ANTH 111 - Cultural Anthropology - Topic 4 (Language and Communication)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What is linguistic relativity?
The notion that all languages will develop the distinctive categories necessary for those who speak them to deal with the realities around them.
What hypothesis is linked to linguistic relativity? Define it as well.
Sapir-Whorf hypothesis: The idea that different languages create different ways of thinking.
Often misunderstood —> it assumes culture and language are constant, and that ideas, beliefs, ect do not change.
What are sociolinguistics?
The study of the ways culture shapes language and how language shapes culture. It explores the overlap of language with cultural categories and systems of power like gender, class, age, race, sexuality and ethnicity.
How is language and social status related?
Language often acts as a marker of social class. The use of honorifics (words/phrases used to show respect to showcase a certain social status) such as Mr., Mrs., Dr., Prof is an example of that.
think: honorifics = social status
What is code switching?
The act of switching between languages or forms of a language (like a dialect) depending on the social context.
It is found in different groups, often in high-populated areas.
What are genderlects?
It is the varieties of speech associated with particular genders. It explores how men and women use language differently.
Who is Deborah Tannen?
She is an American author and professor of linguistics who popularized the term genderlects.
She observed that women tend to rapport while men tend to report.
What are some key differences in how women VS. men talk?
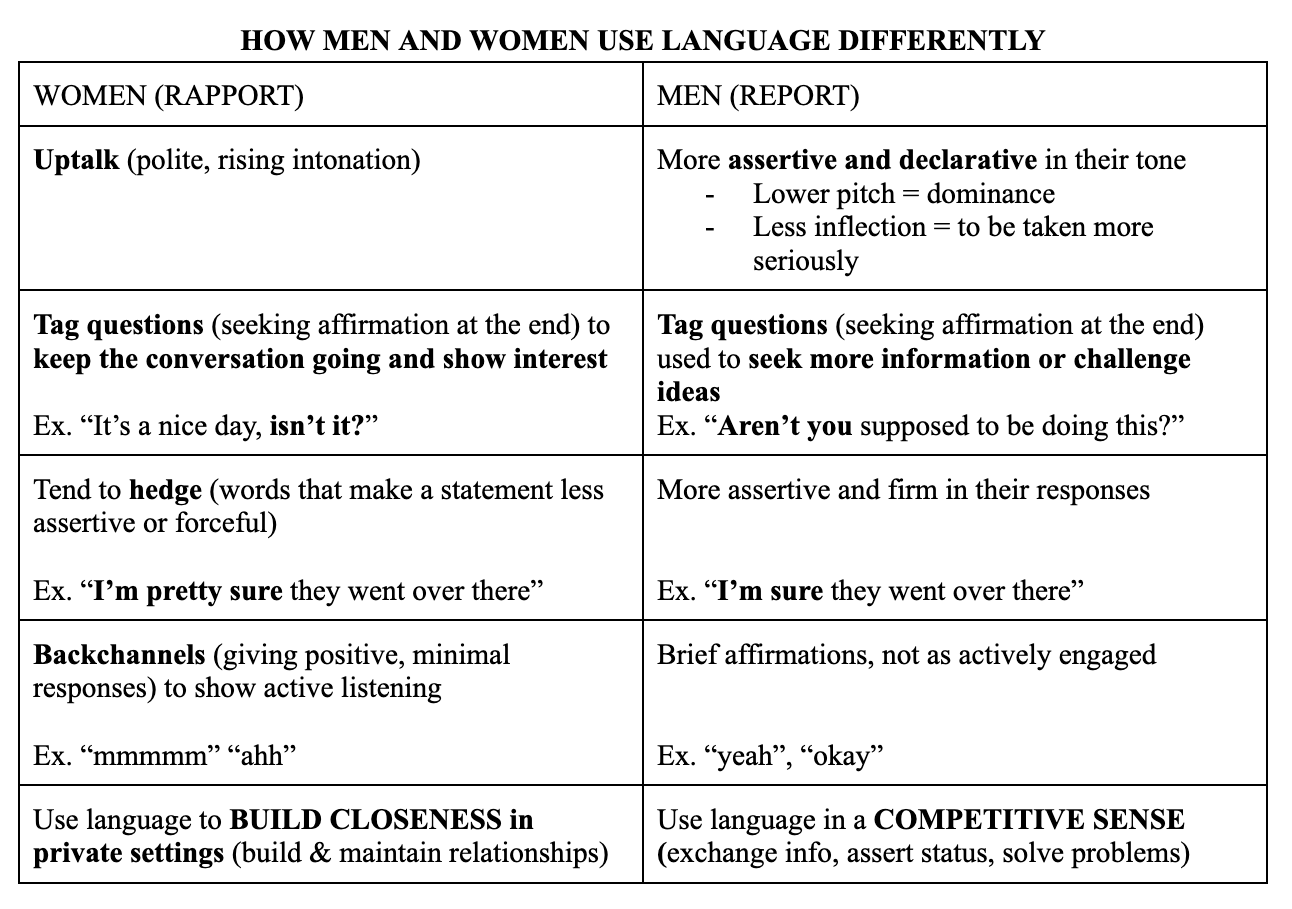
What does context mean?
It is the framework, background & surrounding circumstances in which the communication takes place.
What are high-context cultures? Give me some examples.
They have a low diversity population & share a similar culture.
Communication is indirect, relies heavily on context
Ex. Asia (Japan, Vietnam), Middle East (Iran), Africa, South America (Chile), Southern US
What are low-context cultures? Give me some examples.
They have a highly diverse population & share different cultures.
Communication is direct & unambiguous (easy to understand), meaning is shown by the words themselves —> need more affirmation
Ex. Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Great Britain, Northern US
What is silence?
How does silence apply to high context communicators VS. low context communicators?
