AP Biology Cell Signaling and Mitosis Unit 4 MUST KNOW
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
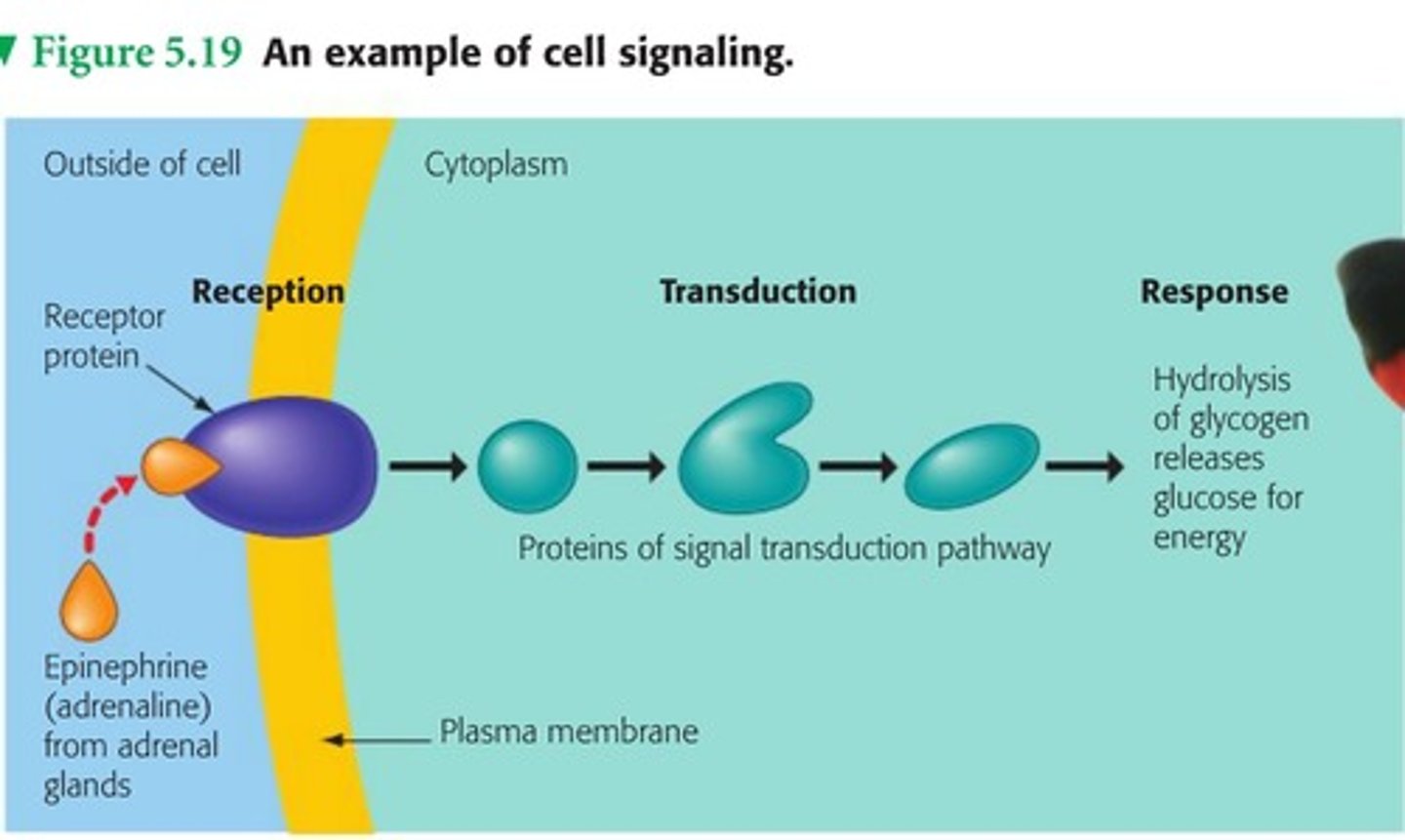
signal transduction pathway
process where surface cellular responses cause responses within the cell
growth factors
compounds that stimulate nearby target cells to grow and divide
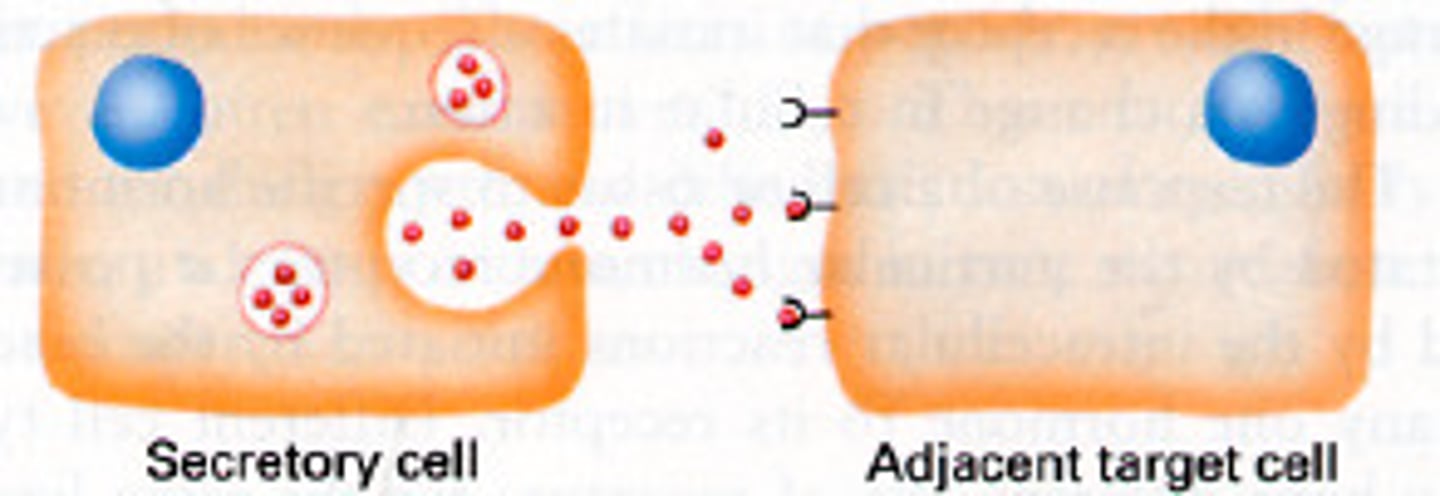
paracrine signaling
a type of local signaling where the target cell is close to the signal-releasing cell
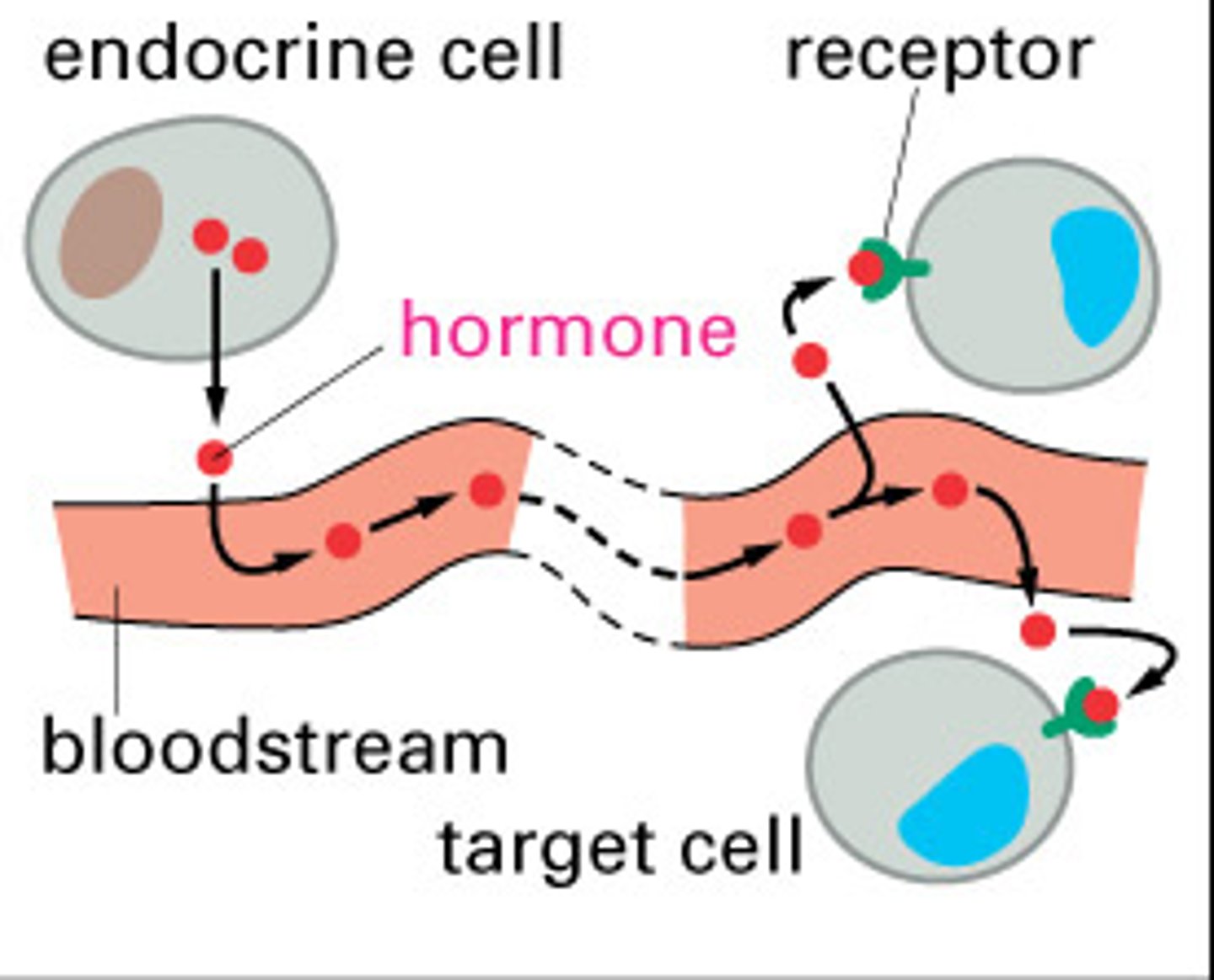
endocrine signaling
secreted molecules diffuse into the bloodstream and trigger responses in target cells anywhere in the body
juxtacrine signaling
requires direct contact between the signaling and responding cell

hormone
