Bacteria Types
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
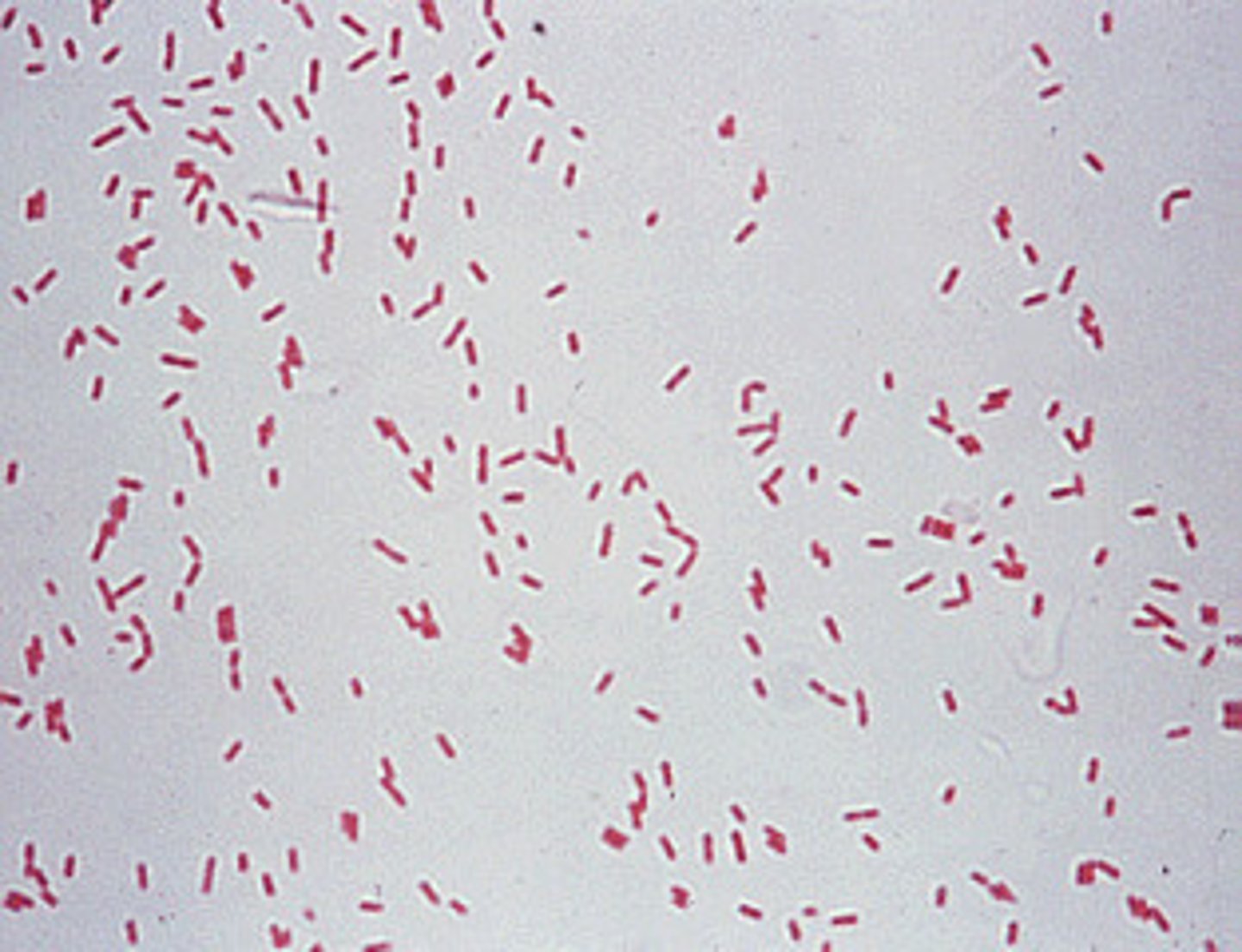
Streptococcus mutans
- +ve cocci
- facultative anaerobe
- dental caries
- prod lactic acid from sugar metabolism, leading to enamel demineralisation
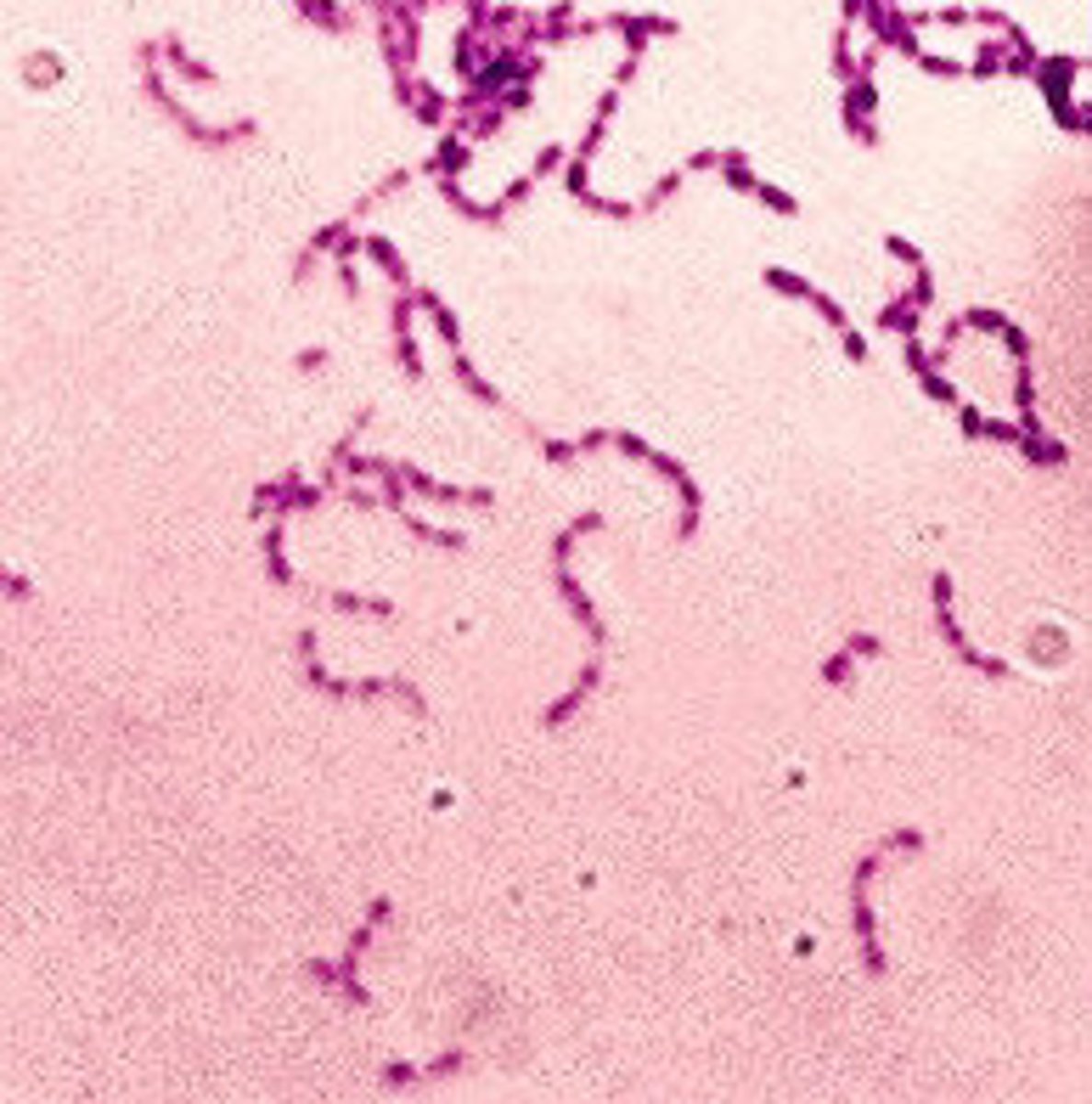
Streptococcus mitis
- +ve cocci (part of the viridans group of strep)
- can cause endocarditis
- prod biofilms & contributes to dental plaque formation
- alpha-hemolysis on blood agar (greenish discoloration)
- Optochin-resistant (differentiates from S. pneumoniae)
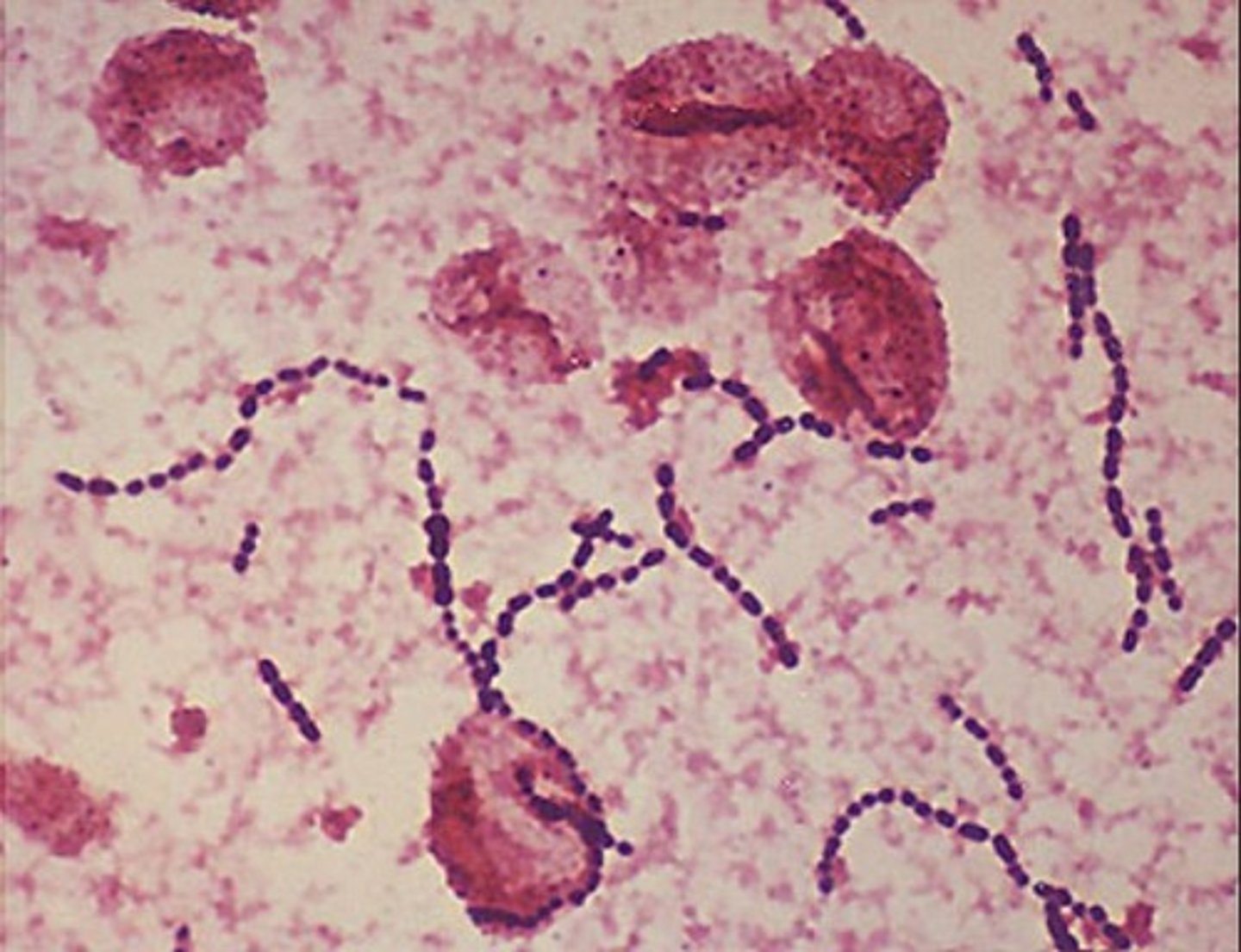
