Chapter 8: The Competitive Firm - Market Structure, Profit Maximization, and Supply Decisions
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What is the primary goal of the chapter on competitive firms?
To explain how businesses make price and production decisions.
What are the learning objectives of this chapter?
To understand profit computation, characteristics of competitive firms, profit maximization, shutdown conditions, production vs. investment decisions, and factors shaping a firm's supply curve.
How is profit defined in the context of competitive firms?
Profit is the difference between total revenue and total cost.
What is the profit motive?
The expectation of profit serves as the basic incentive for firms to produce goods and services that consumers desire.
What are explicit and implicit costs?
Explicit costs are payments made for resource use, while implicit costs are the value of resources used without payment.
How do economic and accounting profits differ?
Economic profit includes both explicit and implicit costs, while accounting profit includes only explicit costs.

What is normal profit?
Normal profit is the opportunity cost of capital, expected when economic profit is zero.
What is the role of an entrepreneur in a competitive market?
An entrepreneur starts a business when the prospect of earnings exceeds the alternative use of resources, accepting the risk of potential losses.
What defines market structure?
Market structure refers to the number and relative size of firms in an industry, ranging from monopoly to perfect competition.
What are the characteristics of perfect competition?
Many firms compete, products are identical, low entry barriers exist, no firm has market power, and firms are price takers.
What is the demand curve perception for a firm in perfect competition?
The individual firm perceives its demand curve as horizontal because it is a price taker.
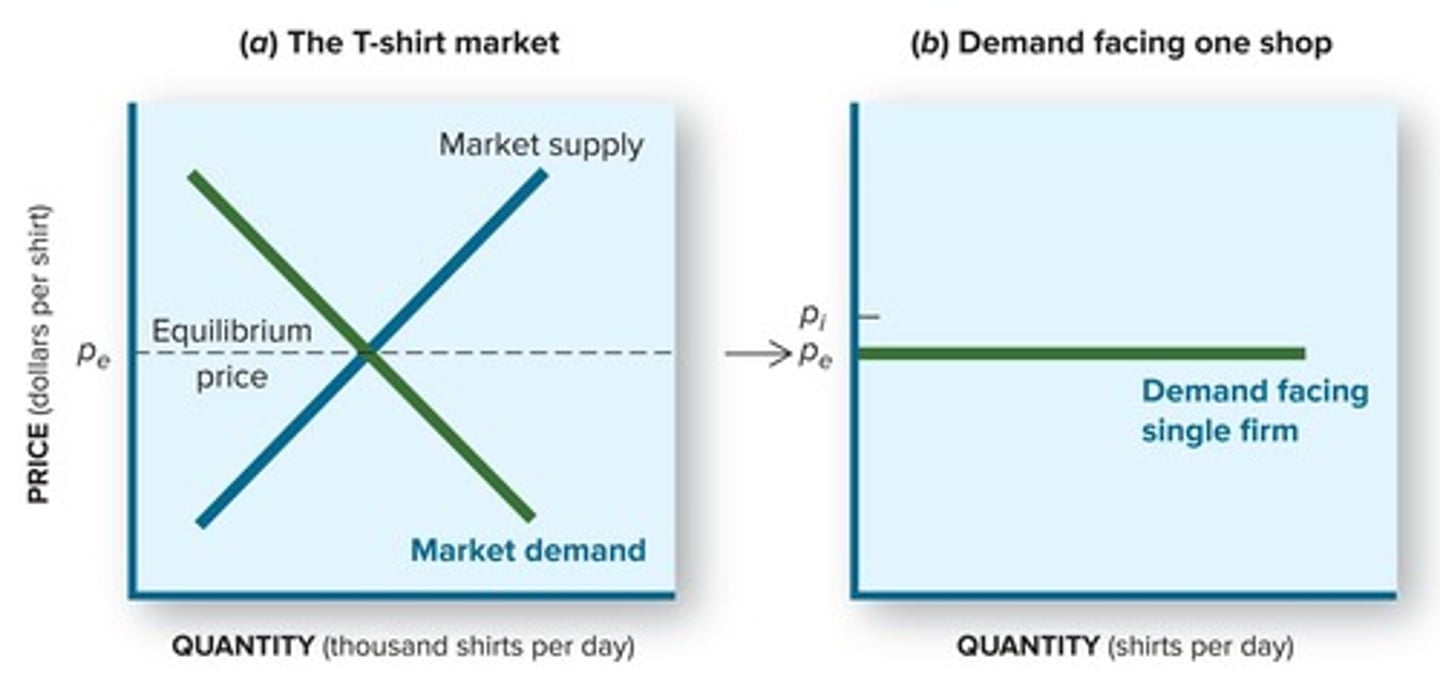
What happens to a firm's sales if it raises its price in a competitive market?
