Heart Vocab and Anatomy
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Arteries
Blood vessels that transport blood AWAY from the heart; usually carry oxygenated blood except pulmonary arteries
Veins
Blood vessels that transport blood TO the heart; usually carry deoxygenated blood except pulmonary veins
Capillaries
Smallest blood vessels where gas, nutrient, and waste exchange occurs between blood and tissues
Pulmonary Circulation
Blood circulation from right side of heart → lungs → left side of heart; purpose is gas exchange
Systemic Circulation
Blood circulation from left side of heart → body tissues → right side of heart; delivers oxygen and nutrients
Mediastinum
Middle compartment of thoracic cavity where the heart is located
Pericardium
Fibrous sac surrounding the heart; consists of fibrous and serous layers
Fibrous Pericardium
Tough, dense outer layer of pericardium that anchors heart and prevents overexpansion
Serous Pericardium
Inner double-layered membrane of pericardium with parietal and visceral layers
Pericardial Cavity
Potential space between parietal and visceral layers of serous pericardium containing lubricating fluid
Epicardium
Outermost layer of heart wall; same as visceral layer of serous pericardium
Myocardium
Middle layer of heart wall composed of cardiac muscle; thickest layer that generates contractile force
Myocardium
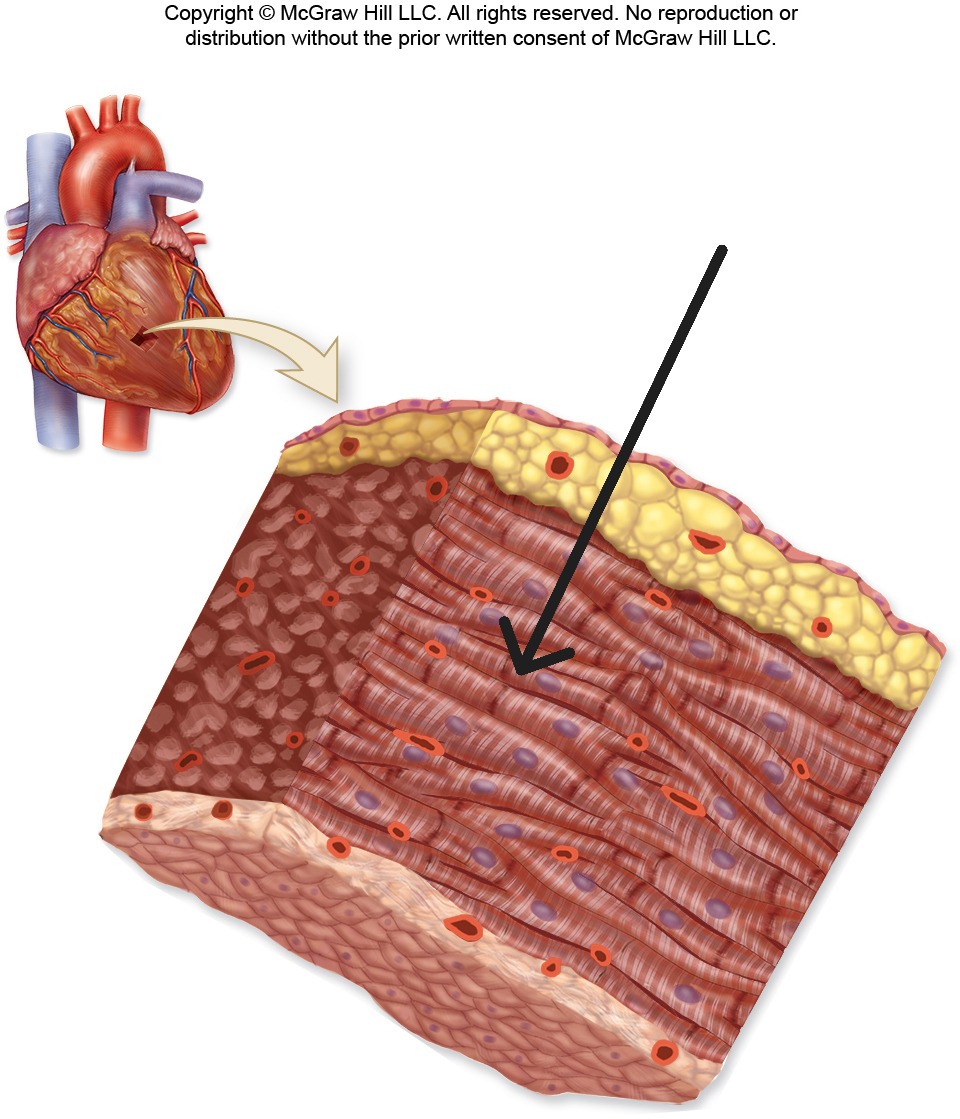
Endocardium
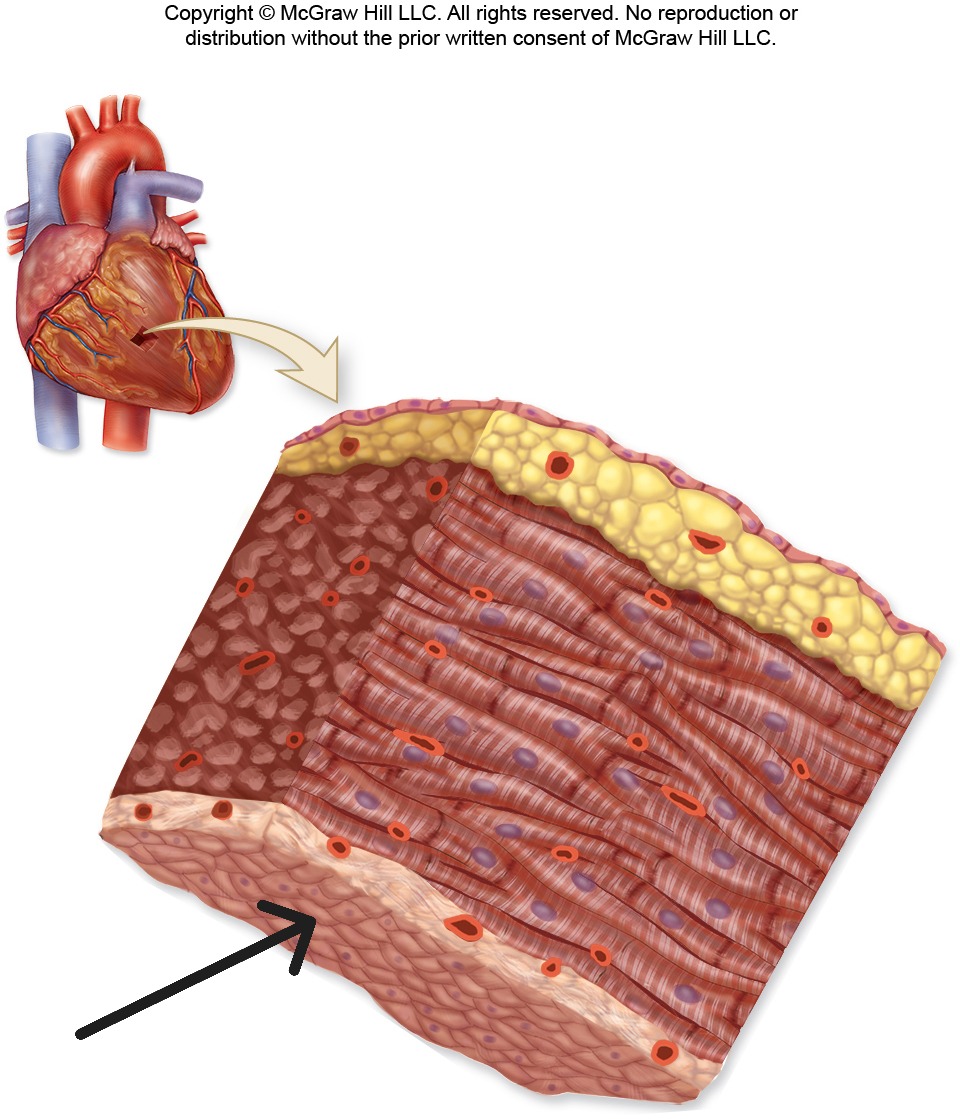
Innermost layer of heart wall that lines chambers and covers valve surfaces; smooth endothelial lining
Endocardium
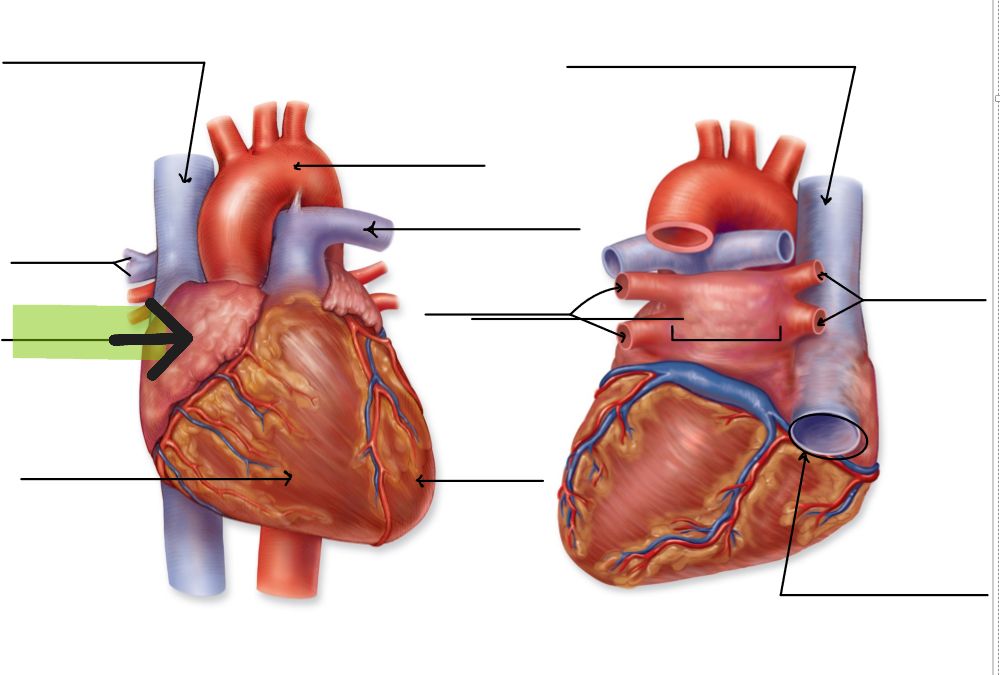
Right Atrium
