Chapter 26 Amniotes intro + nonavian reptiles
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
general characteristics of amniotes
1. Amniotic Egg
2. Thicker, more keratinized and more waterproof skin
3. Better developed lungs with negative pressure ventilation
4. Stronger jaws and muscular, mobile tongue
5. High-pressure cardiovascular system
6. Water-conserving nitrogen excretion
7. Expanded brain & sensory organs
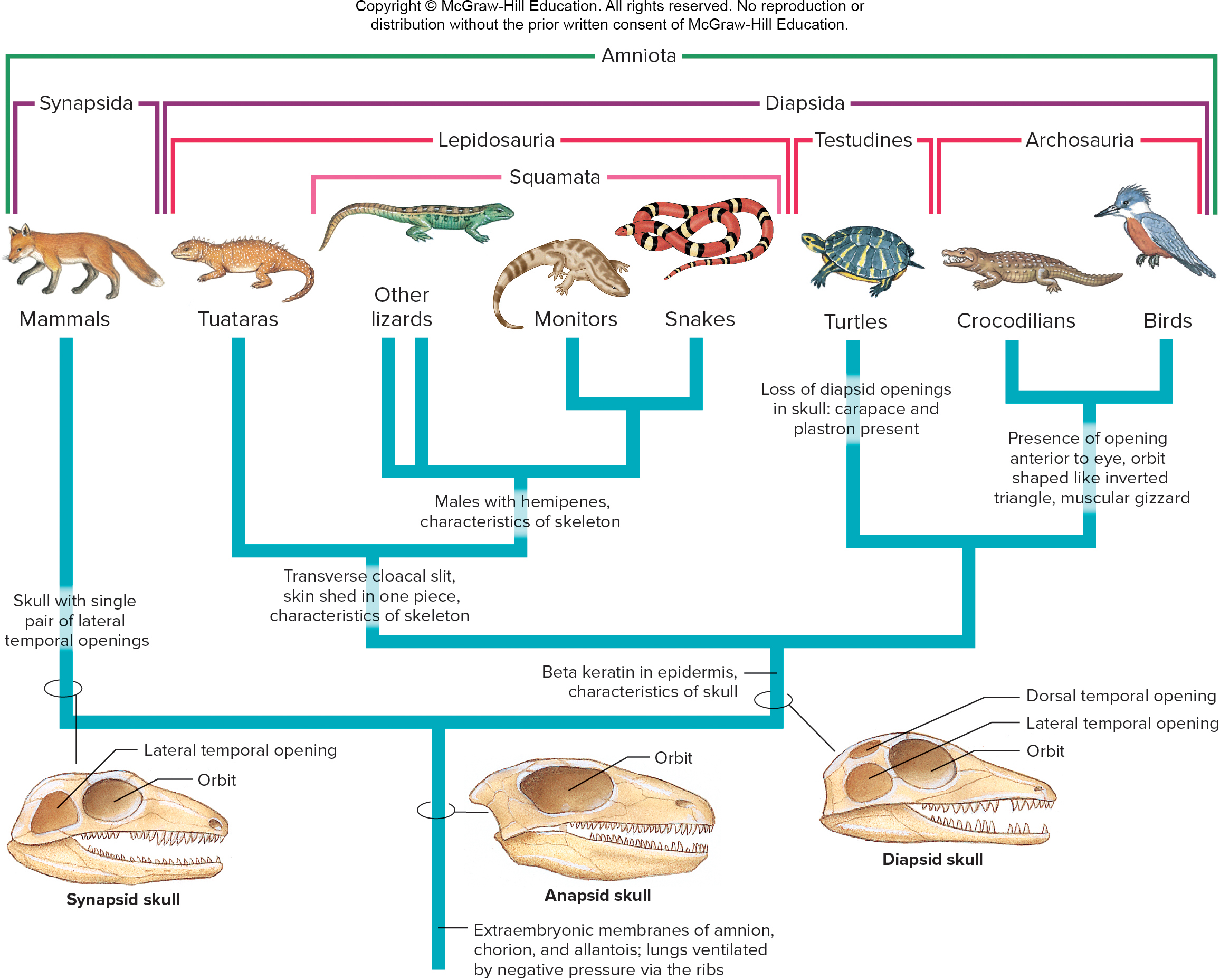
Anapsid skull
no holes (turtles+ the ‘og’ amnitoe)

