Chapter 3 Biological Molecules
1/86
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
hydrocarbons
Consist of carbon and hydrogen.
Covalent bonds store considerable energy.
These are nonpolar → when functional groups ARE ADDED, THEY CONFER chemical properties to the molecule
Functional groups
Small, reactive groups of atoms which give larger molecules specific chemical properties
(Ex. hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, phosphate, sulfhydryl)
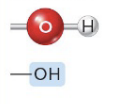
Hydroxyl
(—OH) (Ex. Alcohols)
Polar
Hydrogen bonds with water, facilitating dissolving of organic molecules
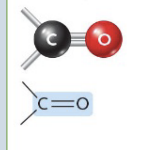
Carbonyl
(C = O) (Ex. Aldehydes and Ketones)
Building blocks of carbohydrates + supply energy for cell activities
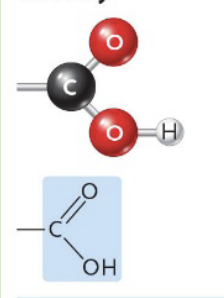
Carboxyl
(Ex. Carboxylic acids)
Give organic molecules acid properties (-OH group releases H+)
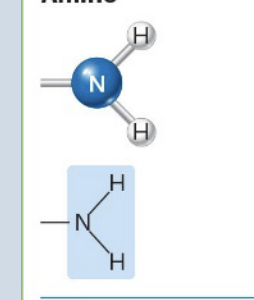
Amino
Acts as an organic base by accepting a proton (H+)
→ Converts from non-ionized to ionized
(Ex. Amines)
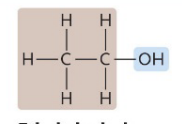
Ethyl alcohol
A type of alcohol
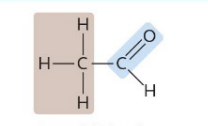
Acetaldehyde
A type of aldehyde
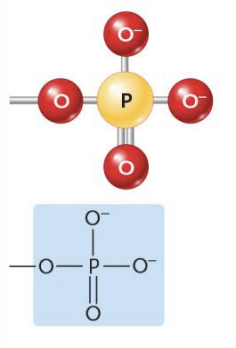
Phosphate
(Ex. Organic Phosphates)
Molecules that contain these act as weak acids
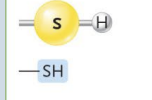
Sulfhydryl
(Ex. Thiols)
Easily converted into covalent bond → loses its hydrogen atom as it binds
In many reactions, two of these groups form a disulfide linkage
Isomers
Molecules with the same molecular or empirical formula but different molecular structures
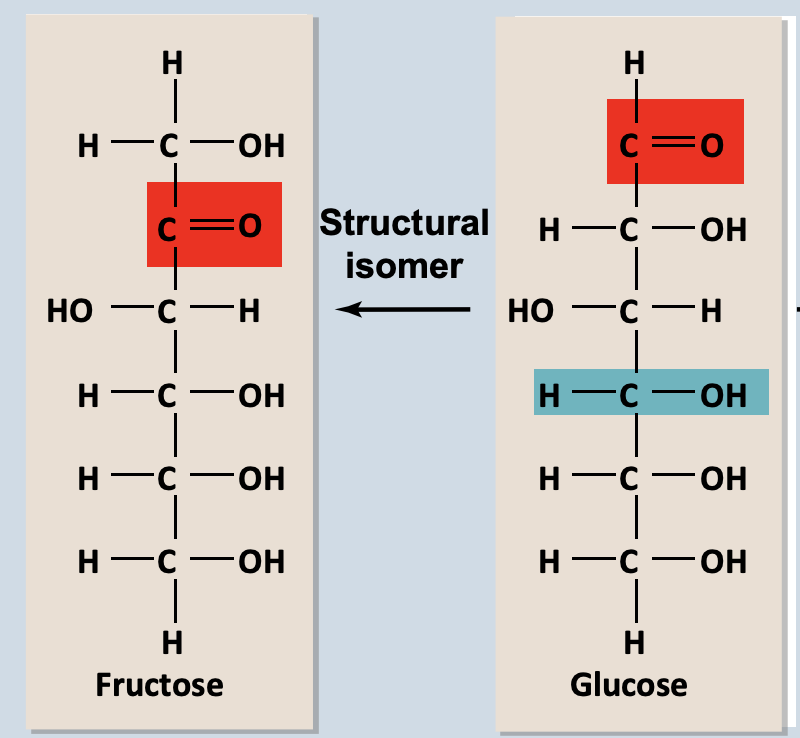
Structural Isomers
Same chemical formula but arrangement of atoms are different
Example: glucose – aldehyde and fructose - Ketone
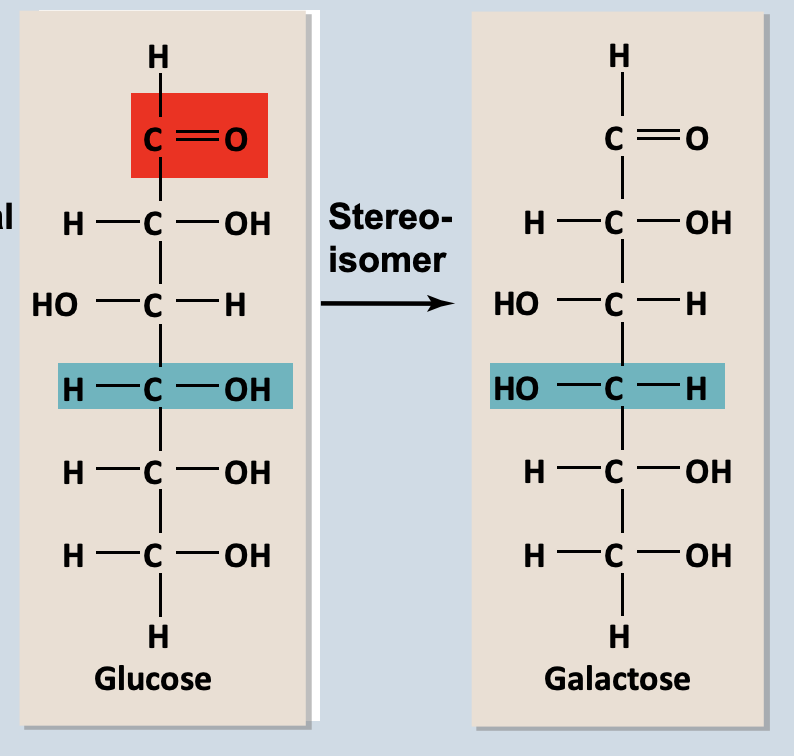
Stereoisomers
Differ in how groups attached
Examples are D-sugars and L-sugars
Enantiomers → mirror image molecules, chiral carbon
