Cell biology lecture 21
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Kinetics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
what determines rate of a reaction?
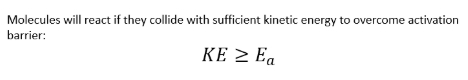
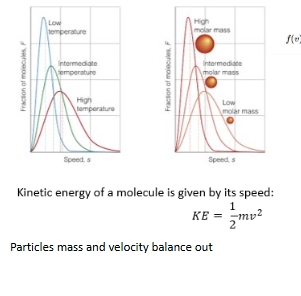
what does Maxwell Boltzmann distribution describe?
distribution of molecule speeds in a gas or liquid
Particles in a box can collide with each other or the box
If we started them all with the same speed and let them equilibrate, collisions would transfer energy between particles and we get a distribution of speed
Probability distribution plot
Most molecules have similar speed
A few have very high speed
A few have very low speed
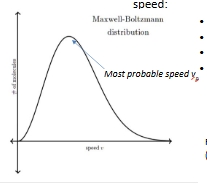
Distriibution plot with changes in mass or temp
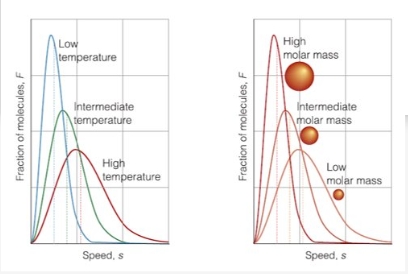
MB and particle kinetic energy distribution
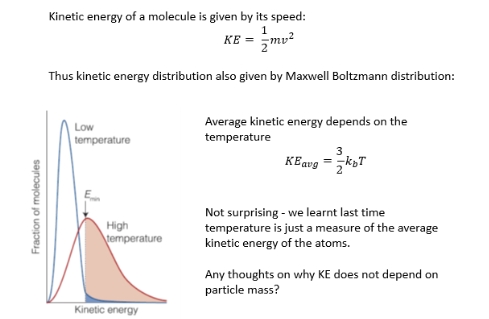
Why KE does not depend on particle mass?
What determines a rate of reaction?
Three major factors:
1. Temperature
Higher T
Average kinetic energy increases
more molecules exceed activation energy
(Enzymatic) catalysis
Enzymes lower activation energy
More molecules exceed activation energy
Concentration
As concentration increases
Same fraction of molecules have KE greater than activation energy
But more molecules in total
more molecules enough KE to react
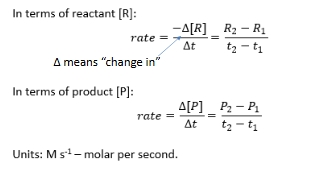
Rate of reaction reminder
Change in conc/time
Reaction orders
Consider reaction:
A + B C + D
Rate of decrease of reactants given by:
rate = k[A]x[B]y
x, y are orders of reaction with respect to A, B respectively
Overall order of reaction is x+y
k (rate constant) is dependent on temp
First order reactions
A FIRST ORDER reaction is one in which a single atom or molecule determinesthe rate
rate = k [A]
Eg radioactive decay:
In a first order reaction: if we double the amount of A, the rate doubles
![<ul><li><p class="Paragraph WhiteSpaceCollapse SCXP198914318 BCX8" style="text-align: left;"><span style="line-height: 0px;"><span>A FIRST ORDER reaction is one in which a single atom or molecule determinesthe rate</span></span></p></li></ul><p class="Paragraph WhiteSpaceCollapse SCXP198914318 BCX8" style="text-align: center;"><span style="line-height: 0px;"><span>rate = k [A]</span></span></p><ul><li><p class="Paragraph WhiteSpaceCollapse SCXP198914318 BCX8" style="text-align: left;"><span style="line-height: 0px;"><span>Eg radioactive decay:</span></span></p></li></ul><ul><li><p class="Paragraph WhiteSpaceCollapse BCX8 SCXP249869298" style="text-align: left;"><span style="line-height: 0px;"><span>In a first order reaction: if we double the amount of A, the rate doubles</span></span></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0a3ad2bd-118f-446b-a4f1-7e7c06db5c66.jpg)
Second order reactions
When two molecules collide to determine the rate, the reaction is SECOND ORDER
Consider reaction:
A+A to B
with rate = k[A]squared
This reaction is second order w.r.t. A and overall second order
Or
Bimolecular interaction:
A + B to C
with rate = k[A][B]
This reaction is first order w.r.t. A and B and second order overall