Upper right chamber that receives deoxygenated blood from superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, and coronary sinus
Right Atrium
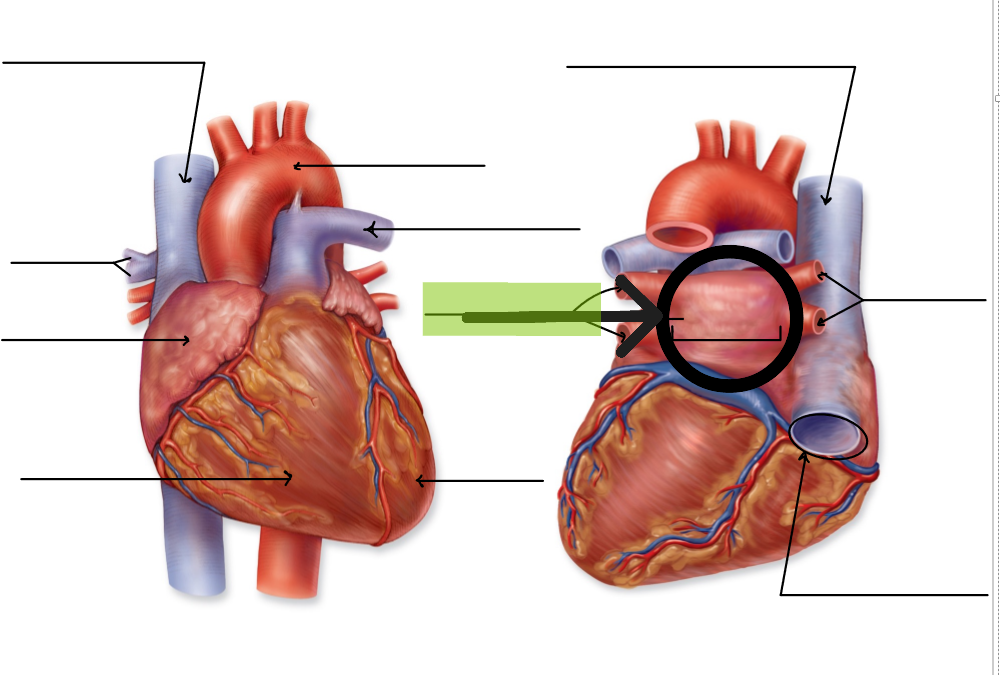
Left Atrium
Upper left chamber that receives oxygenated blood from four pulmonary veins
Left Atrium
Right Ventricle
Lower right chamber that pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs via pulmonary trunk
Right Ventricle
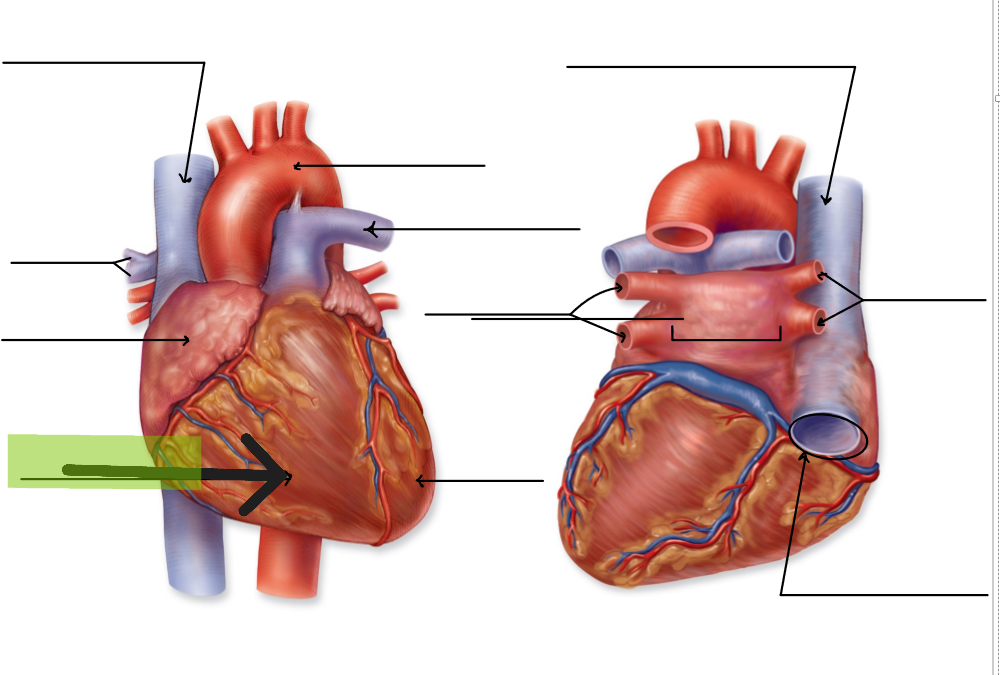
Left Ventricle
Lower left chamber that pumps oxygenated blood to body via aorta; has walls 3x thicker than right ventricle
Left Ventricle
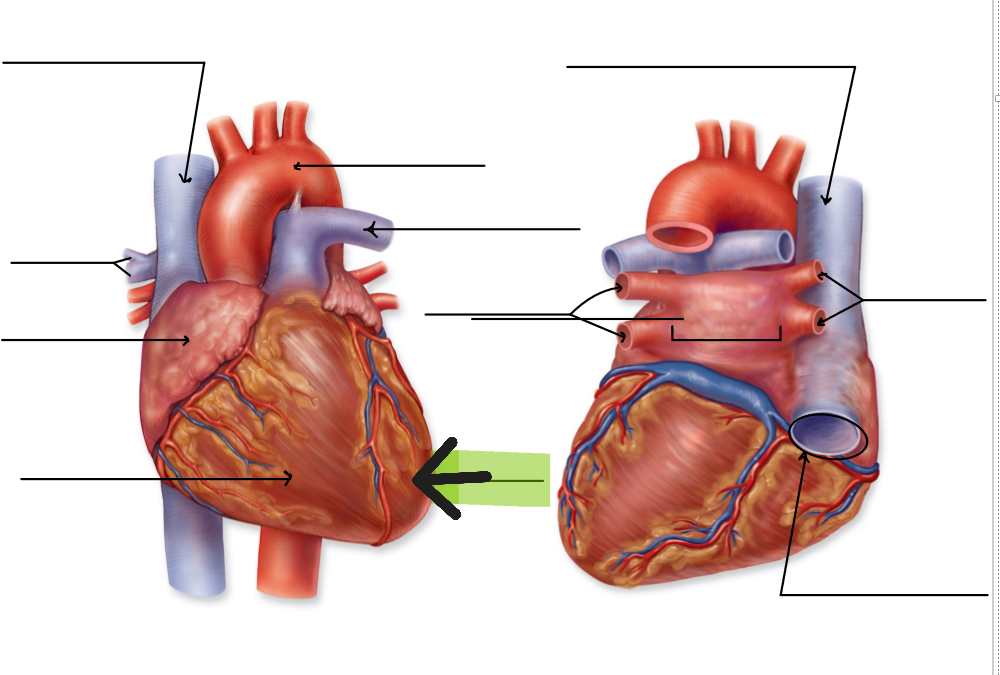
Interatrial Septum
Wall separating right and left atria
Interatrial Septum
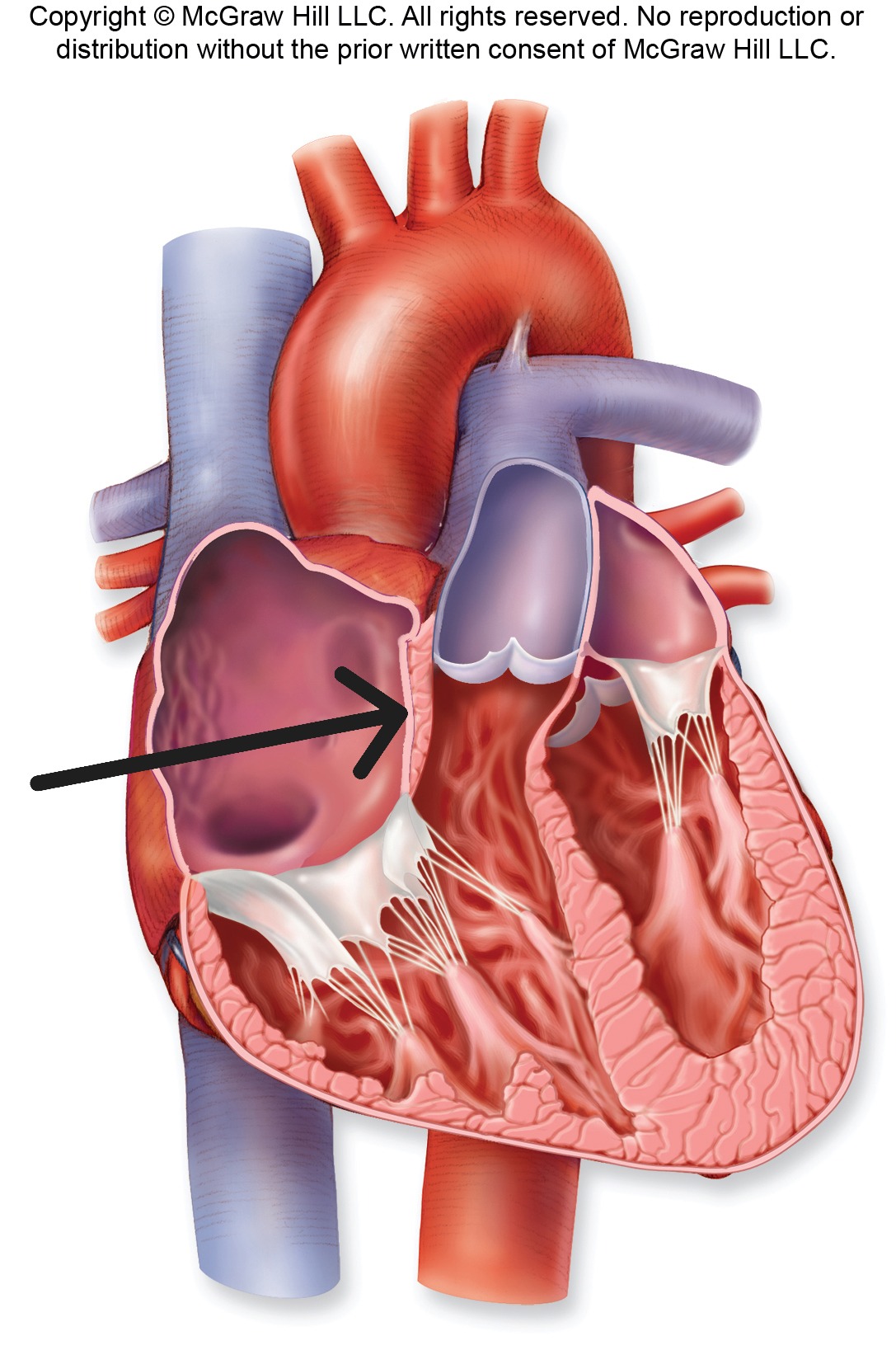
Interventricular Septum
Wall separating right and left ventricles