Diapsid skull
2 openings (nonavian reptiles and birds)
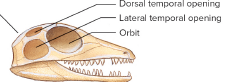
Synapsid skull
1 opening in skull (mammals)
Which order are birds most related to + clade, and what clades are they NOT as close?
Order crocodilia (archosaurian clade) , lepidosaurians (tuataras, lizards & snakes) and testudines (turtles)
amniotic egg
-no need for water to keep eggs wet
-allows for larger + faster growing embryos
-calcium in shell is dissolved + absorbed by embryo = skeleton!
-4 extra-embryonic membranes
amnion
‘amniotic fluid’
fluid-filled sac that embryo floats/develops in; provides protection/ cushioning
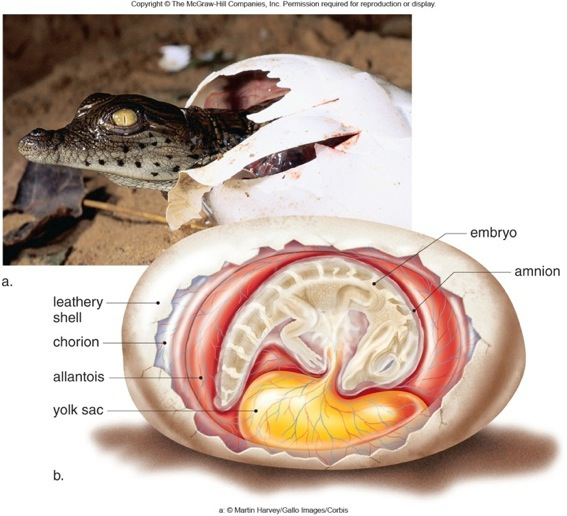
chorion
gas exchange that surrounds the entire egg
yolk sac
nutrient storage
aliantois
stores nitrogenous + metabolic waste and used for gas exchange
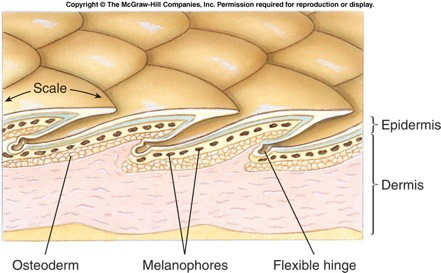
thicker skin
shift away from skin respiration
keratin: hair, feathers, scale, claws, nail, hooves etc. (physical protection)
Beta keratin in reptile skin makes it very hard
Lipids: metabolic protection (reduce water loss from skin)
crocodiles + lizards have an osteodermis under their scales
reptile scales come from epidermis, ectoderm, for fish they come from the dermis, mesoderm
contrast shedding (lizard and snake v crocodile and turtles)
snakes and lizards: shed ENTIRE skin
crocodile and turtles: progressively lose scales/scutes over time, bit by bit
negative pressure breathing
air is drawn in instead of buccal pumping by aspiration when the thoracic cavity + lungs expand
lung adaptations
greater surface area
negative pressure breathing
birds have parabronchi
mammals have alveoli
reptiles have faveoli
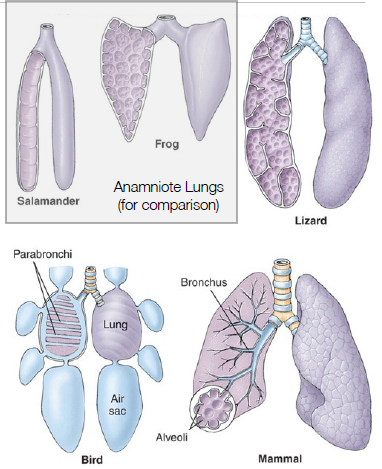
parabronchi
birds have… (veoli)
alveoli
mammals have… (veoli)
faveoli
reptiles have… (veoli)
skull adaptations
-diapsid skull = more complex jaw muscles
-muscles are larger + longer + better arranged for nipping, chewing, and crushing (compared to amphibians and fish for swallowing prey quickly)
tongue adaptations
muscular and mobile, moves food in the mouth to better chewing and swallowing
cardiovascular system adaptations
-better separation of pulmonary + systemic circuits
(complete in crocodiles, birds, and mammals)
high blood pressure = higher metabolic rates + activity levels