![<ul><li><p class="Paragraph WhiteSpaceCollapse SCXP84208626 BCX8" style="text-align: left;"><span style="line-height: 0px;"><span>When two molecules collide to determine the rate, the reaction is SECOND ORDER</span></span></p></li><li><p class="Paragraph WhiteSpaceCollapse SCXP84208626 BCX8" style="text-align: left;"><span style="line-height: 0px;"><span>Consider reaction:</span></span></p></li></ul><p class="Paragraph WhiteSpaceCollapse SCXP84208626 BCX8" style="text-align: center;"><span style="line-height: 0px;"><span>A+A to B</span></span></p><p class="Paragraph WhiteSpaceCollapse SCXP84208626 BCX8" style="text-align: left;"><span style="line-height: 0px;"><span>with rate = k[A]squared</span></span></p><ul><li><p class="Paragraph WhiteSpaceCollapse SCXP84208626 BCX8" style="text-align: left;"><span style="line-height: 0px;"><span></span></span></p></li><li><p class="Paragraph WhiteSpaceCollapse SCXP84208626 BCX8" style="text-align: left;"><span style="line-height: 0px;"><span>This reaction is second order w.r.t. A </span><strong><span>and </span></strong><span>overall second order </span></span></p></li></ul><p class="Paragraph WhiteSpaceCollapse SCXP84208626 BCX8" style="text-align: left;"></p><p class="Paragraph WhiteSpaceCollapse SCXP84208626 BCX8" style="text-align: left;">Or </p><ul><li><p class="Paragraph WhiteSpaceCollapse SCXP46615837 BCX8" style="text-align: left;"><span style="line-height: 0px;"><span>Bimolecular interaction:</span></span></p></li></ul><p class="Paragraph WhiteSpaceCollapse SCXP46615837 BCX8" style="text-align: center;"><span style="line-height: 0px;"><span>A + B to C</span></span></p><p class="Paragraph WhiteSpaceCollapse SCXP46615837 BCX8" style="text-align: left;"><span style="line-height: 0px;"><span>with rate = k[A][B]</span></span></p><ul><li><p class="Paragraph WhiteSpaceCollapse SCXP46615837 BCX8" style="text-align: left;"><span style="line-height: 0px;"><span></span></span></p></li><li><p class="Paragraph WhiteSpaceCollapse SCXP46615837 BCX8" style="text-align: left;"><span style="line-height: 0px;"><span>This reaction is first order w.r.t. A and B </span><strong><span>and </span></strong><span>second order overall</span></span></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1db9e90d-8431-4380-83cf-bb415ed87872.jpg)
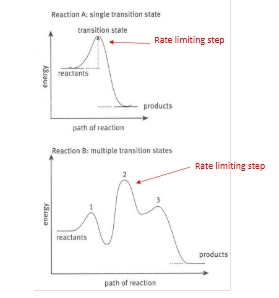
how do we determine the order of a reaction?
Experimentally, determined by the slowest RATE LIMITING/DETERMINING step of a reaction
Order of reaction and rate limiting steps
So to get the reaction order we need to measure the rate
Because there may well be intermediate steps in a reaction
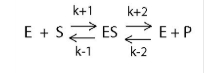
Famous biological example:
Michaelis-Menten enzyme kinetics
Rate limiting intermediate step
Equilibrium and equilibrium constant Kc

why is Kc useful?
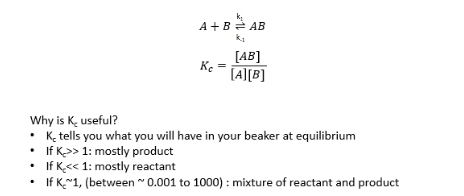
Kc process
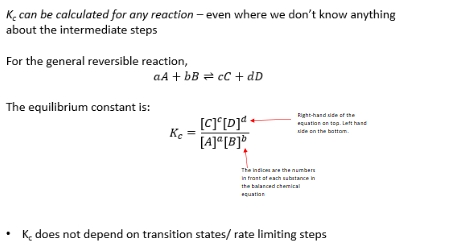
Why is Kc calculated without consideration of rate limiting steps and intermediates?
This is the equilibrium constant at equilibrium, so all the rates must balance (principle of detailed balance) so only the first and last states need to be considered.
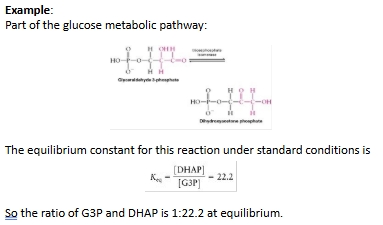
Kc example Q

Equilibrium constant biological example
How do systems at equilibrium respond to perturbation?
If we add more reactant A or B, the system readjusts back towards equilibrium by making more product C + D
If we add more product C or D, the system readjusts back towards equilibrium by making more product A + B
Example of Le Chatelier’s principle:
When a system at equilibrium is subjected to disturbance, the composition of the system adjusts to minimize the disturbance
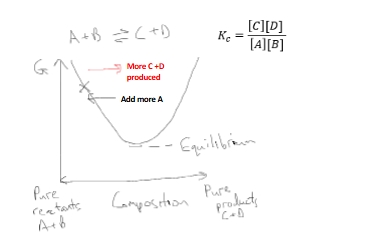
Free energy and equilibrium links
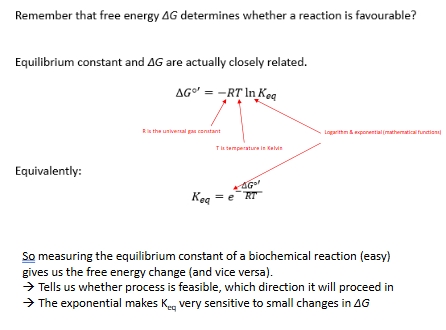
Free energy and equilibrium example *