Streptococcus salivarius
- +ve cocci
- commensal in the mouth & URT
- contributes to early biofilm formation on teeth
- rarely pathogenic but can cause bacteremia in immunocompromised indv's
- facultative anaerobe; prod polysaccharides in sucrose-rich envs
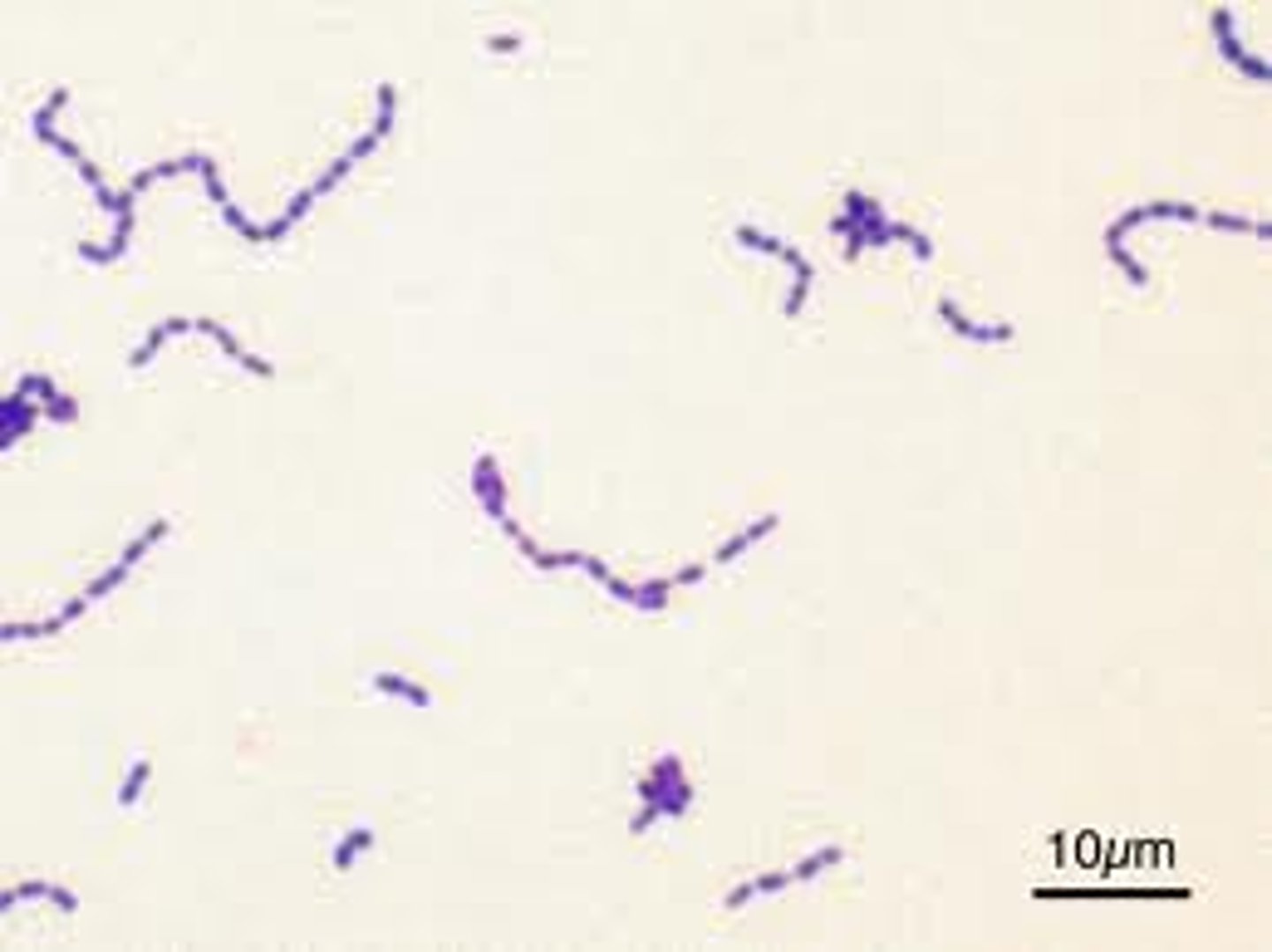
Streptococcus pneumoniae
- +ve lancet-shaped cocci
- facultative anaerobe
- causes CAP; also ass w/ meningitis & otitis media
- virulence factors: polysaccharide capsule, pneumolysin
- alpha-hemolysis on blood agar (green discoloration)
- +ve bile solubility test
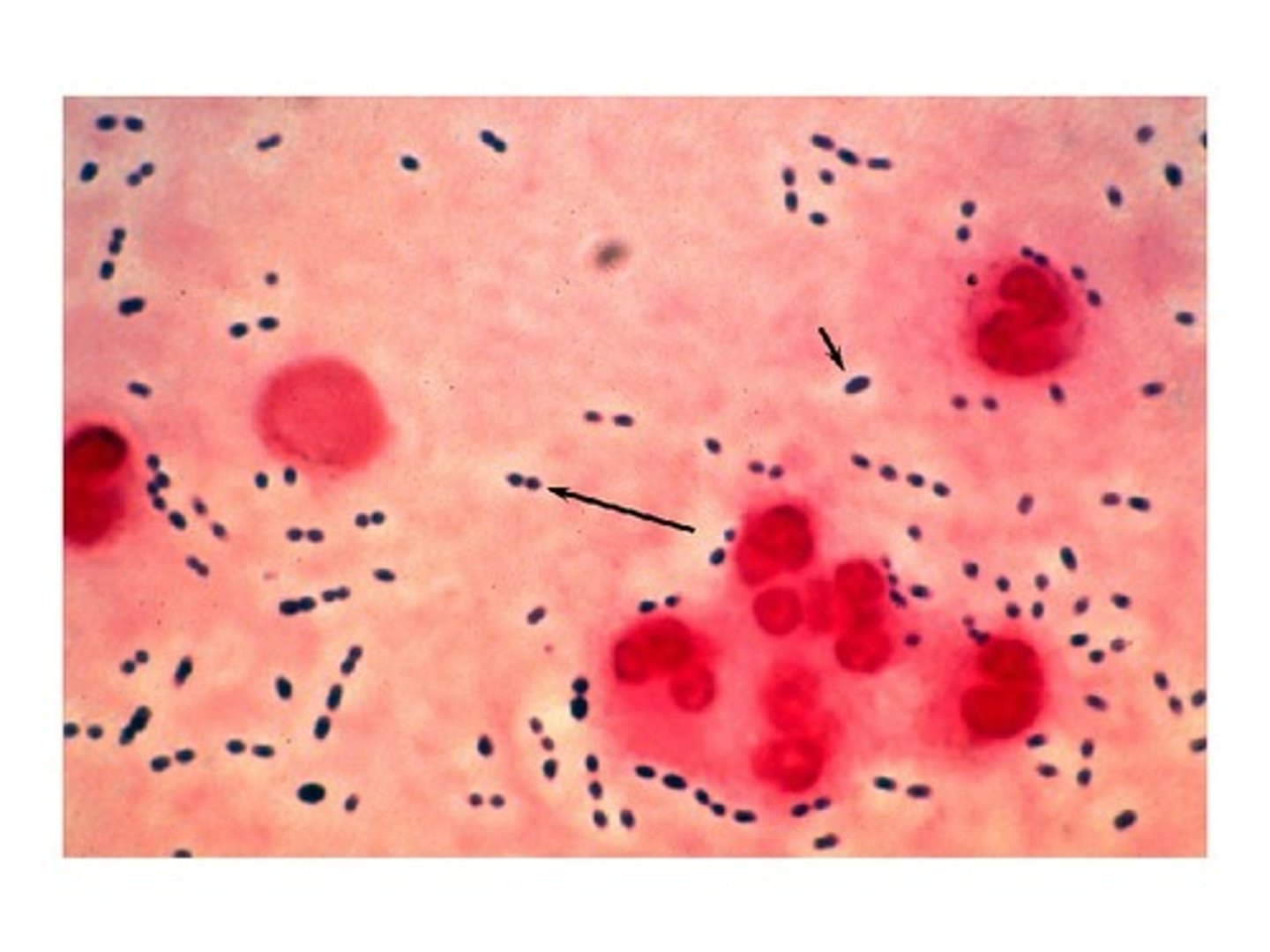