a released, long-distance signaling molecule which travels between the secreting cell (endocrine) and the target cell
reception
when a signaling molecule binds to a receptor protein
transduction
the relay of molecules in a cell via a signal transduction pathway
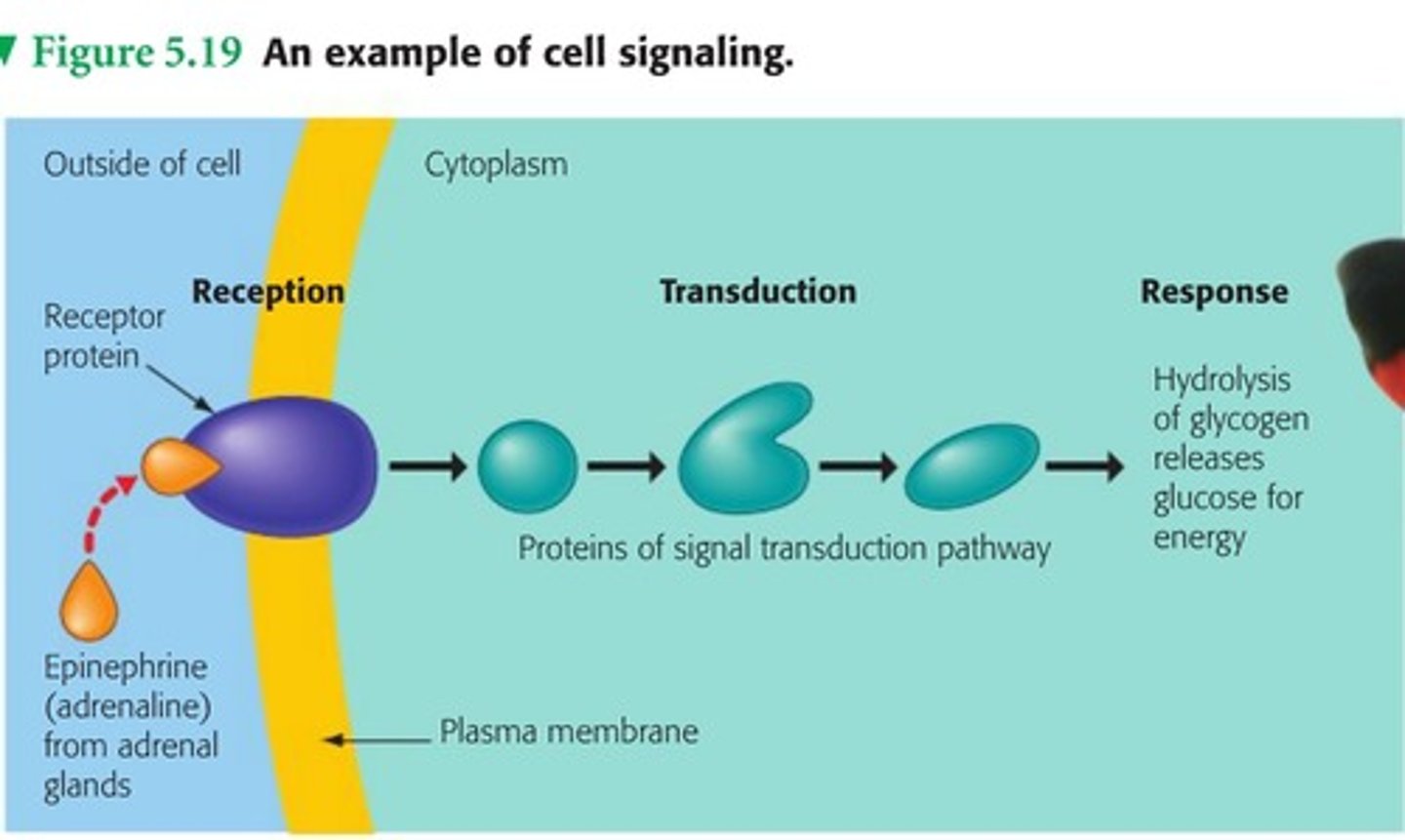
response
when an enzyme is activated to do an activity in a cell
ligand
a midget signaling molecule which binds to another giant (larger) molecule; aka a signaling molecule
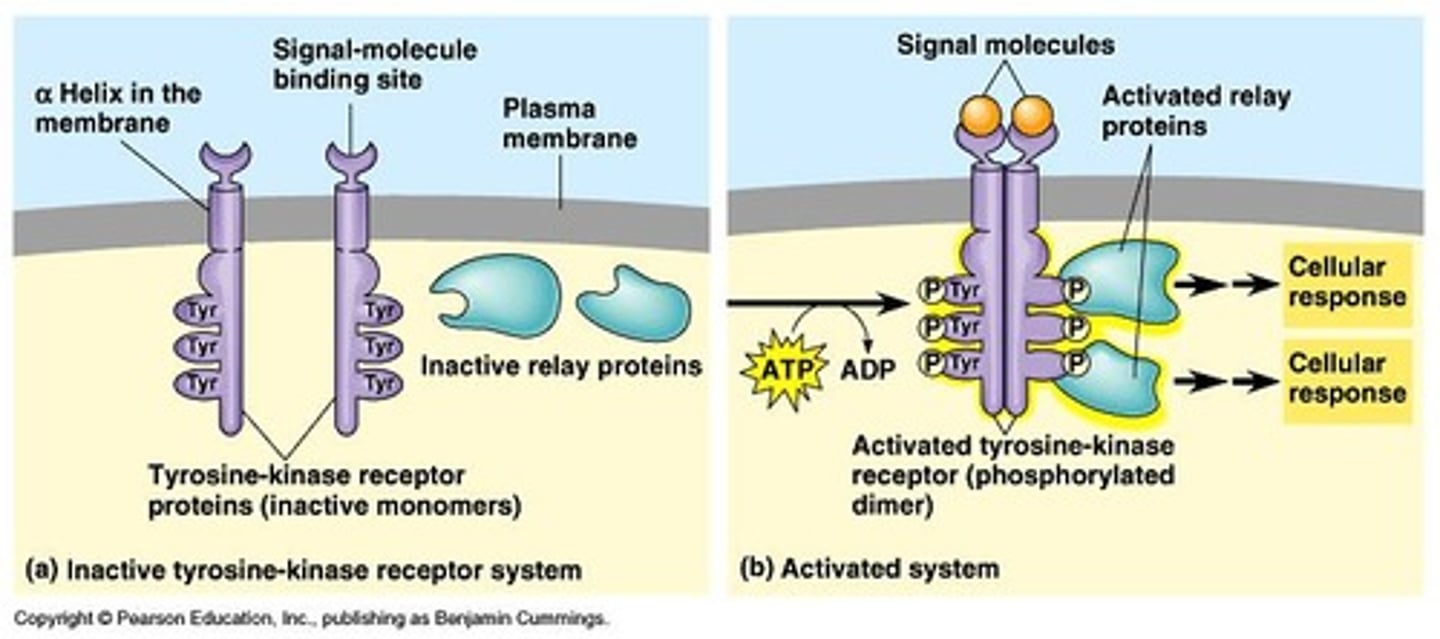
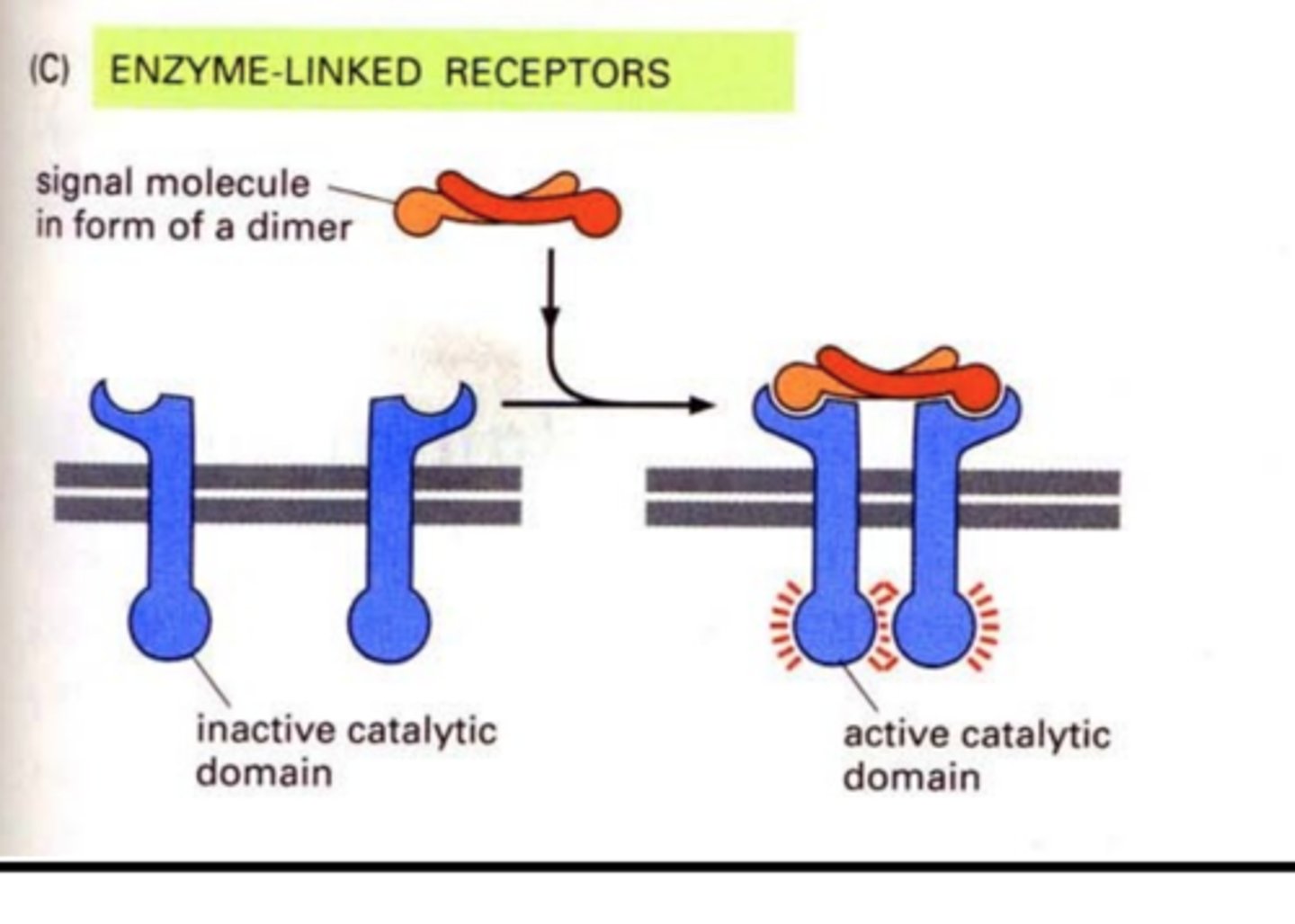
tyrosine kinase receptors / enzyme linked receptors
membrane receptors that attach phosphates to protein tyrosines
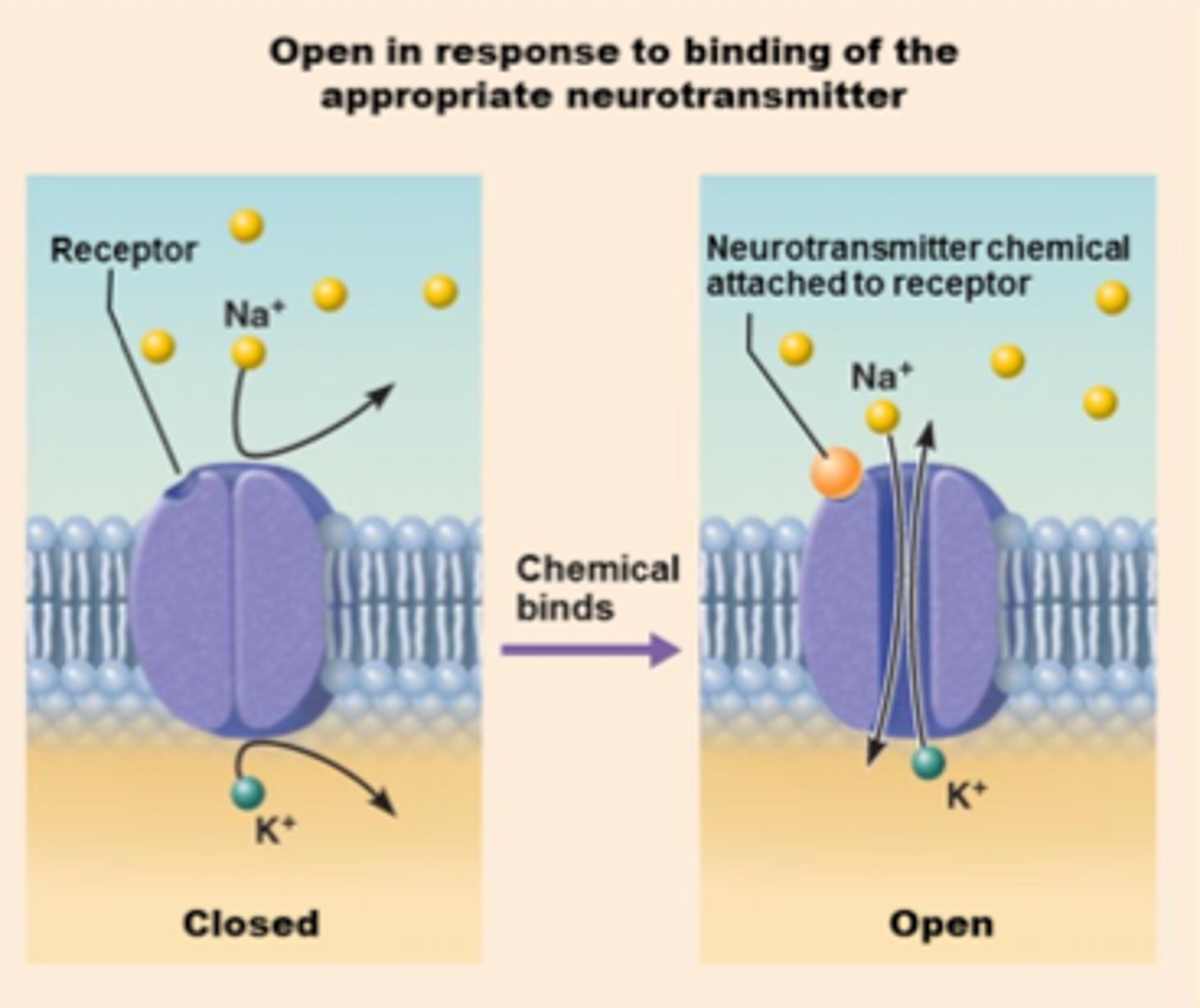
ligand gated ion channel receptors