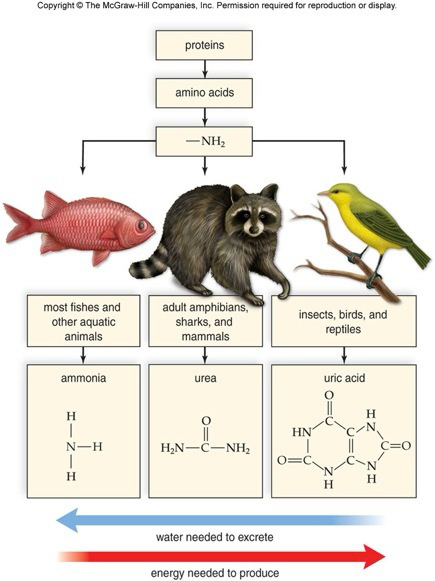
excretory system
mammals excrete urea, reptiles excrete uric acid
-mammals: water loss reduced by mammal kidney to concentrate urine
-reptiles can’t concentrate urine, so their bladder gets diluted urine→h2o + salt reabsorbed in bladder → N waste becomes semisolid mass (uric acid)→ salt glands remove excess salt in seabirds + reptiles
nervous system adaptations
large cerebrum + cerebellum =better use of sensory info + muscle control
visual systems are very precise in reptiles, and smell is developed in snakes, lizards and birds
special sensory capabilities
-Chemoreception: Jacobson’s organ in nonavian reptiles
-Thermoreception: detection of radiant energy (heat) by pit organs in pit vipers
-Electroreception in the platypus
-Magnetoreception in some birds & naked mole rats
-Echolocation in bats and toothed whales & dolphins (sonar)
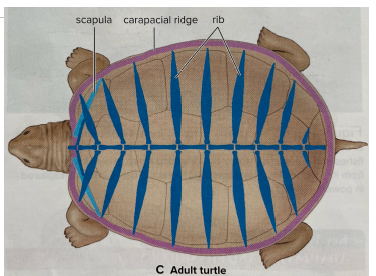
testudines
turtles + tortoises
shell is a bone covered by keratin scales (skutes) + fused, broad ribs
limbs + limb girdles are under ribs, unique in vertebrates
internal fertilization, oviparous, no maternal care, nest temp determines sex (low = males, high = female, opp for croc)
anapsid skull, not diapsid
carpace = top, plastron = bottom
squamata
lizard + snakes + monitors
95% of all non bird reptiles
kinetic skull: diapsid skulls with no bone in the back, so they have a skull with moveable joints (seize + manipulate prey, close jaw with force)
most oviparous, but some ovoviviparous
ectotherm
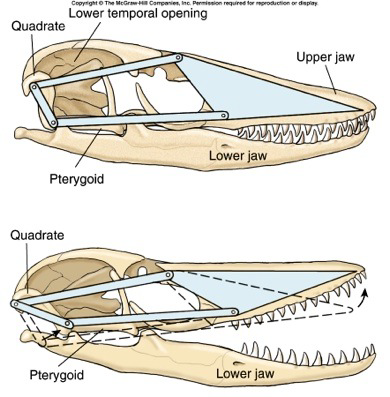
Suborder Sauria (2 guys)
Lizards
moveable eyelids, external ear
Amphisbaenian
no limbs, eyes + ears under skin

Suborder Serpentes
Snakes
Fake their own deaths

Snake feeding
nonvenomous: kill prey by constricting, or biting and swallowing alive
venomous: kill prey by injecting venom
neurotoxic: nervous system = stop breathing or become blind
hemolytis/hemotoxic: break down blood vessels and leaks into tissue spaces
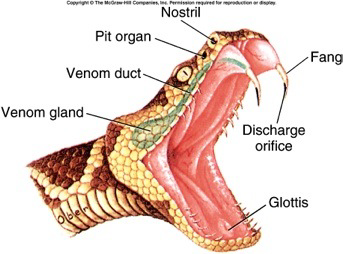
sphenodonta
tuatara
only 2 living species (og reptiles), live in new zealand and live in holes shared with petrels (bird)
very slow growing
skull is identical to diapsid skulls 200 mil years ago
median parietal eye: under skin, function not well known but maybe role in seasonal rhythm since it can notice change in light
Slowest rate of evolution in vertebrates

Crocodilia
alligator+ caiman + crocodile + gharial
reinforced skull + jaw muscles for powerful bite. teeth in sockets = thecodont dentition, typical in birds + mammals
complete secondary plate: (same like mammals) lets them breath when mouth is full
four chamber heart: like bird and mammals
oviparous but care for young for about 2+ years
3 types in crocodilia
Alligator + caiman(Smaller gator) : new world, broad snout
Crocodile: all around world, lower jaw visible
Gavial/gharial: india + nepal, slender snout, eat fish
