Immunology exam 3 - transplantation immunology
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
all done
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
how many people in NL have chronic kidney disease
1.7 million
how many patients in NL on dialysis
6500
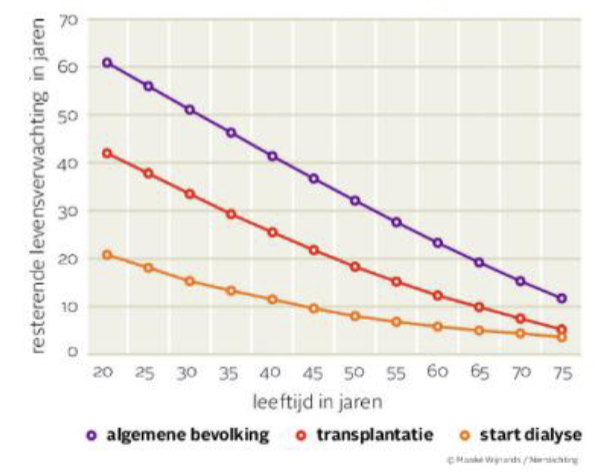
What does this graph mean?
getting a kidney transplant reduces you life expectation but being on dialysis does so even more
peritoneal dialysis explanation
catheter in tummy which does fluid exchange
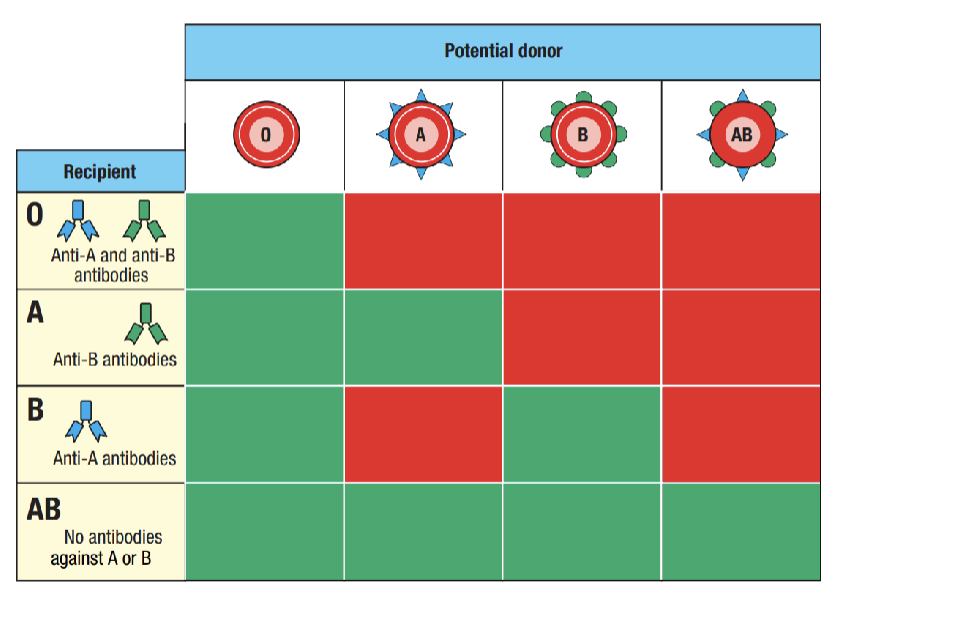
What does the image show?
What antibodies you have depending on blood type- what donors are compatible with what recipients
What is the most favorable blood type to be theoretically to get donations? what is it in practice though?
AB- no antibodies against A or B, best in practice is A because the donor pool is larger
What antibodies do you have if you are blood type O?
Anti-A and Anti-B antibodies
what antibodies do you have if you’re blood type A
anti-B antibodies
what transplant is most likely to be successful
between twins! because they have identical antibodies
incompatibility meaning in transplants
when transplant is rejected
what did they discover that joining white blood cells does?
leads to agglutination- reaction against each other
when does agglutination happen especially, why?
people who had received multiple blood transfusions, women who had been pregnant before - both have had most exposure to other peoples blood
what gene is important for tolerance?
HLA
what parts of the HLA gene are especially important in transplants and tested for?
HLA-A, B (both for MHC-I), DR (for MHC-II, most important!)
what determines where someone is on the postmortal waiting list?
screening of the recipient, waiting points per day of dialysism average waiting time differs by blood type but between 1.5 and 4 yrs
average lifespan of live kidney transplant?