If a firm raises its price, it will sell nothing because consumers will not buy at the higher price.
What occurs if a firm lowers its price in a competitive market?
If a firm lowers its price, it will sell out but can do so only at the market price.
What is the significance of low entry barriers in perfect competition?
Low entry barriers allow new firms to easily enter the market, increasing competition.
What is the relationship between the degree of competition and profitability?
Less competition makes it easier for firms to be profitable, while more competition makes it more difficult.
What is the implication of producing goods that consumers do not want?
A firm will struggle to make a profit if it produces goods that consumers do not desire or are unwilling to pay for.
What does the term 'price taker' mean in the context of competitive firms?
A price taker is a firm that cannot set its own prices and must accept the market price.
What is the typical case regarding economic profit?
The typical case is that economic profit is zero, meaning firms earn a normal profit.
What is the potential reward for entrepreneurs in competitive markets?
The potential for economic profit serves as an inducement for entrepreneurs to take risks.
What is the impact of the profit motive on market adaptation?
The profit motive encourages firms to adapt to changing economic conditions and customer preferences.
What is the significance of the production decision for competitive firms?
Firms in perfect competition do not make pricing decisions; they accept the market price.
What is the primary goal of firms in production decisions?
To maximize profits, not revenues.
What is the formula for profit?
Profit equals total revenue minus total costs.
What does marginal cost (MC) represent?
The increase in total cost associated with a one-unit increase in production.
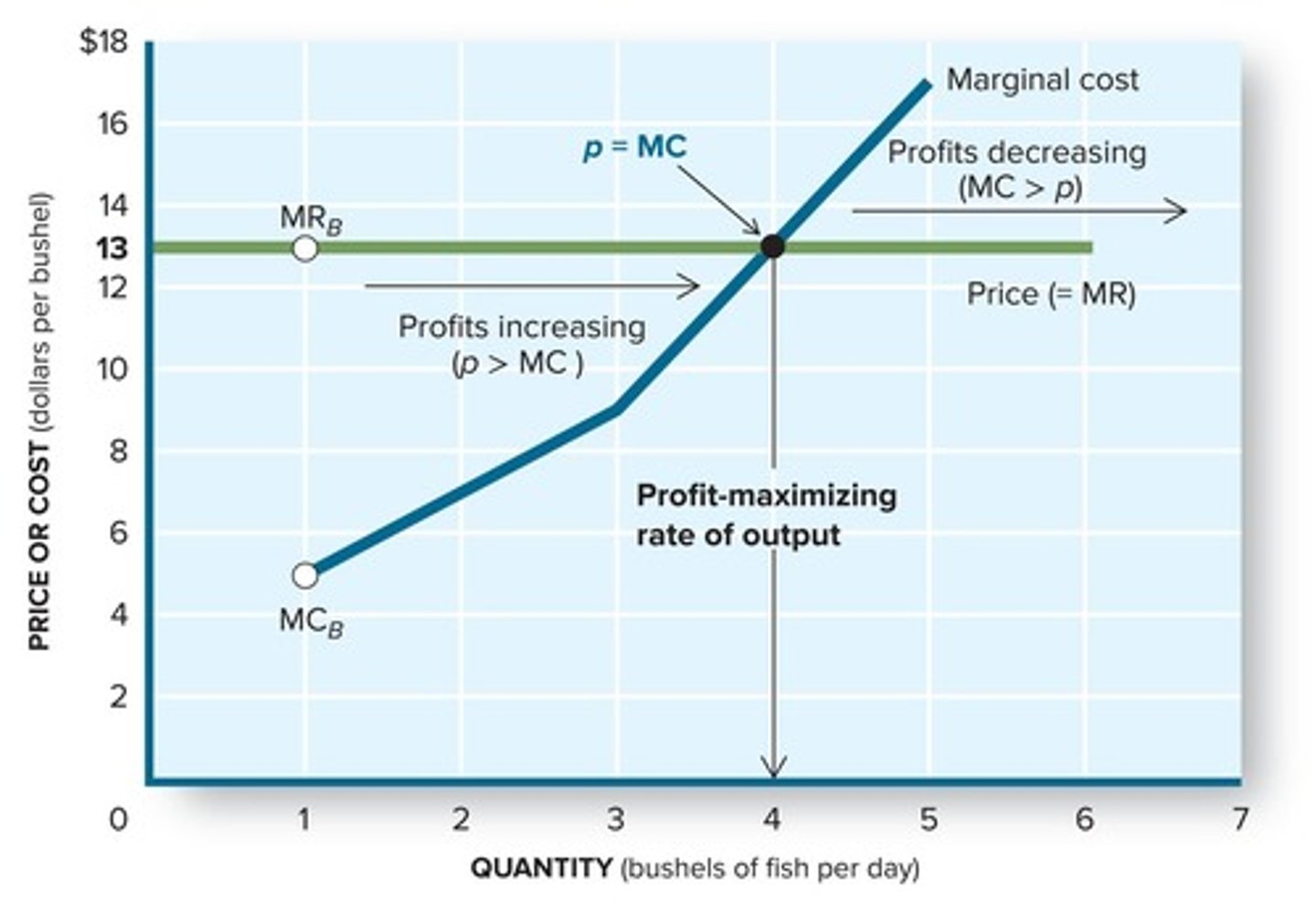
What is the Profit-Maximizing Rule?
Never produce a unit of output that yields less revenue than it costs.
How is marginal revenue (MR) defined in perfect competition?
Marginal revenue is equal to price (MR = P).
What should a firm do if the price (P) is greater than marginal cost (MC)?
Increase output to add to profit.
What does it mean when price (P) equals marginal cost (MC)?
The firm is producing at the output level that maximizes profits.
What happens if a firm cannot cover its fixed costs?
It may need to shut down if losses exceed fixed costs.
What is the shutdown point?
The output level where price equals minimum average variable cost (AVC).
What is the difference between short-run and long-run investment decisions?
Short-run decisions are about shutting down, while long-run decisions involve building, buying, or leasing plants and equipment.
What factors determine a firm's willingness to supply a product?
Price of factor inputs, technology, expectations, taxes, and subsidies.