Polymer
built by linking monomers
Monomer
small, similar chemical subunits
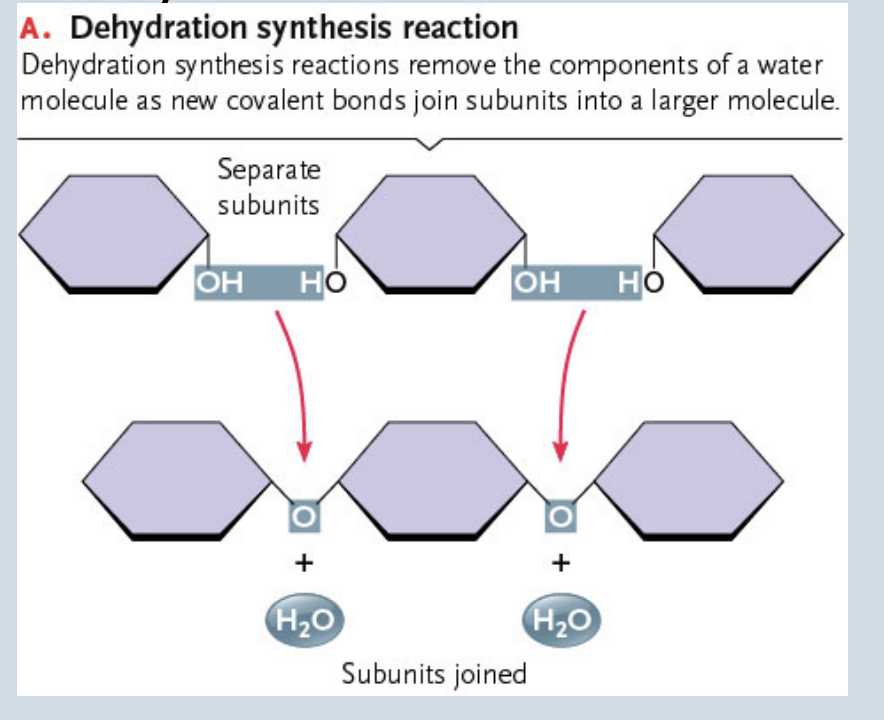
Dehydration synthesis
Formation of large molecules by the removal of water
Monomers are joined to form polymers
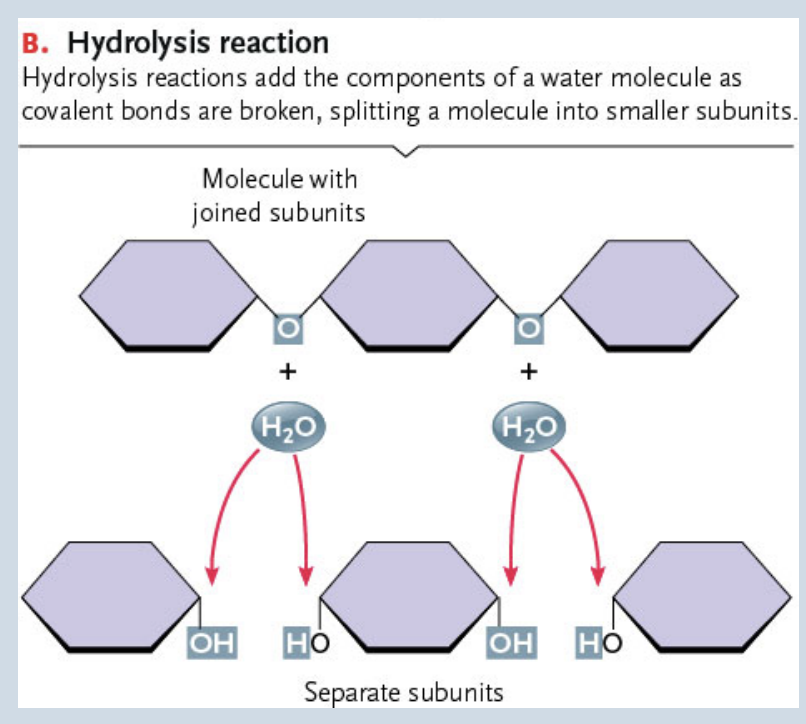
Hydrolysis
Breakdown of large molecules by the addition of water
Polymers are broken down to monomers
Carbohydrates
Molecules with a 1:2:1 ratio of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
C—H covalent bonds hold much energy
Monosaccharides
Simplest carbohydrate
(Ex. Glucose)
All occur in linear form
If they have 5+ carbons they can fold back and form a ring
α-glucose (Alpha glucose)
—OH group pointing below the plane of the ring
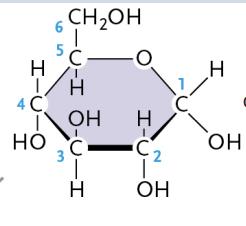
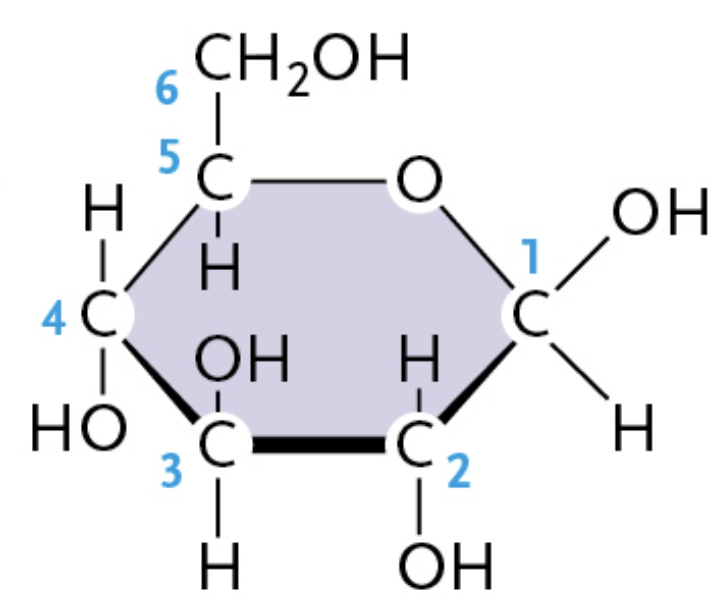
β-glucose (Beta glucose)
—OH group pointing above the plane
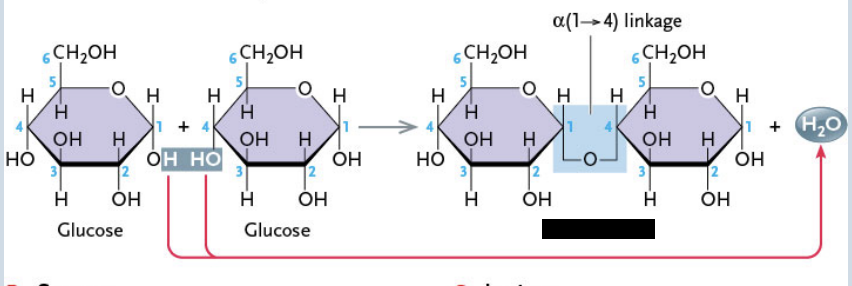
Disaccharides
Assembled from two monosaccharides covalently joined by a dehydration synthesis reaction
Ex. Maltose formed by a glycosidic bond that links two α-glucose molecules with oxygen
Maltose
Assembled from two α-glucose molecules (1 → 4 carbon linkage)
Sucrose
Formed from an α-glucose and fructose (1 → 2 linkage)
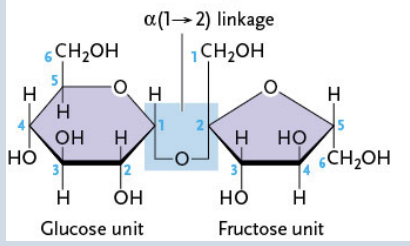
Lactose
Assembled from galactose and β-glucose (1 → 4 linkage)
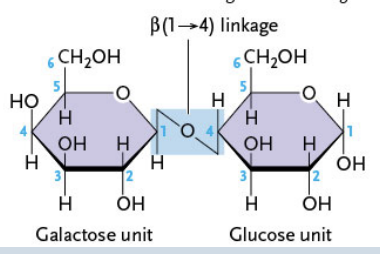
Polysaccharides
Long chains (10+) of monosaccharides → linked through dehydration synthesis
May be linear, unbranched molecules or may contain branches which side chains of sugar units are attached
Ex. Amylose and Glycogen
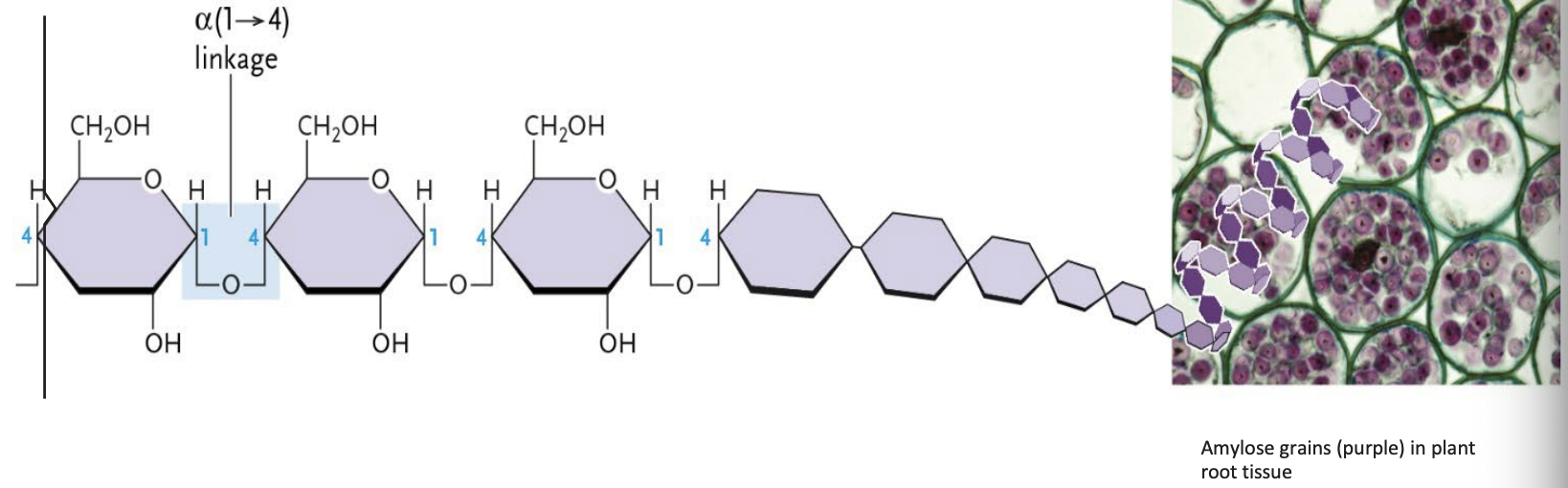
Amylose
A plant starch
Formed from α-glucose units joined end to end in alpha (1 → 4) linkages
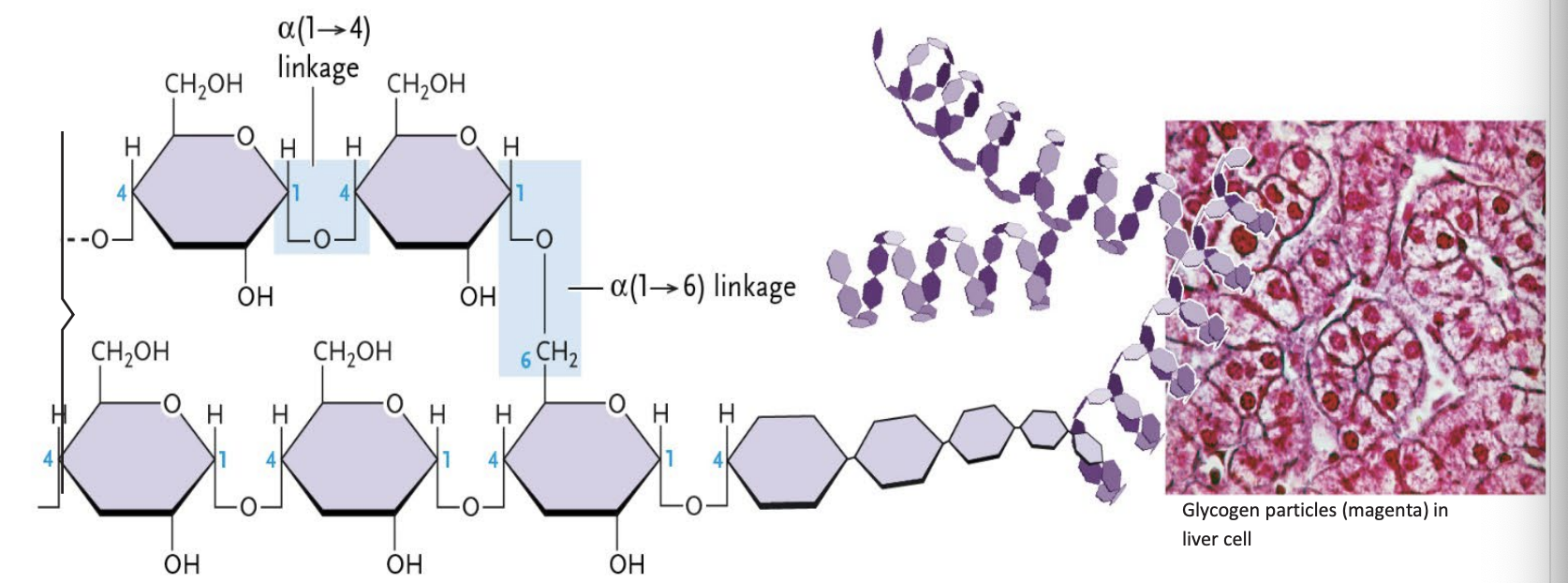
Glycogen
Found in animal tissues
Formed from glucose units joined in chains by α( 1 → 4 ) linkages
Side branches are linked to the chains by α(1 → 6) linkages (boxed in blue).