Streptococcus oralis
- +ve cocci
- associated w/ biofilm formation and mild infections.
- can contribute to endocarditis following dental procedures
- optochin-resistant, alpha-hemolytic on blood agar
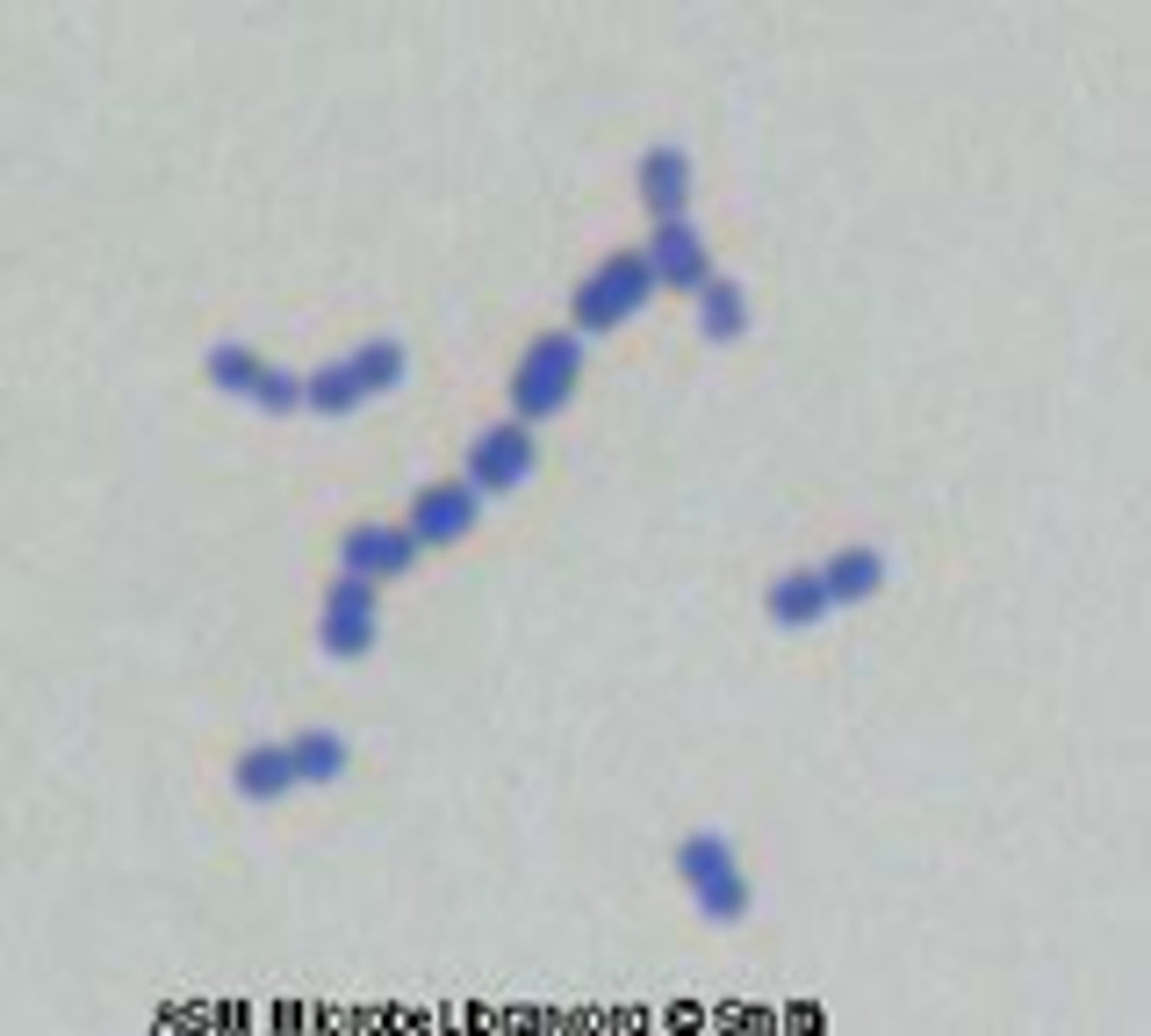
Porphyromonas gingivalis
- -ve rod
- anaerobic
- periodontitis
- prod proteases (e.g., gingipains) that degrade host tissue
- black-pigmented colonies on blood agar (heme accumulation)
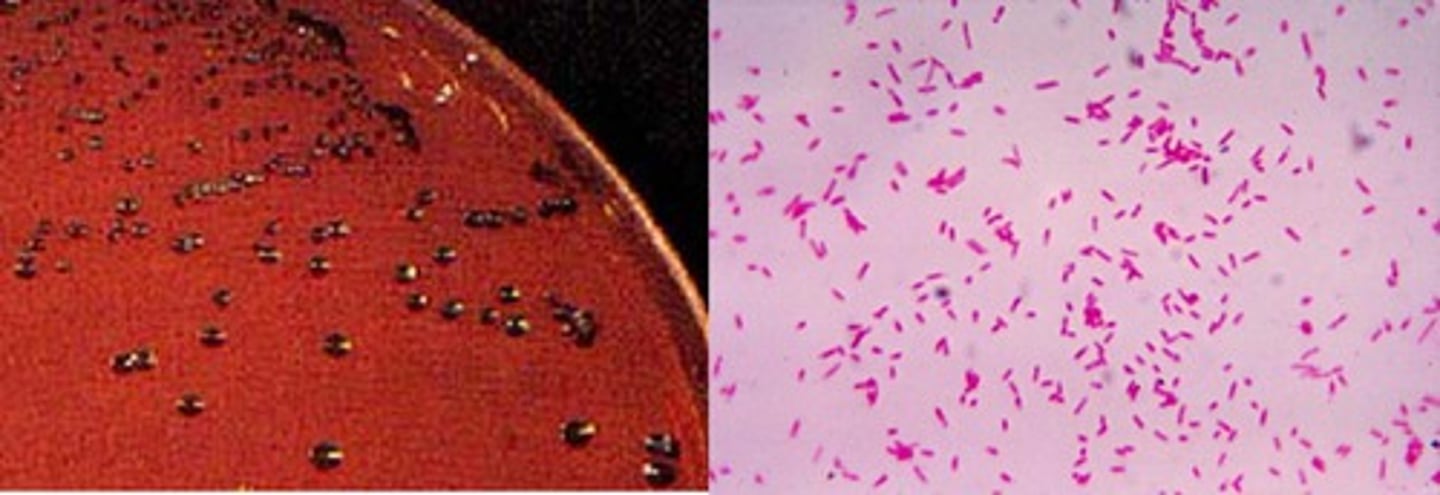
Prevotella intermedia
- -ve rod
- anaerobic
- found in perio pockets; associated w/ gingivitis & periodontitis.