15 years
crossmatching- basic info
developed to avoid hyperacute rejection, result of donor-specific antibodies (DSA), add patient serum to donor leukocytes (from spleen normally), diff methods available- if Ab kill the cells present- positive cross match- should not do transplant
what is the organ being very big after transplant a sign of?
huge immune response or lymphoma
standard transplantation treatment (4) & functions
corticosteroids - prednisolone, supress all immune cells, effective but toxic in the long run, increases circulating leukocytes (by preventing adhesion and movement to tissue)
Calcineurin inhibitor - CNI, tacrolimus, enzyme, neurological side effects
Antimetabolite - MMF, suppress T and B cells, interference in cell cycle
Anti-CD25 - binds to IL-2 receptor, inhibits activated T cells
drawback of antimetabolites
cause reduced immune response to vaccinations- many on it died in COVID and couldnt get effectively vaccinated
when is anti-CD25 given?
twice, once directly before transplant, once a few days after
mechanism of action of CNI
nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT), broadly distributed in the body, regulates T cell activity
CNI inhibits NFAT to be dephosphorylated
how many mismatches would you ideally have
0-0-0 (0 mismatches on each of HLA 1, B and DR)
what is the total HLA mismatch if you have a mismatch of 2-2-2
total 6
when should a kidney start working after live transplant
immediately- if not often something is wrong
what do you do if kidney is not working properly
kidney biopsy- CT scan and ultrasound do not show enough
two types of graft rejection
humoral (b cell, antibody) and cellular (T cells)
if 7 days after transplant there are many Ab against the graft what does it mean?