block and allow ions in and out of the cell
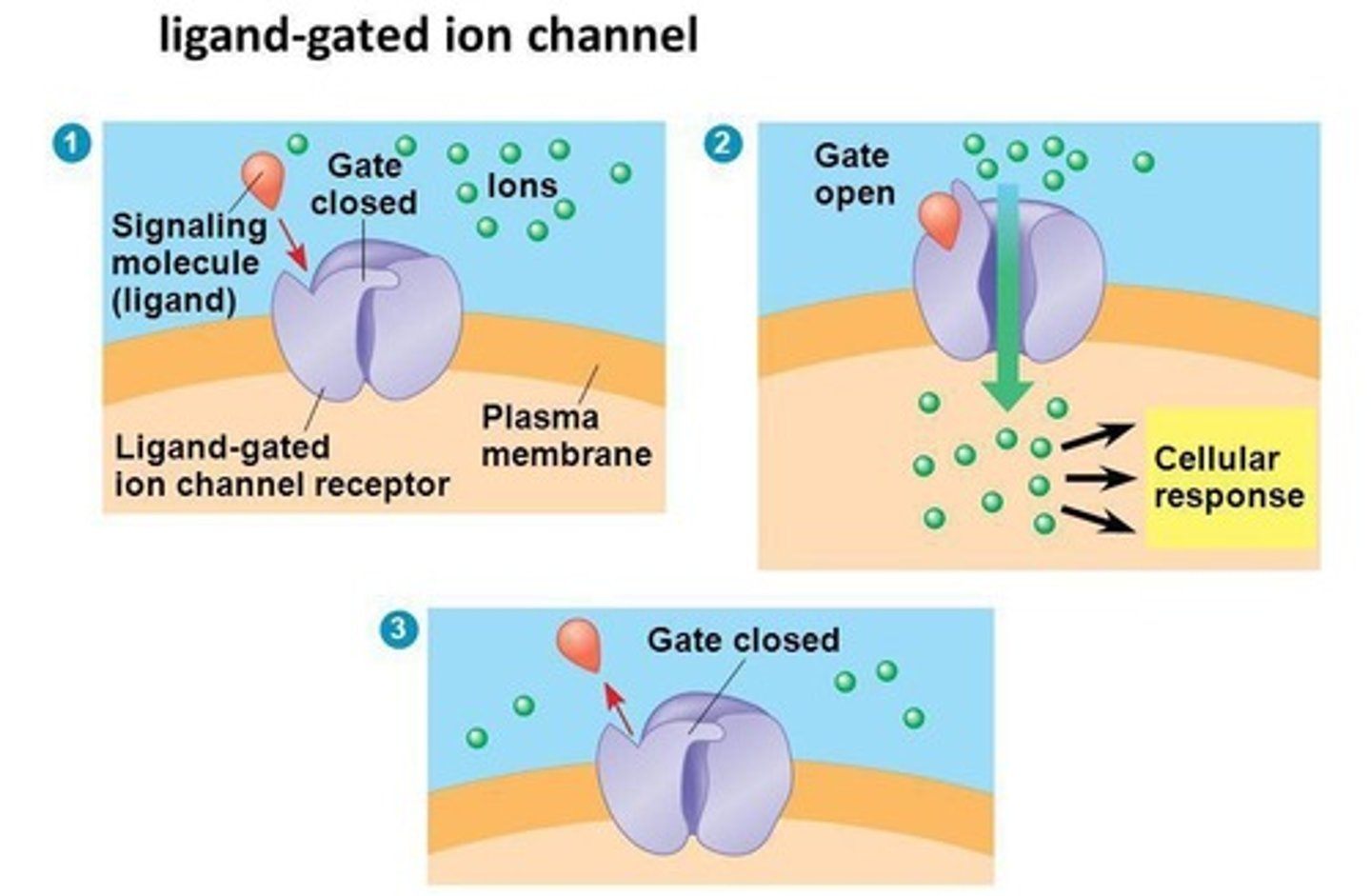
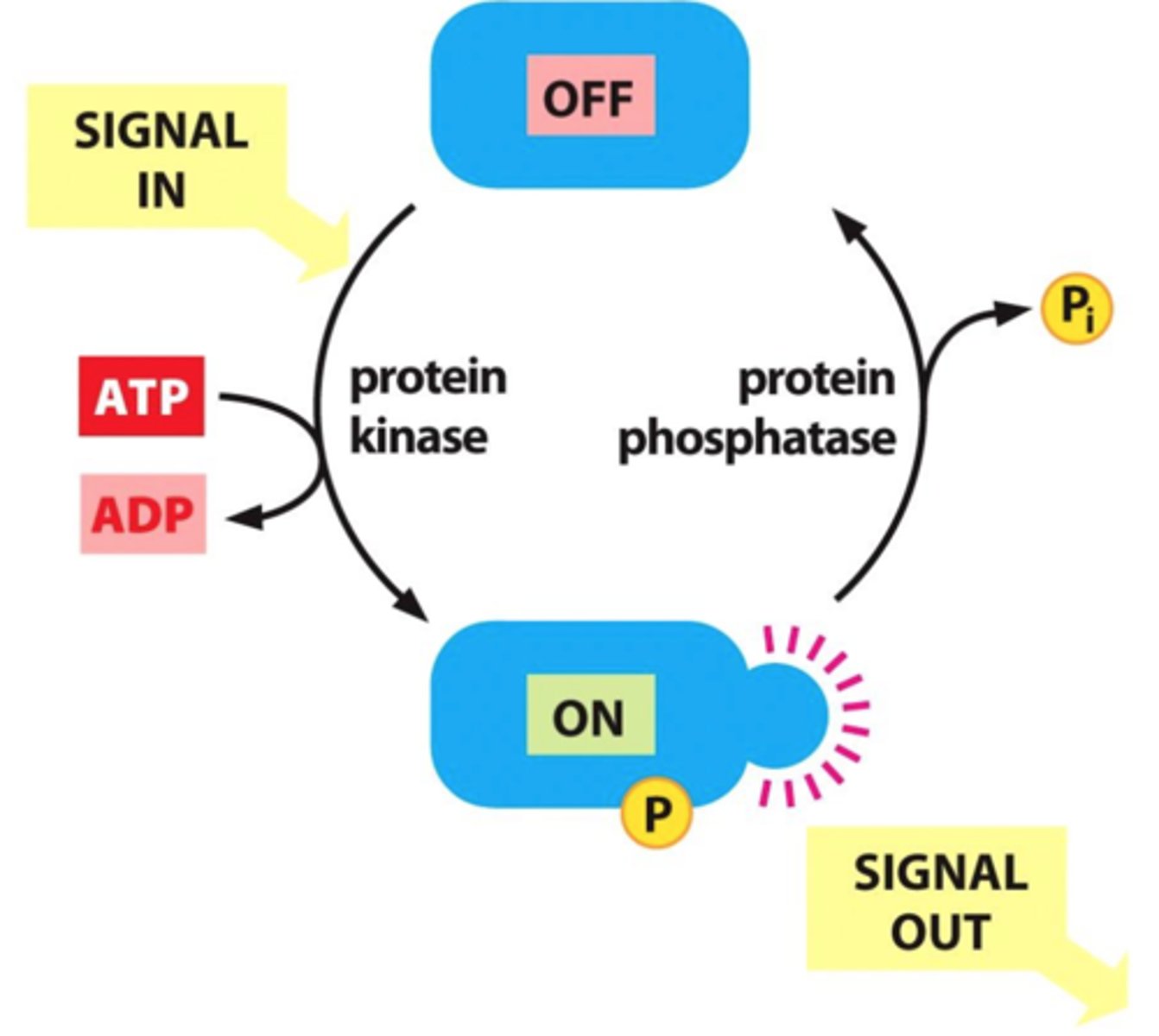
protein kinase
general name for an enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from ATP to a protein
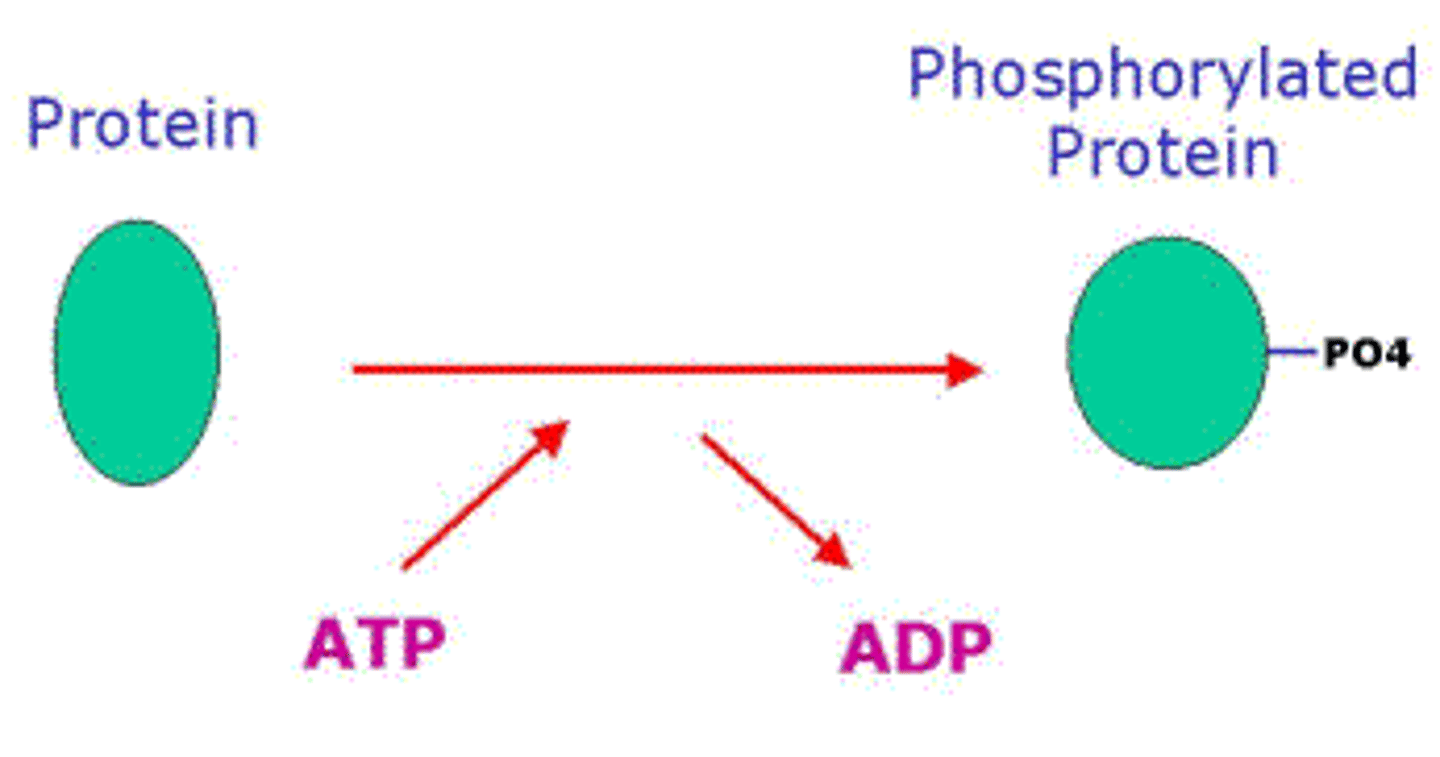
secondary messengers
small, non-protein, water-soluble molecules/ions that act as the signaling molecule/ligand
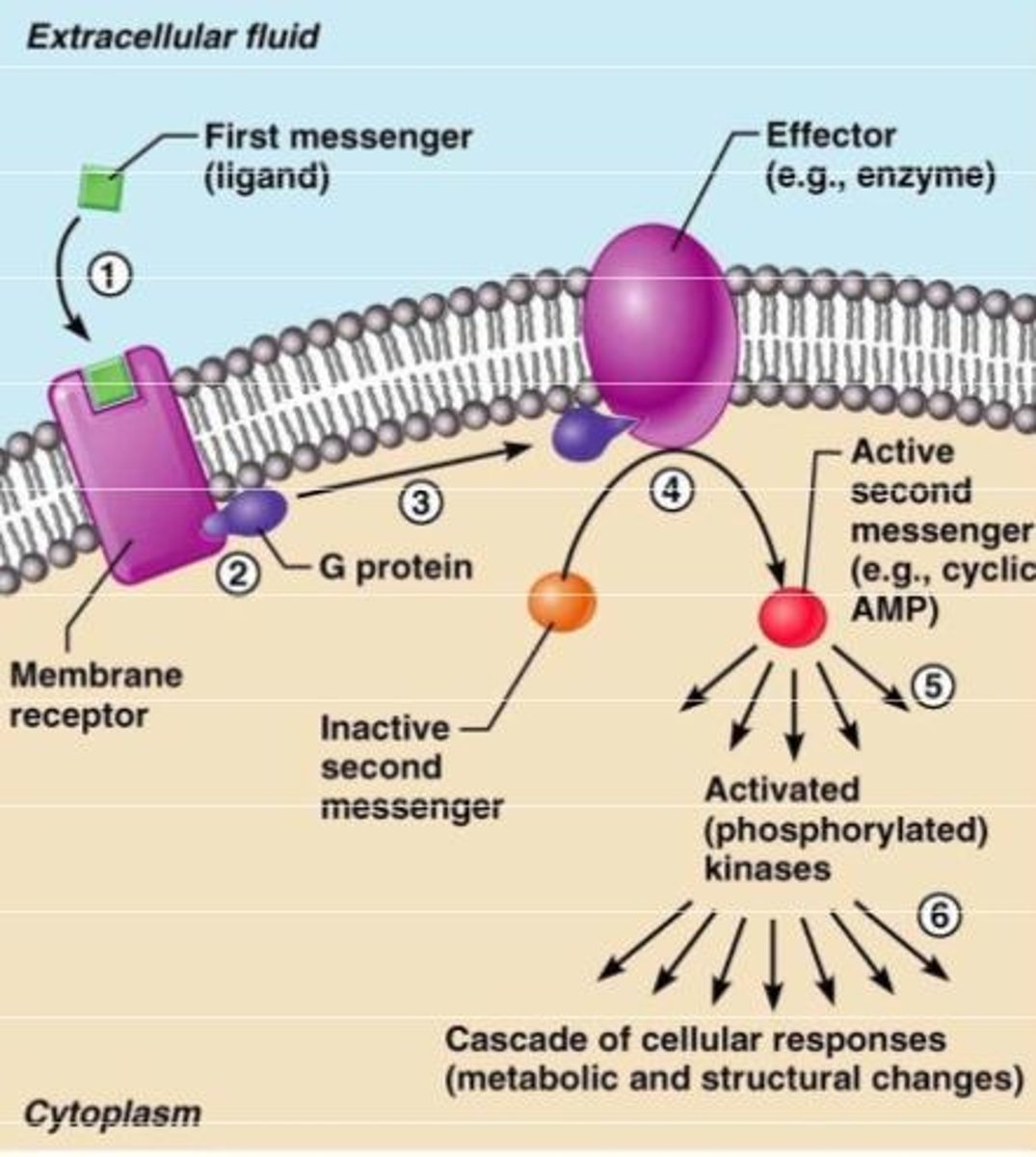
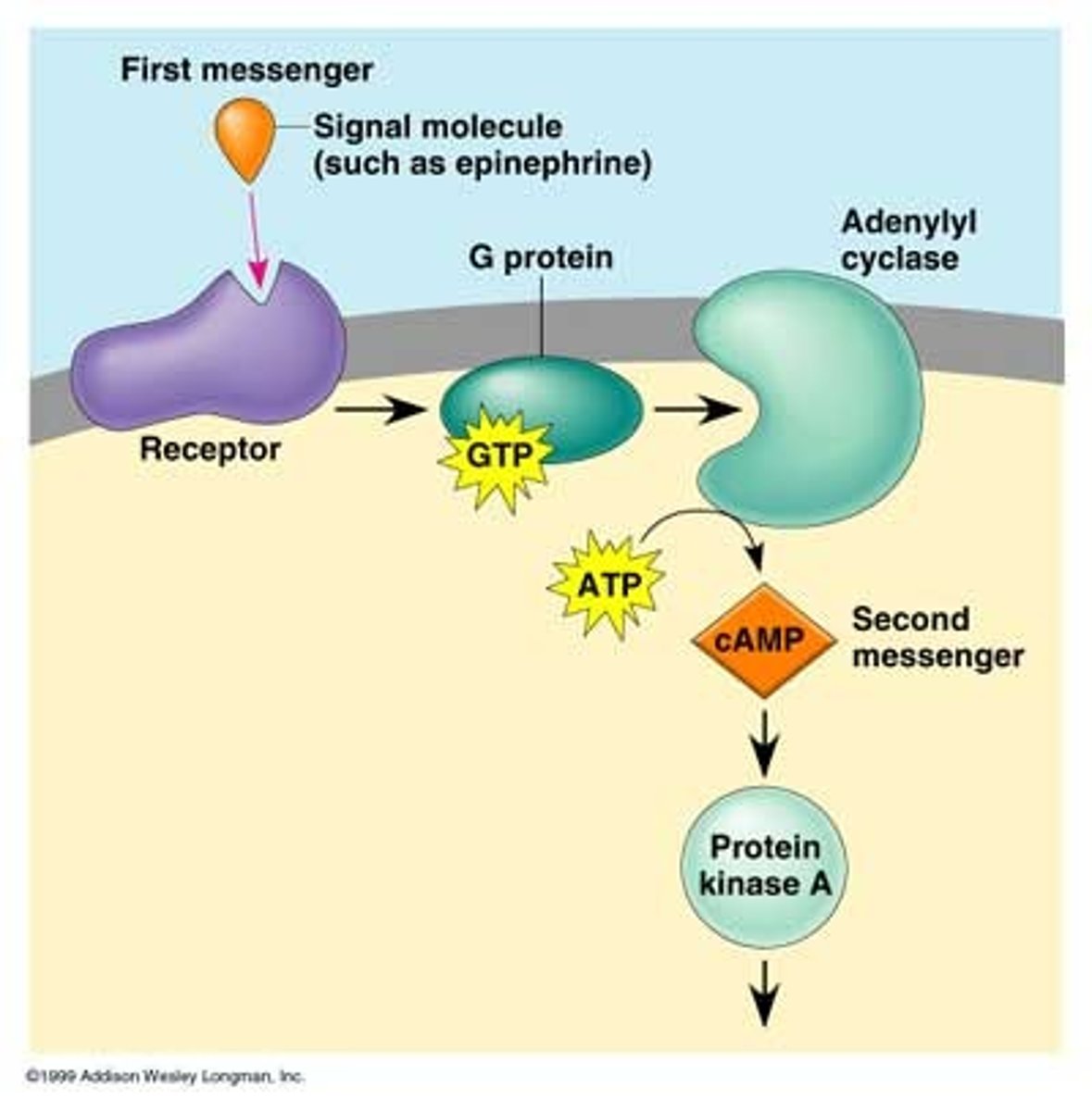
G-protein coupled receptors
A special class of membrane receptors with an associated GTP binding protein; activation of a G protein-coupled receptor involves dissociation and GTP hydrolysis
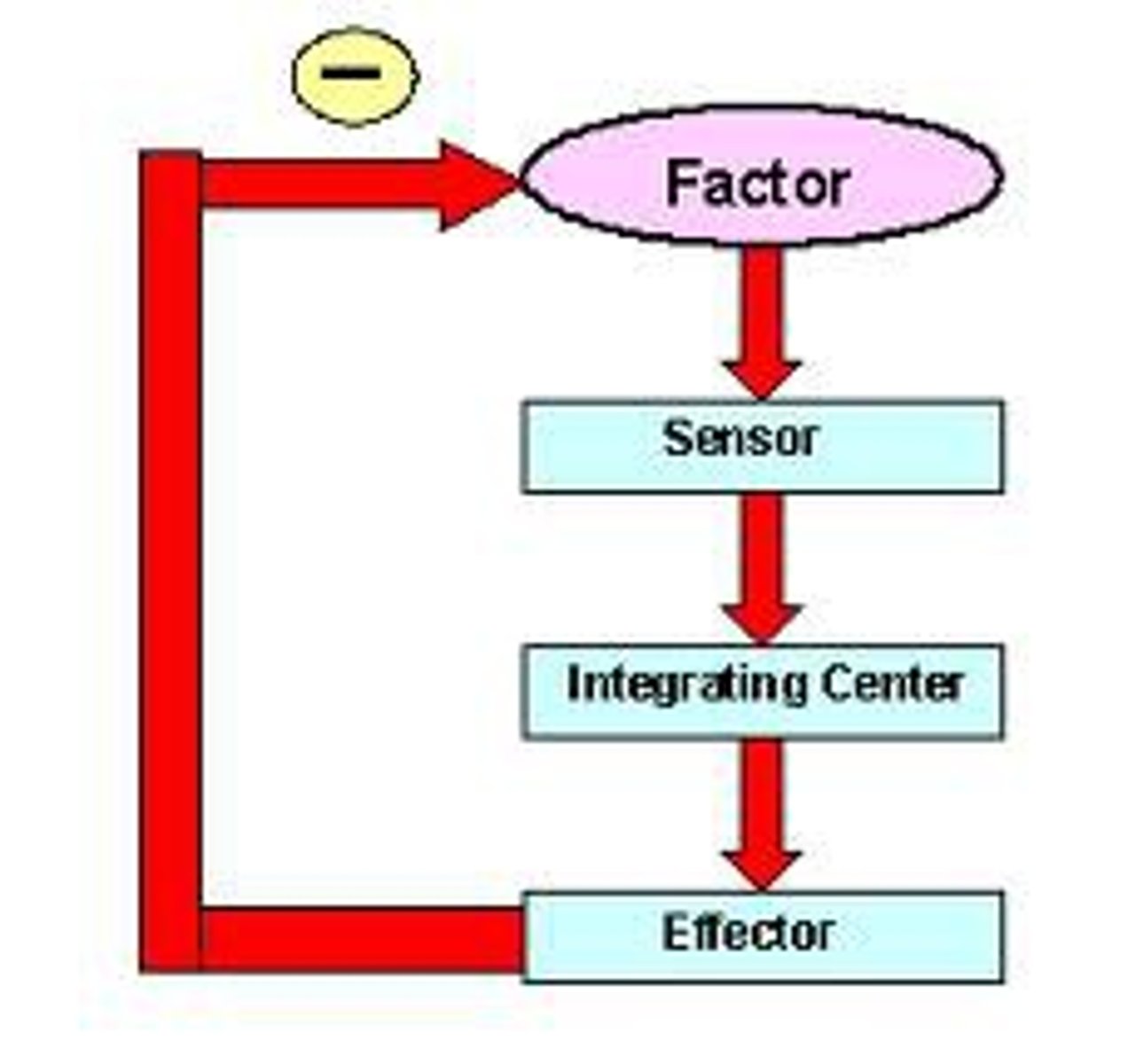
negative feedback