- virulence incl proteolytic enzymes that degrade host tissues
- black-pigmented colonies on anaerobic blood agar
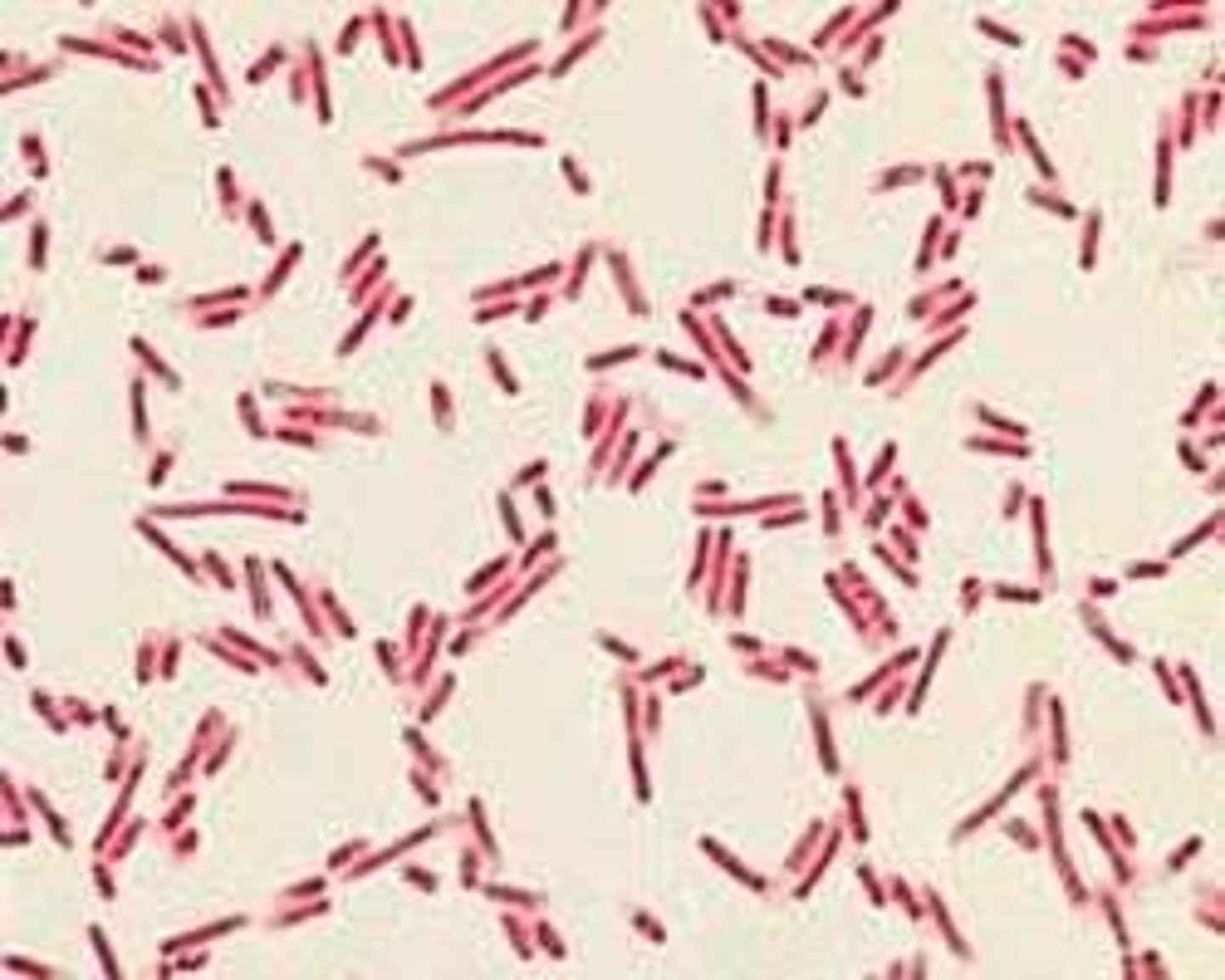
Lactobacillus spp.
- +ve rod
- facultative anaerobes
- found in OC & GIT; contributes to oral health
- rarely pathogenic but can cause bacteremia in immunocompromised pts
- prod lactic acid; catalase -ve
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- +ve (acid-fast) bacilli
- aerobic
- causes chronic pneumonia; hallmark is granuloma formation in lungs.
- ZN stain
- grows on Lowenstein-Jensen agar (slow-growing)
Chlamydia pnemoniae
- -ve coccoid
- obligate intracellular pathogen
- causes atypical pneumonia, pharyngitis, & bronchitis
- associated w/ gradual onset and&prolonged cough.
- req cell culture for growth (unable to grow on standard media)
- detected using PCR or serology

Enterococcus faecalis
- +ve cocci
- facultative anaerobe
- causes root canal infections, UTI & endocarditis (secondary endodontic)
- known for high AB resistance (e.g., vancomycin-resistant enterococci, VRE).
- grows in 6.5% NaCl
- bile-esculin +ve (blackening of media)
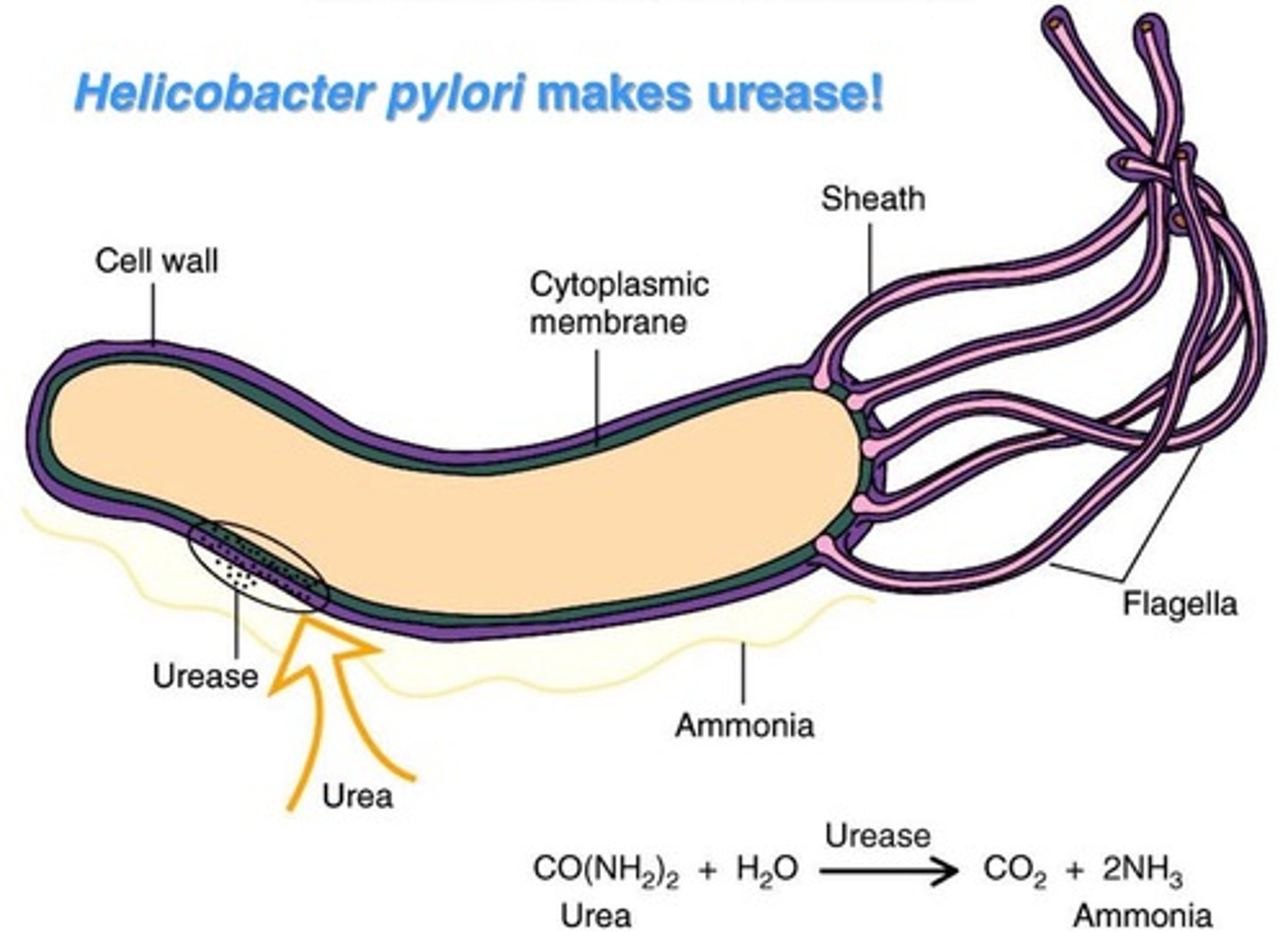
Helicobacter pylori
- -ve spiral
- microaerophilic.
