Chemical Bonds Continued, and Functional Groups
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
ionic bonds
transfer of electrons from one atom to another
results in the formation of cations and anions
oppositely charged ions are strongly attracted to each other
hydration shell
what does water form around charged solutes
the positive ion
the negative side of the water molecule orients to what?
the negative ion
the positive side of the water molecule orients to what?
van der waals bonds
are weak intermolecular interactions observed in condensed phrases like solid and liquid
van der waals bonds
are secondary bonds (uneven charge distribution) in molecules where ionic and covalent bonds form the primary bonds
they can attract atoms or molecules from all directions
Van der waals interactions are non-directional, which means what?
weaker
Are van der waals interactions stronger or weaker than ionic and covalent bonds?
helps in stabilizing the protein structure
responsible for stability of polymer chain
account for the cohesion of inert gases in solid and liquid states
accounts for physical absorption of molecules to solid surfaces
What are the major roles of van der waals interactions
autoionization of water
pure water or indeed any aqueous solution, water acts both as an acid and a base
acid
What increases the concentration of H+ in the solution and decreases the concentration of OH-
Base
What decreases the concentration of H+ in the solution and increases the concentration of OH-
Acids
donate H+ in aqueous solutions
bases
donate OH- or accept H+ in aqueous solutions
Acids and Bases
homeostatic imbalances are caused by what?
acidosis
excessive acidity of the blood
alkalosis
excessive alkaline (basic) of blood
buffers
substances that minimize changes in concentration of H+ and OH- in a solution
hydrophilic
water loving
able to interact with water
polar and or charged (ions) molecules
hydrophobic
water fearing
do not interact with water
nonpolar molecules
Nonpolar molecules
no significant partial charges
symmetrical distribution of electrons
polar molecules
unequal distribution of electrons
partial positive and a partial negative charge
asymmetrical
Carbon
can form 4 bonds and therefore has the ability to form large, diverse and complex molecules
carbon skeletons
molecular diversity arises from variations in length and shape of carbon chains
hydrocarbon
any of a class of organic chemical compounds composed only of the elements carbon (C) and hydrogen (H)
non-polar (hydrophobic)
insoluble
functional groups
determine the characteristics and chemical reactivity of organic molecules
less stable than carbon backbone
more likely to participate in chemical reactions
hydroxyl group
polar, involved in hydrogen bonding. Often participates in condensation reactions. Required inside chain for phosphorylation of proteins
example: alcohols
carbonyl group
polar, very reactive. Important in energy releasing reactions
examples: Aldehydes
Carboxyl group
charged and acidic. ionizes in cells to form R-COO- and H+
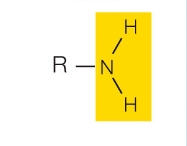
amino group
charged and basic. In cells, accepts H+ to form R-NH3+
Examples: amines
Sulfhydryl group
polar. Can form disulfide bridges
examples: Thiols
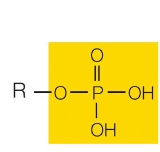
phosphate group
charged and acidic
ionizes cells to form O-P-O32-
example: organic phosphates
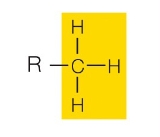
hydroxyl group
what functional group is this?
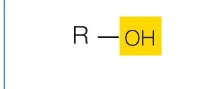
carbonyl
What functional group is this?
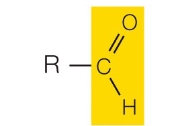
Carboxyl group
What functional group is this?
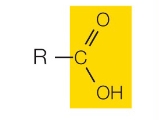
Amino Group
What functional group is this?
Sulfhydryl group
What functional group is this?
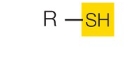
Phosphate Group
What functional group is this?
Methyl group
What functional group is this?