MGMT 4513 Midterm Exam
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
Strategic management
The study of why some firms outperform others
Analysis
Strategic goals (vision, mission, strategic objectives)
Internal and external environment of the firm
Strategic decisions
Where to compete?
How to compete?
When to compete?
Energizing actions
Vision, leadership, problem solving process, people development, organizational infrastructure, communications, performance measurement
Strategic direction
Mission, vision, strategy
Mission
Statement explaining why a company exists
- Provides context for all decisions within the organization
- Describes an enduring reality
- Is capable of infinite fulfillment (no time frame)
- Useful for both internal and external audiences
Vision
Crystalization of what leaders want firms to be
- Guides development of strategy and organization
- Describes an inspiring new reality
- Is achievable within a specific time period
- Primarily useful internally (slogans can be used externally)
Strategy plan
How to beat present and potential competitors
- Lists set of actions to provide products or services that create more value than their cost
- Constantly changes in response to analysis, customer experience, trial and error
- For internal use
2 approaches for evaluating firm performance
- Financial ratio analysis
- Stakeholder perspective
Stakeholders
Individuals and groups who can affect, and are affected by, the strategic outcomes achieved and who have enforceable claims on a firm's performance
External environments
General, industry, competitor
Attractive industry
- High entry barriers
- Suppliers and buyers have weak positions
- Few threats from substitute products
- Moderate rivalry among competitors
Unattractive industries
- Low barriers to entry
- Strong supplier and buyer bargaining power
- Strong threat from substitutes
- Intense rivalry
- Low profit potential
- No two firms are totally different
- No two firms are exactly the same
2 unassailable assumptions in industry analysis
Claims
Enforced by the stakeholder's ability to withhold essential participation
The 3 stakeholder groups
- Capital market stakeholders
- Product market stakeholders
- Organizational stakeholders
Capital market stakeholders
- Shareholders and lenders expect the firm to preserve and enhance the wealth they have entrusted to it
- Returns should be commensurate with the degree of risk to the shareholder (shareholders major suppliers of capital (e.g., banks)
Product market stakeholders
Primary customers, suppliers, host communities, union officials
Primary customers
Demand reliable products at low prices
Suppliers
Seek loyal customers willing to pay highest sustainable prices for goods and services
Host communities
Want companies willing to be long-term employers and providers of tax revenues while minimizing demands on public support services
Union officials
Want secure jobs and desirable working conditions
Organizational stakeholders
Employees, managers, nonmanagers
Employees
- Expect a dynamic, stimulating and rewarding work environment
- Are satisfied by a company that is growing and actively developing their skills
Two issues affect the extent of stakeholder involvement in the firm
- How to divide returns to keep stakeholders involved?
- How to increase returns so everyone has more to share?
Corporate governance
The relationships among various participants in determining the direction and performance corporations
- Shareholders
- Management (led by the CEO)
- Board of directors
The firm
- Goals and values
- Resources and capabilities
- Structure and systems
The industry environment
- Competitors
- Customers
- Suppliers
Strategic competitiveness
When a firm successfully formulates and implements a value-creating strategy
Sustainable competitive advantage
When competitors are unable to duplicate a company's value-creating strategy
Strategic management process
The full set of commitments, decisions, and actions required for a firm to achieve strategic competitiveness and earn above-average returns
Risk
An investor's uncertainty about the economic gains or losses that will result from a particular investment
Average returns
Returns equal to those an investor expects to earn from other investments with a similar amount of risk
Above-average returns
Returns in excess of what an investor expects tp earn from other investments with a similar amount of risk
Alternative views of "outperform others"
- The economic value model
- Objectives other than wealth creation
- Stakeholder surplus model
The economic value model
Strategy objective is to maximize shareholder wealth
Objectives other than wealth creation
Objectives that are used as surrogates for eventual wealth or the fulfillment of a mission
Stakeholder surplus model
Defines beneficiary group and maximizes wealth for total group
- To replace assets a firm must earn return on capital in excess of cost of capital
- To survive acquisition, firm must achieve stock market value in excess of break-up value
How do we know if a company is performing well at the minimum?
