Bio exam 3 - Exceptions to Mendelian Genetics and Pedigrees
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Incomplete dominance
“In between” phenotype; the phenotype of heterozygotes is between both of the homozygote phenotypes; ex red snapdragon x white snapdragon = pink snapdragon
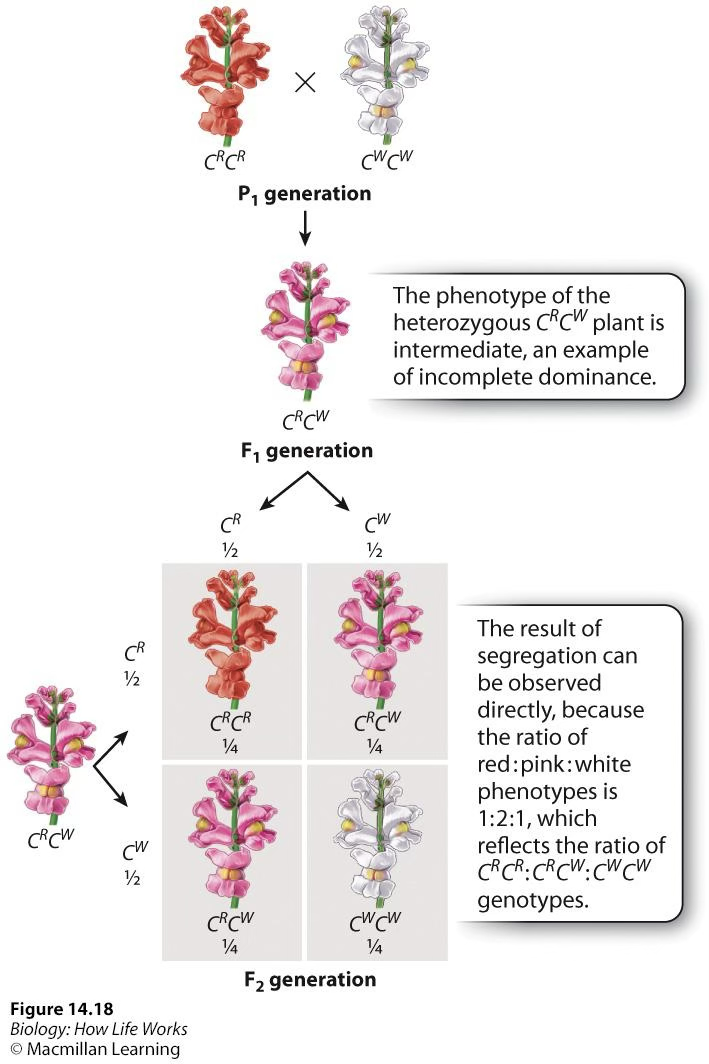
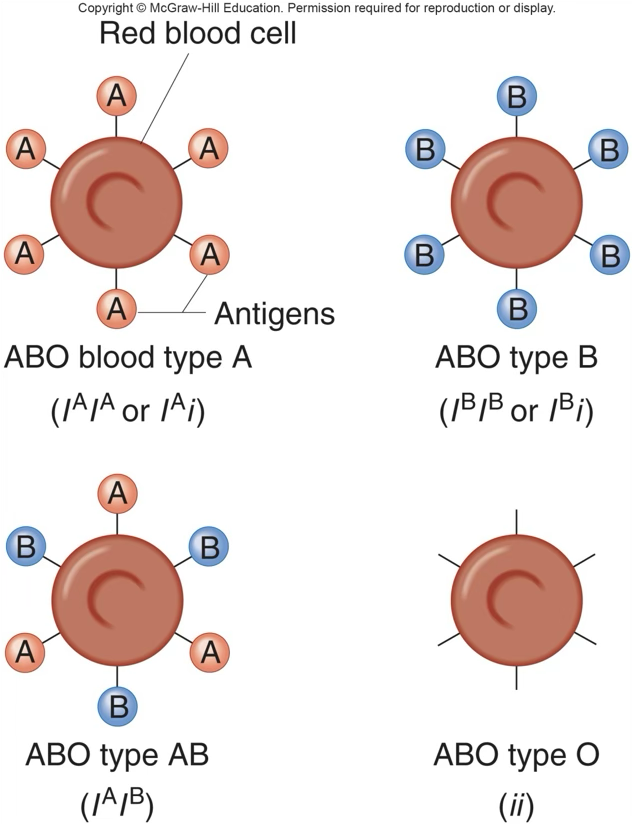
Codominance
2 different alleles can be expressed at the same time; each allele produces a distinct phenotype that can be detected in heterozygous individuals; ex red blood cells - IA/IB = type A or B, II = type O, but AB = type AB and both the A antigen and B antigen are expressed
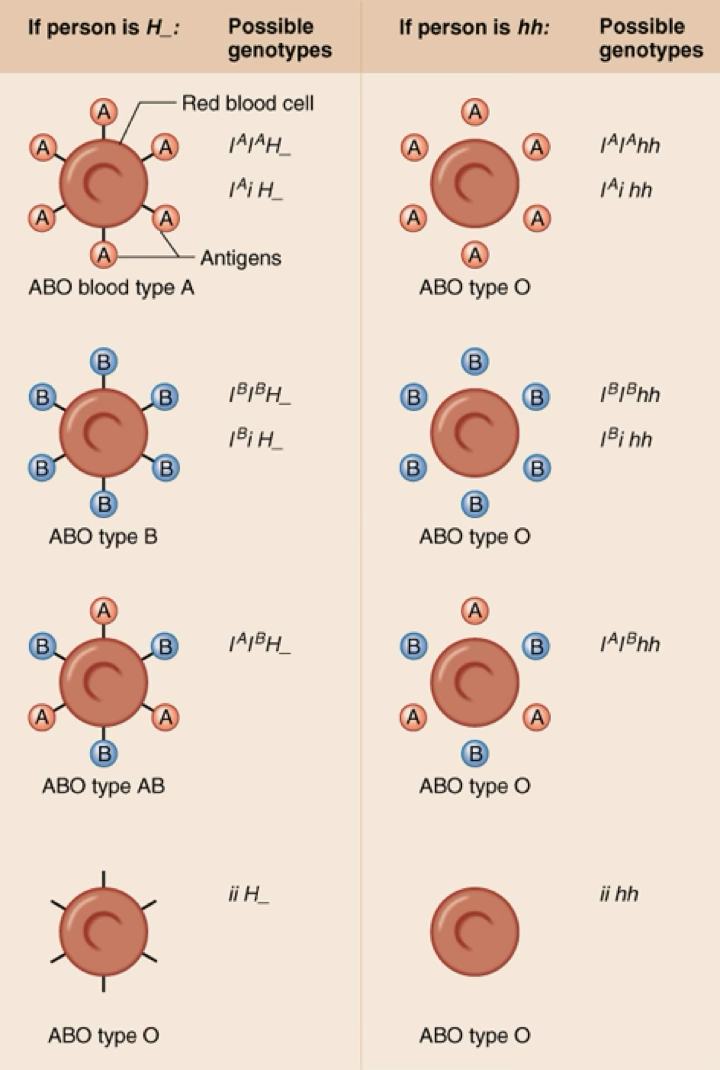
Epistasis
When one gene changes the phenotype of another gene; phenomenon where one gene affects the expression of a second gene; ex red blood cells - protein made by H gene attaches