Interventricular Septum
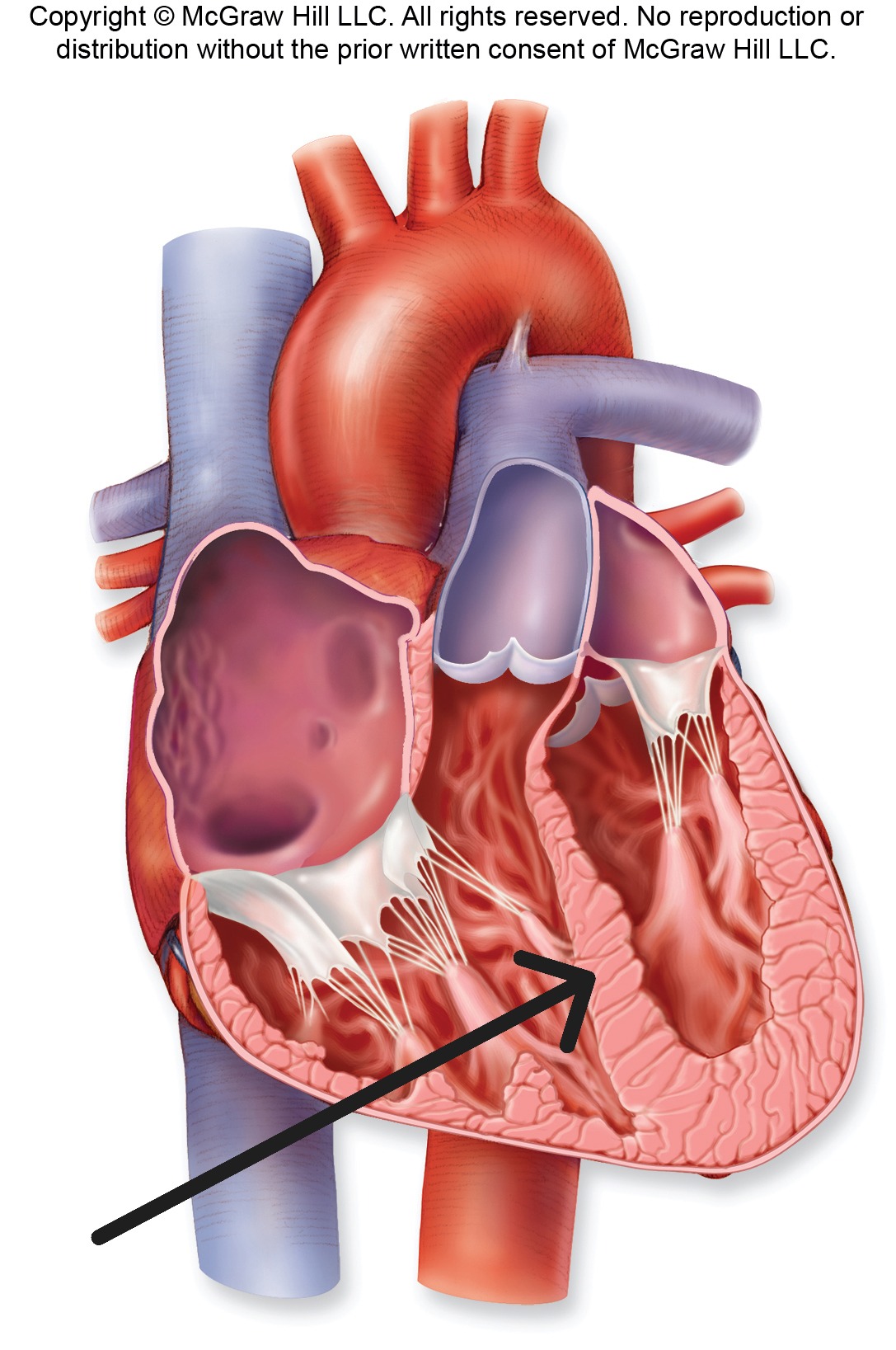
Fossa Ovalis
Oval depression in interatrial septum; remnant of fetal foramen ovale
Fossa Ovalis
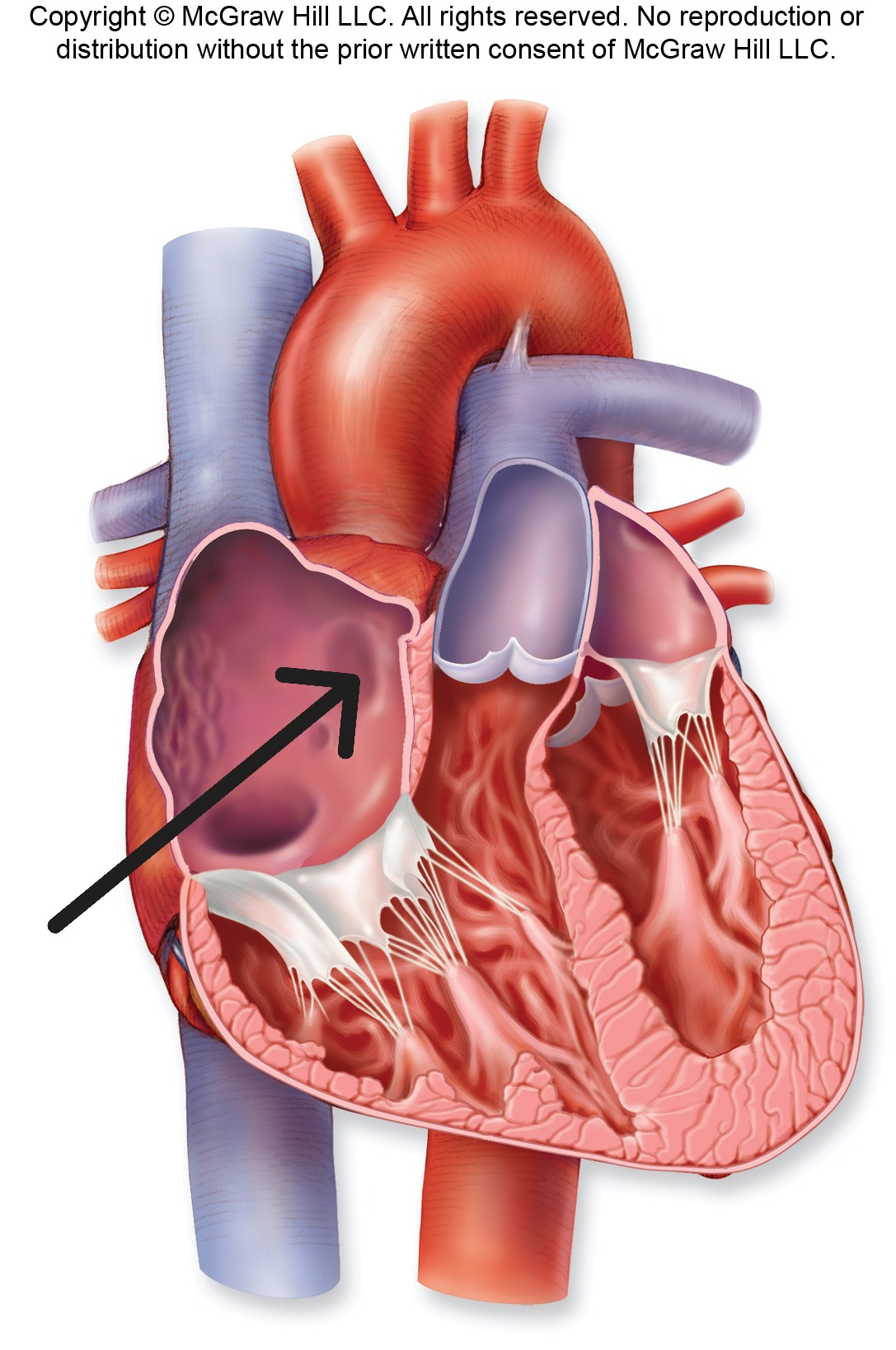
Pectinate Muscles
Muscular ridges found in anterior walls and auricles of atria
Trabeculae Carneae
Large, irregular muscular ridges on interior surfaces of ventricles
Trabeculae Carneae
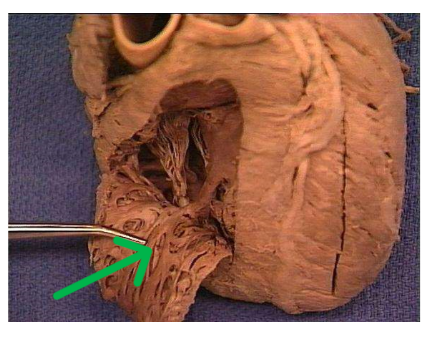
Right atrioventricular valve
Tricuspid Valve with three cusps; prevents backflow from right ventricle to right atrium
Right atrioventricular valve
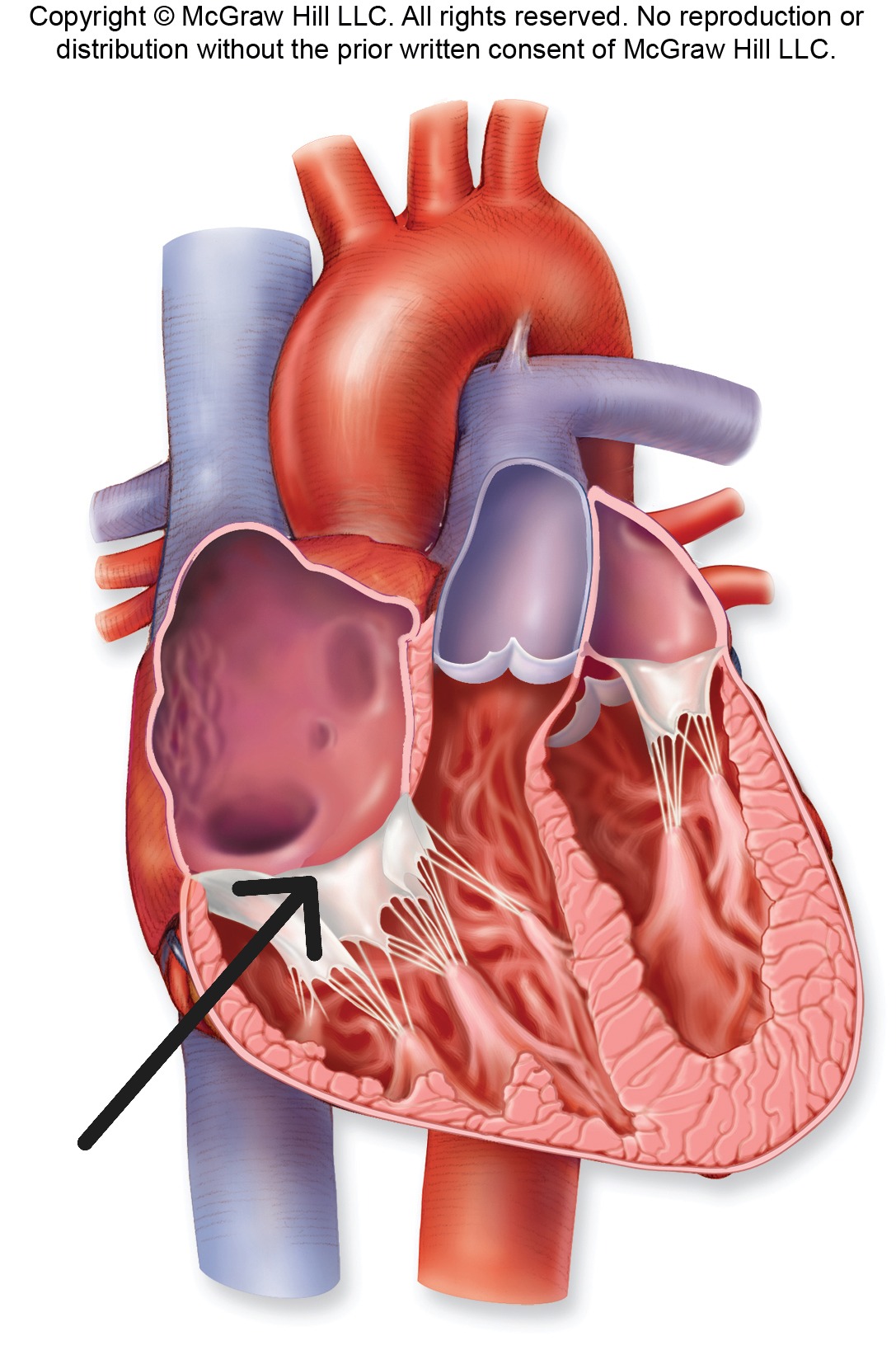
Left atrioventricular valve
Bicuspid Valve with two cusps; also called mitral valve; prevents backflow from left ventricle to left atrium
Left atrioventricular valve
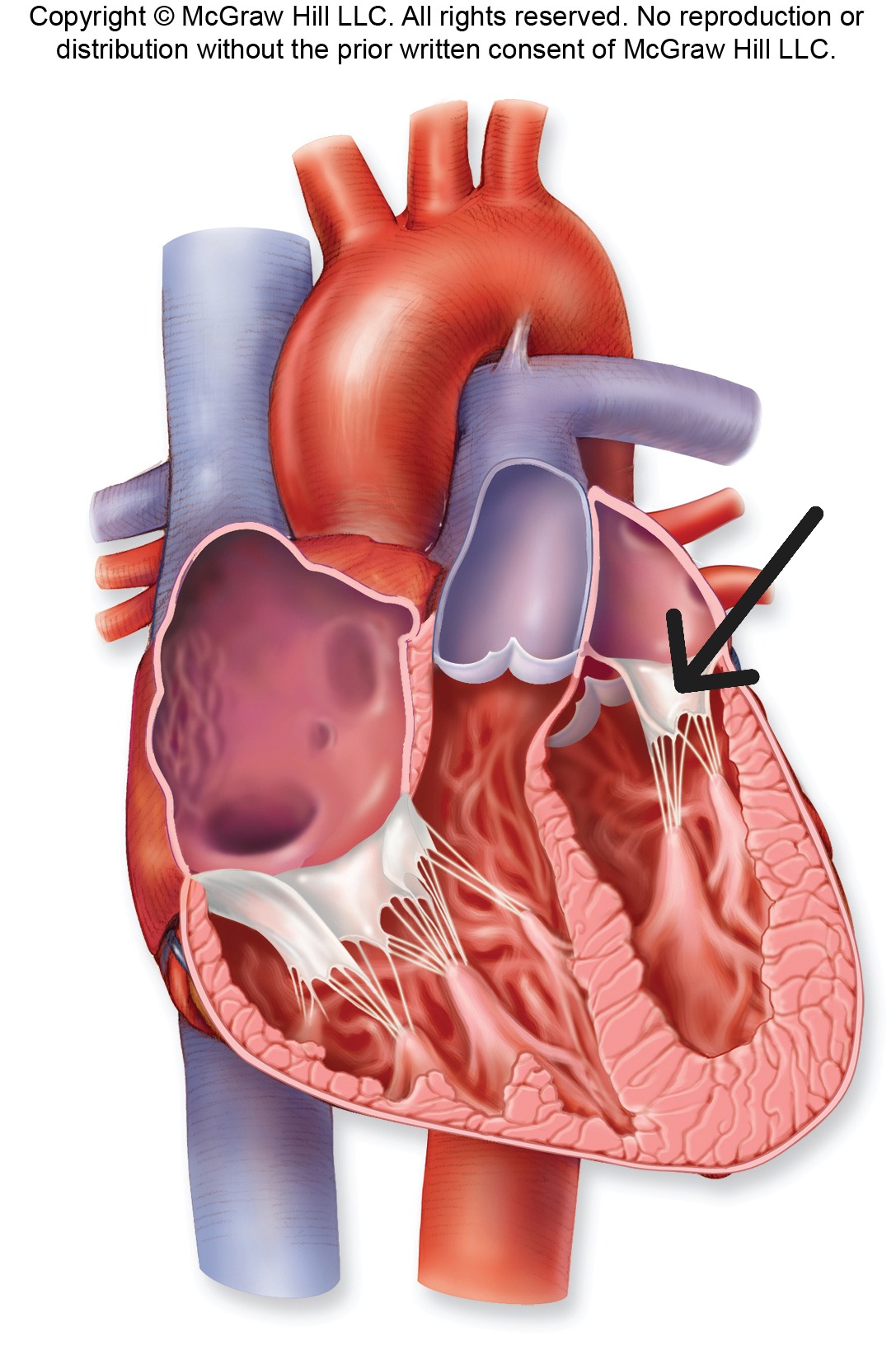
