → Decreasing iq scores
Possible rationales
○ Poorer environment
■ Increased air pollution
○ Worsening nutrition and health standards
○ Less intelligently stimulating environment
■ electronics (TV, internet, social media)
Iq predicts school achievement but not very well for college grades, motivation plays a big role
Adolescent creativity
Idea elaboration ability increases in middle school
Creativity can be fostered through play, by parents and school system to help develop talent and nurture creative endeavors
Adult Intelligence
Iq remains stable into older adulthood
Terminal drop
Poor health
○ Diseases
○ Unstimulating lifestyle
Strongest predictor of iq in old age is their iq at 11
Professional and technical workers
score higher on IQ tests than white-
collar workers
Hi iq, hi occupational success and healthier
Adult creativity
Creative production increases from 20-40, then declines, peak times vary
Creativity is possible throughout life
Factors that influence iq across lifespan
Genes and env → iq is heritable, environment gene interaction, mother iq associated w offspring iq
Race and ethnicity, differences exist bc:
Bias in tests
Motivational factors
Gene diffs
Environmental diffs among groups
Stereotype threat