- causes peptic ulcers, gastritis, & gastric cancer
- virulence factors: urease, cytotoxins.
- urease test +ve (biopsy or breath test)
- grows on Skirrow agar
Treponema pallidum
- -ve spirochete
- causes syphilis, characterised by primary (chancre), secondary (rash), & tertiary (gummas) stages
- cannot be cultured in vitro.
- detected by DFM or serologic tests
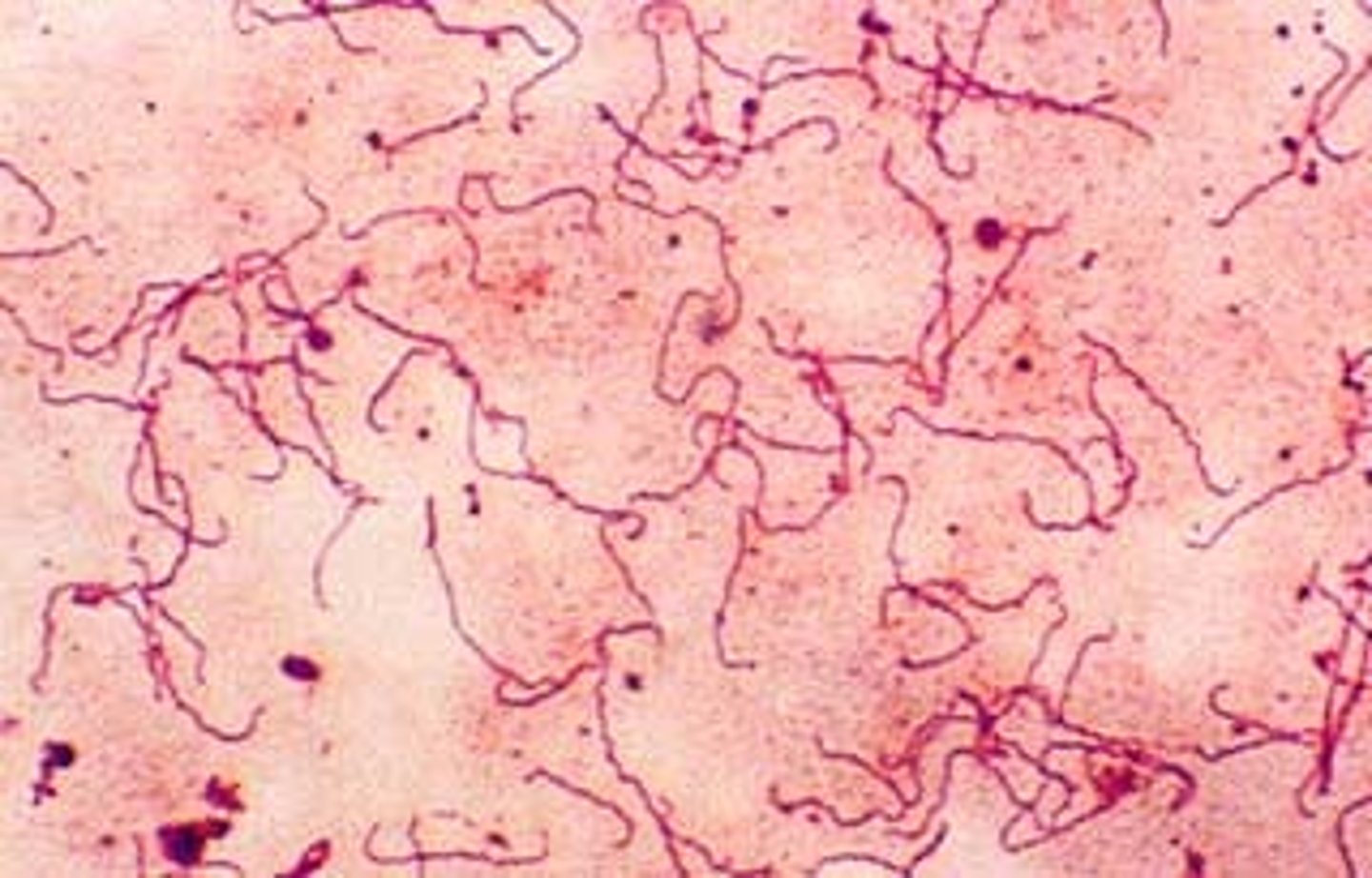
Fusobacterium nucleatum
- -ve spindle
- anaerobe
- gingivitis, periodontitis, & dental abscesses
- forms biofilms & promotes coaggregation w/ other oral pathogens
- sensitive to kanamycin in culture

Bordatella pertussis
- -ve coccobacillus
- aerobic
- causes whooping cough
- virulence factors: pertussis toxin, tracheal cytotocin
