lda 150 quiz 1
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
what is a GIS?
Geographical Information System: computer-based system for capturing, storing, querying, analyzing, and displaying geospatial data
components of a GIS
hardware, software, data, people, and methods
what is geospatial data?
information that has a geographic component (includes location details like coordinates, addresses, or postal codes)
three features that make a good map
north arrow, citation, scale
a closed figure composed of x-y coordinates is called a
polygon
a raster portraying a ___ is an example of continuous data
precipitation map
data that has been tied to a specific location on the Earth’s surface is said to be ___
georeferenced
the basic element of data storage in a raster is called a ___
layer
You are planning a hike. You measure the trail on a 1:24,000 scale map and discover that it is 30 cm long. How long is the hike in kilometers?
7.2 kilometers (multiply 24,000 by the converted value of 30 cm to km)
information about a data set, such as who created it and why, is called_
metadata
citing the source of data used in a map or a report___
is a professional and ethical responsibility
which one of the ArcGIS family of products is most tightly coupled to ArcGIS Online?
ArcGIS Pro
the geometric figure that most accurately represents the earth's surface is the ___
geoid
which of the following accurately describes the key components of a datum?
a reference ellipsoid or spheroid, an origin point, and reference points
degrees of latitude and longitude measure….
angles from the center of an ellipsoid
if choosing a datum for a coordinate system in the conterminous United States, which one of the
following is usually the best choice and why?
NAD 1983 (2011), because it is the most recent
the distance represented by a degree at the equator is approximately
111 kilometers
the best choice of a geographic coordinate system for a world map would usually be___
an Earth-centered datum (centered at the center of the Earth)
the most precise positional measurements must record the epoch, or time of measurement to
account for continental drift (T or F)
true
it is best practice to convert all data used in a GIS project to the same datum and coordinate system (T or F)
true
a position in the NAD83 datum typically differs by up to 1 to 2 meters from that same position in the WGS84 datum (T or F)
true
a conic map projection best preserves the combined properties of__
distance and area
two GPS units lying next to each other are set to collect locations in NAD 1983 UTM Zone 10 and NAD 1927 UTM Zone 10 respectively. Which statement best characterizes the readings given by the two units?
the locations reported by the units may differ by a couple hundred meters
select all the statements that are true about vertical datums
Datums can be established through trigonometric leveling
geoid models have improved through time
NGVD29 was matched to more tidal stations than NAVD8
if you are creating a map of the United States comparing the areas of different weather systems, the best projection to use would be__
a conic projection (preserves distance and area)
Two layers are being displayed in a map view, which has been set to a State Plane coordinate system with units of feet. The box showing the cursor location lists the values in miles. One layer is stored in a GCS with units of degrees. The second layer is stored in UTM with units of meters. What are the map units?
feet (based on the first layer brought in, so the State Plane)
a projection from one coordinate system to another projected coordinate system must involve a datum transformation (T or F)
false (can change projections w/o changing datums)
select the best definition of the term "spatial reference"
the complete description of a coordinate system's properties and parameters
You have obtained data in a WGS84, UTM coordinate system and wish to include it in a project using NAD83(2011), also in a UTM coordinate system, collected via GPS a decade later. Your allowable error is 1 m. Which of the following are the minimum operations to convert your data, and still meet your accuracy/error requirement.
Apply a projection from UTM to geographic coordinates, apply an appropriate datum transformation from WGS84 to NAD83(2011), and then project from geographic coordinates to UTM coordinates
what is a datum?
a set of parameters to describe feature on Earth’s surface (reference points, origin, reference surface — spheroid, ellipsoid, geoid)
explain the difference between NAD27 and NAD83
they have different origins and orientations
what is WGS84
average positioning around the Earth based on ellipsoidal model
explain the importance of map projection
map projection is crucial because it allows the representation of the 3D Earth on a 2D surface while minimizing distortion in area, shape, distance, or direction. difficult to do analysis w/ latitude and longitude
describe the four types of map projections by the preserved property
The four types of map projections are equal-area (preserving area), conformal (preserving shape), equidistant (preserving distance), and azimuthal (preserving direction)
explain the difference between the standard line and the central line
the standard line is where the map projection maintains true scale, while the central line is the primary reference line of a projection that best preserves properties like shape or area (least distortion)
explain how a UTM zone is defined in terms of its central meridian, standard meridian, and scale factor
a UTM is made up of 60 zones of 60 degrees, with each zone defined by a central meridian (origin), a standard meridian for true scale, and a scale factor that accounts for distortion across the zone. distortion is minimized around central meridian
if a data set’s features have x coordinates between –180 and +180, what is the coordinate system likely to be? In what units are the coordinates?
UTM, coordinates in degrees of latitude and longitude
explain why the UTM projection would not be a good choice for making a map of the contiguous United States
mostly good for North/South vertical projections, not for wide East/West, can lead to distortion
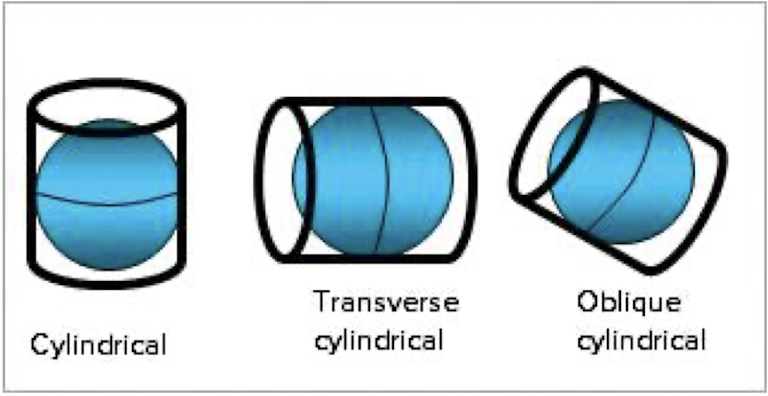
examine the figures below and explain why conic projections usually conserve area and distance but cylindrical projections typically preserve direction
conic projections maintain area and distance by projecting the earth's surface onto a cone tangent to the globe, minimizing distortion in those aspects. cylindrical projections preserve direction by mapping the globe onto a cylinder, but they distort area and distance as you move away from the equator.