Pulmonary Semilunar Valve
Valve with three half-moon cusps between right ventricle and pulmonary trunk
Pulmonary Semilunar Valve
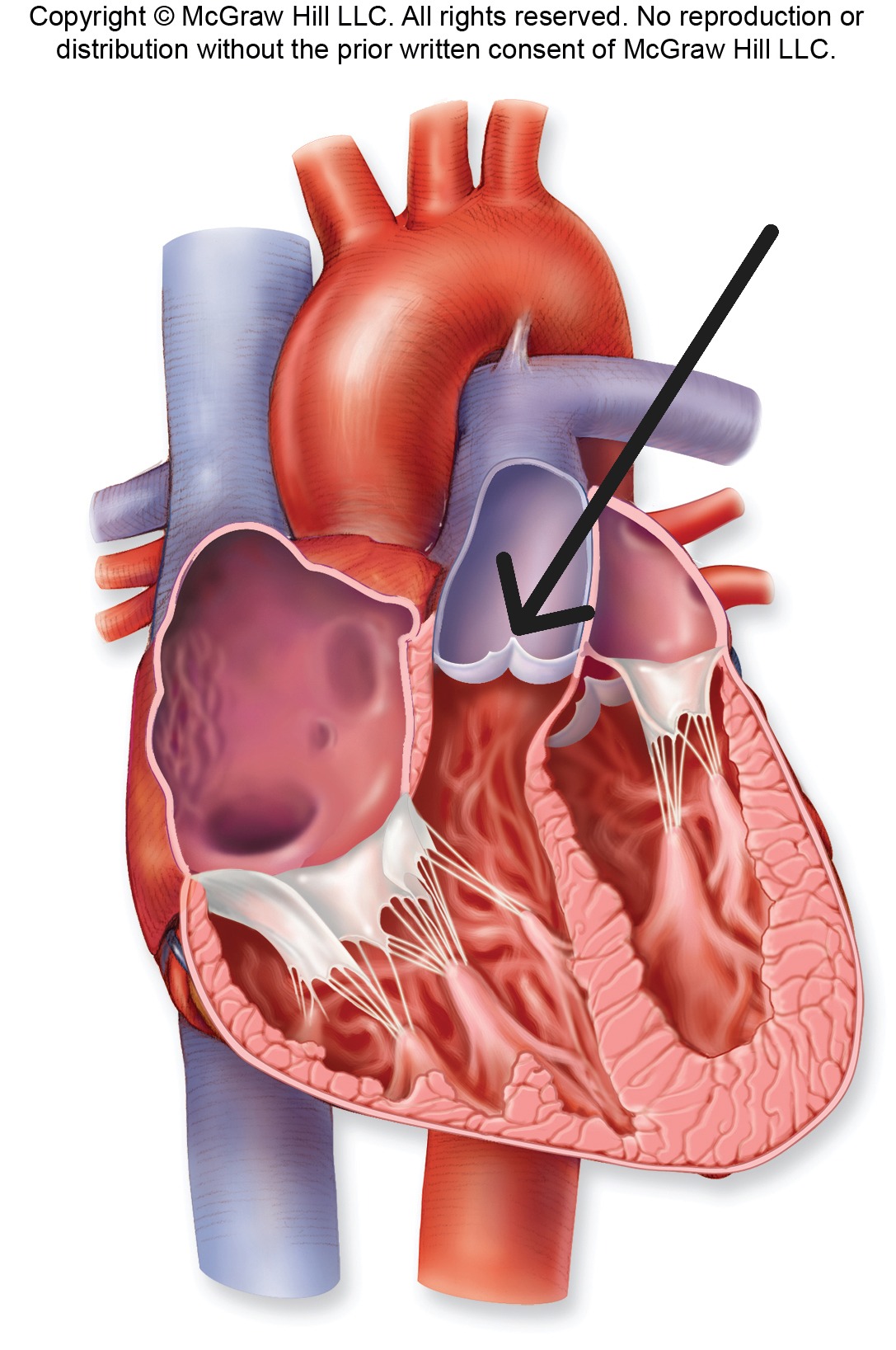
Aortic Semilunar Valve
Valve with three half-moon cusps between left ventricle and aorta
Aortic Semilunar Valve
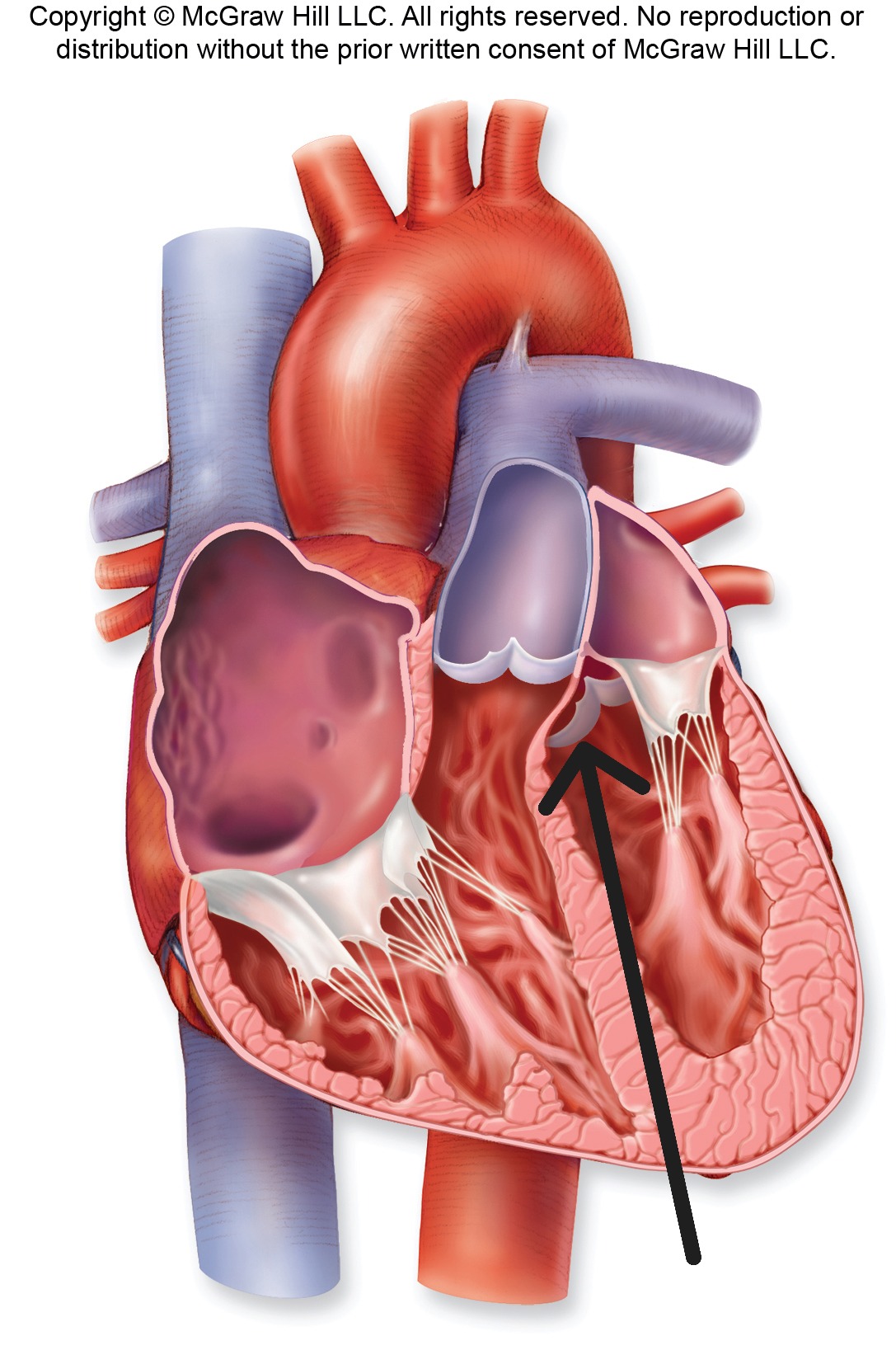
Chordae Tendineae
String-like connective tissue strands that attach AV valve cusps to papillary muscles
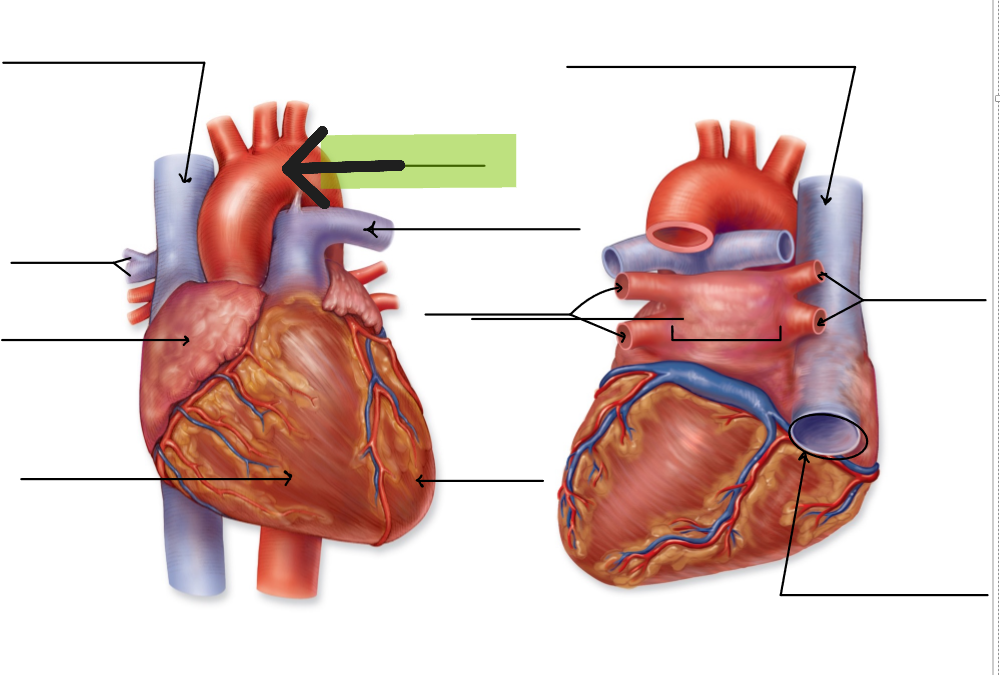
Superior Vena Cava
Large vein that returns deoxygenated blood from head, neck, upper limbs to right atrium
Superior Vena Cava
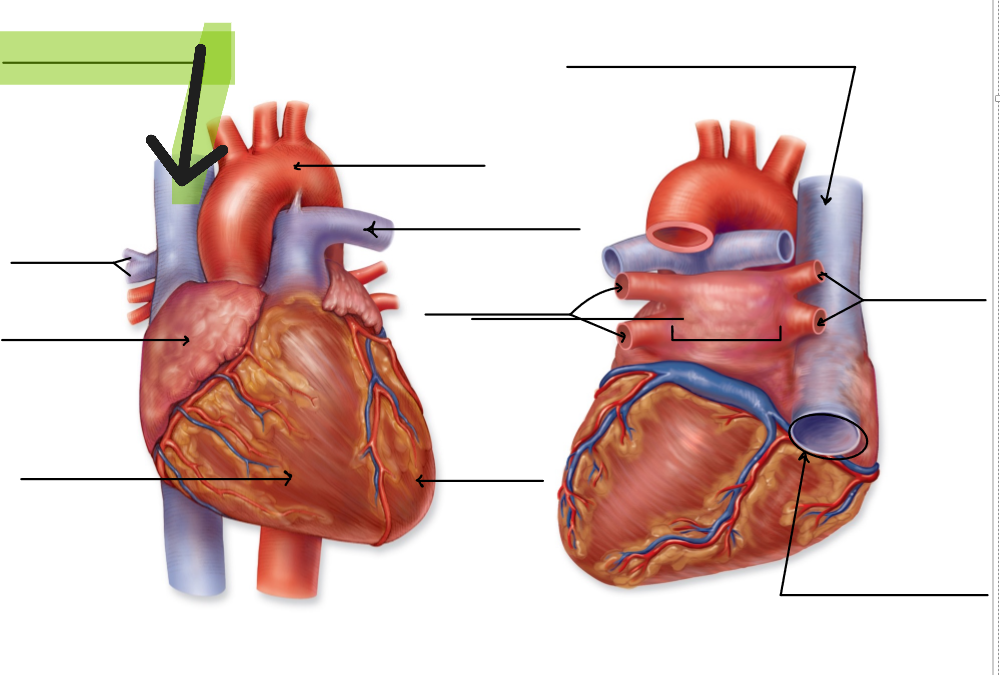
Inferior Vena Cava
Large vein that returns deoxygenated blood from lower limbs and trunk to right atrium
Inferior Vena Cava
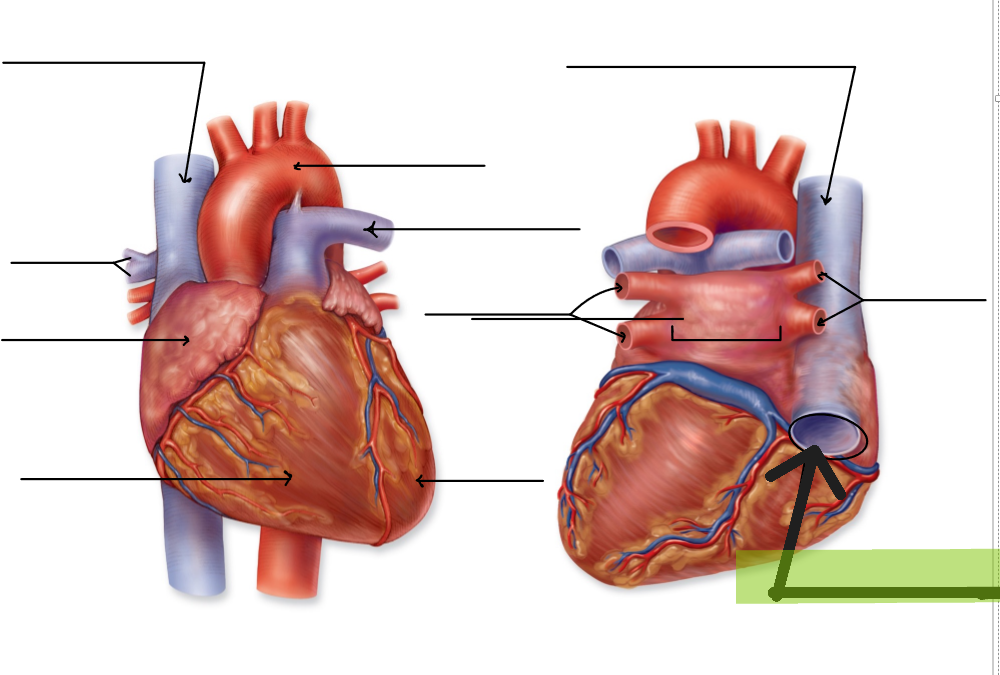
