Freshman Biology Unit 1: Cells
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Nucleus
Contains genetic information and directs all cell activities.
Mitochondria
Storing and creating all energy from food using cellular respiration.
Ribosome
Makes protein by reading genetic information
Chloroplast
Converts energy from the sun with carbon dioxide and water into glucose using photosynthesis.
rough ER (endoplasmic reticulum)
The transportation system of the cells transports proteins. Contains ribosome
Golgi
Packages things up during the cell and sorts proteins and other cellular substances.
Vacuole
Storage facility, store water
Cell Membrane
Provide a protective barrier for the cell, and regulates what enters and exits the cell
Lysosome
Recycling and waste disposal system, breaking down proteins and molecules.
Active transport
The process of moving substances across a cell membrane against their from a low-concentration area to a high-concentration area.
Passive Transport
Natural movement of substances from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Osmosis
The movement of water across a cell's membrane
Diffusion
Natural movement of molecules from an area where they are crowded together (high concentration) to an area where they are more spread out (low concentration)
Facilitated Diffusion
A type of passive transport that helps molecules cross the cell membrane
Isotonic
Water and substances diffuse into and out of the cell at the same rate.
*if there are 11 cells on the outside and inside they are = making it isotonic.
Hypotonic
Solute concentration is higher (more water inside), and water diffuses into the cell, making the cell swell.
*more in the picture
Hypertonic
Solute concentration is higher outside the cell less water inside
less inside picture
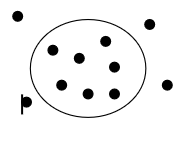
Which solution is this?
Hypotonic
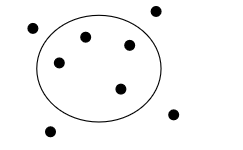
what solution is this
hypertonic
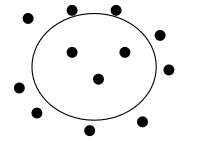
Which solution is this
Isotonic
Where does photosynthesis occur?
where chlorphyll (a pigment) absorbs light energy
Cellular respiration
Once food (glucose) is created it needs to break it down to release energy
Aerobic
type of respiration with oxygen
Anaerobic
type of respiration without oxygen
ATP (energy)
A cell uses the energy from ATP to do all of its work, such as moving, growing, and building important molecules. (like a battery)
Prokaryote
no nucleus
Eukaryotic
has a membrane bound nucleus.
What is the largest cell in the human body?
The egg cell
Name an organelle that is not found in an animal cell
Chloroplast
Name an organelle that is not found in a plant cell and contains digestive enzymes for breaking down material in the cell
Lysosomes
What organelle in plants has a pigment in it that gives plants their green color
Chloroplast
What type of cell respiration will result in 36 ATP (energy molecules)?
Aerobic
What is the movement of oxygen from a greater concentration in the alveoli to a less concentration in the capillaries
Diffusion
When using scanning power which adjustment knob should you use first
Coarse adjustment knob
What is interesting when comparing the reaction for photosynthesis and cell respiration
The switch up (opposite)
What is the movement of H20 across the membrane of a cell called
Osmosis
What type of solution are you creating when you overwater plants
hypotonic
What happens if you put a freshwater plant in saltwater
it will shrink