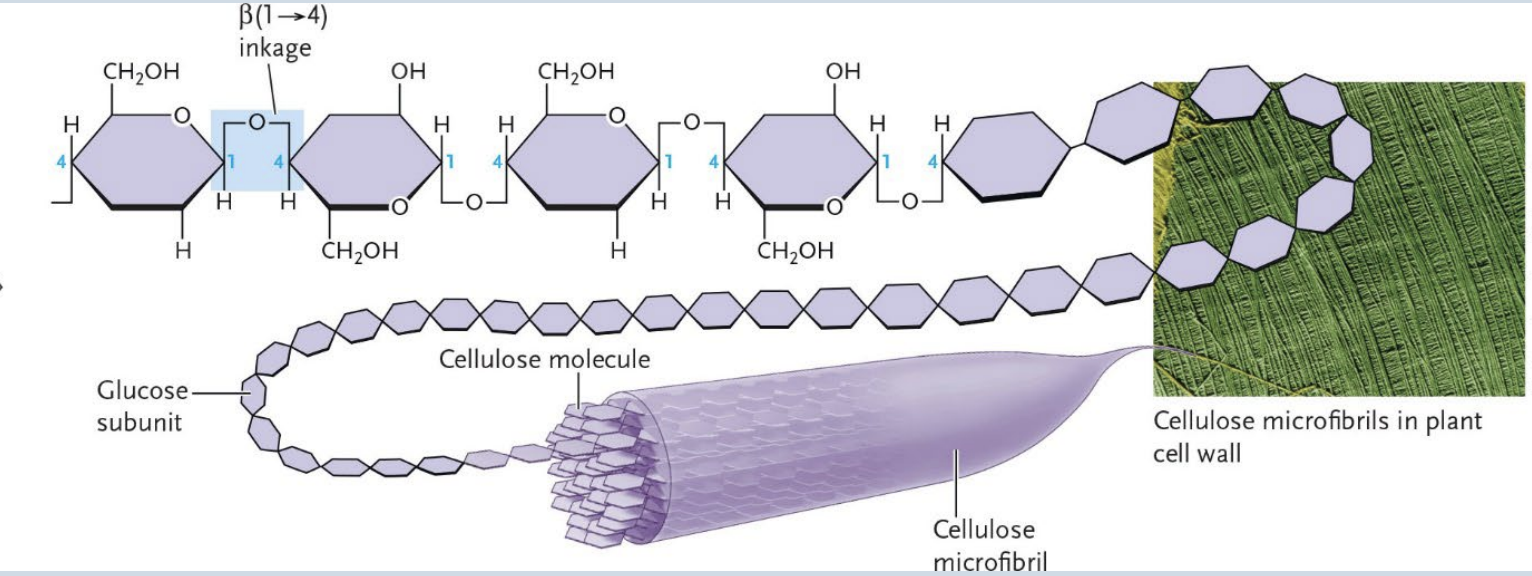
Cellulose
Primary fiber in plant cell walls
Formed from glucose units joined end to end by beta (1 → 4) linkages
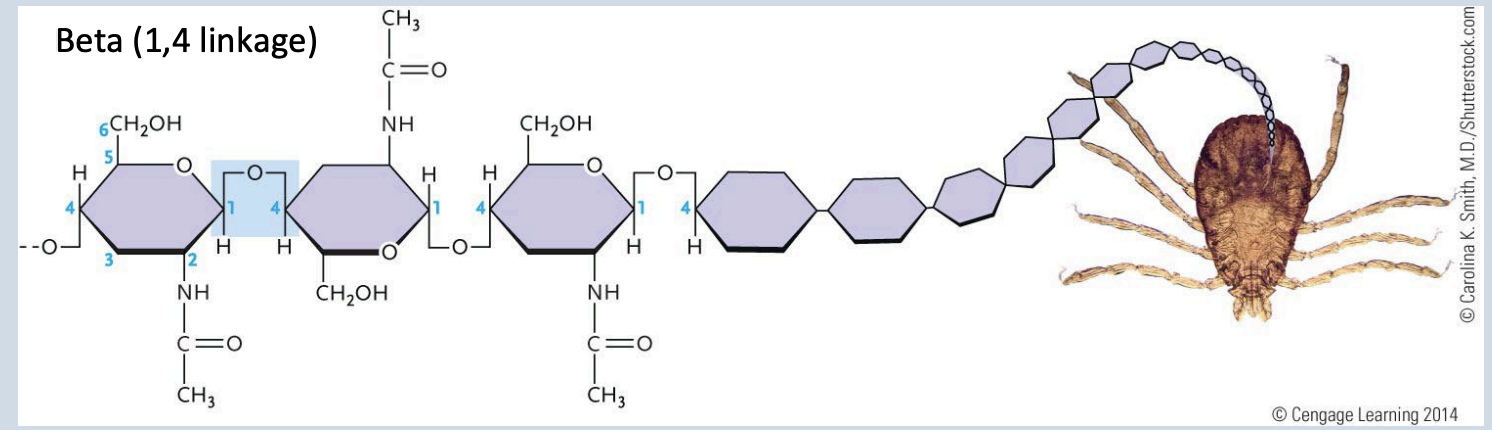
Chitin
A reinforcing fiber in the external skeleton of arthropods and the cell walls of some fungi
Beta (1 → 4 linkage)
Lipids
Water-insoluble, primary nonpolar biological molecules composed of mostly hydrocarbons
Three common types: neutral, phospho-, and steroids
Neutral Lipids
Found in cells as energy-storage molecules and have no charged groups (nonpolar)
Two types:
Oils → liquid at biological temps
Fats → semisolid
Fatty Acid
A type of lipid that contains a single hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group (—COOH) at one end
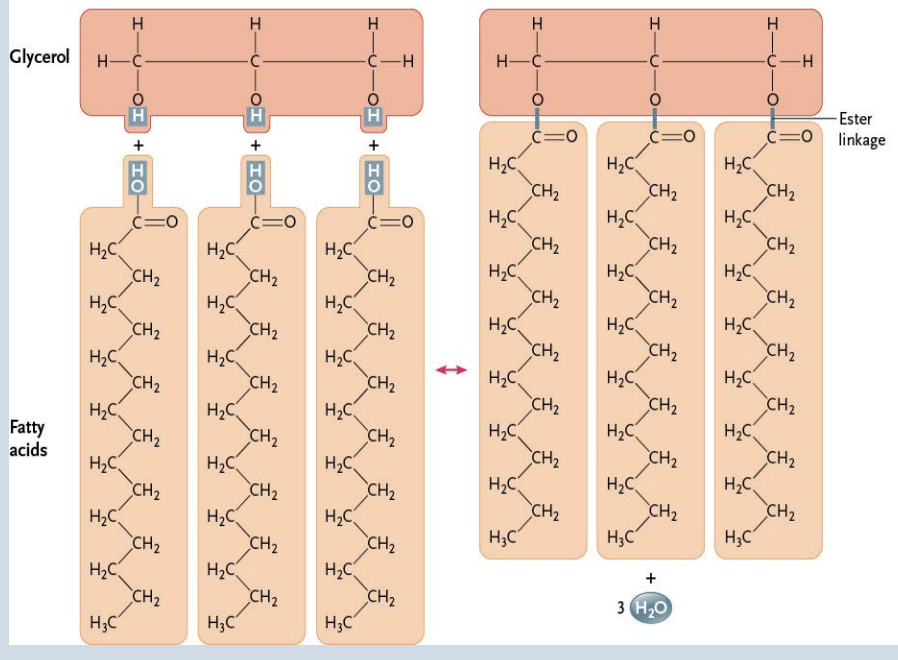
Triglycerides
Form by dehydration synthesis between three-carbon glycerol (an alcohol) and three fatty acid side chains
→ ester linkage forms between -COOH group of the fatty acid and the -OH group of the glycerol
→ Polar groups of glycerol eliminated which forms a nonpolar molecule
Serve as energy reserves in animals
Saturated fatty acid
A fatty acid that binds the maximum number of hydrogen atoms
→ only single bonds exist between carbon atoms
Monounsaturated
Fatty acids with one double bond
Polyunsaturated
Fatty acids with more than one double bond
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Fatty acids (such as vegetable oils) bend at a double bond and are more fluid at biological temperatures
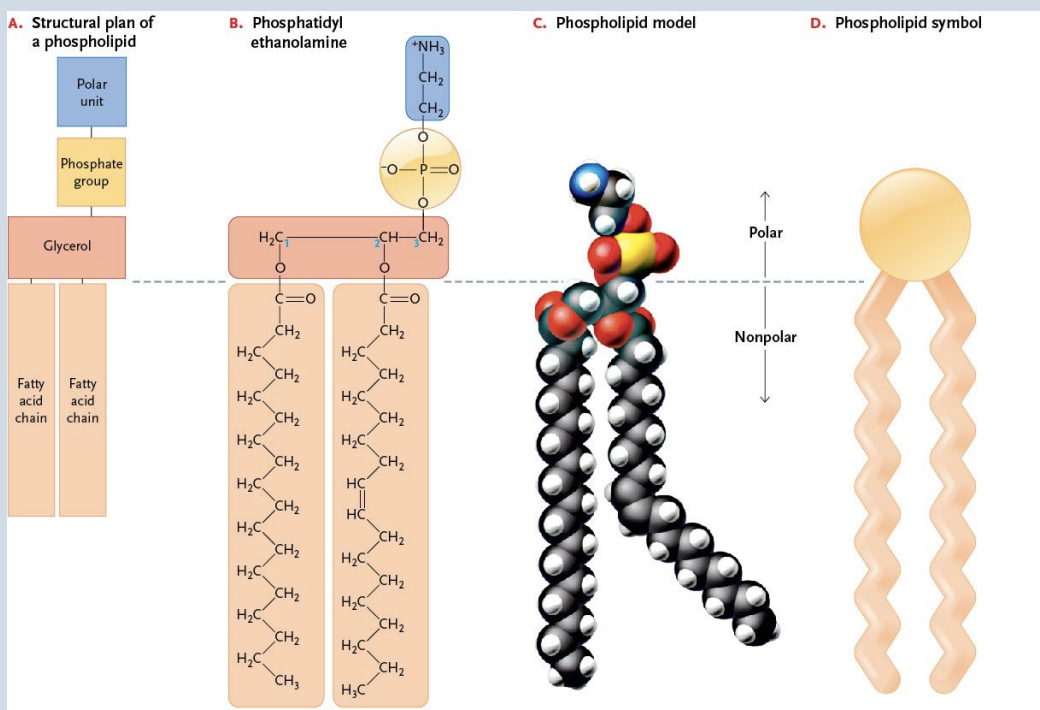
Phospholipids
Composed of → Glycerol + 2 fatty acids (nonpolar “tails”) + a phosphate group (polar “head”)
Form all biological membranes
Four types → – Serine, ethanolamine, Choline, and Inositol
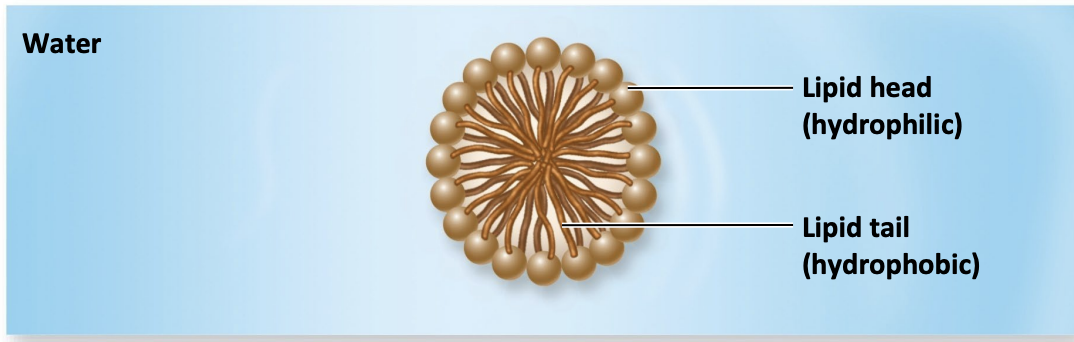
Micelles