a mechanism of response in which a stimulus initiates reactions that reduce the stimulus. Used to maintain homeostasis.
positive feedback
A type of regulation that responds to a change in conditions by initiating responses that will amplify the change. Takes organism away from a steady state.
protein phosphatase
An enzyme that removes phosphate groups from (dephosphorylates) proteins, often functioning to reverse the effect of a protein kinase.
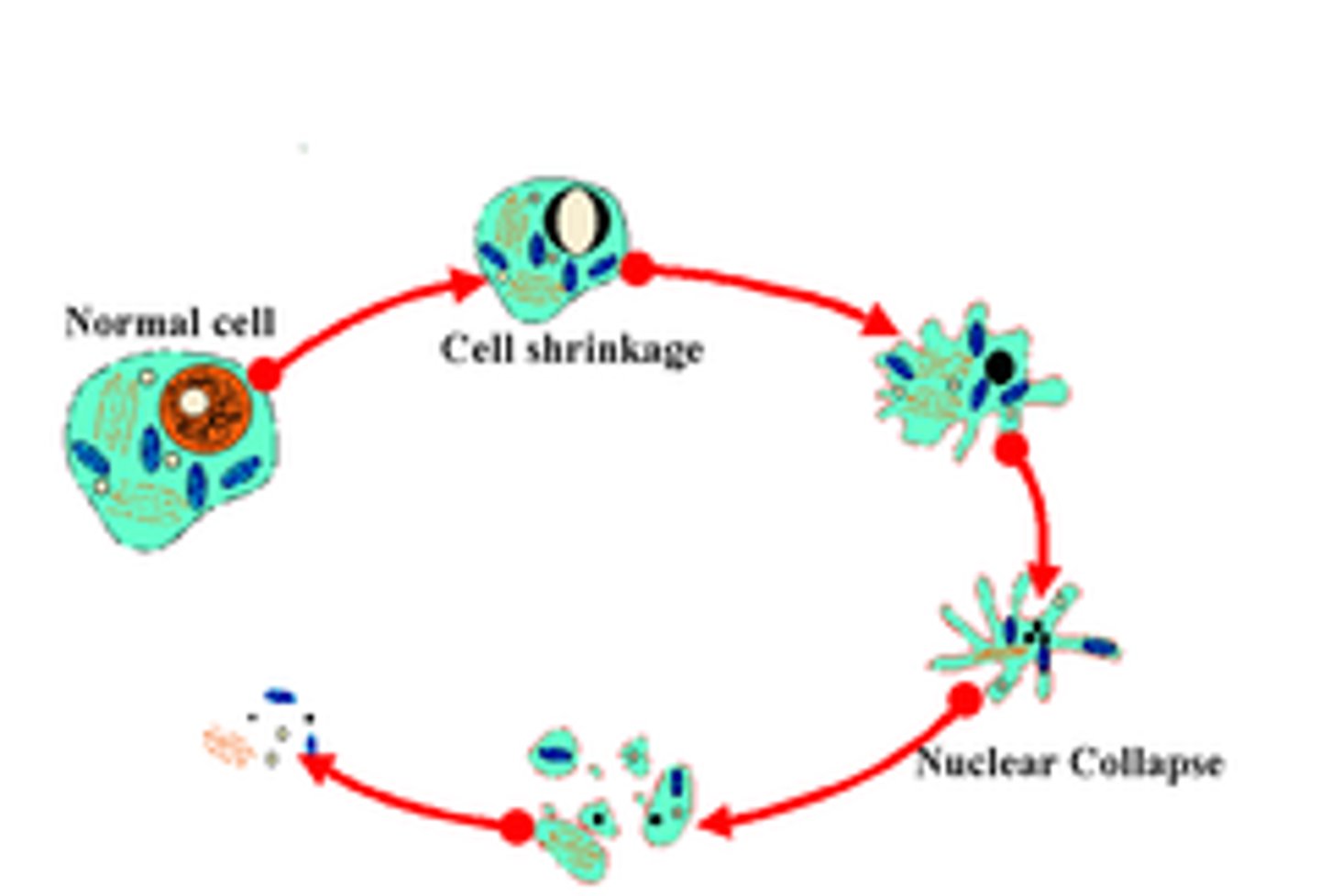
apoptosis
process of programmed cell death
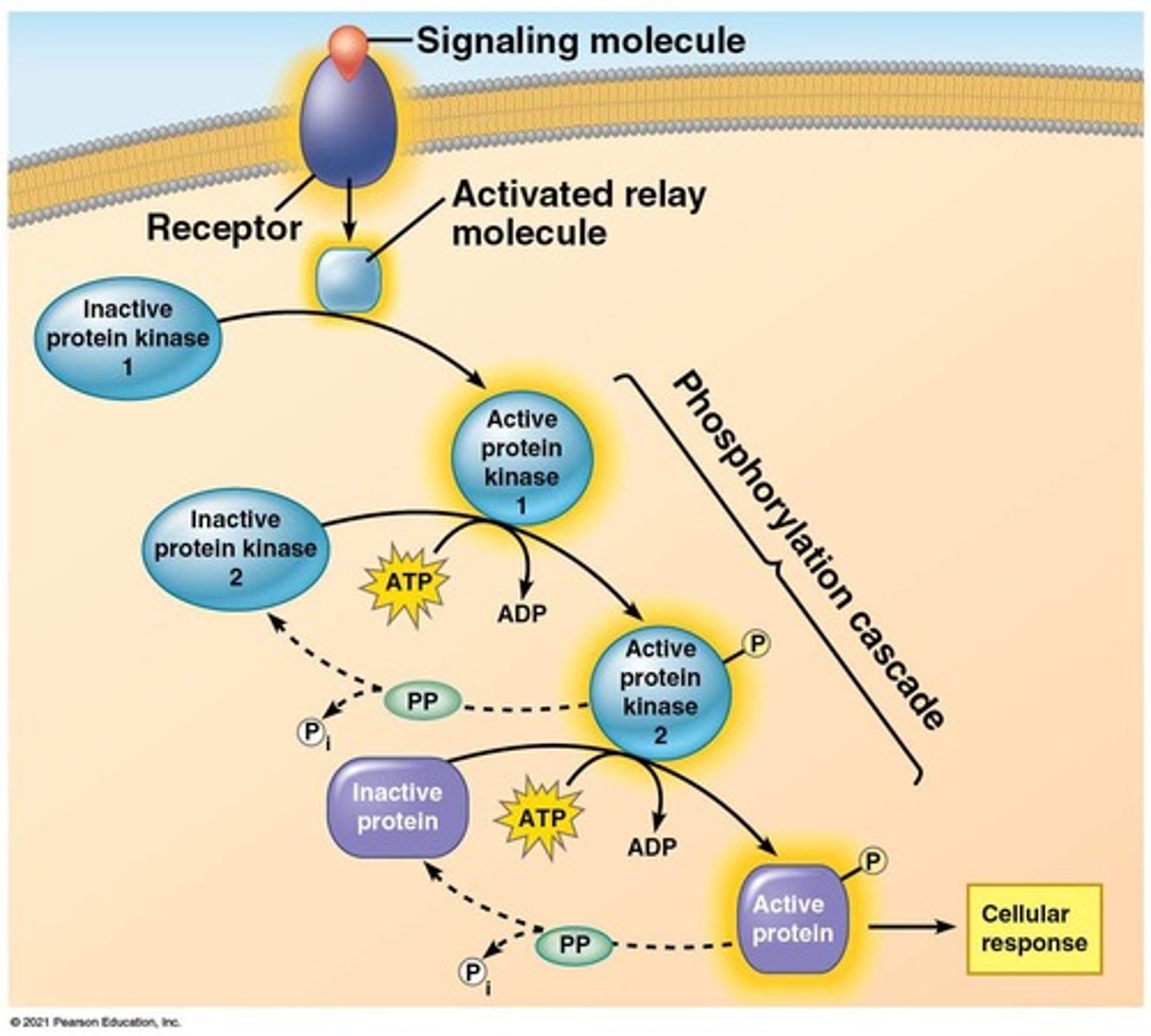
signal amplification
Enzyme cascades amp the cell's response to a signal. At each step in the cascade, the number of activated products is much greater than the previous step.