- grows on Bordet-Gengou or Regan-Lowe agar
- PCR-based diag
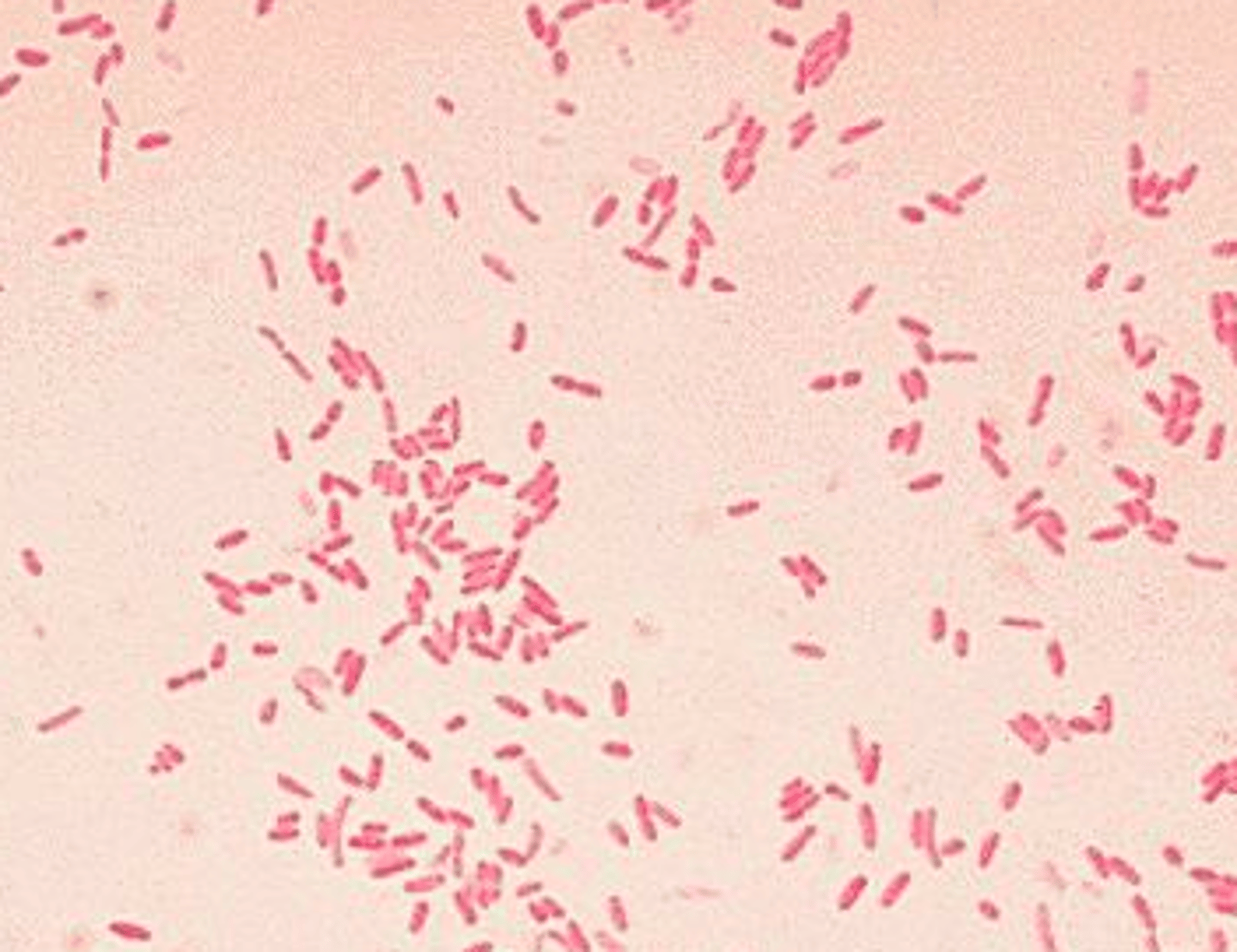
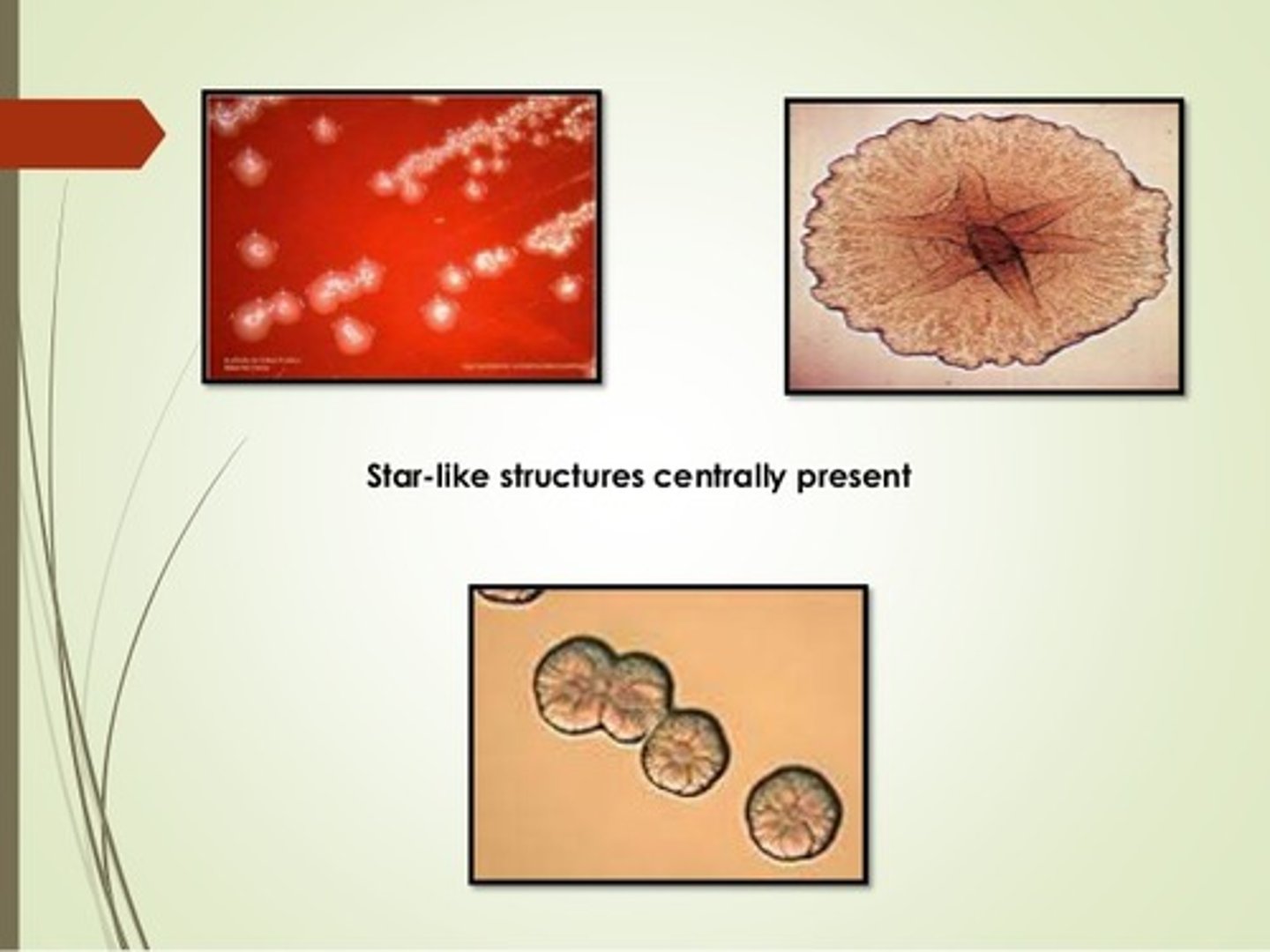
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans
- -ve coccobacillus
- facultative anaerobe
- key pathogen in aggressive periodontitis
- prod leukotoxin & endotoxin.
- star-shaped colonies on agar
- catalase +ve
Tannerella forsythia
- -ve rod-shaped
- anaerobe, non-motile
- often found in conjunction w/ other pathogens in periodontitis.
- prod enzymes (e.g., sialidases) that degrade host tissues.
- identified through molecular methods (e.g., PCR)

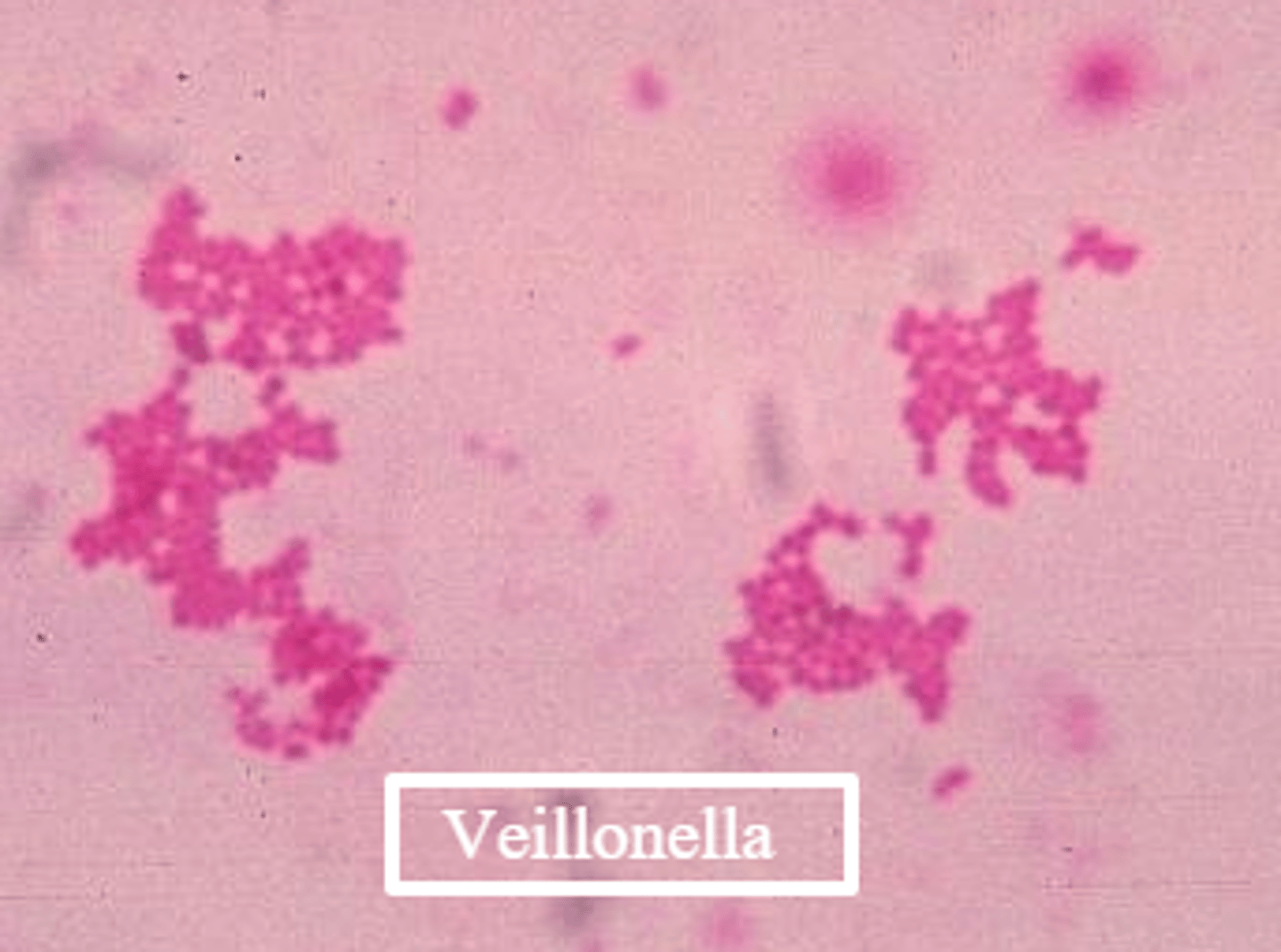
Veillonella
- -ve cocci
- anaerobic
- associated w/ dental plaque & gingival health, as they metabolise lactate