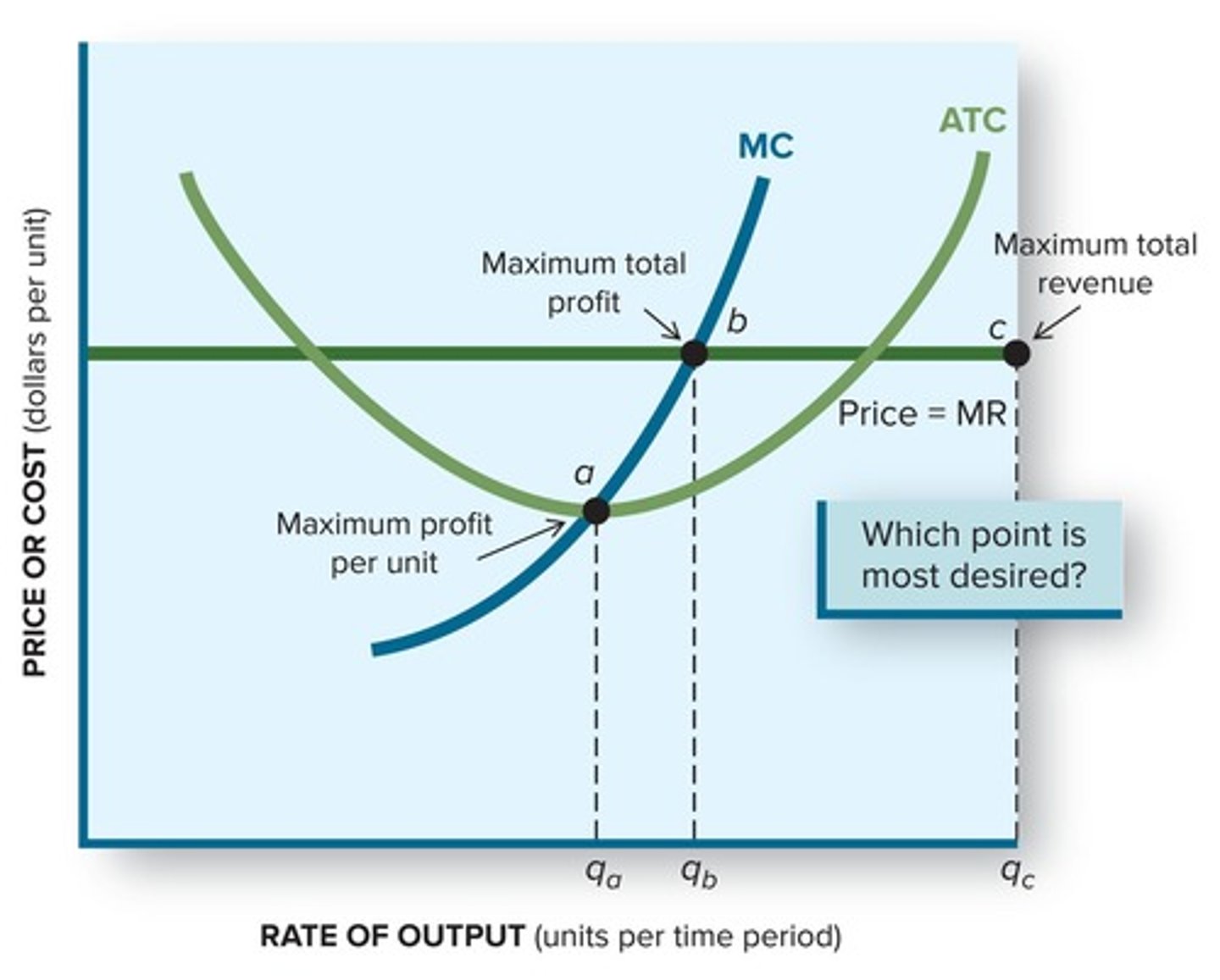
How does the supply curve relate to the profit maximization rule?
The firm sets output where price (P) equals marginal revenue (MR) equals marginal cost (MC).