Lipid molecules orient with polar (hydrophilic) head toward water and nonpolar (hydrophobic) tails away from water
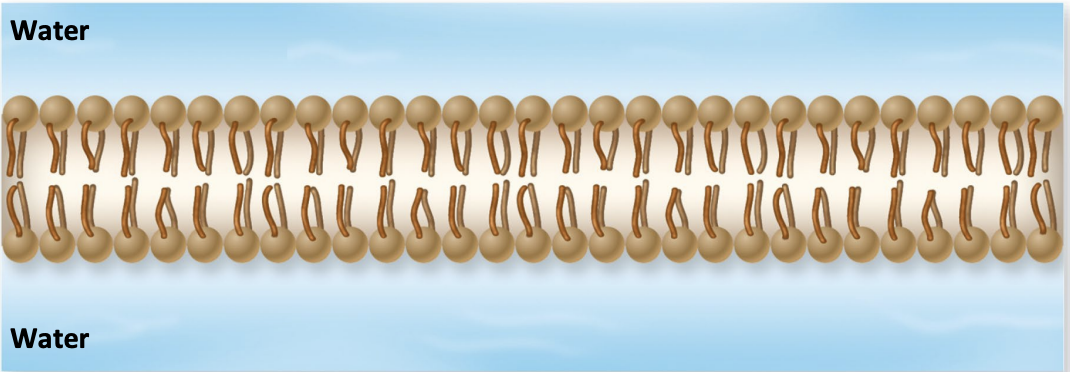
Phospholipid bilayer
More complicated lipid structure where 2 layers form
→ Hydrophilic heads point outward
→ Hydrophobic tails point inward toward each other
The structural basis of membranes
Waxes
Formed when fatty acids combine with long-chain alcohols/hydrocarbon structures
Harder and less greasy than fats
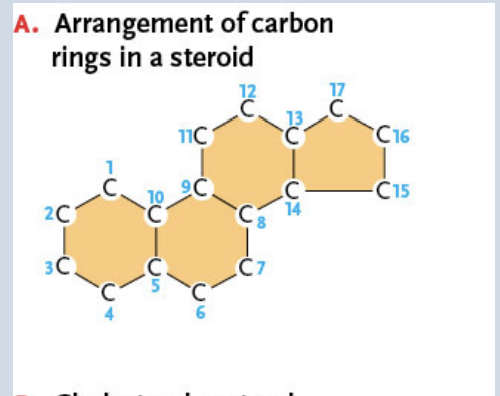
Steroids
Lipids with structures based on a framework of four carbon rings
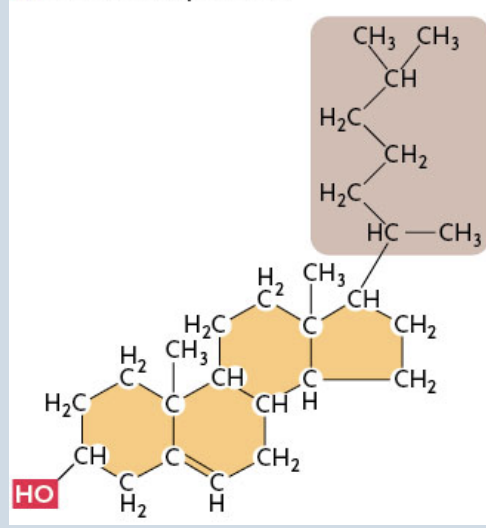
Sterols
The most common steroids
Have a single polar OH group linked to one end of the ring framework and a complex, nonpolar hydrocarbon chain at the other end
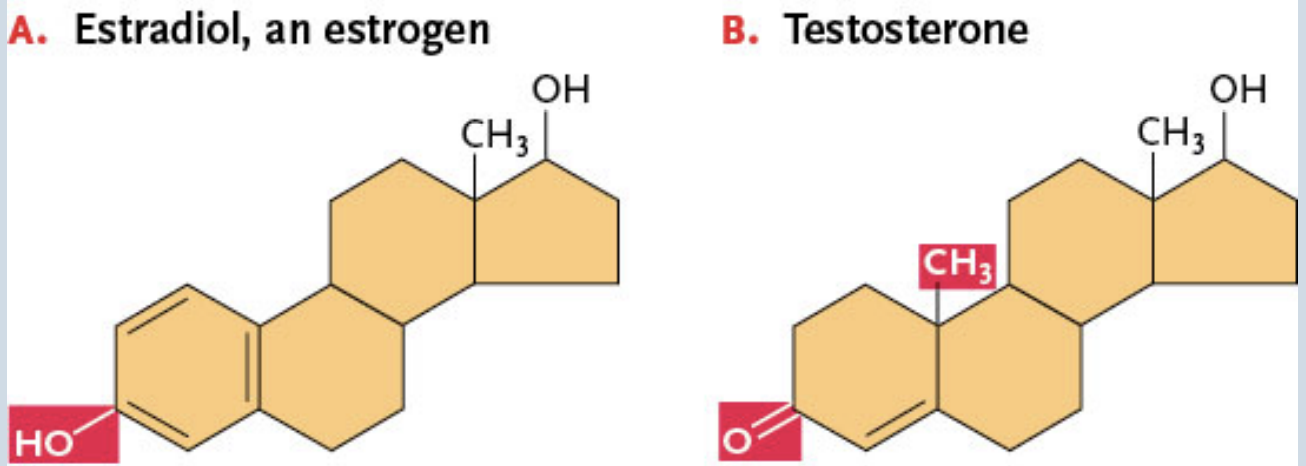
Ex. Cholesterol (picture shown)
Steroid hormones
Control development, behavior, and many internal biochemical processes
Examples: Sex hormones
→ Estradiol (an estrogen) → has an —OH
→ Testosterone → has an =O where the —OH was + an extra estradiol
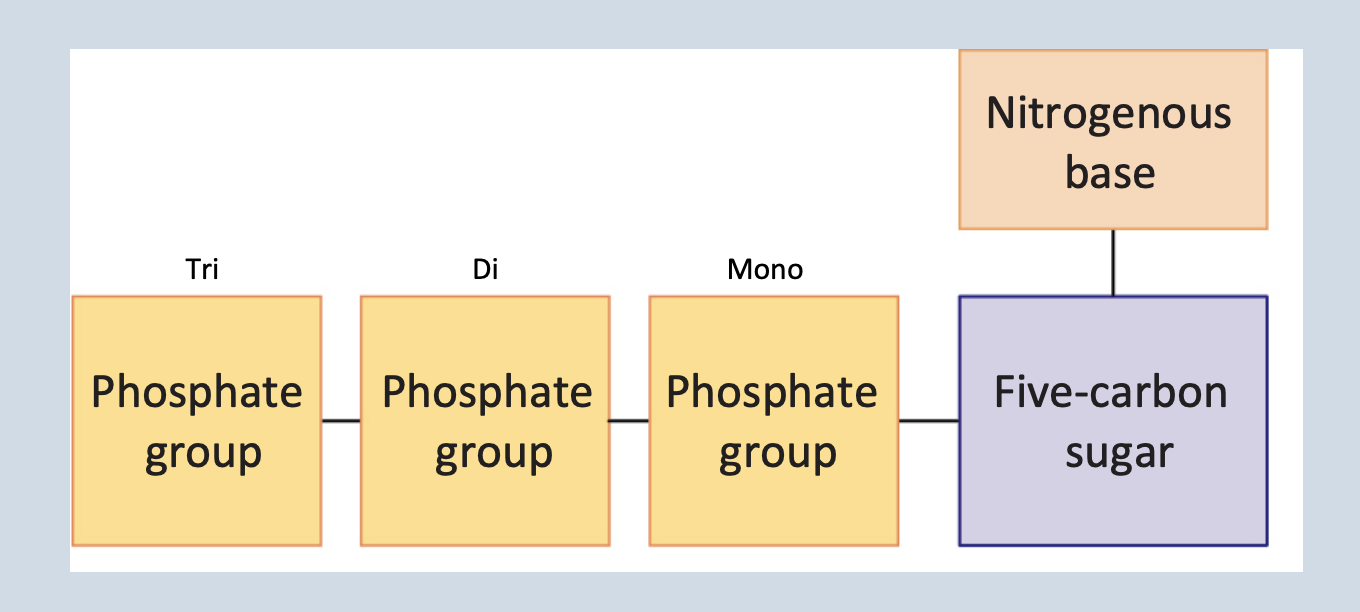
Nucleic Acids
A polymer (ex. DNA and RNA)
Monomers → nucleotides that are connected by phosphodiester bonds
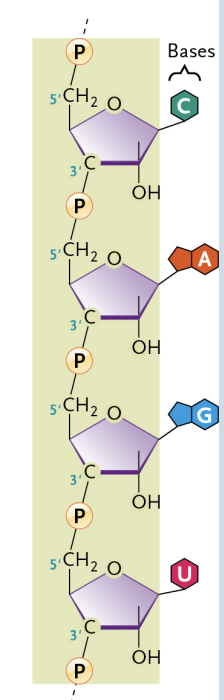
Nucleotide
Monomers that are sugar + phosphate + nitrogenous base
Connected by phosphodiester bonds
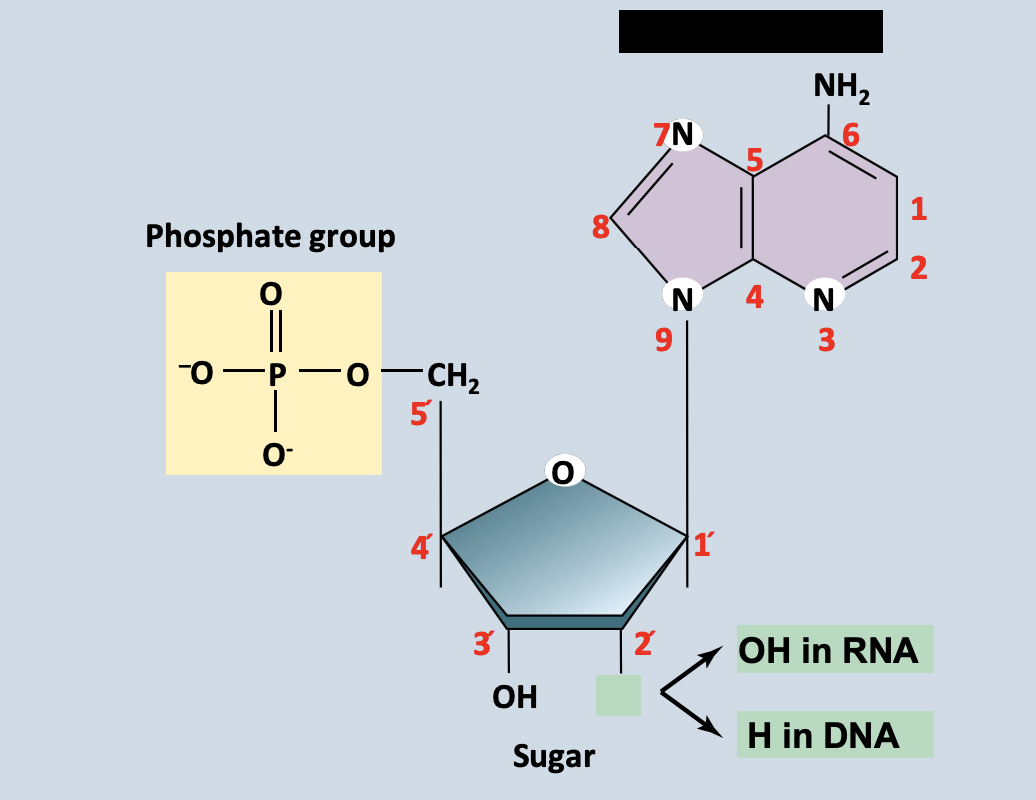
Nucleosides
A structure containing only a nitrogenous base and a five-carbon sugar
Nitrogenous base
Link covalently to a five-carbon sugar
Ex. Deoxyribose in DNA deoxyribonucleotides + Ribose in RNA ribonucleotides
Pyrimidines
Nitrogenous bases with one carbon-nitrogen ring
Ex. Uracil (U), thymine (T), and cytosine (C)
Purines
Nitrogenous bases with two carbon–nitrogen rings
Adenine (A) and guanine (G)
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