- grows on anaerobic media
- does not ferment carbohydrates (uses lactate)
Actinomyces israelii
- +ve filaementous
- anaerobe
- causes actinomycosis, leading to lumpy jaw or chronic oral abscesses w/ S granules
- slow-growing colonies resembling "molar tooth" on agar
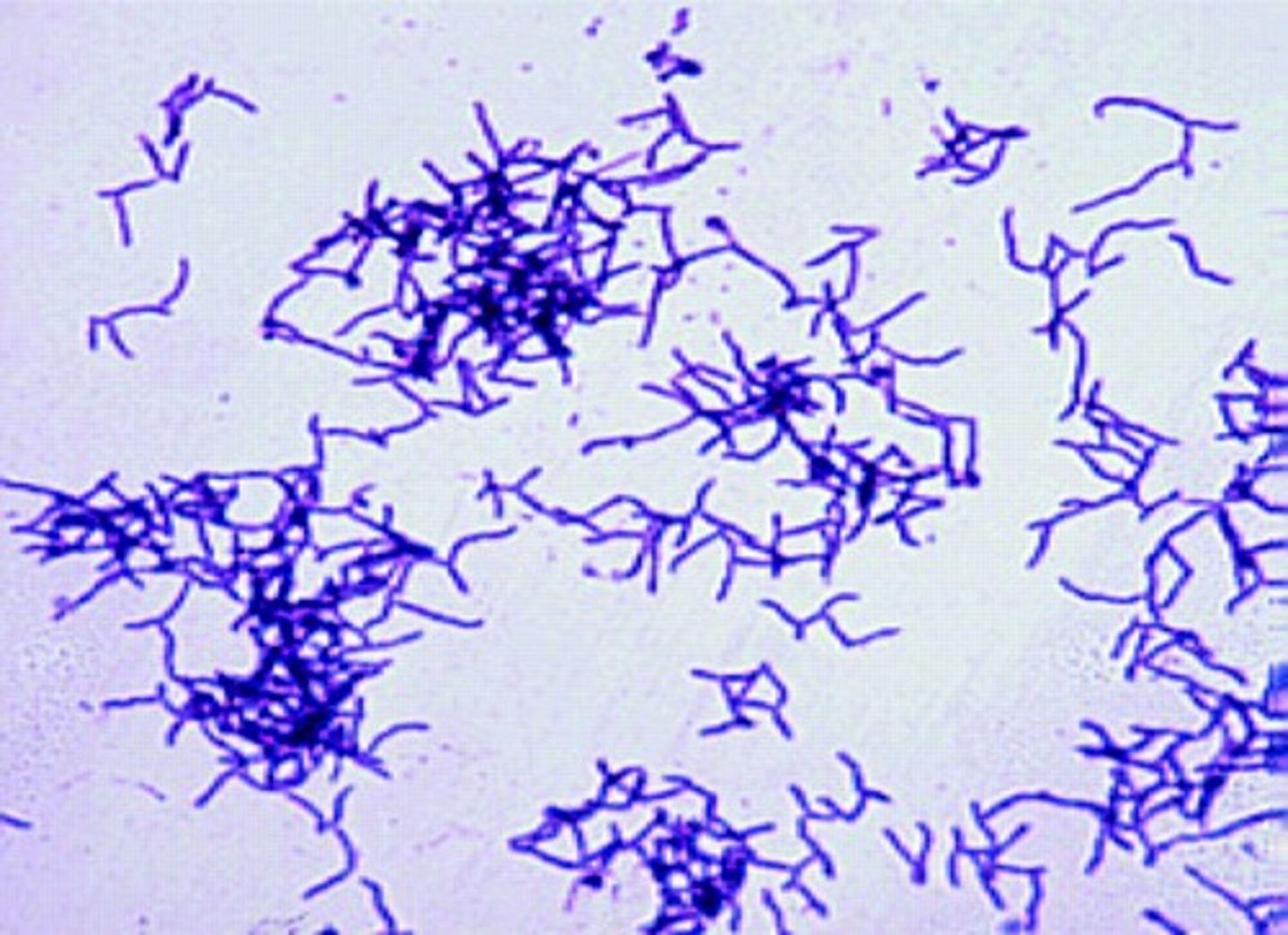
Haemophilus influenzae
- -ve coccobacillus
- facultative anaerobe
- causes CAP, esp in indv's w/ COPD or after viral infections.
Type b (Hib) strains cause more severe infections.
- req X (hemin) & V (NAD) factors for growth
- satellite phenomenon when grown near S. aureus
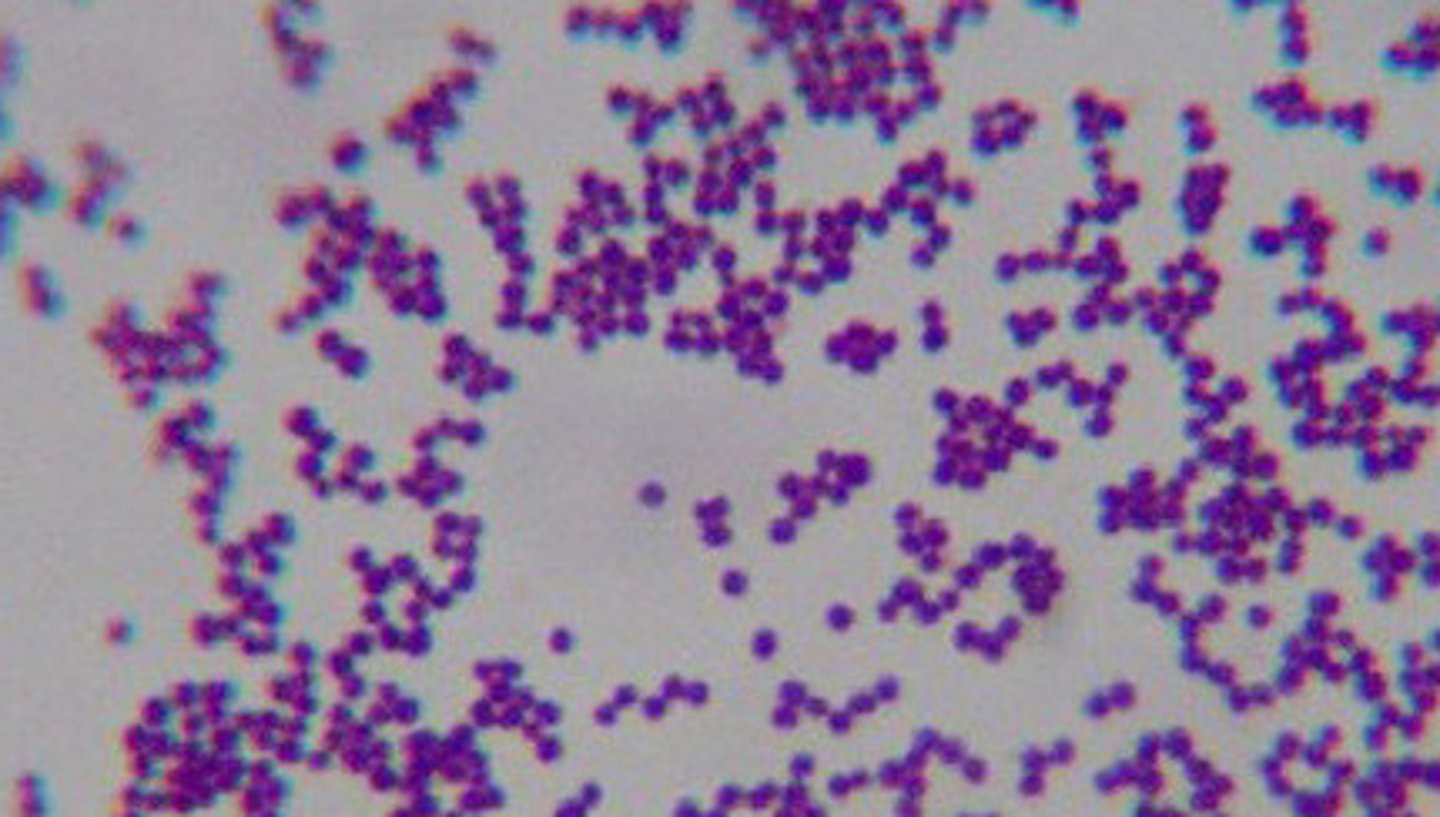
Staphylococcus aureus
- +ve cocci
- facultative anaerobe
- causes HAP & CAP; associated w/ necrotising pneumonia.