Converting from geographic coordinates to cartesian coordinates results in distortions in distances. What is the distance between Baton Rouge, LA, and Houston, TX, calculated using geodetic distance and planar distances? What is the difference in distance based on the two approaches?
geodetic distance accounts for the curvature of the Earth, while planar distance measures as if on a flat surface. geodetic distance being more accurate over long distances like Baton Rouge, LA, to Houston, TX, whereas planar distance may underestimate the true distance
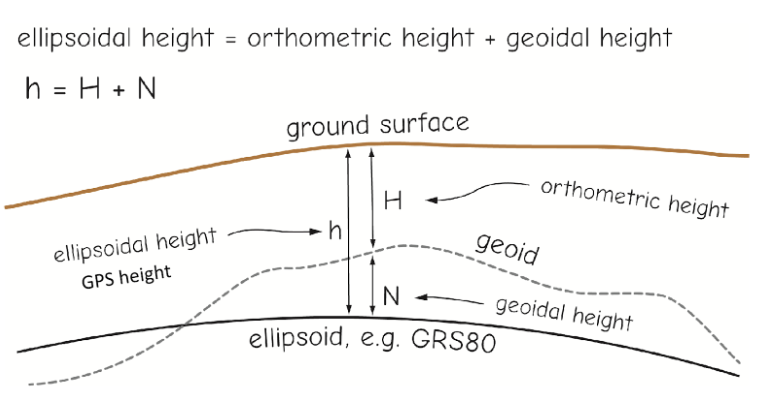
You're standing on a point where you know the geoidal height to be 30 meters, and your GPS says your orthometric height is 472 meters. What is your ellipsoidal height?
ellipsoidal height = orthometric + geoidal — 472 + 30 = 502 meters
You're standing on a point where you know the ellipsoidal height to be 80 meters, and your geoidal height is 10. What is your orthometric height?
orthometric height = ellipsoidal - geoidal —- 80-10 = 70 meters
which one of the following statements is TRUE?
a polygon feature contains vertices but not nodes.
select the example that best characterizes the term "multipart feature".
a feature with multiple records and one polygon
which one of the following is NOT a characteristic of GIS data?
GIS data files are never shared by multiple users
why should one avoid using spaces and special characters like $#% in folder names?
not all software packages work correctly when they encounter these names
why is it advantageous to separate downloaded and in-production files from permanent datasets?
because it facilitates cleaning temporary data from folders with minimal risk to permanent data
on Windows computers, why should GIS data be stored on the main C:\ drive rather than the default buser library folder or Desktop?
because on a network, the Library folders can get mixed up between different users
data found in ArcGIS Online can be downloaded and stored in a local folder___ (always, sometimes, never)
sometimes
if a club is creating a map for hikers to use in the backcountry, the target source scale for downloaded data would be about__
1:20,000 — the smallest number for the highest resolution
when using x-y fields in a table to create points on a map, it is important to specify the coordinate
system as__
the coordinate system reflected in the table's x-y fields
when importing data for your home state, the Clip tool would most likely be needed to extract___
rivers
the_________ tool merges features together if they share the same attribute values in a specified field or list of fields.
dissolve
select the definition of the term "feature dataset"
a collection of feature classes related to each other in some way (same spatial reference, theme, or geometry)
feature classes in a feature dataset must__
all have the same coordinate system
which one of the following describes an advantage of shapefiles over geodatabases?
shapefiles can be read by many different GIS programs and are now commonly used to share data
which one of the following would be most likely to use an enterprise geodatabase?
a city planning department with multiple divisions editing the same data
which one of the following can a geodatabase NOT store?
coverages
it is equally satisfactory to use Windows to manage (copy, rename, delete) GIS data as to use the tools and Catalog in Pro to do it. (T or F)
false
the project (.aprx) file__
keeps track of the data, settings, and resources needed to make the project work
which ONE of the following statements is TRUE?
a layer points to a feature class and contains properties that can be set for the feature class
which of the following is a legal pathname for GIS data?
C:\my_data\mgisdata\usa\roadnum.shp (not valid: C:\my data\southdakota\custer\roads.shp, D:\europe\census2000\euc$bounds\france.shp, D:\gisfolder\oregon\water_data\stream#.shp)
select the definition of a "feature ID" or "FID"
a unique integer used to identify a feature in an attribute table
name three types of simple features used in GIS and their geometric properties
points (0D w/ location), lines (1D w/ location and length), and polygons (2D w/ area, perimeter, and location)
explain the importance of topology in GIS
defines the spatial relationships between features, whether features are adjacent/connected/overlapping/intersecting
main advantages of using shapefiles
display faster on computer than topology-based data and can be used across softwares, simple for data management/exchange
difference between georelational data model and object-based data model
georelational data model describes spatial data and geometries as separate from attribute data, object-based data model integrates spatial and attribute data into a single object, allowing for more complex representations
difference between personal geodatabase and file geodatabase
personal geodatabase is limited to a single user and has a small storage capacity, while a file geodatabase is stored in a folder and supports multiple users and larger datasets
difference between vector data model and raster data model
vector data model represents geographic features as points, lines, and polygons, while raster data model represents them as a grid of cells or pixels (good for continuous data)
can you convert a vector to a raster layer?
yes, through rasterization