Encodes information for amino acid sequence of proteins
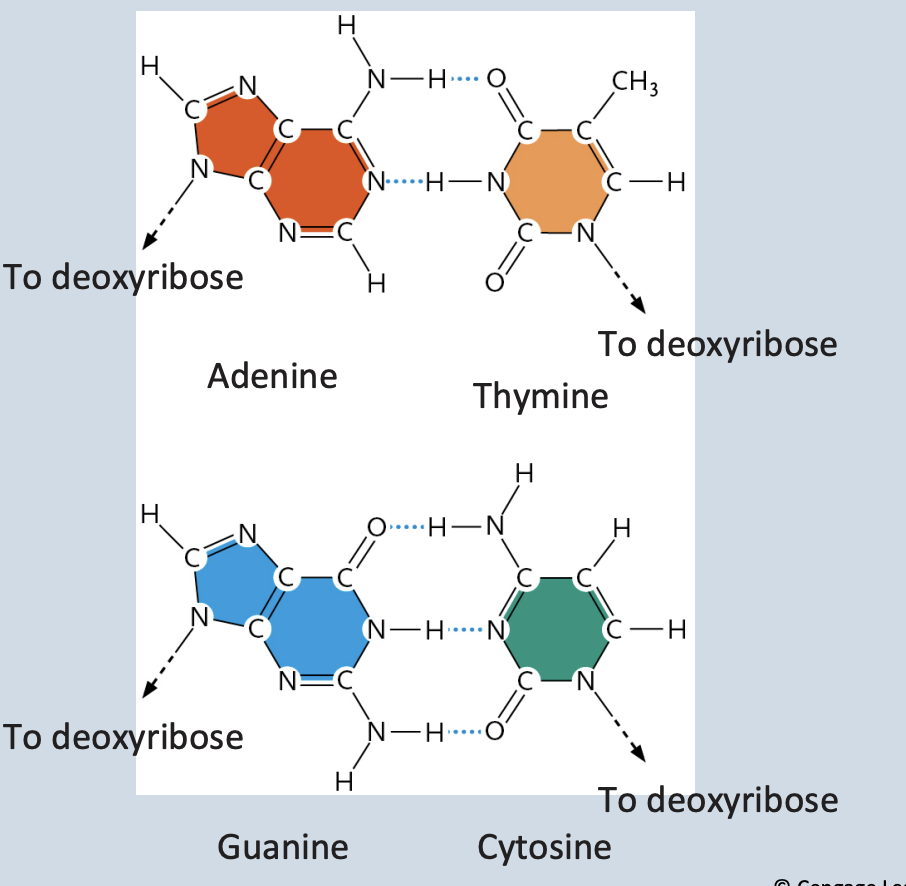
Double helix → 2 polynucleotide strands connected by hydrogen bonds
Base-pairing rules → A with T → G with C
Consist of polynucleotide chains, with one nucleotide linked to the next by a phosphodiester bond
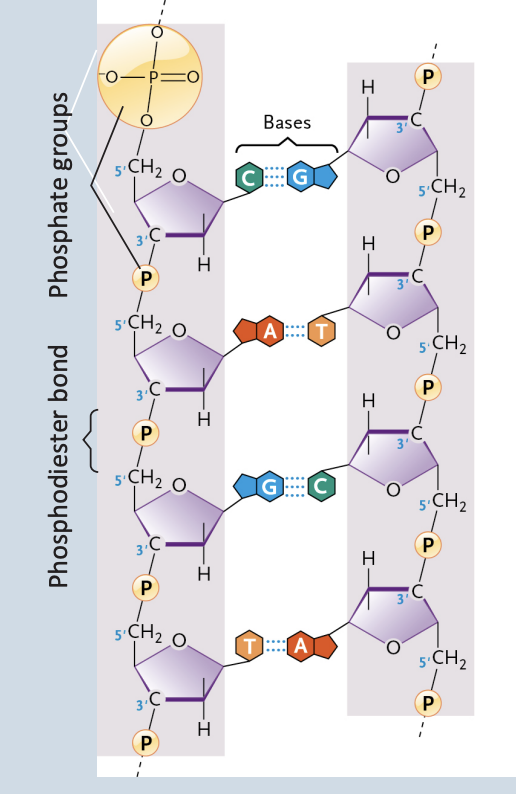
DNA base pairs
Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
Exist mainly as single polynucleotide chains (singlestranded) → however, these molecules can fold back on themselves to form double-helical regions
The uracil (U) base takes the place of thymine (T), forming A–U base pairs
adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
Primary energy currency of the cell
A type of nucleotide
NAD+ and FAD+
Electron carriers for many cellular reactions
A type of nucleotide
Proteins
Polymers of amino acid monomers → contain an animo and a carboxyl group
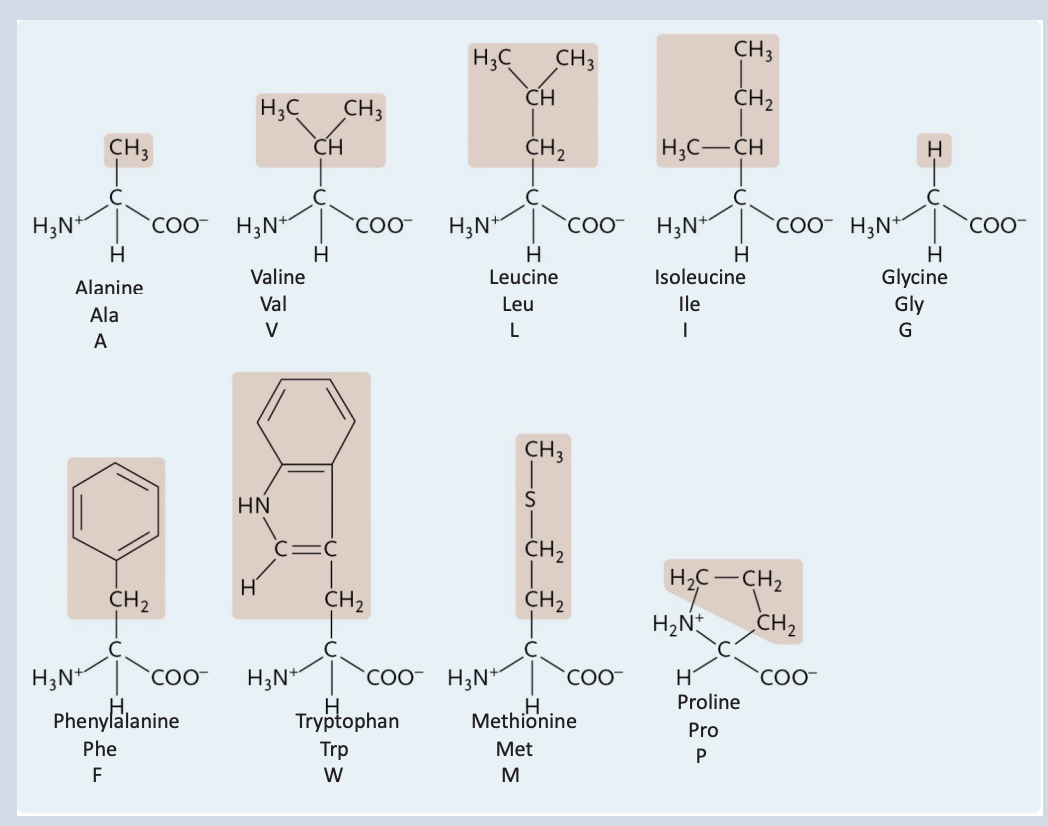
Amino Acids
TWENTY common ones that get grouped into five classes based on side groups
→ nonpolar, polar, charged (positive or negative charge)
Many chemical groups contain reactive functional groups, such as —NH2, —OH, —COOH, or —SH, which interact with other atoms in the same protein or outside the protein
All of them can act as acids or bases
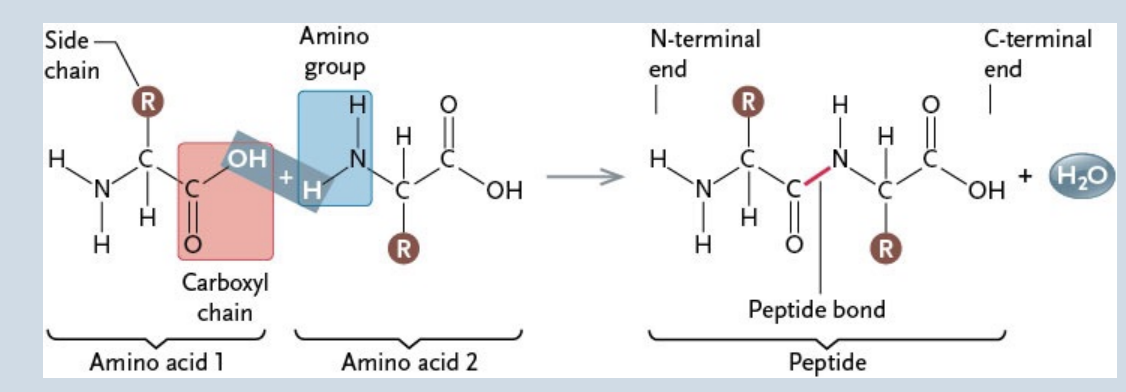
Peptide Bonds
Link amino acids into polypeptide chains (the subunits of proteins)
Formed by a dehydration synthesis reaction between the —NH2 group of one amino acid and the —COOH group of another amino acid
Polypeptide Chain
Has an N-terminal end and a C-terminal end
→ New amino acids are linked only to the C-terminal end
Nonpolar Amino Acids
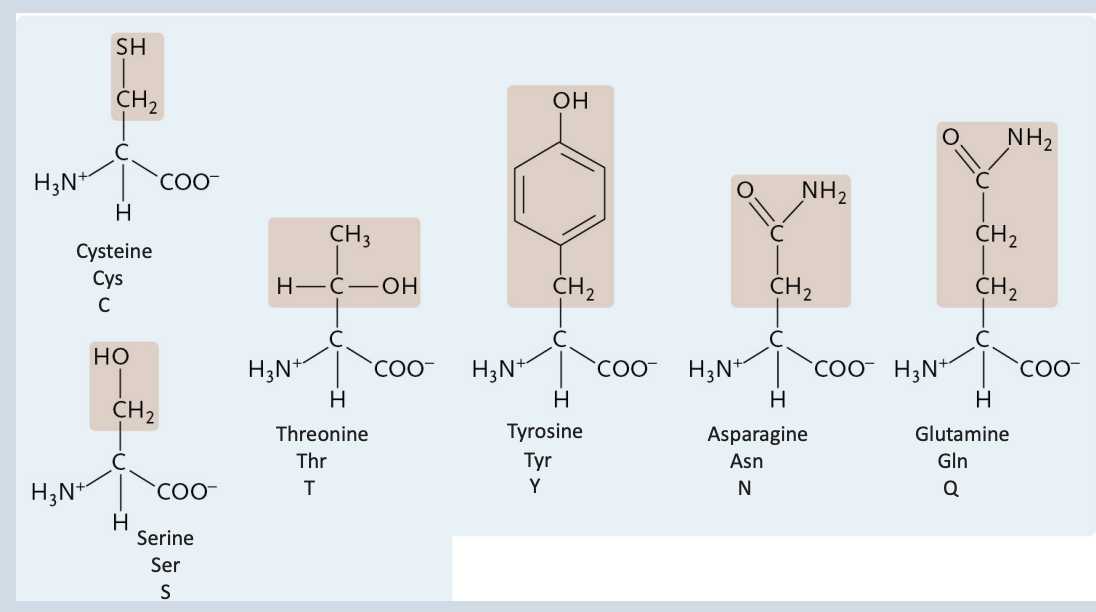
Uncharged Polar Amino Acids
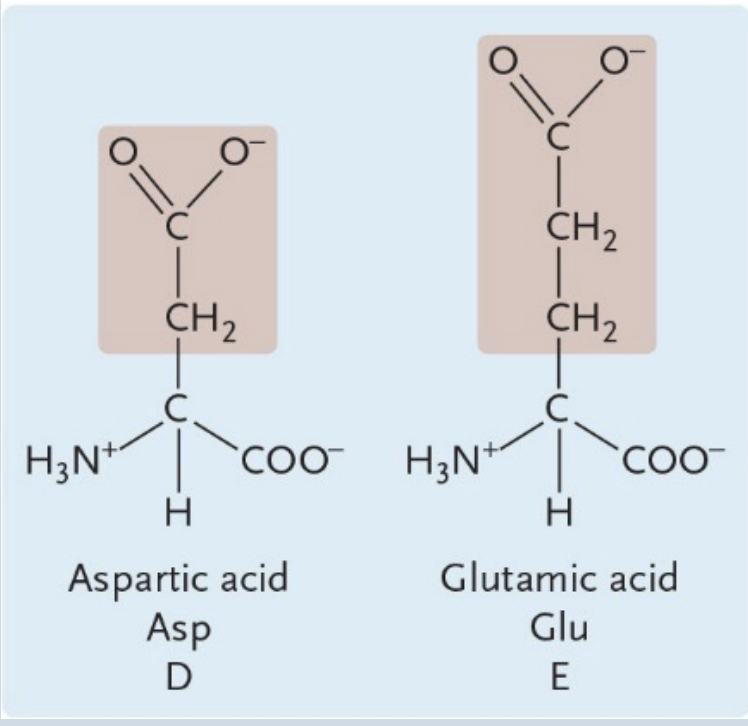
Negatively Charged Amino Acids
