Middle Ear Physiology
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
acoustic impedance
the opposition of sound flow through an acoustic system
Acoustic admittance
the ease of sound flow through an acoustic system
A system’s resonant frequency
when mass reactance = stiffness reactance
The volume of air in the middle ear is not easily compressed and is governed by:
stiffness
Massive objects
Impede high frequency sounds
Low-pass
Massive objects, impede high-frequency sounds
Stiff objects
Impede low frequency sounds
High-pass
Stiff objects, impede low frequency sounds
Stiffness governed system
Middle ear
Middle ear resonant frequency
~1200 Hz
Stiffness reactance (negative reactance)
Dominates at frequencies below 800 Hz
Mass reactance (positive reactance)
Dominates at frequencies above 5000 Hz
Pinna resonance
5000 Hz
Ear canal resonance
3000-4000 Hz
Middle ear resonance
Increase gain at 1200 Hz, decrease gain below 800 Hz
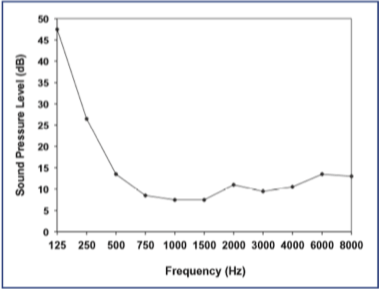
Minimum audibility curve, lowest can hear in db SPL. According to this we can hear better in mid frequencies than high and low. Everyone would have a hearing loss based on SPL.
Audiometric zero
the lowest detectable sound intensity for a given frequency in a person with normal hearing
Tympanometry
measures changes in stiffness at the TM and middle ear
Tymp probe tone for adults
226 Hz at 80 dB SPL
Types of tympanograms
A, As, Ad, B, C
How does wide band tymp differ from standard?
WBT uses clicks or chirps from 220 Hz up to 1000 Hz, WBT measures absorbance, 3D model of pressure, absorbance, and frequency
WBT sensitive to
Ear canal or ME maturation
changes in middle ear status caused by different disorders
Acoustic impedance is greater in ME or IE and why
Greater in IE because it is filled with fluid
How much energy is lost when sound travels from air to water (sound from ME to IE)?
35 dB
Energy transduction of ear
Acoustic, mechanical, hydraulic
ME mechanisms for impedance matching
Buckling effect, pressure transformer, ossicular lever
Buckling effect
TM curves to help amplify sound pressure, increasing force.
Increases gain by 6dB
Surface area of TM
55mm2
Surface area of stapes footplate
3.2mm2
Size ratio of TM vs stapes footplate
17:1
Explain pressure transformer
Increase in sound pressure to transfer energy from air filled ME to fluid filled IE
Pressure from the TM is moved through the ossicles and into the stapes footplate in the round window. Pressure is amplified due to the TM having a greater surface area than the stapes footplate
Ossicular lever
Malleus and incus form a lever and provide further increase in pressure at the oval window
Amount of gain from ossicular lever
2 dB
Amount of gain from Areal transformation
25 dB
How to force Eustachian tube open
Valsalva maneuver
Acoustic reflex
Muscle/tendon contraction in response to intense stimuli
Contraction of muscle/tendon causes ossicular fixation, increasing impedance of the middle
ART increase or decrease stiffness of ME
Increase. Protects against low frequency sounds
How much protection does ART provide
15 dB
air conduction
sound waves travel from outer ear, middle ear, to the inner ear
bone conduction
vibrations go through the skull, bypass the outer ear and middle ear, directly stimulate the inner ear
How would bone conduction play a role in hearing or in audio testing?
Figure out the type of hearing loss
Occlusion effect
Sensation of increased loudness of self generated sound, mostly in the low frequencies.
Why are low frequency sounds louder with occlusion effect?
When plugging your ears, you lose the resonance frequency of the ear, which is high frequency.
Why is occlusion effect a concern to audiologists?
Masking for bone conduction
Occlusion effect for inserts
15 dB @ 500
10 dB @ 1k
0 dB @ 2k