Pulmonary Trunk
Large artery that carries deoxygenated blood from right ventricle; splits into right and left pulmonary arteries
Aorta
Large artery that carries oxygenated blood from left ventricle to systemic circulation
Aortic arch
Cardiac Muscle
Specialized muscle tissue of myocardium; short, branched cells with intercalated discs
Intercalated Discs
Specialized cell junctions in cardiac muscle containing desmosomes and gap junctions
Gap Junctions
Protein channels in intercalated discs that allow rapid electrical impulse transmission between cardiac cells
Desmosomes
Strong cell adhesions in intercalated discs that prevent cardiac muscle cells from separating during contraction
Autorhythmicity
Ability of heart to generate its own electrical impulses without external stimulation
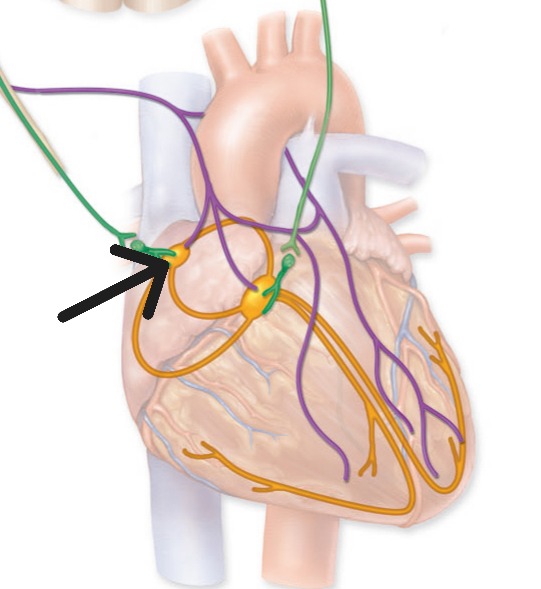