phosphorylation cascade / signaling cascade
A series of enzyme-catalyzed phosphorylation reactions (done by kinases) commonly used in signal transduction pathways to amplify and convey a signal inward from the plasma membrane.
Enzyme-linked receptors
cell-surface receptors with intracellular domains that are associated with an enzyme (ex. tyrosine kinase receptors)
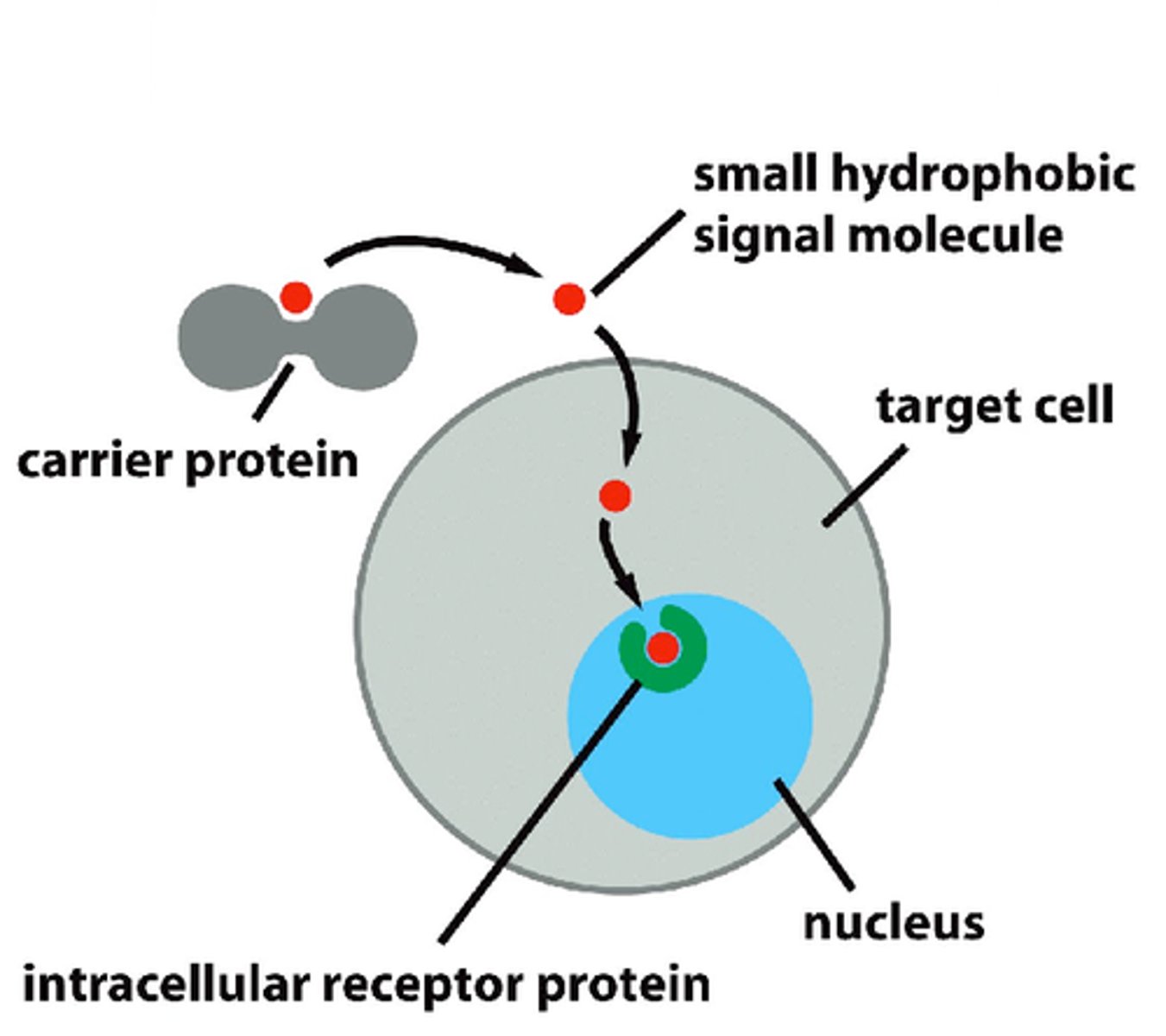
intracellular receptor
receptors located inside the cell rather than on its cell membrane
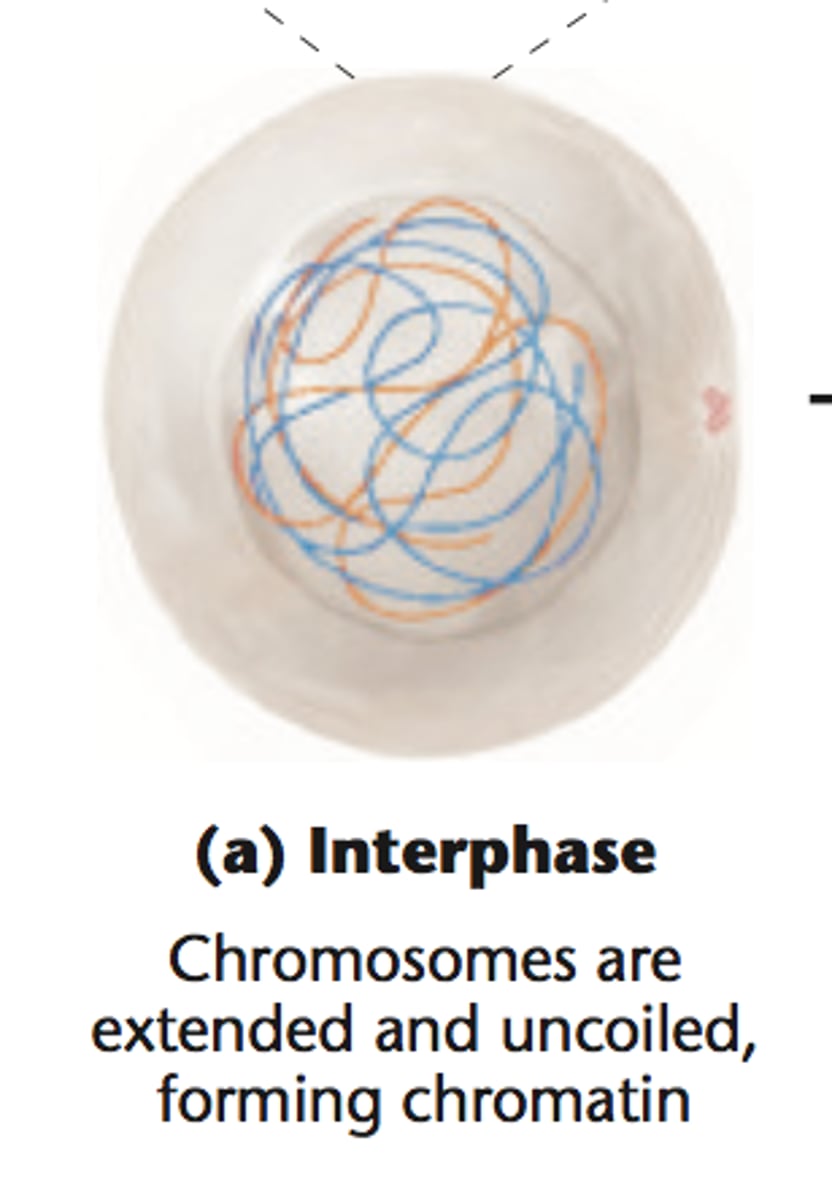
Interphase
Cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division; consists of G1, S, and G2 phases
G phase
cell grows and synthesizes structures other than DNA
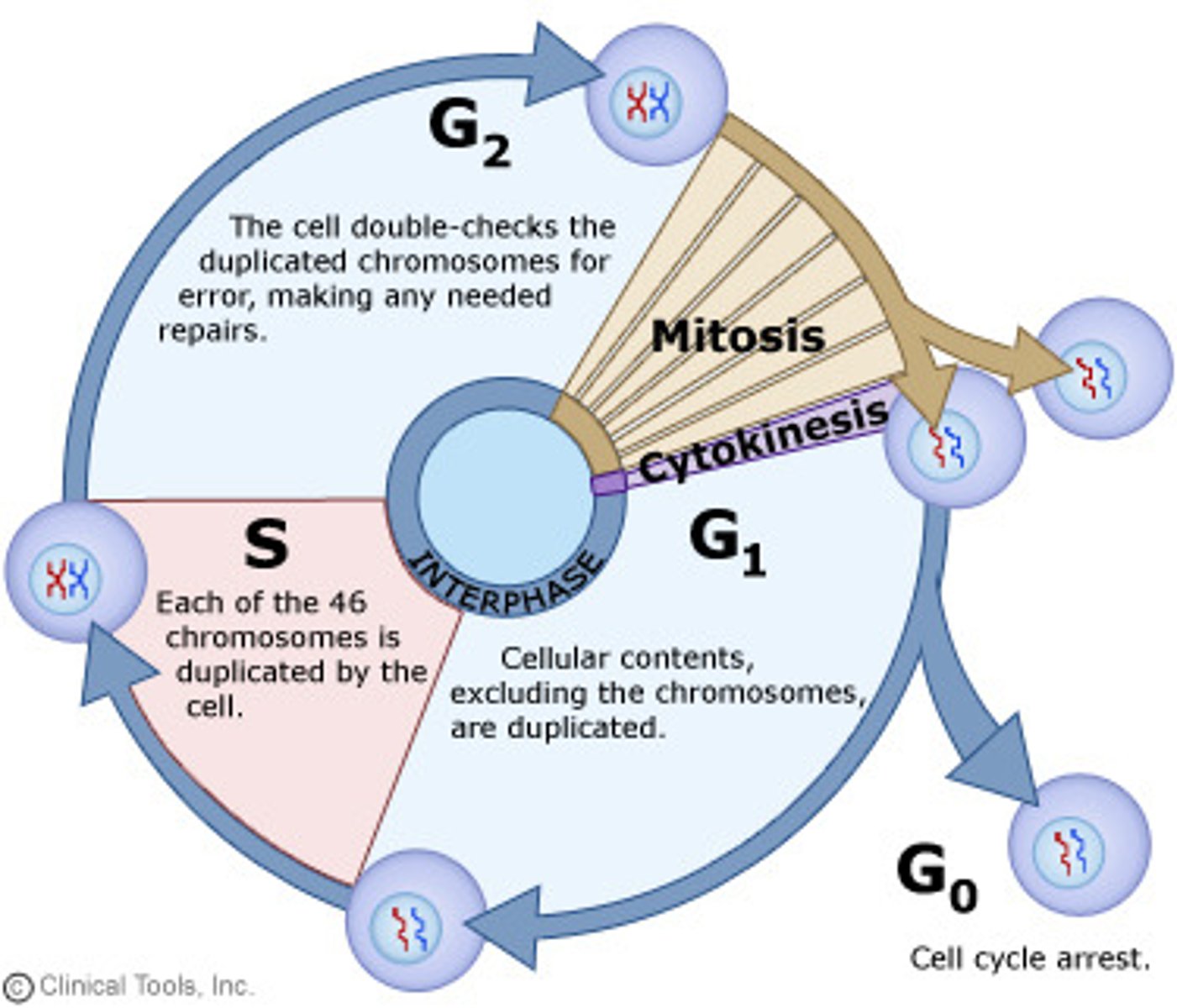
S phase (synthesis)
The synthesis phase of the cell cycle; the portion of interphase during which DNA is replicated.