that Ab were present in body before transplant already
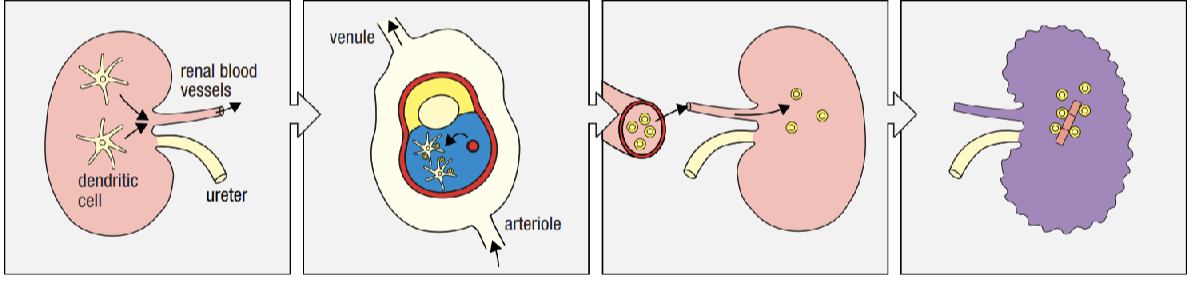
explain steps of transplant rejection
kidney graft with DCs, DCs migrate to the spleen where they activate effector T-cells, effector T cells migrate to graft via blood, graft destroyed by effector T cells
treatment for transplant rejection (3)
more immune suppresion drugs- high dose methylprednisolone (IV), plasmapheresis, anti-thymocyte globulins (ATG)
plasmatheresis explanation, how often, drawback
plasma exchange, 7x in 10 days, take plasma out with an IV, leads to a temporary decline in IgG and a susceptability for infections
ATG explain
very toxic, infusion of horse or rabbit-derived antibodies against human T cells, can only do this treatment once in a life (if you try again you would die from the immune exposure)
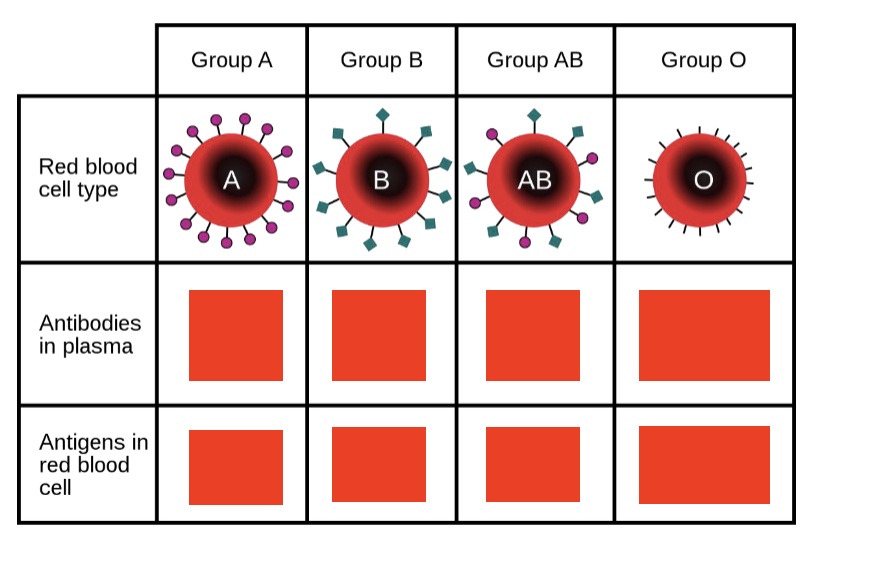
label Ab in plasma row
anti-B, anti-A, none, both anti-A and anti-B

label Ab in RBC
A antigen, B antigen, A and B antigen, none
Immunoadsorption description (4 points)
use of binding columns to bind Ab, only usable to filter specific Ab such as anti-A or anti-B., good option for ABOi transplantation, very expensive
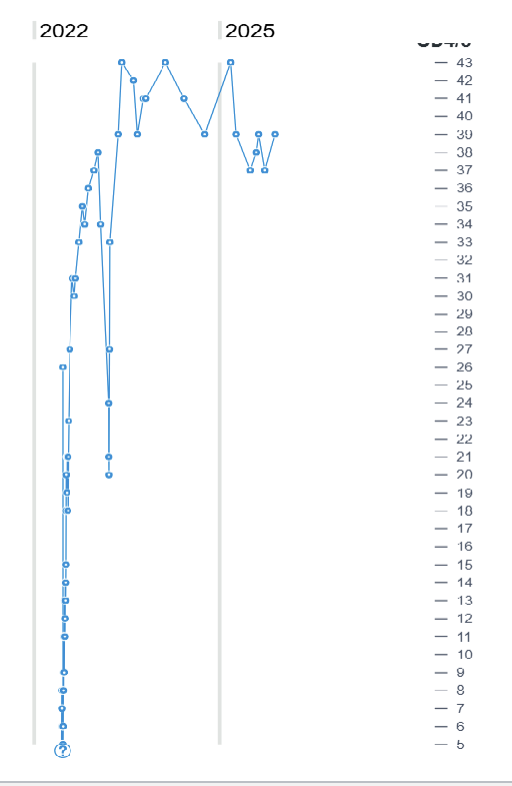
(this is kidney function in mL/min, should be 120-150 in healthy person) what is the big drop caused by?
infection
procedure for ABO incompatible transplant (7 drugs/procedures)
start with rituximab 30 days before infection, then 2 weeks before start on tacrolimus/MMF/prednisone and continue lifelong, then just before do IVIG, then right after and 4 days after basiliximab, then biopt 10 days after
what do you do if there is chronic antibody mediated rejection?
no effective treatment

what does this show?