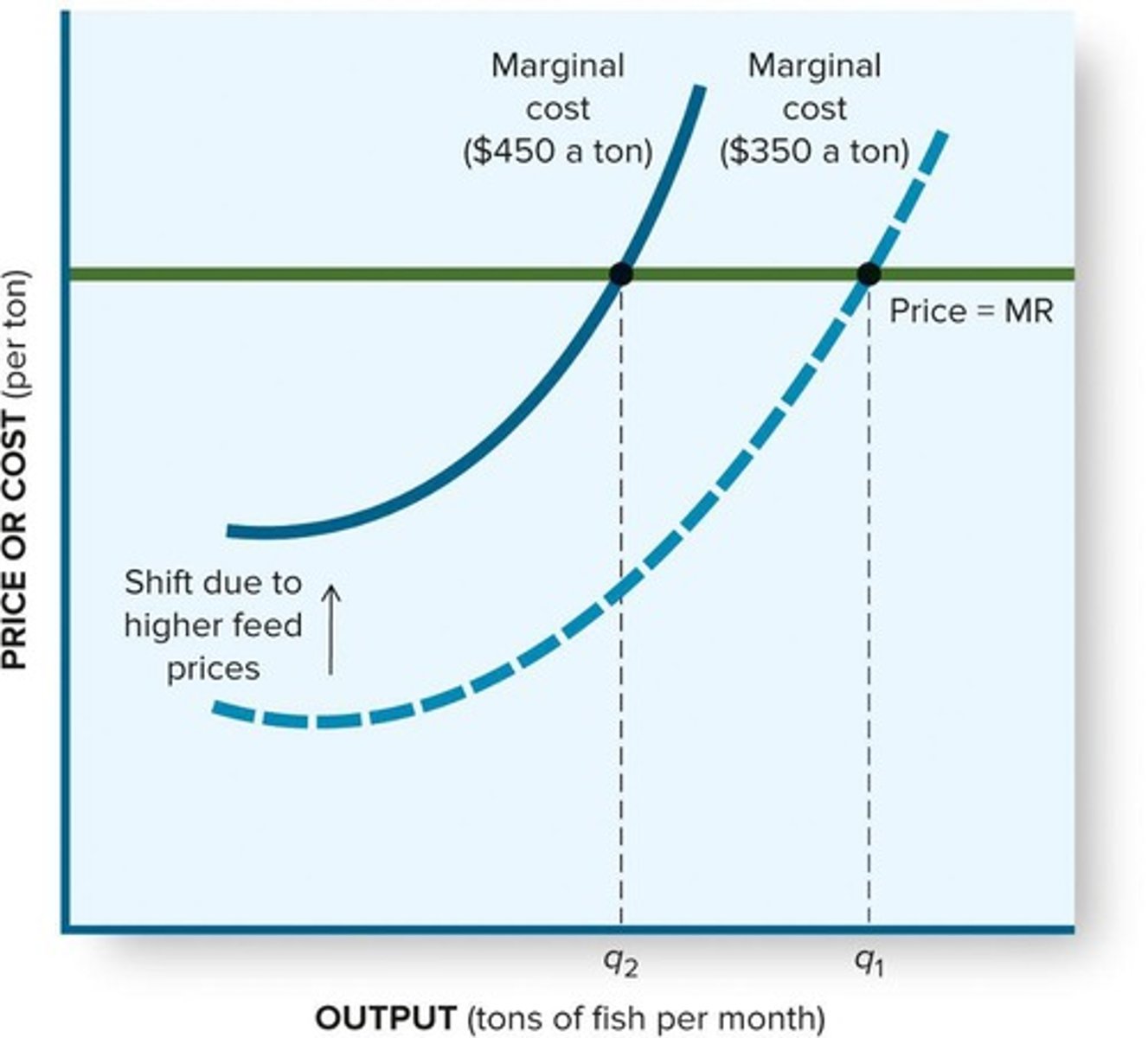
What happens to the supply curve if production costs decrease?
The supply curve shifts to the right.
What is the impact of an increase in input prices on the supply curve?
It shifts the marginal cost (MC) curve upward, causing the supply curve to shift left.
