GI Quiz 3
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Esophagus, Stomach, Pancreas
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What are some risk factors for GERD?
Smoking/Alcohol mainly. Others include obesity, diet etc.
What is the main way to treat GERD?
Lifestyle management and antacids
If GERD is more moderate/severe, what medications are used to treat
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or H2 blockers to lower gastric acidity
When there is rapid onset dysphagia in 40+ aged adults, rapid weight loss followed by subsequent lab test, what might be the condition?
Barrett’s esophagus
What is a major problem GERD can lead to?
Barrett’s Esophagus or esophageal cancer
How does H. Pylori generate peptic ulcers generally?
Burrows into cell membrane, attaches via adhesins
Makes enzymes damaging mucosal cells, degrades bicarb layer
gastric inflammation occurs w/ liberation of cytokines
Has urease which generates ammonia - toxic to cells
Some make cytotoxins
Decreases somatostatin production increasing gastric acid output
Describe Vitamin B12 Metabolism
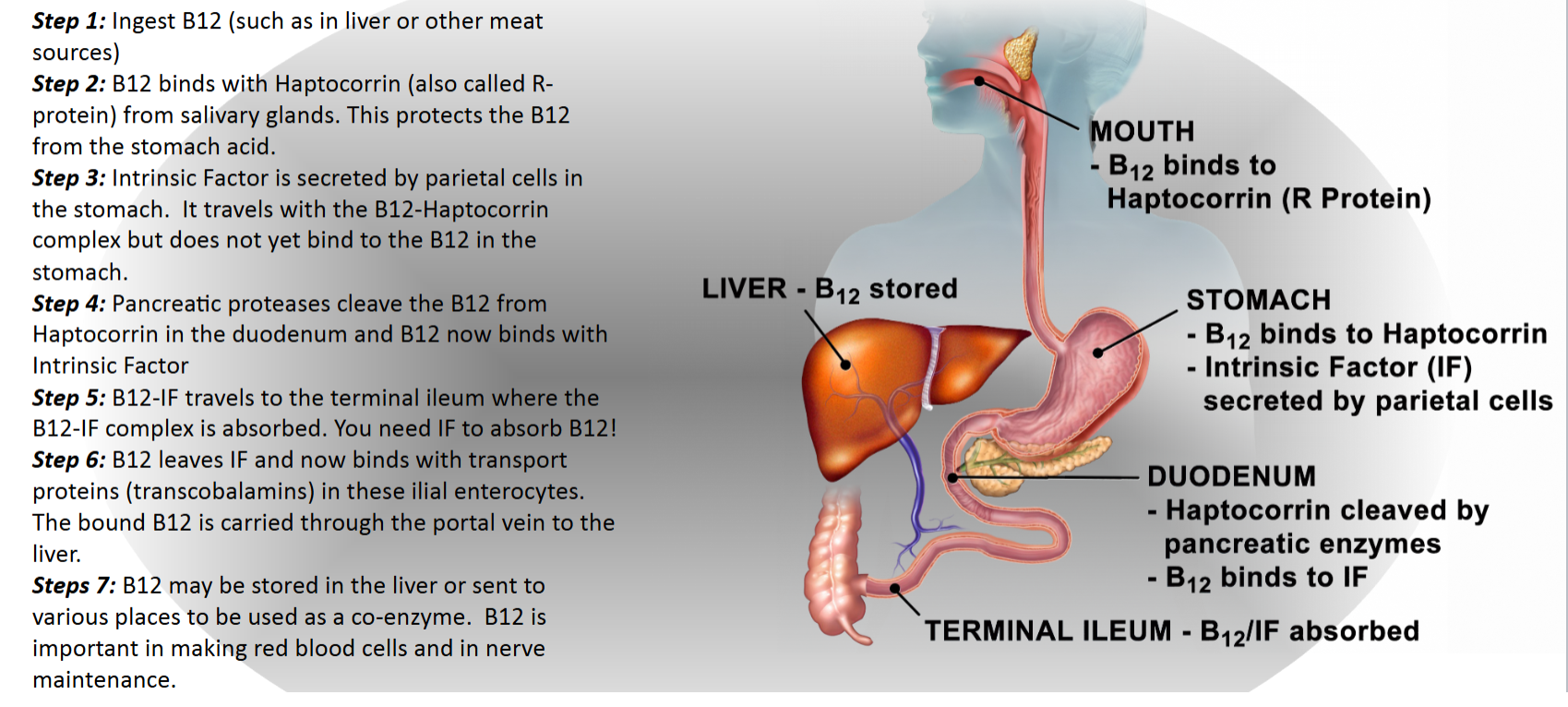
What secretes bicarbonate and what does it do
Pancreas, neutralizes gastric acid entering duodenum, provides optimal pH for gigestive enzymes
What are ways the pancreas prevents autodigestion (3 ways)
1) It packages its digestive enzymes as zymogen granules (proenzymes that are inactive) and don’t activate until it reaches the gut lumen
2) Has a trypsin inhibitor. which is important to activate the enzymes
3) High pH in duct from bicarb is too high for trypsin activity
What two cells are sensor cells in the duodenum
S cells - secretes secretin when low pH and FFA
CCK-RF Cells - respond to proteins and fats
What is the process to secrete bicarbonate?
S cells in duodenum sense HCl and FFA and secrete secretin, which signals the pancreas to secrete bicarb
What is the role of the CFTR in the duodenum?
1) Exchange of Cl and bicarb
2) Keeps lumen from drying by pulling water in due to Na+ and Cl-
What role does CCK have and what is the process to get it secreted
Promotes pancreas to secrete enzymes and proenzymes and gallbladder to contract
CCK-RF travels by paracrine to I cells to release CCK
Process of activating trypsinogen to trypsin
Comes in contact of enzyme enterokinase on border of duodenum which converts it to trypsin
What is immediate action for someone that might/is in shock?
Administer IV
Most of the causes of acute pancreatitis is due to (2)
gallstones and excessive alcohol
Mechanism of hypocalcemia in acute pancreatitis?
fat binds to the Ca forming calcium soaps that reduce serum Ca
Two regions of the stomach and what they make
Fundic glands (STORAGE) - IF via parietal, gastric lipase via chief, histamine & cytokines and somatostatin via D cells
Antral glands (GRIND & MIX)- gastrin via G cells and somatostatin via D cells
what importance does somatostatin have?
Regulate gastric acid, if present then gastric acid production is reduced
What is the most important stimulator of gastric acid?
Histamine via H2 cells on parietal cells, also further downregulates somatostatin
What is the main role of gastrin?
Stimulates parietal cells and ECL cells to make histamine to further stimulate gastric acid production
Which deficiency is likely to occur if there is a surgical procedure that removes the fundus?
Iron deficiency because acid reduces iron to get absorbed
Folate and B12 deficiency due to lack of parietal cells releasing intrinsic factor to bind to and help absorption.
What is the difference between the Meissner’s Plexus and Auerbach’s Plexus?
MP controls the blood flow to the mucosa
AP controls peristalsis
What is an important concept to keep in mind of the enteric nervous system and GI tract?
Modulated by the Vagus nerve, but the enteric system acts entirely on its OWN, can operate if the Vagus nerve is cut or severed.
T/F Pt with GERD have MORE tSELRs that cause the acid reflux
False, the # of them remains normal but the will reflux more material in each one.
Achlasia vs Scleroderma
Scleroderma is autoimmune destruction of smooth muscle
Achlasia destruction of enteric nervous system in esophagus and failure of LES to relax