targets for the immunosuppresive drugs used in organ transplants
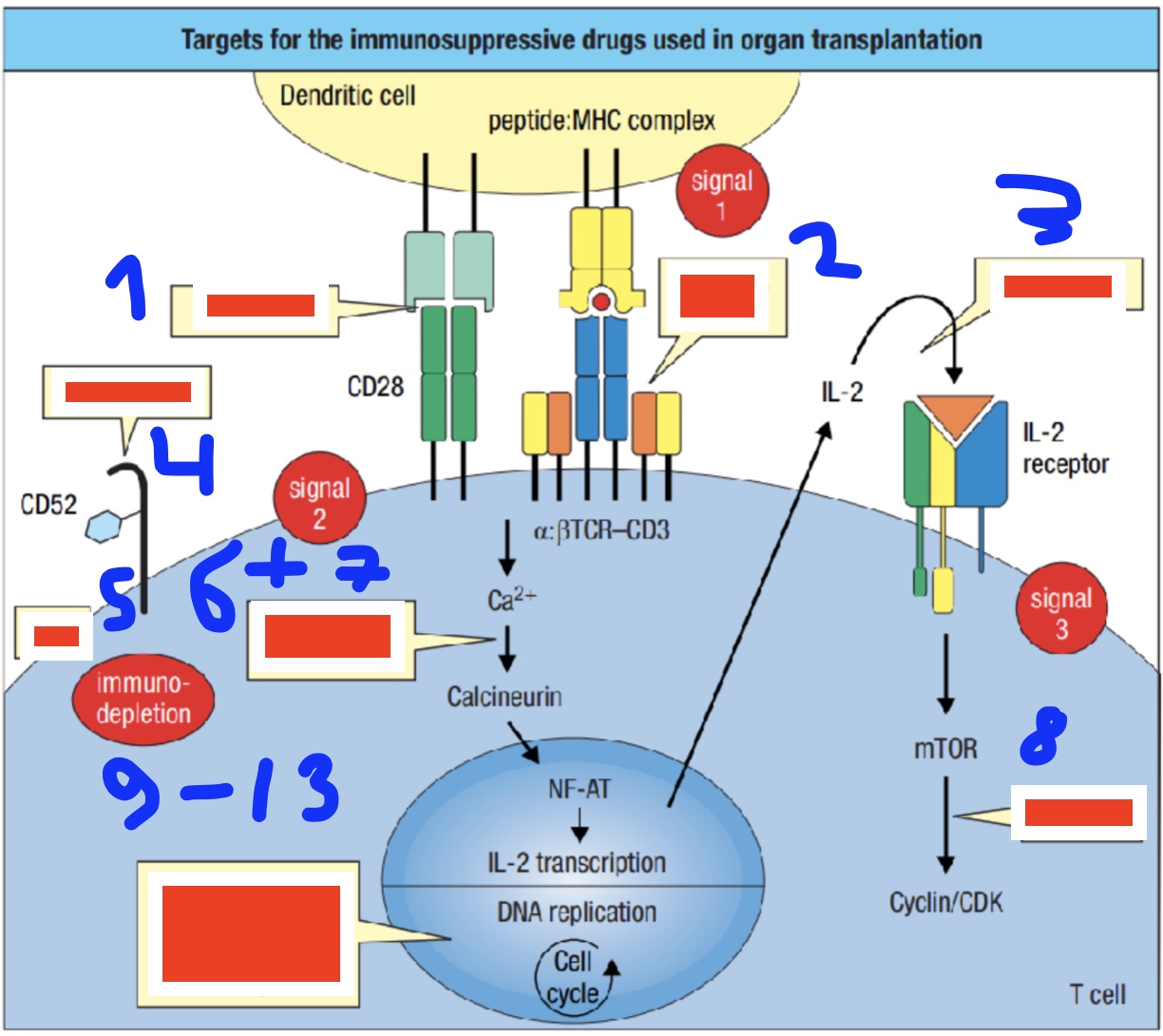
label 1-4 (2 is two diff ones)
belatacept, anti-CD3 & mAB, basiliximab, alemtuzumab

label 5-8
rATG, cyclosporin, tacrolimus, sirolimus

label 9-13 (one thats impact the cell cycle)
methotrexate, mycophenolate, cyclophosphamide, azathioprine
which immunosuppresive drugs target signal 1, signal 2, signal 3
signal 1: anti-CD3, mAB
signal 2: belatacept
signal 3: basiliximab
which immunosuppresive drugs target DNA replication (4)
methotrexate, mycophenolate, cyclophosphamide, azathioprine
which immunosuppresive drugs target: conversion Ca into calcineurin (2), mTOR into cyclin, CD52, immunodepletion
conversion Ca into calcineurin: cyclosporin, tacrolimus
mTOR into cyclin: sirolimus
CD52: alemtuzumab
immunodepletion: rATG
what two things do you have to match to do a kidney transplant?
both blood group and HLA (A, B and DR)
what happens with chronic Ab mediated rejection
Immune complex is deposited in the blood vessel walls of the transplanted kidney recruit inflammatory cells, enables immune affecters to enter the tissue of the blood vessel wall to inflict increasing damage
most important drug for transplants
tacrolimus- starting trials using just it long term
take home messages of lecture (6)
kidney transplants are still necessary, blood group matching, immunosuppressive treatment, rejection can be acute or chronic, complications