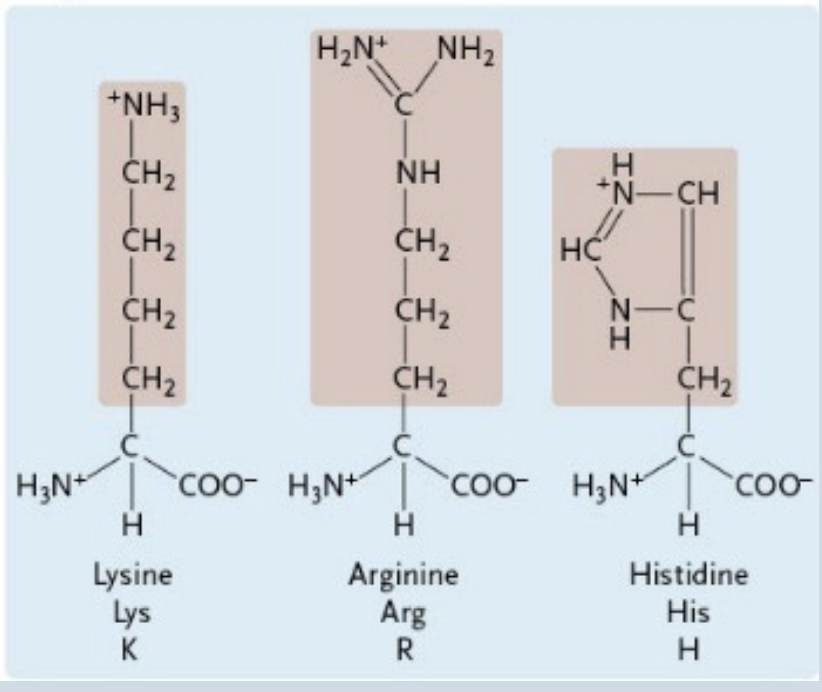
Positively Charged Amino Acids
Primary structure
The precise sequence in which amino acids are linked
Changing even a single amino acid alters secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures – which can alter or destroy the biological function of a protein
Secondary structure
The amino acid chain (primary structure) is folded into arrangements that form the protein’s structure
alpha (α) helix → twisted into a regular right-hand spiral
beta (β) strand → zigzags in a flat plane, forming a sheet
→ Most proteins have segments of both arrangements
Tertiary structure
Gives a protein its overall three-dimensional shape (conformation)
Determines a protein’s function and chemical activity and solubility
Quaternary structure
The presence and arrangement of two or more polypeptide chains
Hydrogen bonds, polar and nonpolar attractions, and disulfide linkages hold the multiple polypeptide chains together
The Random Coil
Has an irregularly folded arrangement
Segments of this provide flexible sites that allow α-helical or β-strand segments to bend or fold back on themselves
→ also act as “hinges” that allow major parts of proteins to move with respect to one another
Denaturation
Unfolding a protein from its active conformation so that it loses its structure and function
Caused by chemicals, changes in pH, or high temperatures
For some proteins it’s permanent and for others it’s reversible
Chaperonins
“Guide proteins” that bind temporarily with newly synthesized proteins, directing their conformation toward the correct tertiary structure and inhibiting incorrect arrangements
Domains
The large subdivision caused by folding of the amino acid chain(s)
In proteins with multiple functions, individual functions are often located in different ____.
