Econ Stuff
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Aggregate Expenditures/Spending
The total amount of spending in an economy, including consumer spending, investment spending, government spending, and net exports.
Aggregate Output
The total quantity of goods and services produced in an economy over a specific period.
Aggregate Price Level
A measure of the overall level of prices in the economy, typically represented by a price index like the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
Base Year
A reference year used in economic calculations, especially in index numbers like GDP or inflation.
Bond
A financial instrument representing a loan made by an investor to a borrower, where the borrower agrees to pay back the loan with interest.
Chain-linking
A method used to calculate real GDP that accounts for changes in the price level over time by using a continuously shifting base year.
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
A measure that examines the average price level of a basket of consumer goods and services over time, used to estimate inflation.
Consumer Spending/Personal Consumption Expenditures
The total value of all goods and services consumed by households in an economy.
Consumption of Fixed Capital (Depreciation)
The decrease in the value of an asset over time due to wear and tear, age, or obsolescence.
Cyclical Unemployment
Unemployment that results from economic downturns or recessions, occurring when demand for goods and services falls.
Discouraged Workers
Individuals who are no longer looking for work because they believe no jobs are available for them.
Disinflation
A reduction in the rate of inflation, where prices are still rising but at a slower rate.
Disposable Income
The amount of money that households have available for spending and saving after paying income taxes.
Efficiency Wages
Wages set above the market equilibrium level by employers to increase worker productivity and reduce turnover.
Employed
People who are currently working for pay or profit.
Expenditures Approach
A method of calculating GDP by adding up all expenditures made in an economy.
Exports
Goods and services produced domestically and sold to other countries.
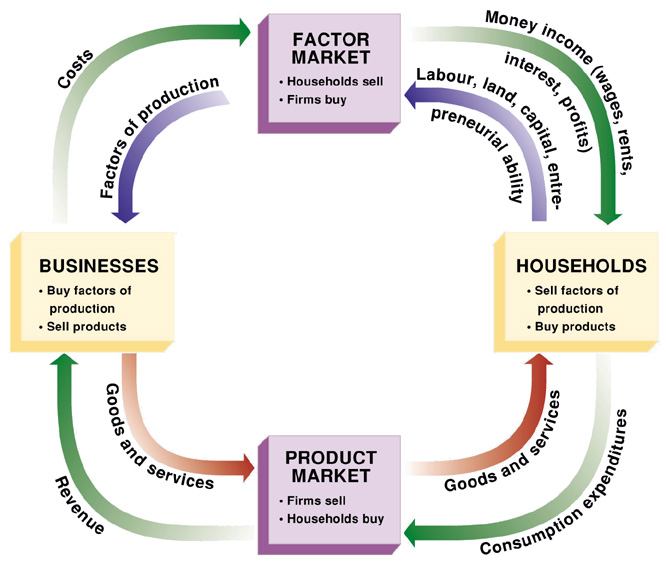
Factor Markets
Markets where resources, especially labor and capital, are bought and sold.
Final Goods and Services
Goods and services produced for final use by consumers or firms.
Financial Markets
Markets where people trade financial securities, commodities, and other fungible items.
Firm
A business organization that uses resources to produce goods or services for profit.
Frictional (Job Search) Unemployment
Unemployment that occurs when people are between jobs or entering the labor market for the first time.
GDP Deflator
A price index that measures the price level of all goods and services included in GDP.
GDP Per Capita
Gross Domestic Product divided by the population, representing average economic output per person.
Government Borrowing
When the government borrows money to cover expenditures that exceed revenue.
Government Purchases (of Goods and Services)
Total spending by governments on goods and services, excluding transfer payments.
Government Transfers
Payments made by the government to individuals without receiving goods or services in return.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The total value of all goods and services produced in a country within a specific period.
Gross National Product (GNP)
The total value of goods and services produced by a country's residents, regardless of where production takes place.
Gross Private Domestic Investment
Total spending on capital goods by the private sector.
Household
A group of individuals living together who make joint decisions about consumption and resource allocation.
Hyperinflation
An extremely high and typically accelerating rate of inflation, often exceeding 50% per month.
Imports
Goods and services produced in other countries and purchased domestically.
Income Approach
A method of calculating GDP by adding up all incomes earned by households and firms in an economy.
Inflation
An increase in the overall price level of goods and services in an economy over time.
Intermediate Goods and Services
Goods and services used as inputs in the production of other goods.
Inventory
The goods that have been produced but not yet sold.
Labor Force
The total number of people who are either employed or actively seeking employment.
Labor Force Participation Rate
The percentage of the working-age population that is either employed or actively seeking work.
Marginally Attached Workers
Individuals not currently in the labor force but have shown interest in finding a job within the past year.
Market Basket
A representative collection of goods and services used to measure changes in the overall price level.
Menu Costs
The costs to firms of changing prices, such as printing new menus or price tags.
National Income (Product Accounts/National Accounts)
A system used to measure the overall economic activity of a nation.
Natural Rate of Unemployment
The level of unemployment that occurs even when the economy is at full employment.
Net Exports
The value of a country��s exports minus its imports.
Nominal GDP
Gross Domestic Product measured at current prices, without adjusting for inflation.
Nonmarket Transaction
Economic activities that do not involve a market transaction, such as unpaid work.