A comprehensive value metrics framework
1. Value drivers
2. Financial indicators
3. Intrinsic value
4. Shareholder value
Value drivers sources
- Market share
- Scale economies
- Innovation
- Brands
Financial indicators measures
- Return on capital growth (of revenues and operating profits)
- Economic profit (EVA)
Intrinsic value measures
- Discounted cash flows
- Real option values
Shareholder value measures
- Market value of the firm
- Market value added (MVA)
- Return to shareholders
Relationship of economic value to share price
Internal views, external views, and the translation process
Internal views
- Economic value
- Changes in financial efficiency
- Value of additional operating options
- → Economic value of strategy
External views
- → Share value (present strategy)
- → Alternate owners and uses of assets
- → Share price
Translation process
- Generic preference and credibility → market view
- Market view and communication → ____________
Mission statements, vision statements, strategic objectives
The hierarchy of organizational goals is in this order (least specific to most specific)
False
(T/F) Some excellent examples of mission statements are: "To be the happiest place on earth" (Disney) and "restoring patients to full life" (Medtronic)
False
(T/F) Organizational goals and objectives should be vague in order to allow changes in strategy
Economic value
Present operations and balance sheet
Financial ratio analysis
- Balance sheet
- Income statement
Stakeholder perspective
- Employees
- Customers
- Owners
General environment
Focused on the future
Industry environment
Focused on factors and conditions influencing a firm's profitability within an industry
Industry
A group of firms producing products thar are close substitutes
- Firms that influence one another
- Includes a rich mix of competitive strategies that companies use in pursuing strategic competitiveness and above-average returns
Competitive environment
Focused on predicting the dynamics of competitors’ actions, responses and intentions
- Sometimes called the task or industry environment
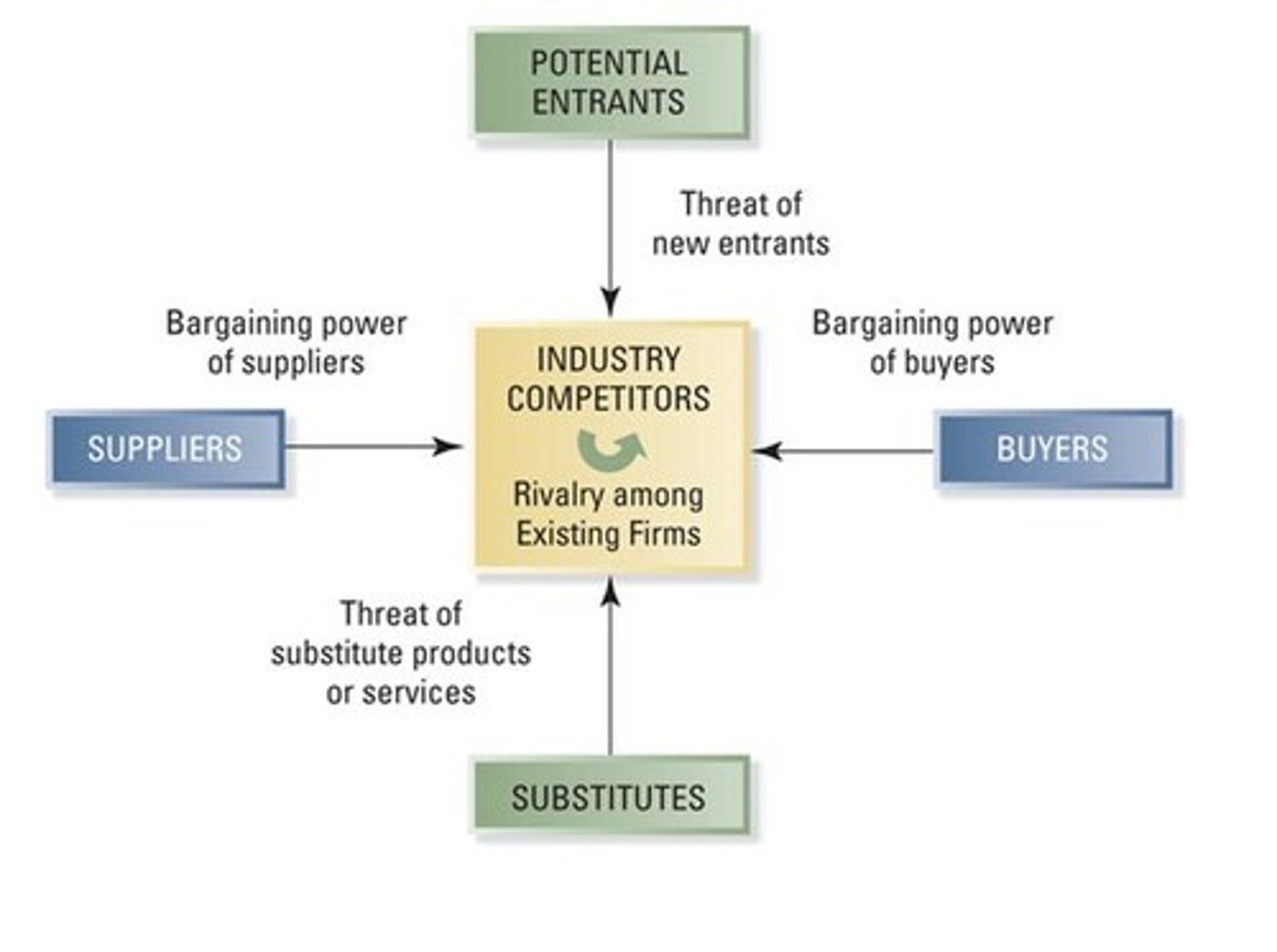
Porter's Five Forces Model
Potential Entrants
Substitutes
Suppliers
Competitors
Attractive Industry
Sociocultural changes
Increasingly larger numbers of women entering the work force since the early 1970s is an example of
An industry is defined as
A group of firms producing products that are close substitutes
Increase in demand for any given price
Shifts in a "textbook" demand curve:
- Price of substitutes rises
- Price of complements decreases
- Income rises
- Increase in desirable product attributes
- Shift in consumer preferences/demographics toward good
Decrease in demand for any given price
Shifts in a "textbook" demand curve:
- Price of substitutes decreases
- Price of complements rises
- Income decreases
- Decrease in desirable product attributes
- Shift in consumer preferences/demographics away from good
Switching price
Price at which product value equals the value of next best alternative for that customer or segment
- Must be for a particular product, given other products in the market
Demand curve
Summarizes relative value to each segment
"Textbook" smooth demand curve
Just approximation of underlying "kinked" demand curve defined by different switching prices for different customer segments
The threat of new entrants
Profits of established firms in the industry may be eroded by new competitors
Reduces threat of new entrants
High barriers of entry
- Economies of scale
- Product differentiation
- Capital requirements
- Switching costs
- Access to distribution channels
- Cost disadvantages independent of scale
- Government policy
- Expected retaliation
Economies of scale
Marginal improvements in efficiency that a firm experiences as it incrementally increases its size
Product differentiation
- Unique products
- Customer loyalty
- Products at competitive prices
Capital requirements
- Physical facilities
- Inventories
- Marketing activities
- Availability of capital
Switching costs
- One-time costs customers incur when they buy from a different supplier
- New equipment