antigens to blood cell (line), so if the blood cell is hh/homozygous recessive, it will be type O even if it has the A or B genotype bc the antigen cannot be attached
Incomplete penetrance
When, of individuals with a specific genotype, a proportion show the phenotype and a proportion do not show the phenotype; penetrance refers to the all or none expression of a genotype; Ex polydactyly genotype is autosomal dominant (DD or Dd) and 80% penetrant, so 80% of people with the gene actually have extra fingers/toes, while 20% don’t even though they have the genotype
Variable expressivity
When all individuals with a specific genotype express the phenotype, but to varying degrees/extents; ex some people with polydactyly have 1 extra toe and some have 5
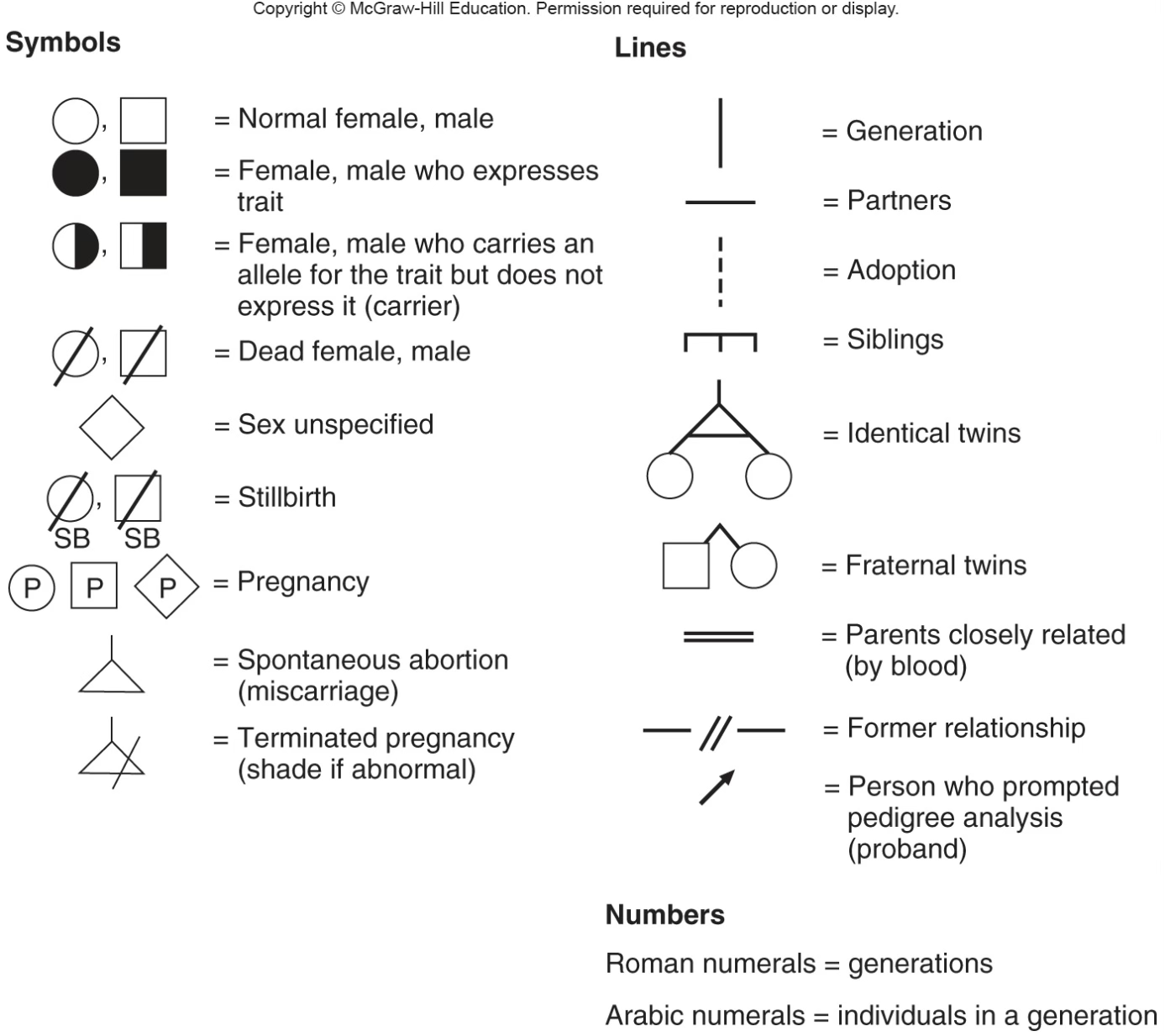
Pedigrees
Symbolic representations of family relationships and the transmission of inherited traits; helps families identify the risk of transmitting an inherited illness
Pedigrees - what do circles and squares mean
Circle - female, square - male
Pedigrees - what do filled in, half filled in, and not filled in mean
Filled in - expresses the trait, half filled in - carrier, not filled in - normal
Pedigrees - what do vertical line, horizontal line, and double horizontal line mean
Vertical line - generation, horizontal line - partners/married, double horizontal line - parents are related by blood
Pedigrees - what do roman numerals and arabic numerals mean
Roman numerals - generations, arabic numerals - individuals in a generation
Autosomal recessive trait
Can skip one or more generations, affected child may have no affected parents; ex albinism
Autosomal dominant trait
Does not skip generations, affected child must have an affected parent; ex polydactyly