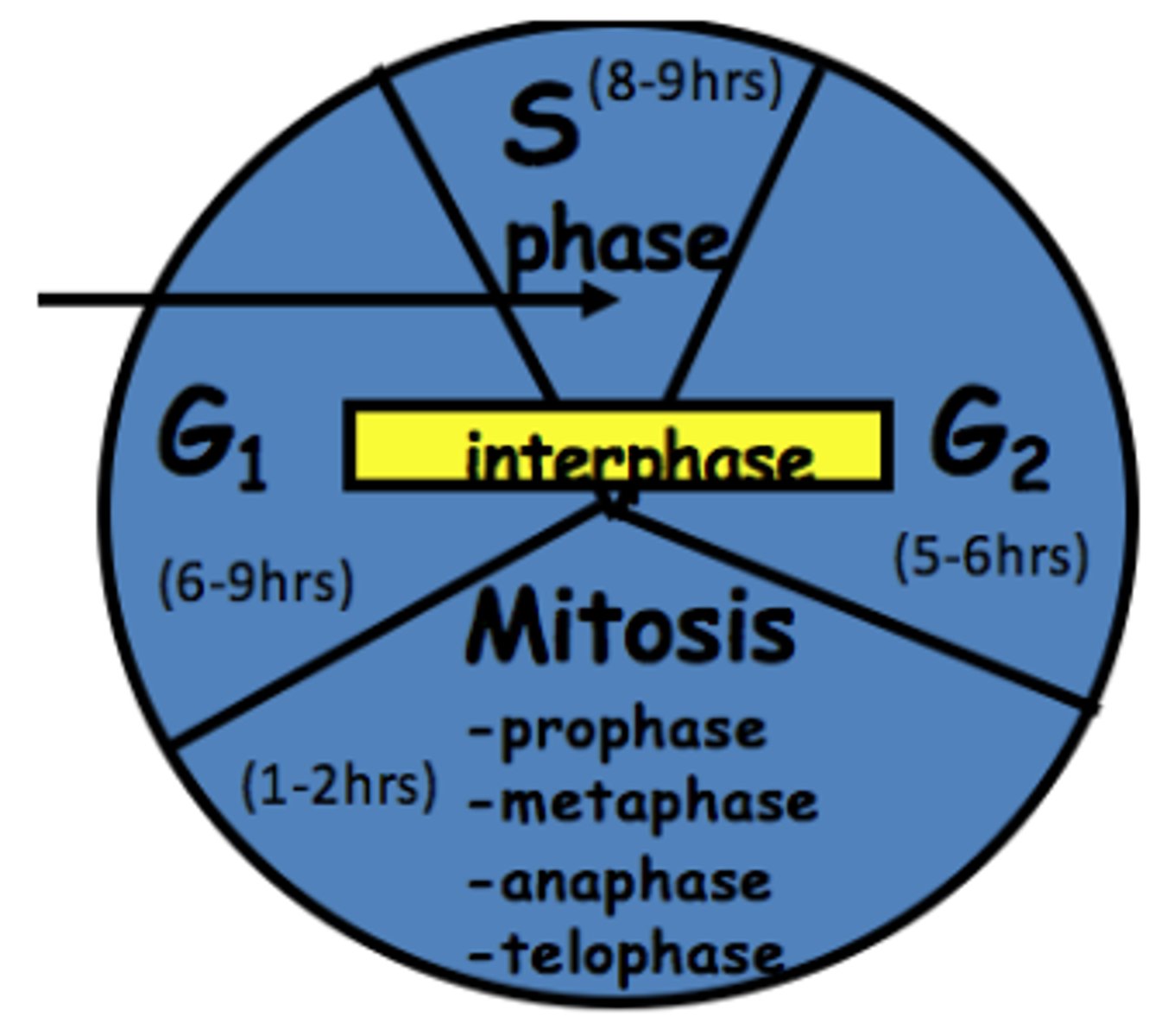
mitosis
cell division in which the nucleus divides into nuclei containing the same number of chromosomes
cyclin
A cellular protein that occurs in a cyclically fluctuating concentration and that plays an important role in regulating the cell cycle.

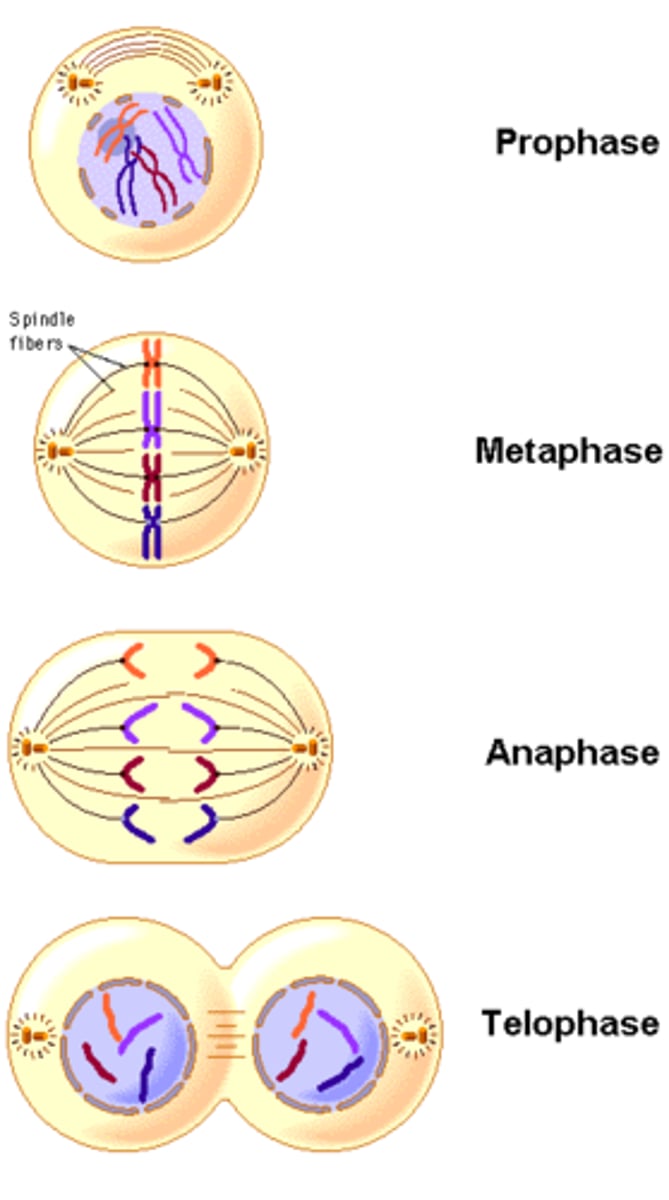
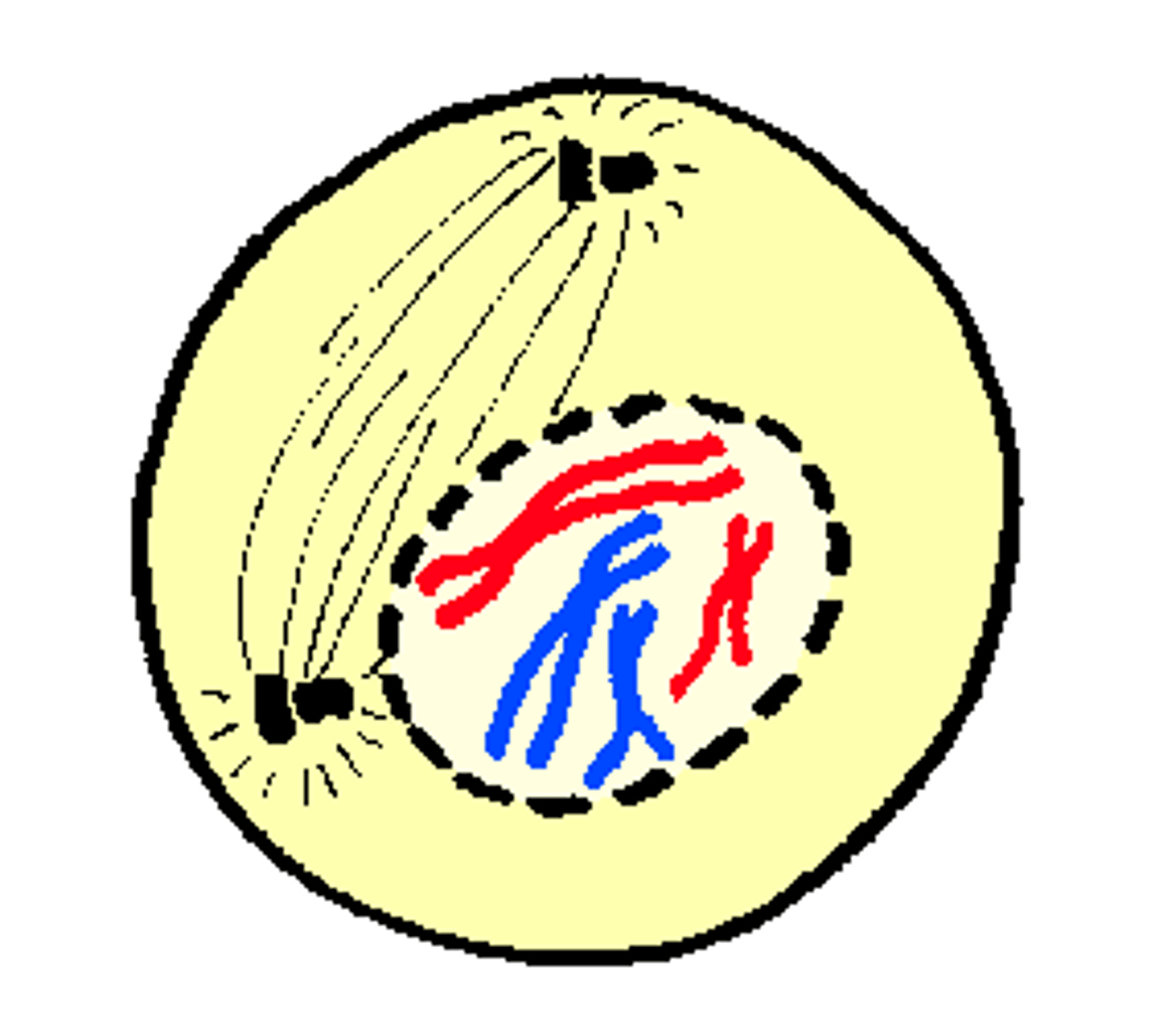
prophase
The first and longest phase of mitosis: chromosomes become visable, nuclear envelope dissolves, spindle fibers form
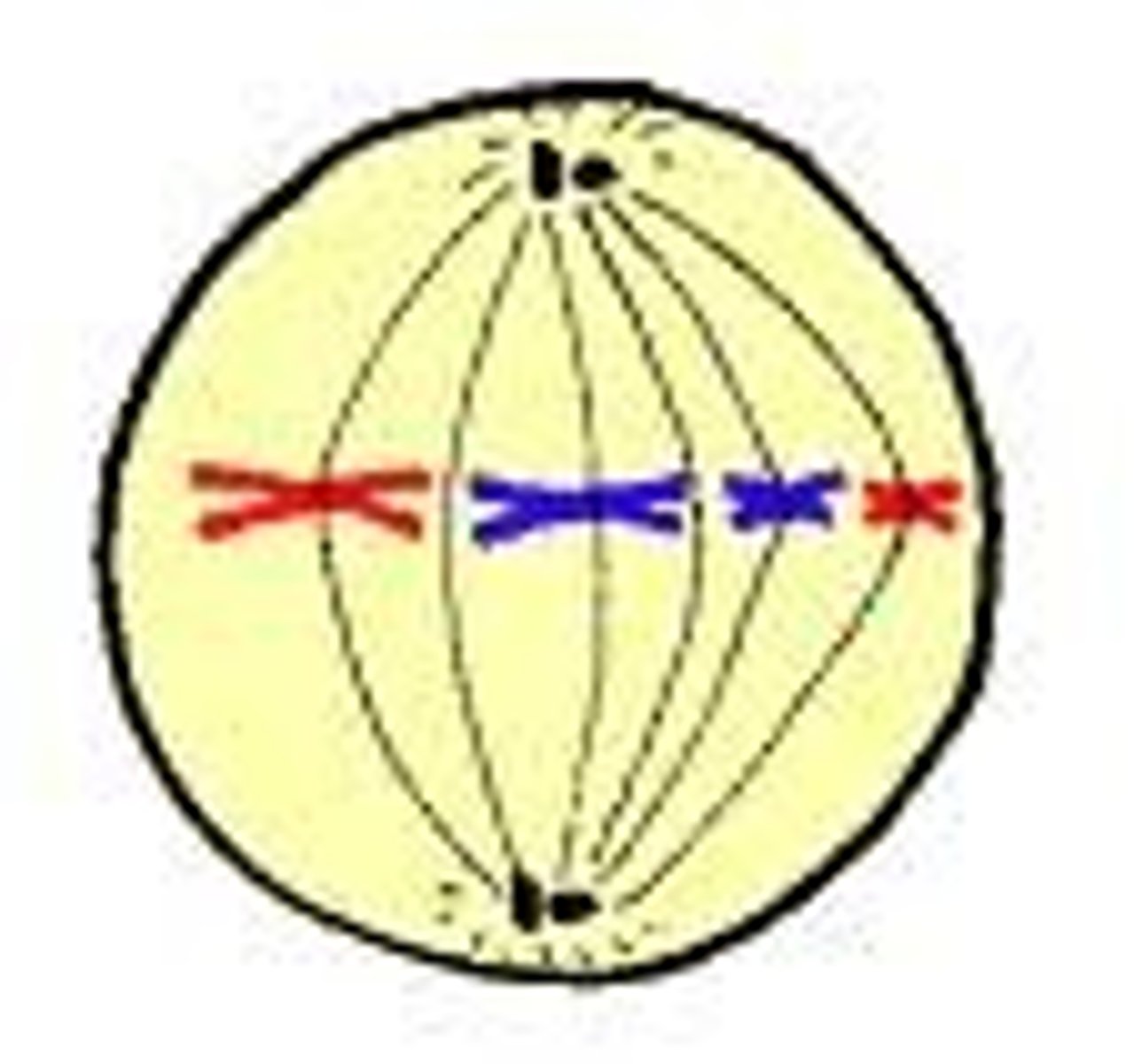
metaphase
second phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
anaphase
Phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell
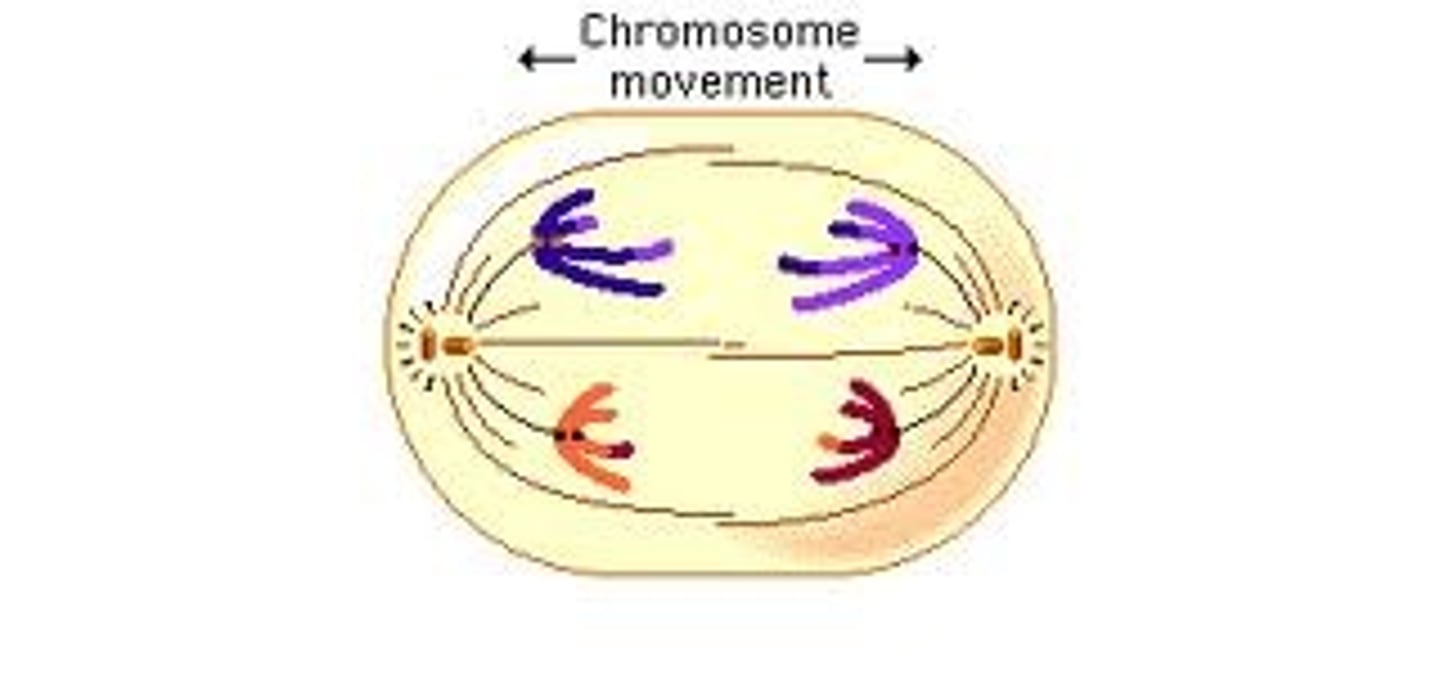
telophase
the final phase of cell division, between anaphase and interphase, in which the chromatids or chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell and two nuclei are formed.