It is a form of nonverbal communication. It is the complete absence of sound. It is also related to social status, wherein those with high social status remain silent to observe and judge compared to those with low social status remain silent due to the fear of offending those above them.
To high context communicators,
Silence = useful
To better understand someone
Ex. Japanese children are encouraged to be silent
To low context communicators,
Silence = avoided
Sees silence as a waste of time
Ex. North Americans are encouraged to speak, fill in the gaps of a conversation
What are kinesics?
It is the study of the relationship between body movements and communication.
The body can function as a text” that conveys messages and can be “read”.
It has cultural meaning to it as well
Includes:
facial expression
Way you stand and sit
How your body augments
What you are saying with your voice (intonation)
Eye movements
Posture
Walking style
What are the 2 subtopics related to kinesics?
1) Gestures — movements (usually with the hands) to convey meaning
2) Greetings — vary by culture, degree of formality or informality & social factors (gender, ethnicity, class and age)
What is paralanguage?
It is an extensive set of noises (laughs, cries, signs and yells) and tones of voice that convey significant information about the speaker. It is used to also convey emotional states.
How are prosodic features & gesticulations related to paralanguage?
Prosodic features — auditory qualities of speech (instonation, stress, loudness & rhythm) that help interpret the meaning of words
Gesticulations — expressed & interpreted unconsciously (is also culturally relative)
Prosodic features shape the tone and emotion of speech while gesticulations provide visual cues that reinforce, complement, or sometimes even contradict verbal messages
As well —> gestures replace language, whereas gesticulations accompany language
What is haptic communication?
It is a form of nonverbal communication. It involves touch. What is determined as “appropriate touching” is specific to each culture.
Touching is used:
In a sexual OR non sexual way
In a ritualistic manner (shaking hands, Hongi aka nose press of the Maōri)
To show affection, support and concern
How is proxemics related to haptic communication?
It refers to how people use space, otherwise known as your personal bubble.
You get uncomfortable when that bubble is breached, but only those who are close to you are allowed (ex. spouse, children, family).