Protein Combinations
• Proteins link with lipids to form lipoproteins, which form parts of cell membranes
• Proteins link with carbohydrates to form glycoproteins, which function as enzymes, antibodies, recognition and receptor molecules, and parts of extracellular supports
• Proteins link with nucleic acids to form nucleoproteins, which form structures such as chromosomes
Uracil
(It is a Pyrimidine)
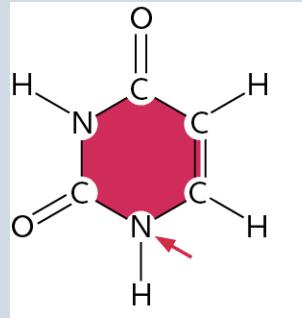
Thymine
(It is a Pyrimidine)
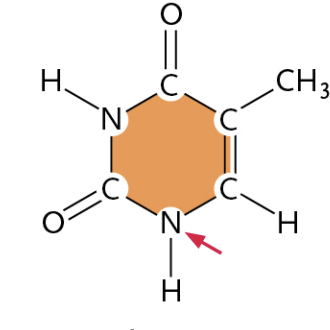
Cytosine
(It is a Pyrimidine)
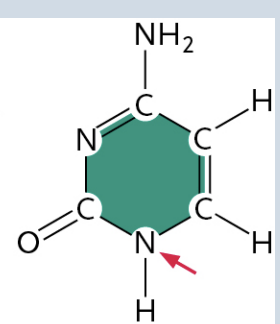
Adenine
(It is a Purine)
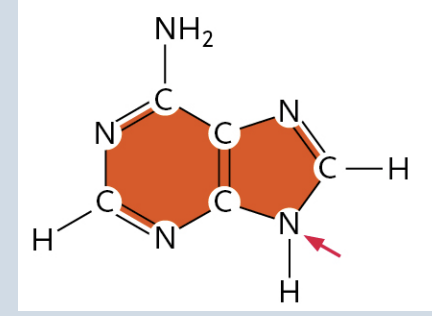
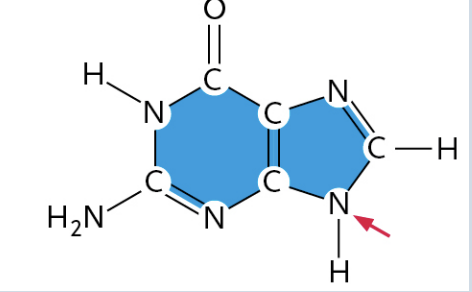
Guanine
