AQA GCSE 9-1 Combined Science Trilogy Comprehensive Flashcards
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:30 PM on 10/31/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
1
New cards
What are the two main types of cell?
prokaryotic and eukaryotic
2
New cards
How is magnification calculated?
the size of the image divided by the size of the real object
3
New cards
What are chromosomes made of?
DNA
4
New cards
Osmosis
the process by which water molecules move across a semi-permeable membrane from a dilute solution to a more concentrated one.
5
New cards
What is an organ?
a group of different tissues working together to perform a specific job.
6
New cards
What are the three main types of digestive enzymes?
protease, lipase and carbohydrase
7
New cards
What are the three different types of blood vessels?
arteries, veins and capillaries
8
New cards
What two treatments can be used for coronary heart disease?
stents to keep coronary arteries open or statins to reduce cholesterol.
9
New cards
Name the process by which water evaporates through stomata in the leaves.
transpiration
10
New cards
What is the vector of malaria?
A type of mosquito
11
New cards
How can a person be made immune to a specific disease?
vaccination
12
New cards
What is MRSA?
a strain of bacteria that is resistant to antibiotics.
13
New cards
Pathogen
a disease-causing microorganism
14
New cards
What two products are produced when carbon dioxide and water combine in photosyntesis?
glucose and oxygen
15
New cards
What is anaerobic respiration in yeast cells called?
fermentation
16
New cards
What are the chemical messengers produced by the glands of the endocrine system?
hormones
17
New cards
What four hormones are involved in the menstrual cycle?
follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), oestrogen, luteinising hormone (LH) and progesterone.
18
New cards
What type of cell division forms gametes?
meiosis
19
New cards
What word describes having two different alleles for a gene?
heterozygous
20
New cards
What process is the gradual change in the inherited characteristics of a population over time?
evolution
21
New cards
What is the classification system called in which organisms are given two-part name made up of their genus + species?
The binomial system.
22
New cards
What is a population?
A group of individuals of one species living in a habitat.
23
New cards
Immune system
the body's defence system against infections and diseases (consists of white blood cells and antibodies)
24
New cards
Phagocytosis
the process by which one cell, such as a white blood cell, surrounds and engulfs another cell
25
New cards
Antibody
a protein produced in the body by the immune system to kill specific pathogens
26
New cards
Antigen
a marker molecule found on the surface of microorganisms
27
New cards
Antitoxin
a chemical released from white blood cells that can neutralise harmful toxins
28
New cards
Immunity
the ability to attack a pathogen before it causes disease due to a previous encounter with the pathogen
29
New cards
Vaccination
a liquid preparation containing inactive or dead pathogens, used to make the body produce antibodies to provide protection against disease
30
New cards
Antibiotics
medication used to kill bacterial pathogens inside the body
31
New cards
MRSA
(Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus) - an antibiotic-resistant bacterium; a 'superbug'
32
New cards
Digitalis
a drug extracted from foxgloves, used to treat heart problems
33
New cards
Aspirin
a painkilling drug first extracted from the bark of willow trees
34
New cards
Penicillin
an antibiotic extracted from the Penicillium fungus
35
New cards
Double-blind trial
a trial where neither the patient nor the doctor know if the patient is receiving the test drug or a placebo
36
New cards
Placebo
a dummy drug given to patients during drug trials
37
New cards
Pathogen
a disease-causing microorganism
38
New cards
vector
an organism that carries a pathogen but does not suffer from the disease
39
New cards
toxin
a poisonous chemical, produced by certain pathogens
40
New cards
nonspecific defences
the first line of defence against pathogens in general, includes skin, hair, mucus, etc.
41
New cards
Oestrogen
controls development of female secondary sexual characteristics; secreted from the ovaries
42
New cards
Progesterone
regulates menstrual cycle; secreted from the ovaries
43
New cards
anti-diuretic hormone
also known as ADH; secreted by the pituitary; controls the water content of the blood; makes the collecting ducts of nephrons more permeable to water so that more water is reabsorbed
44
New cards
adrenalin
prepares the body for physical activity; released from the adrenal glands

45
New cards
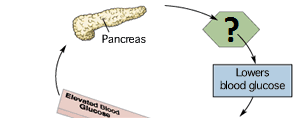
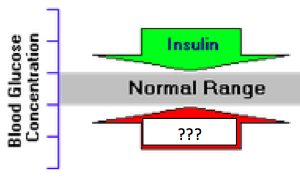
insulin
lowers blood glucose; instructs liver and muscle cells to absorb glucose and store it as glycogen; secreted by the pancreas
46
New cards
glucagon
increases blood glucose levels; instructs liver and muscle cells to convert glycogen to glucose and release it into the blood; secreted by the pancreas
47
New cards
testosterone
controls development of secondary sexual characteristics in males; secreted by the testes
48
New cards
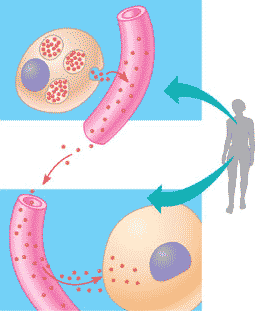
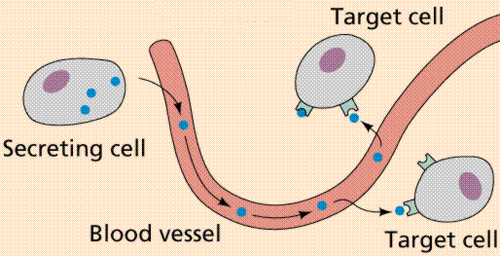
hormone
a chemical messenger; secreted by glands directly into the bloodstream; travels round the body dissolved in blood plasma
49
New cards
target organ
contains receptors on its cells allowing the hormone to bind to the cell membrane and deliver its instructional message
50
New cards
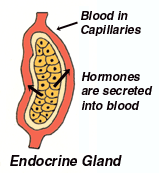
endocrine gland
ductless glands, secreting hormones directly into the blood vessels that pass through the gland