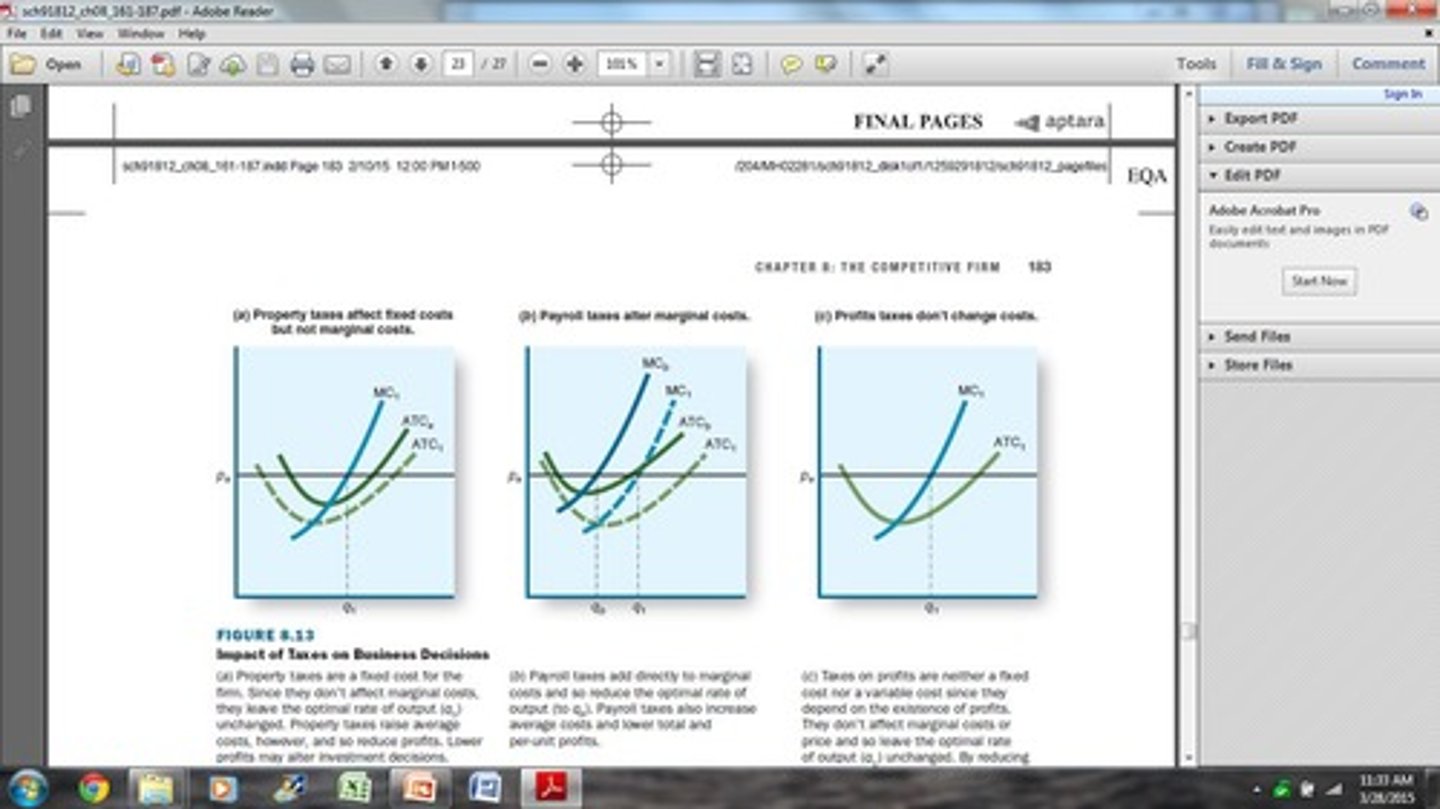
What are property taxes classified as?
A fixed cost that increases average total cost (ATC).
How do payroll taxes affect a firm's costs?
They increase both marginal cost (MC) and average total cost (ATC).
What is the effect of profit taxes on a business?
They reduce take-home profits and may decrease investments in new businesses.
What is the relationship between taxes and business decisions?
Taxes can affect profitability and investment decisions of firms.
What does it mean if a firm is producing at the quantity where MR=MC?
It indicates the firm is maximizing its profits.
What should a firm do if the price falls below average variable cost (AVC)?
Shut down, as it cannot cover labor and supplier costs.