Sinoatrial Node
Primary pacemaker of heart located in right atrial wall; initiates heartbeat at 70-80 beats per minute
Sinoatrial Node
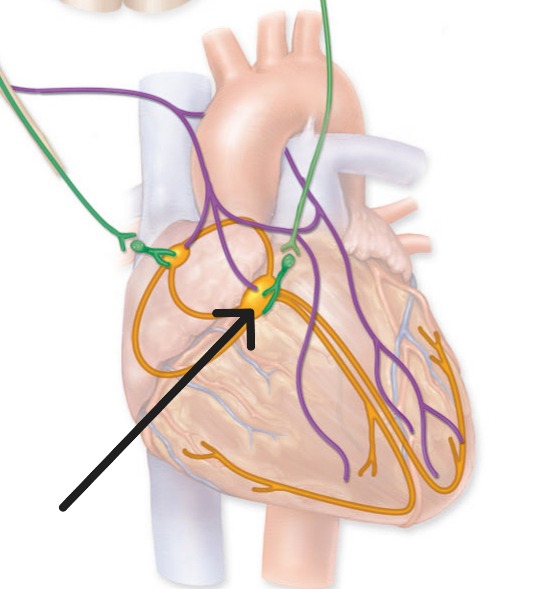
Atrioventricular Node
Secondary pacemaker in right atrial floor that delays electrical impulse for 100 milliseconds
Atrioventricular Node
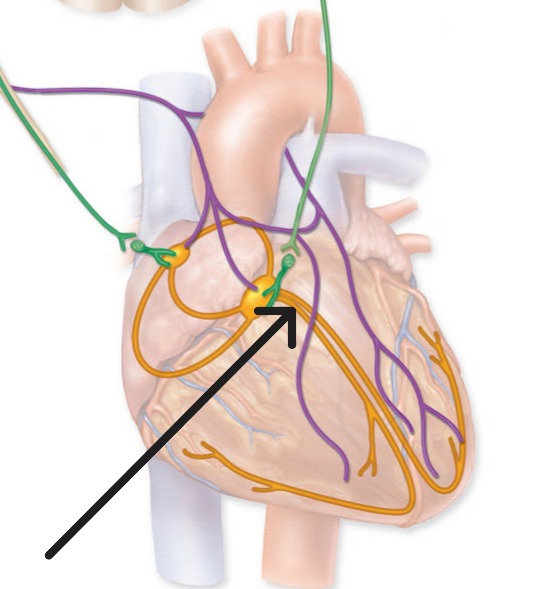
Atrioventricular Bundle
Bundle of His; conducts electrical impulses from AV node through fibrous skeleton to bundle branches
Atrioventricular Bundle
Bundle Branches
Right and left pathways in interventricular septum that conduct electrical impulses to Purkinje fibers
Right bundle branch
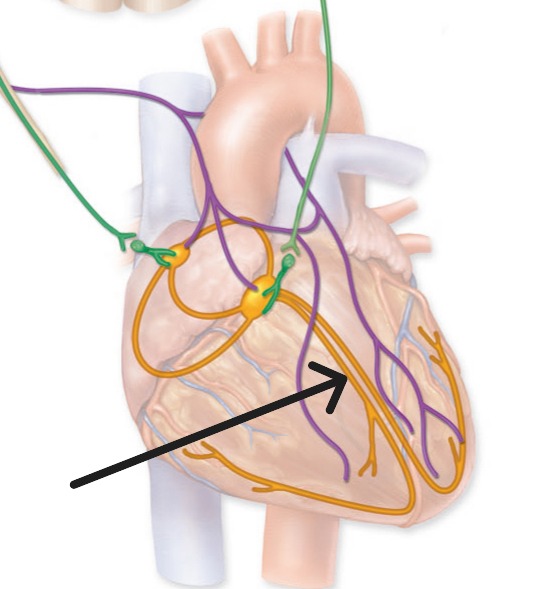
Left bundle branch
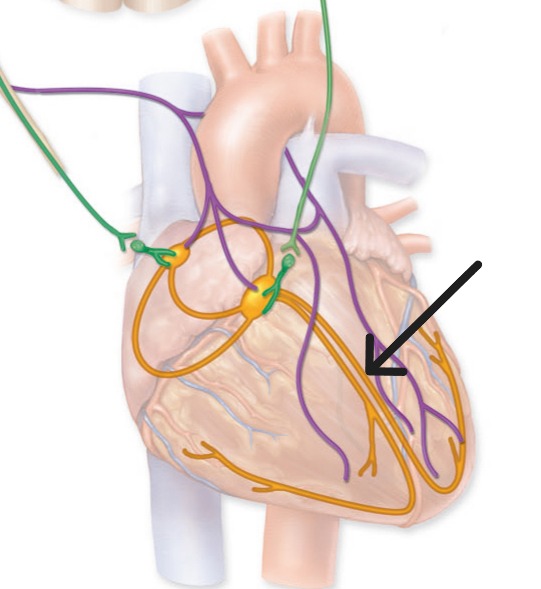
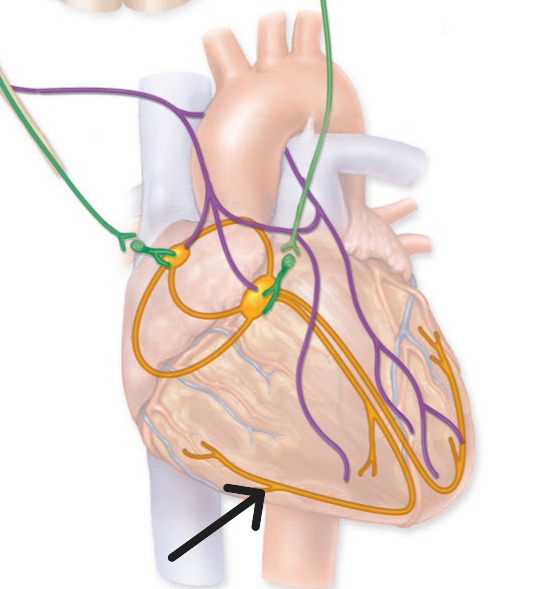
Purkinje Fibers