Okun’s Law
A relationship between unemployment and GDP suggesting that for every 1% increase in unemployment, GDP will be roughly 2% lower than potential output.
Price Index
A measure that examines the weighted average of prices of a basket of consumer goods and services.
Producer Price Index (PPI)
A measure of the average change over time in the selling prices received by domestic producers.
Product Markets
Markets where goods and services are bought and sold.
Real GDP
Gross Domestic Product adjusted for inflation, reflecting the true value of goods and services produced.
Real Income
Income adjusted for inflation, representing the actual purchasing power of income.
Real Wage
The wage rate adjusted for inflation, reflecting the actual purchasing power of wages.
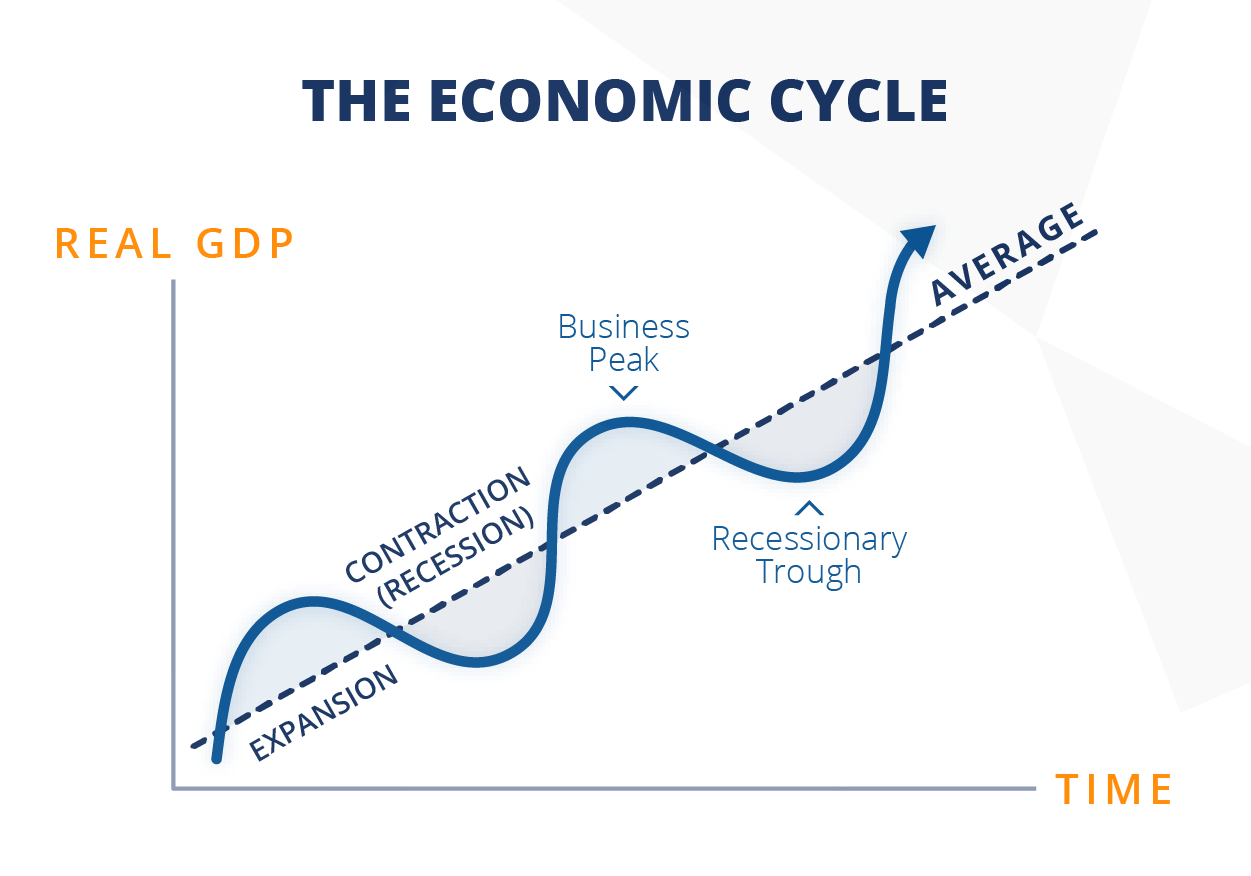
Recession
A period of temporary economic decline, typically identified by a fall in GDP in two successive quarters.
Recovery
A phase of the business cycle in which economic activity starts to increase after a recession.
Seasonal Unemployment
Unemployment caused by seasonal shifts in demand for labor.
Shoe Leather Costs
The costs associated with the effort and time spent to avoid holding cash during periods of inflation.
Stock
A financial asset that represents ownership in a corporation.
Structural Unemployment
Unemployment that occurs when there is a mismatch between the skills of workers and the demands of the job market.
Transfer Payments
Payments made by the government to individuals without requiring any goods or services in return.
Underemployed
Workers who are employed part-time or in jobs that do not fully utilize their skills.
Unemployed
People who are actively seeking work but are not currently employed.
Unemployment Rate
The percentage of the labor force that is unemployed and actively looking for work.
Value Added Approach
A method of calculating GDP by adding up the value added at each stage of production.
Circular Flow Chart
A model that shows the flow of goods and services, resources, and money between households and firms.
Business Cycle