Protein structures
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What are proteins made up of?
Amino acids joined by amino acids linked by peptide bonds
What does the primary structure (sequence) of amino acids determine
The final 3D shape and function of a protein
What is a peptide bond
Covalent bond formed by condensation reactions (removal of water)
What are the functions of a protein
Catalysis, transport, structure and motion
Which proteins (enzymes) play a role in catalysis?
Enolase - envolved in glycolysis (the breakdown of sugar for energy)
DNA polymerase - helps replicate DNA
Which proteins play a role in transport?
Hemoglobin - carries oxygen in blood
Lactose permease - transport of lactose across cell membranes
Which proteins play a role in structural support?
Collagen - found in connective tissue
Keratin - found in hair, nails, feathers…
Which proteins play a role in movement?
Myosin - muscle contraction
Actin - muscle movement and cell motility
How are peptide bonds broken
By hydrolysis (water is added)
What are the ionizable groups of peptides
One free alpha-amino group
One free alpha-carboxyl group
Some R-groups (side chains)
Why are there non-amino acid components in proteins
Proteins → made up of polypeptides
They are not always JUST chains of amino acids
Some proteins require extra components to work correctly
What are the names of non-amino acid components in proteins
Cofactors, coenzymes and prosthetic groups
What are cofactors?
Non-protein molecules that assist protein function
Can be:
Metal ions - help catalyse enzyme reactions
Organic molecules - assist protein function
E.g. Hemoglobin uses iron (Fe2+) in heme group to bind and transport oxygen
What are coenzymes?
Organic molecules that assist the catalysation of molecules
Not permanently attached to protein
What are prosthetic groups?
Permanently bound to the protein
Play role in protein stability and function
E.g. Heme in myoglobin to help store and transport oxygen
What is the different between monomeric and multimeric proteins
Monomeric - one polypeptide chain. E.g. Myoglobin
Multimeric - two or more polypeptide chains. each chain is called a subunit and are non-covalently linked. E.g hemoglobin (4 subunits)
Difference between simple and conjugated proteins
Simple - only composed of amino acids, no additional chem group
Conjugated - contains amino acids + other chemical components (prosthetic group) which are critical for protein function
What are examples of weak, noncovalent interactions
Hydrophobic effect - non polar avoid water
Hydrogen bonding - forms between polar groups
Ionic interactions - attraction between charged side chains
Van der Waals forces - weak short range attractions
What is native conformation
Proteins fold into a specific 3D shape
What are chaperone proteins
Proteins that help proteins fold correctly
How does the hydrophobic effect cause protein folding
Hydrophobic amino acids cluster inside protein
Hydrophilic amino acids stay on the outside
This lowers entropy (low chaos of protein as water-loving molecules are outside and water-fearing molecules are inside) → folding is favourable
How do hydrogen bonds help stabilise folding?
Hydrogen bonds form between backbone atoms and the side chains of polar amino acids
They help maintain protein structure and overall protein stability
How do ionic interactions provide extra stability during folding?
Salt bridges occur between positively and negatively charged amino acid side chains
They increase stability, especially for proteins functioning at extreme pH
How do Van der Waals forces promote protein folding
Van der Waals forces - Short range interractions between nonpolar atoms
Individually are weak, but when combined they provide stability
Help protein maintain tight packing in folded state
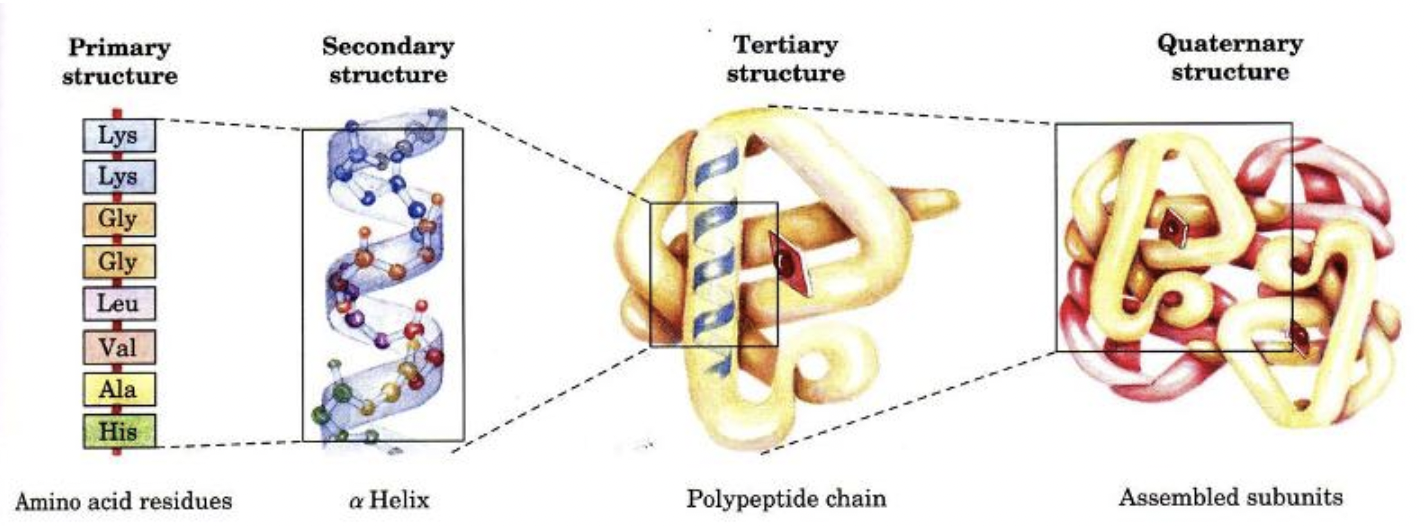
What are the 4 levels of protein structure
Primary - sequence amino acids
Secondary - local structure like alpha helices and beta sheets
Tertiary - overall 3D folding of polypeptide
Quaternary - interaction of multiple polypeptide chains
What are the 4 types of proteins
Fibrous proteins - long strands
Globular proteins - spherical and water soluble
Membrane proteins - found in cell membranes
Intrinsically disordered proteins - lack of fixed shape
What is cellular proteostasis
Cellular system that ensures proteins fold correctly and prevents misfolding
What is denaturation
Loss of structure and function due to; heat, pH changes, organic solvents, chaotropic agents
Misfolded proteins can lead to:
Diseases such as (Alzeimers, Parkinsons, Huntingtons…)
What are amyloid fibers?
Insoluble protein aggregates when proteins misfold
Misfolded proteins stick together and form long, rigid fibrils
These fibers accumulate and cause cell damage in tissue