Subendocardial branches that rapidly distribute electrical impulses throughout ventricular myocardium
Purkinje Fibers
Systole
Contraction phase of cardiac cycle when chamber pressure increases and blood is ejected
Diastole
Relaxation phase of cardiac cycle when chamber fills with blood
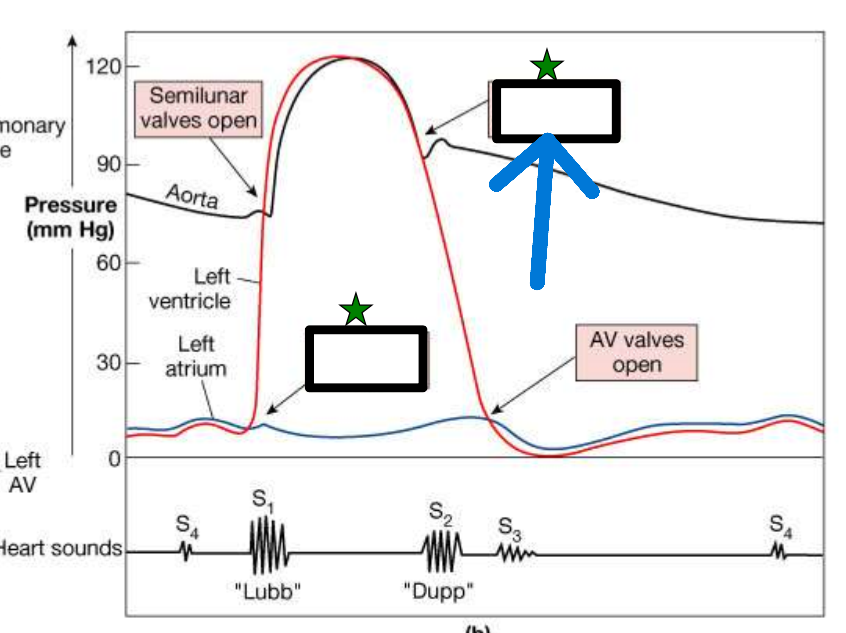
"Lubb" sound
caused by closure of AV valves at start of ventricular systole
AV Valves close
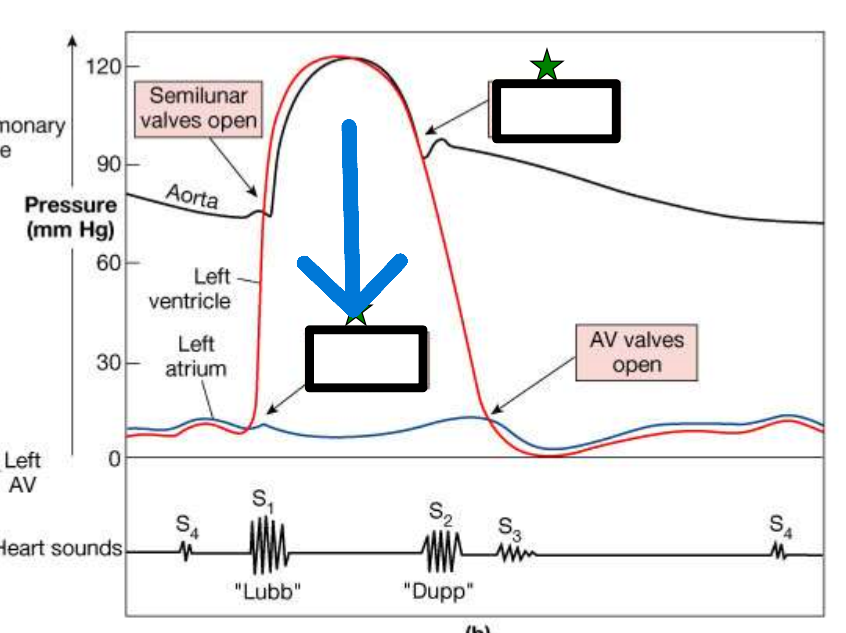
"Dupp" sound
caused by closure of semilunar valves at start of ventricular diastole
Semilunar Valves close
Myocardial Infarction
Heart attack; death of heart muscle due to blocked coronary artery and lack of oxygen
Fibrous Skeleton
Dense connective tissue framework between atria and ventricles that anchors valves and provides electrical insulation