- catalase +ve, coagulase +ve
- beta-hemolysis on blood agar.
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- -ve spindle pleomorphic
- lacks cw (not visible on Gram stain)
- causes "walking pneumonia," more common in younger pts, atypical pneumonia
- virulence factor: P1 adhesin.
- +ve cold agglutinin test
- req specialised media (e.g., Eaton's agar)
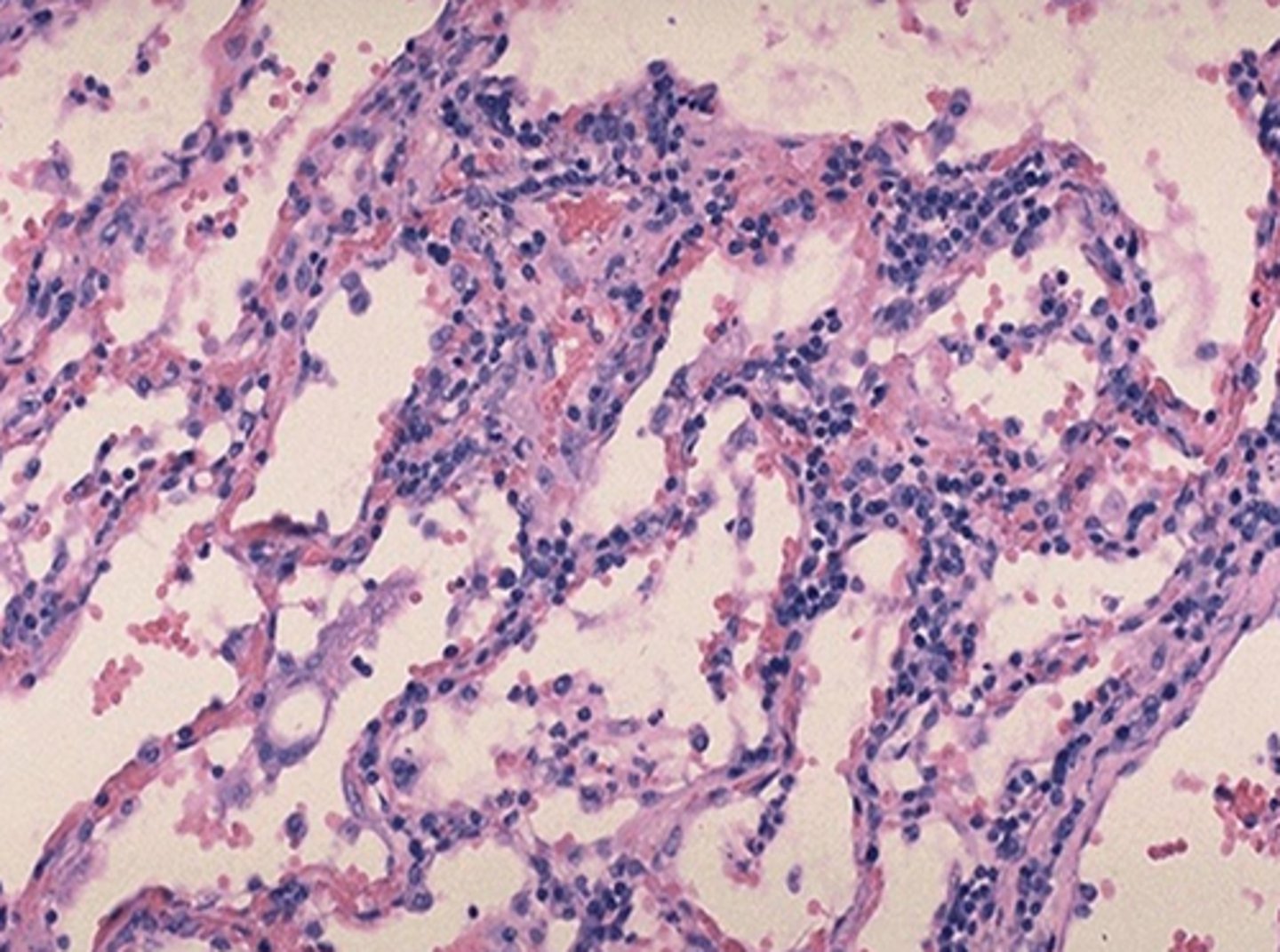
Legionella spp.
- -ve rod
- facultative intracellular
- causes Legionnaires’ disease (severe pneumonia) & Pontiac fever
- acquired via contaminated water systems (e.g., air conditioners)
- req buffered charcoal yeast extract (BCYE) agar
- +ve urinary antigen test for serogroup 1
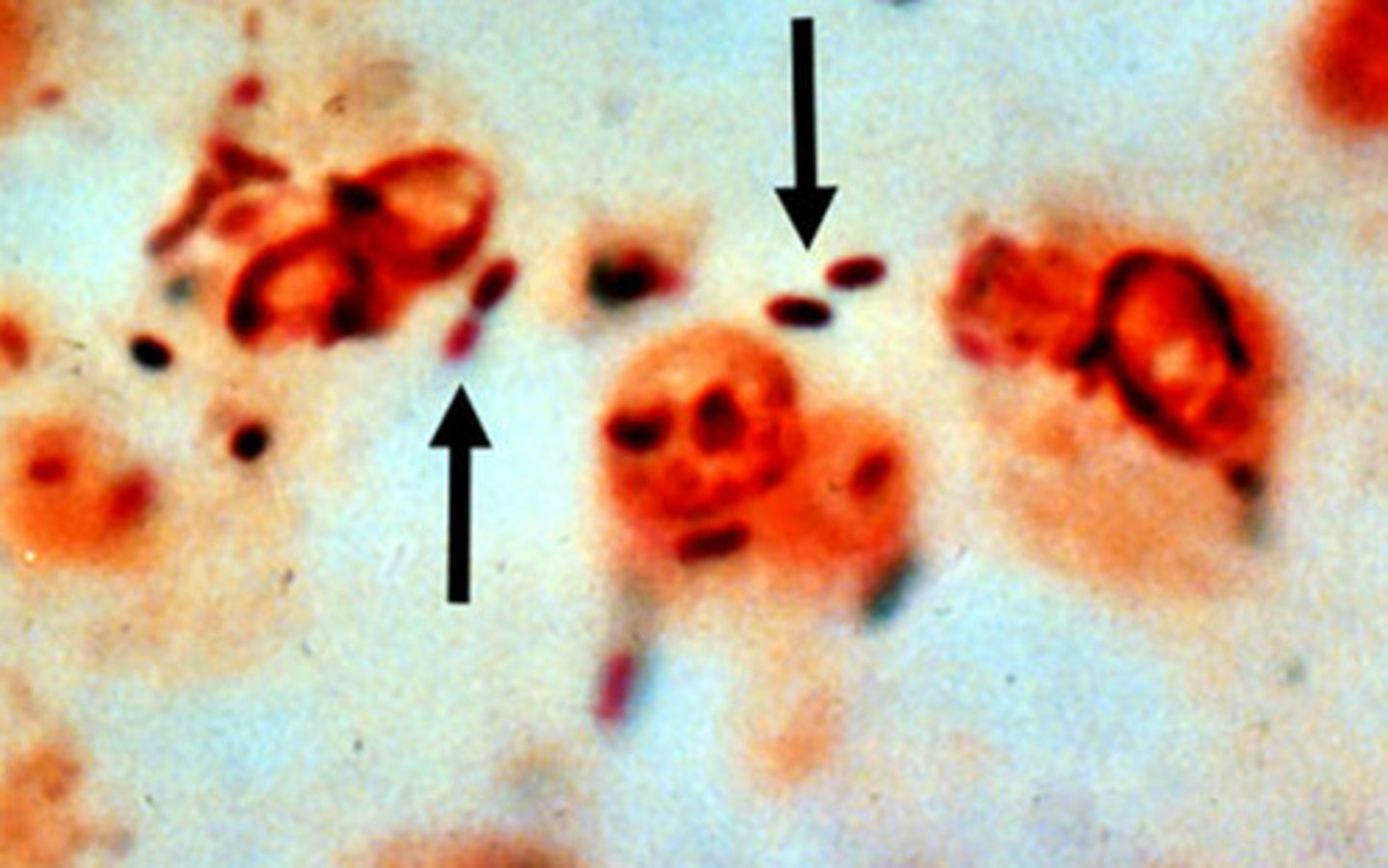
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- -ve rod
- aerobic, motile
- causes HAP, esp in immunocompromised or CF pts
- produces a characteristic green pigment (pyocyanin)
- oxidase +ve
- grows on MacConkey agar w/out lactose fermentation