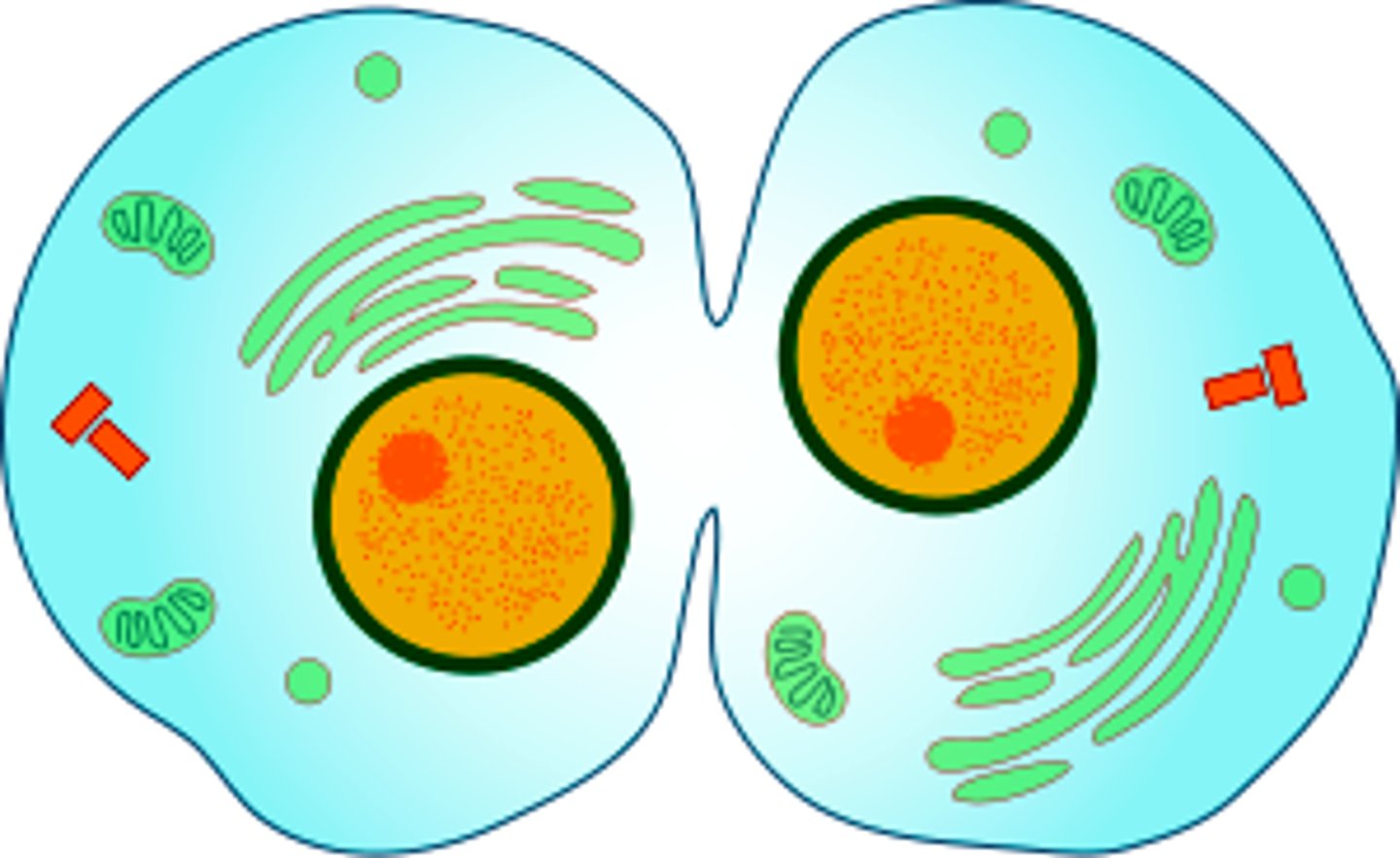
cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells (after telophase)

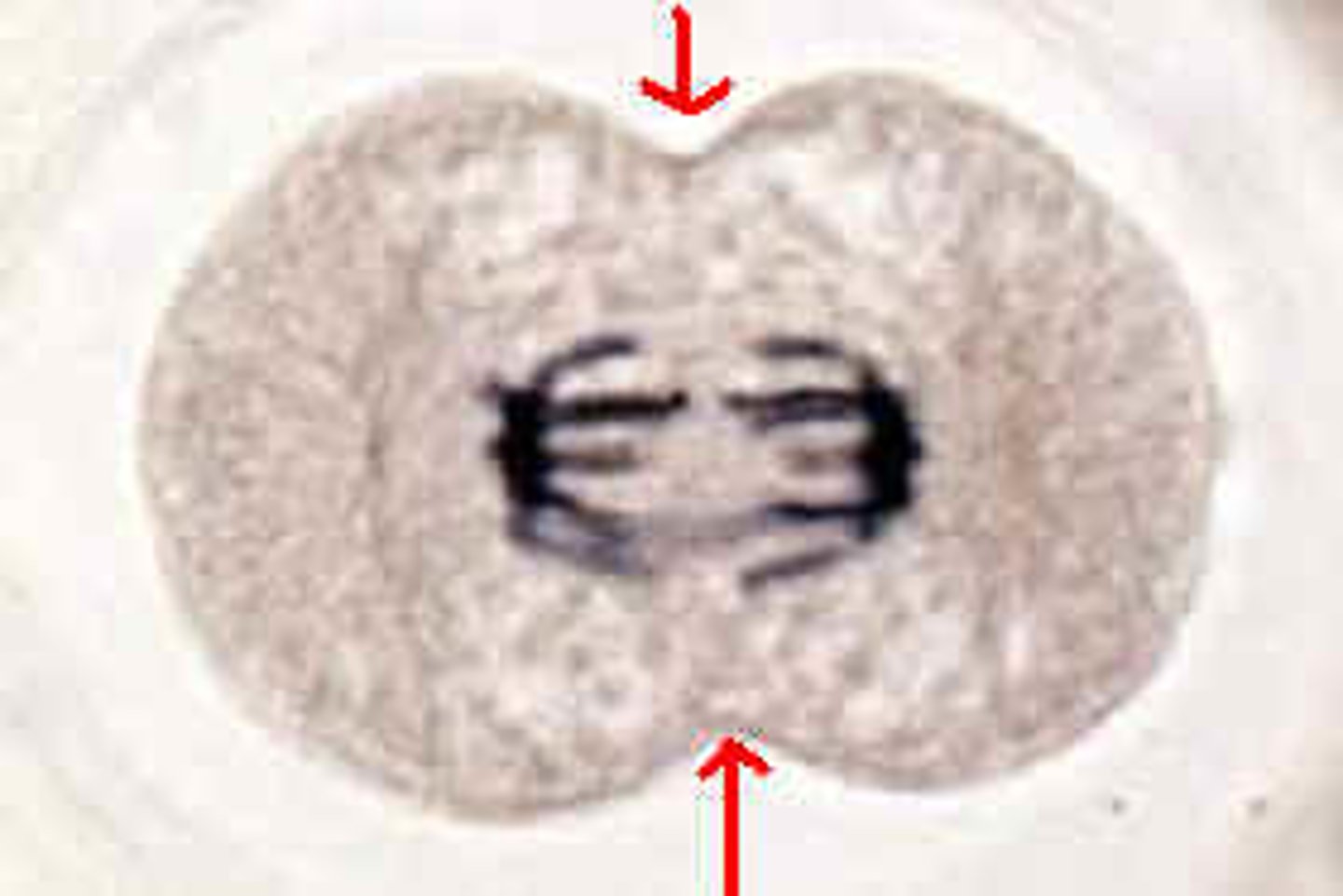
cleavage furrow
the first sign of cytokinesis during cell division in an animal cell; a shallow groove in the cell surface near the old metaphase plate
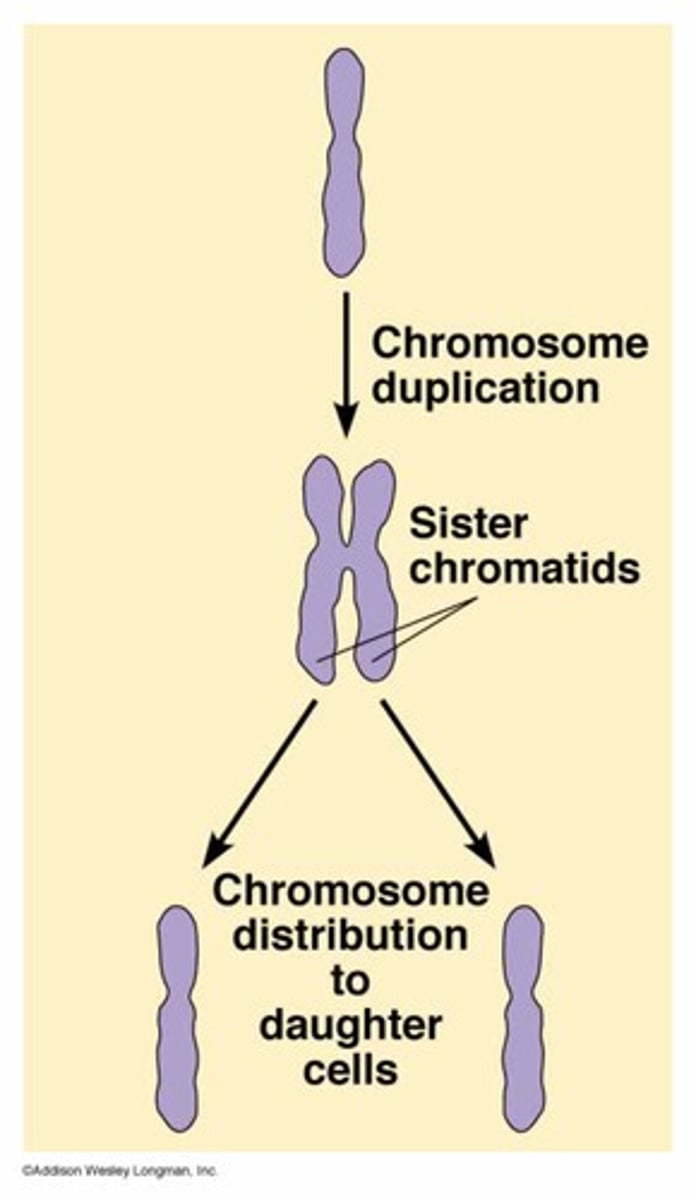
sister chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome that are attached in the middle (forming an X shape); full sets of these are created during the S subphase of interphase.