(It is a Purine)
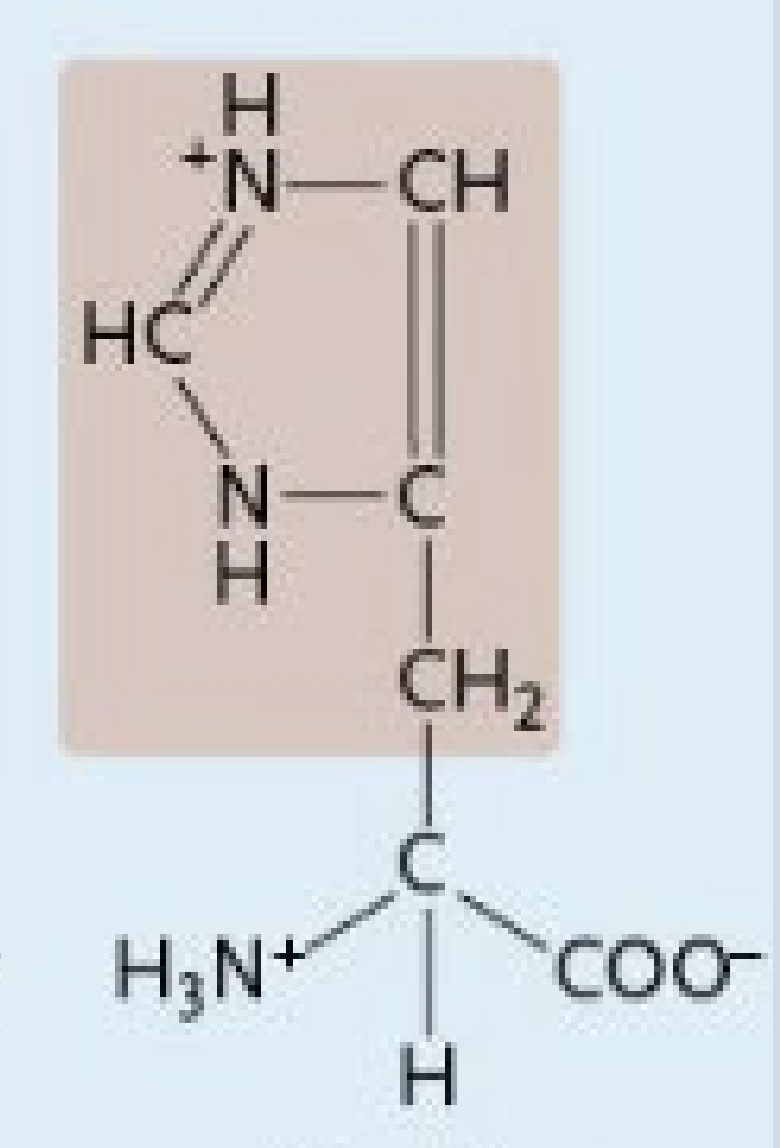
Alanine
A Nonpolar Amino Acid
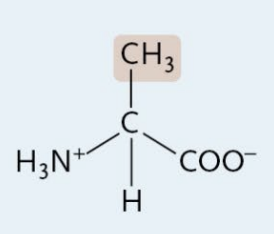
Glycine
A Nonpolar Amino Acid
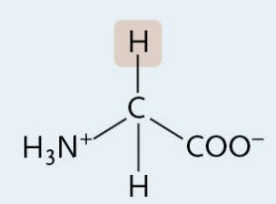
Isoleucine
A Nonpolar Amino Acid
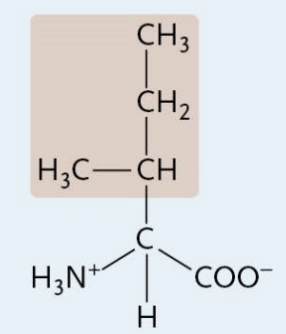
Phenylalanine
A Nonpolar Amino Acid
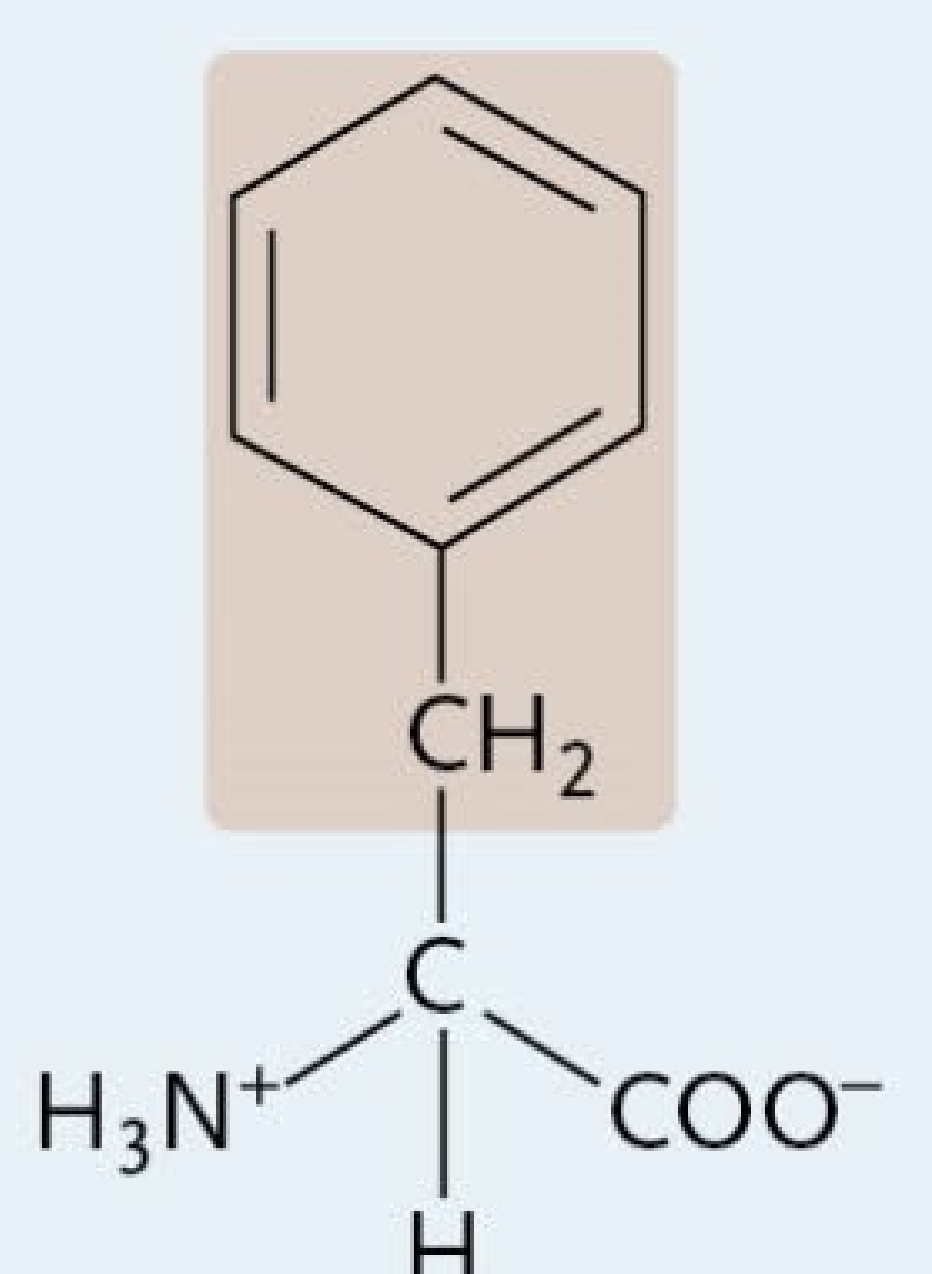
Methionine
A Nonpolar Amino Acid
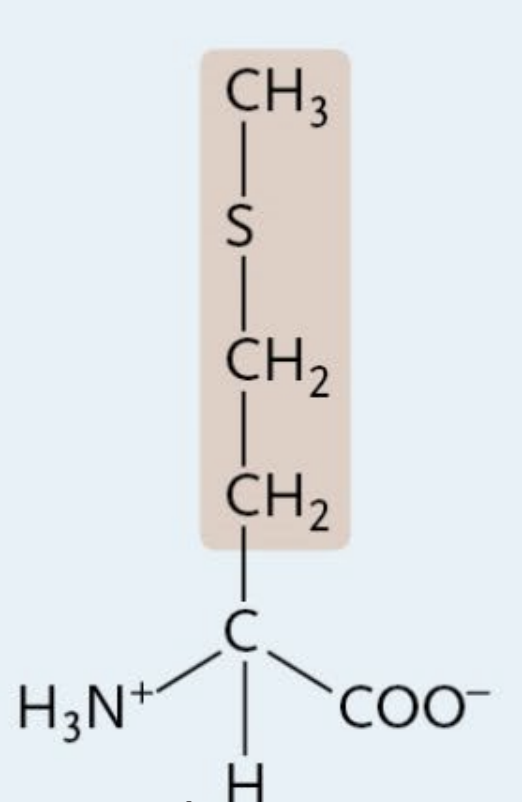
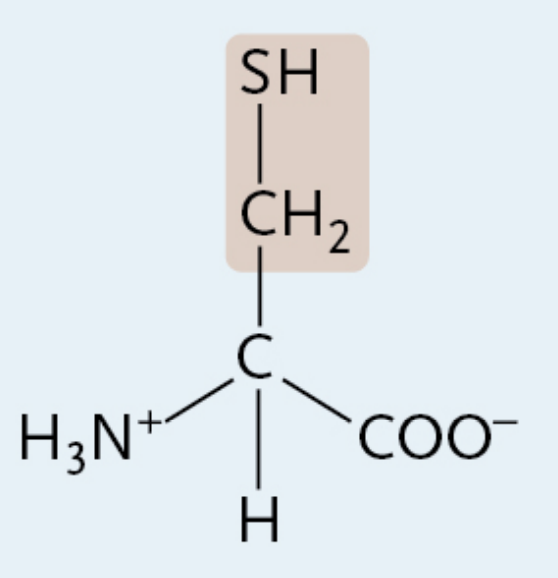
Cysteine
A charged polar amino acid
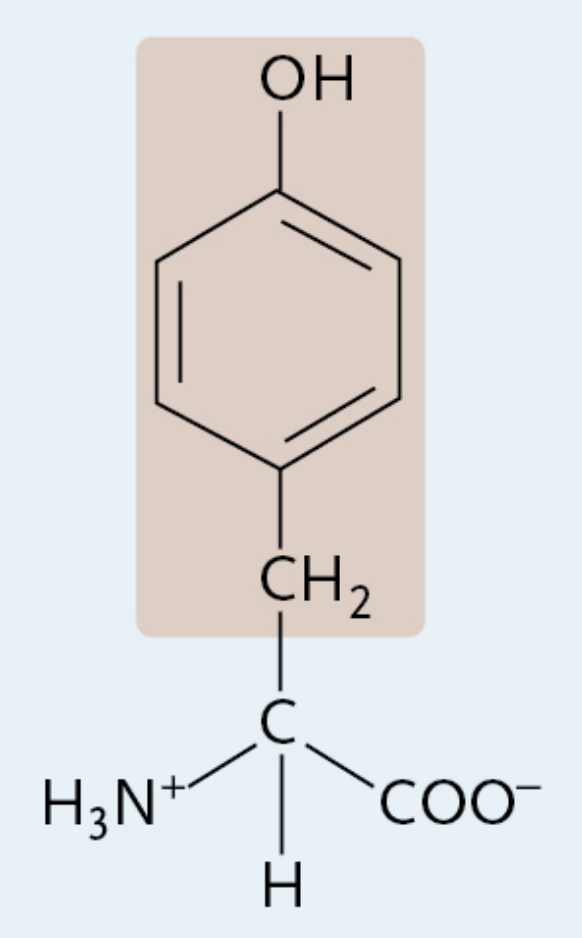
Tyrosine
A charged polar amino acid
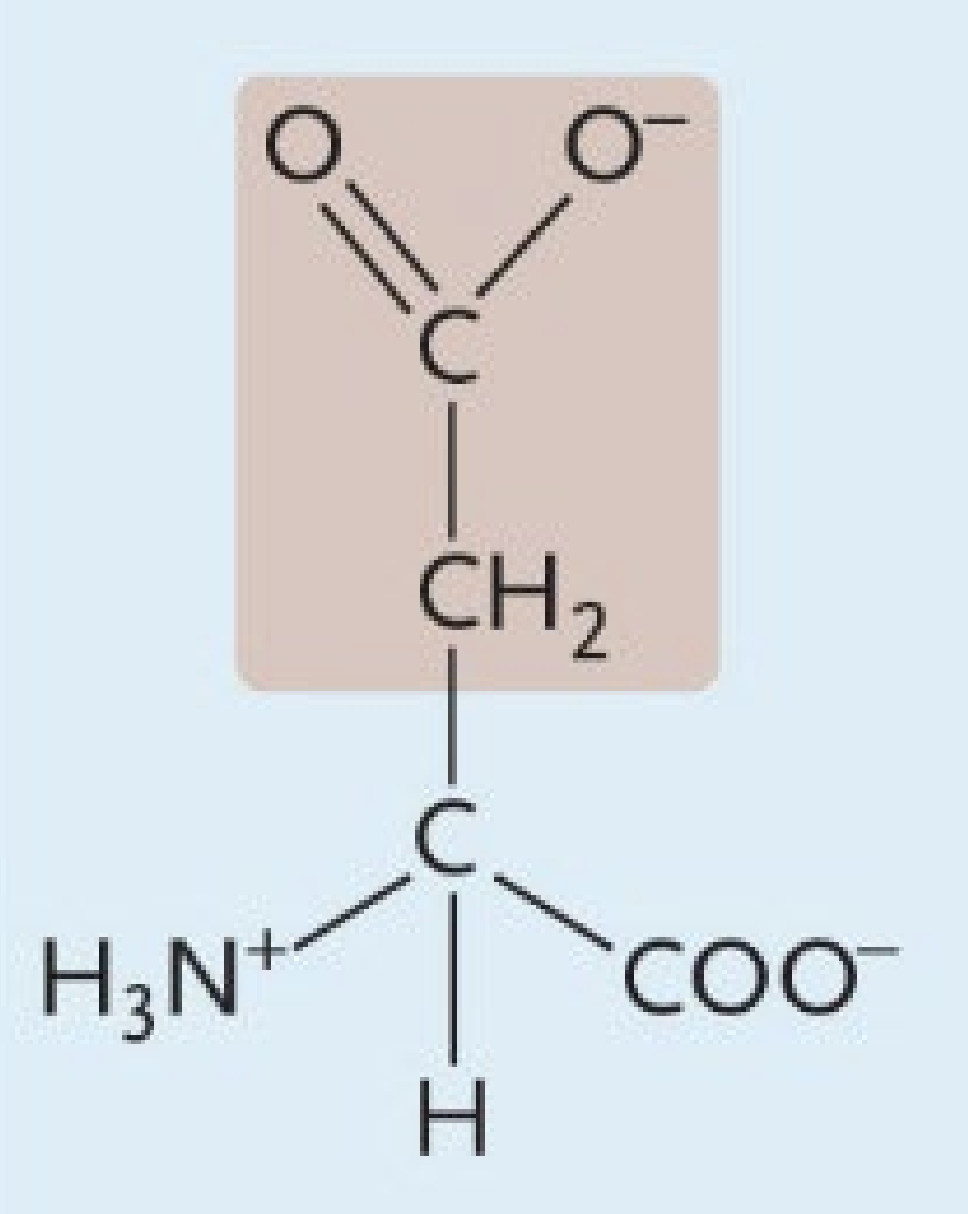
Aspartic Acid
A negatively charged amino acid
Histidine
A positively charged amino acid