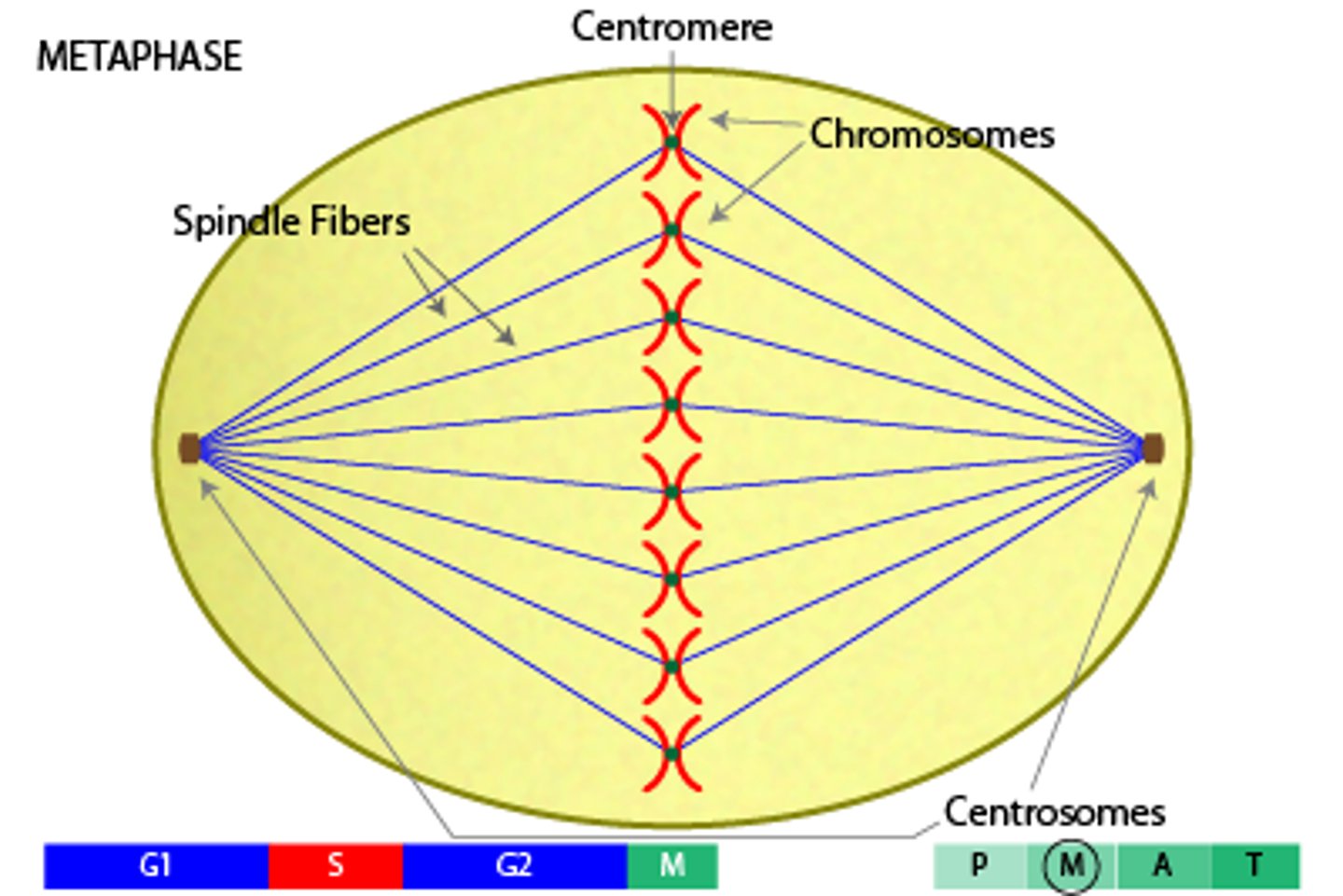
spindle fiber
one of the microtubules that extend across a dividing eukaryotic cell; originates from centrioles in animal cells; assists in the movement of chromosomes
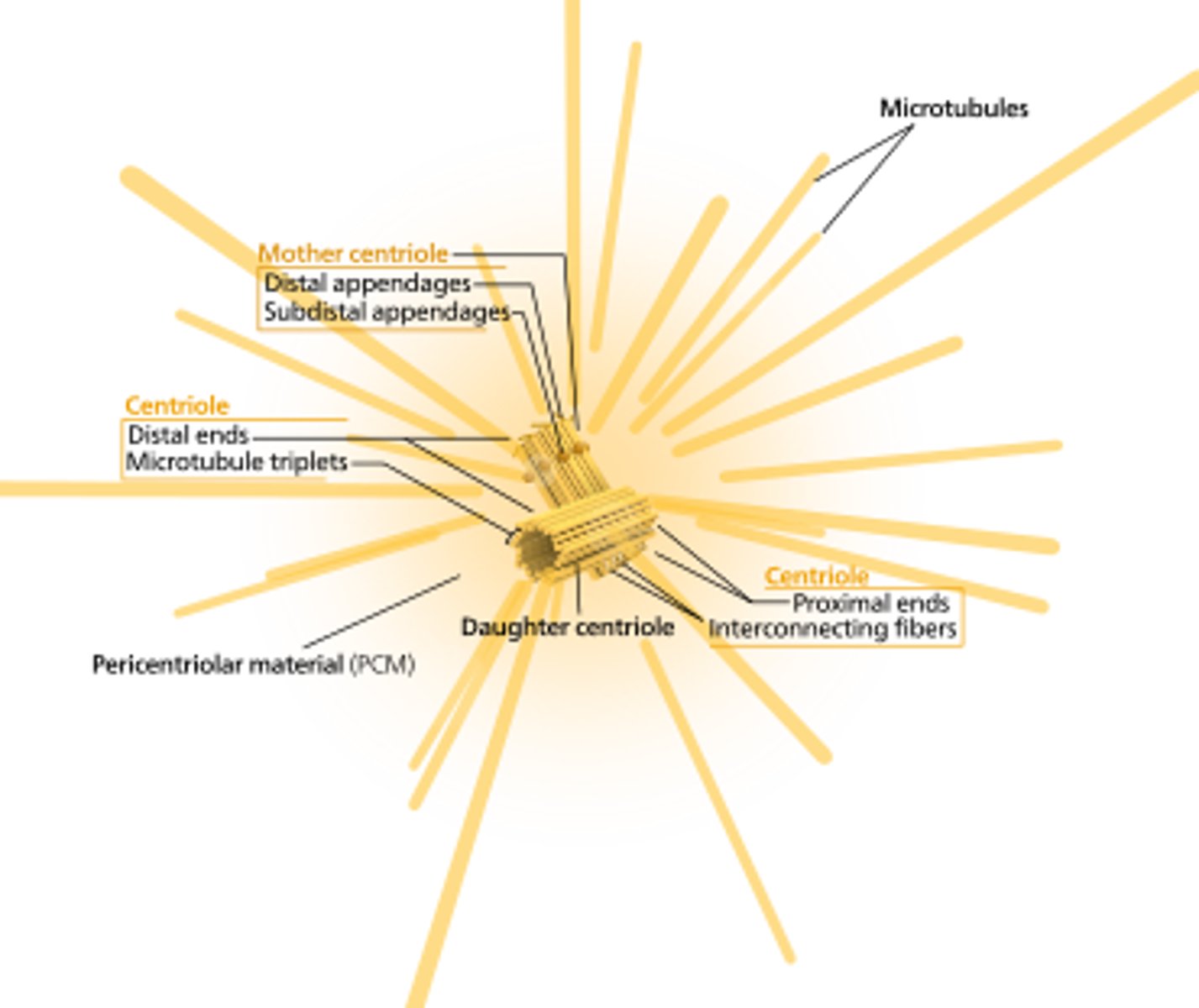
centriole
one of two tiny tubes made of microtubules located in the cytoplasm of animal cells near the nuclear envelope; aids in organizing spindle fibers in mitosis
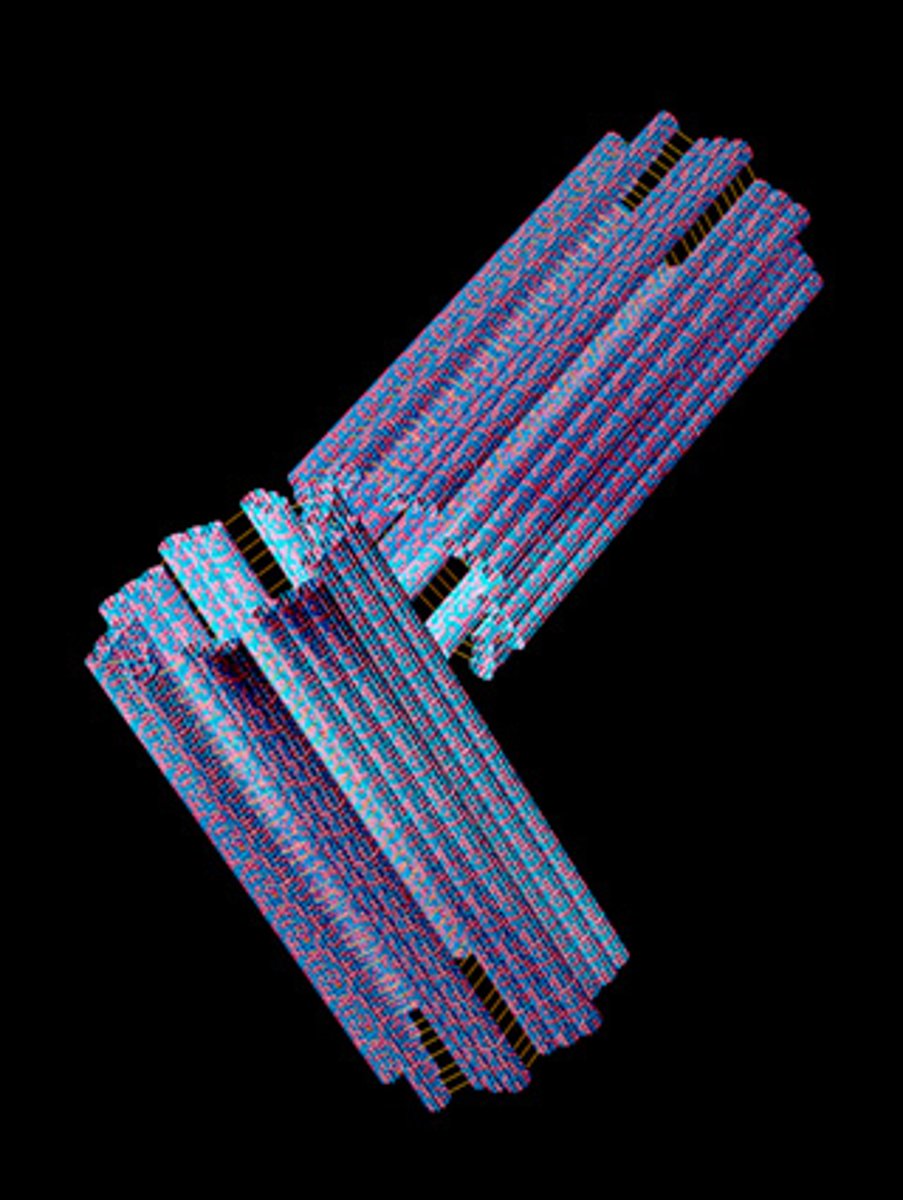
centrosome
A structure in animal cells containing centrioles from which the spindle fibers develop. (Centrosomes contain centrioles, but centrioles do not contain centrosomes.)
cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm during cell division
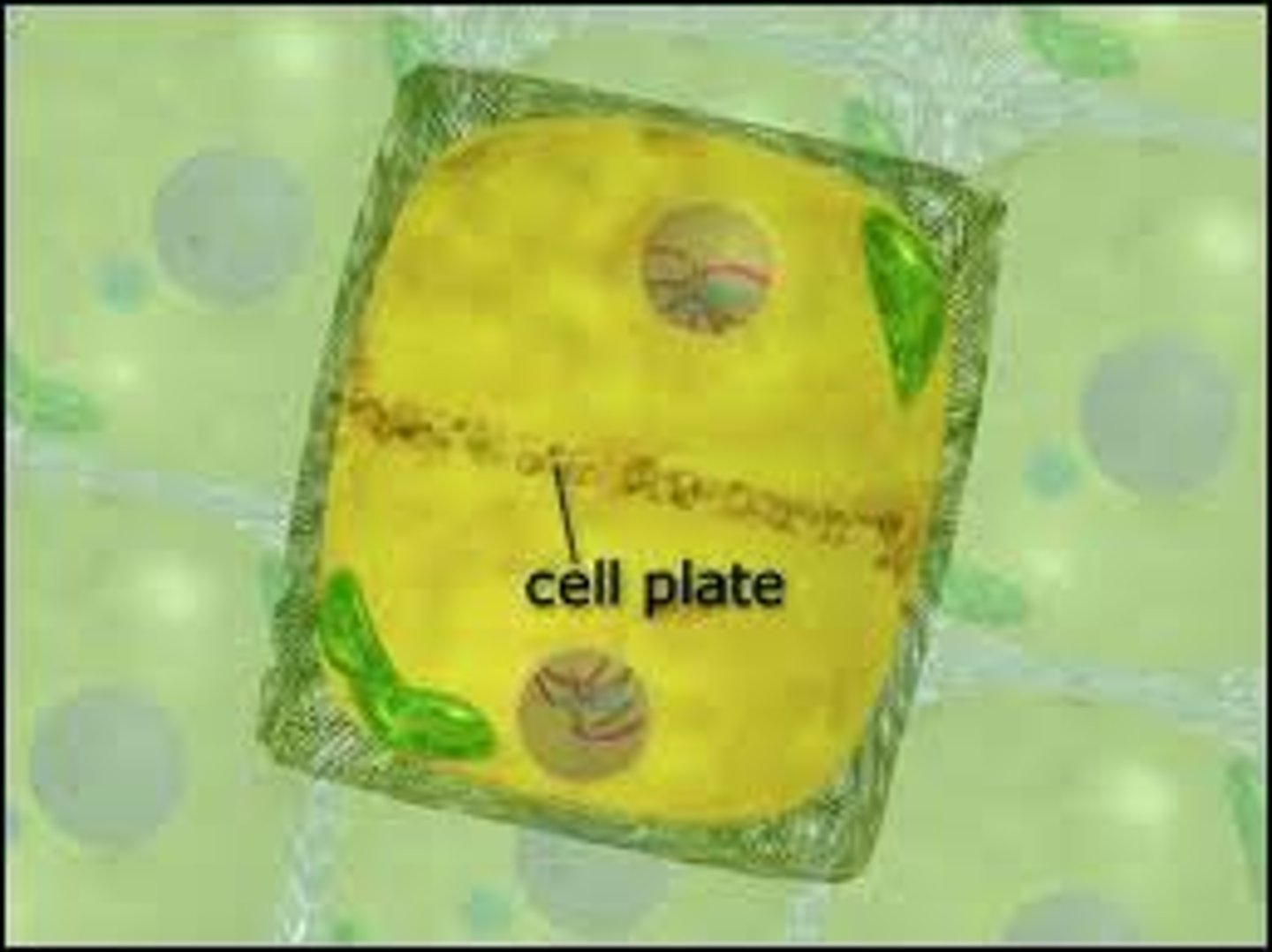
cell plate
The cell plate is a structure that forms when the cytoplasm of a plant cell divides. It eventually forms the cell wall found between plant cells.
target cell
cell that has a receptor for a particular hormone