- Retraining employees
- Psychic costs of ending a relationship
Access to distribution channels
- Stocking or shelf space
- Price breaks
- Cooperative advertising allowances
Cost disadvantages independent of scale
- Proprietary product technology
- Favorable access to raw materials
- Desirable locations
Government policy
- Licensing and permit requirements
- Deregulation of industries
Expected retaliation
Responses by existing competitors may depend on a firm's present stake in the industry (available business options)
Rivalry among competing firms
Which is considered a force in the "Five Forces" model?
Increases the threat of new entrants
Because the internet lowers barriers to entry in most industries, it
Bargaining power of suppliers
Which of the following is NOT an entry barrier to an industry?
True
(T/F) Industries characterized by high economies of scale typically attract fewer new entrants
A competitor to your product where a high switching cost exists
Which of the following firms would likely pose the least competitive threat?
Dominance by a few suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers is enhanced under the following market condition:
The cost of the marble will be expensive because of the bargaining power of the supplier
A certain marble quarry provides a unique type of marble that is richly colored and strikingly veined. It has been used for churches and public buildings throughout the world. The architect of a new headquarters for a prestigious Fortune 500 firms has specified the use of this marble, and this marble only, for this project. which of the following statements is most likely to be true?
Strategic groups
Cluster of firms that share similar strategies
Strategic dimensions
- Extent of technological leadership
- Product quality
- Pricing policies
- Distribution channels/type of distribution system
- Customer service
- Breadth of product and geographic scope
- Degree of vertical integration
Analysis of resources, capabilities, and core competencies
If you believed in a pure five forces model of above-average returns, which of the following things is LEAST important?
Industry B; Industry B
Industry A is characterized by high advertising and R&D expenses (as a proportion of revenues) or, said differently, high differentiation. Industry B has a low advertising and R&D expenses. Which industry would tend to have a higher threat of new entrants? Higher degree of rivalry?
Business-level strategies
Are intended to create differences between the firm's position relative to those of its rivals
Broad scope
The firm competes in many customer segments
Narrow scope
The firm selects a segment or group of segments in the industry and tailors its strategy to serving them at the exclusion of others
Cost leadership strategy
An integrated set of actions taken to produce goods or services with features that are acceptable to customers at the lowest cost, relative to that of competitors with features that are acceptable to customers
A manufacturing business pursuing cost leadership will likely
Rely on experience effects to raise efficiency
Overall cost leadership
Convincing rivals not to enter a price war, protection from customer pressure to lower prices, and the ability to better withstand cost increases from suppliers characterize which type of competitive strategy?
Differentiation strategy
An integrated set of actions taken to produce goods or services (at an acceptable cost) that customers perceive as being different in ways that are important to them
Focus strategies
An integrated set of actions taken to produce goods or services that serve the needs of a particular competitive segment
Decreased emphasis on competition based on price
High product differentiation is generally accompanied by
Offering lower prices to frequent customers
A firm can achieve differentiation through all of the following means except
If several competitors pursue similar differentiation tactics, they may all be perceived as equals in the mind of the consumer
Which statement regarding competitive advantages is true?
Broadly-defined target market is to a cost leadership strategy
A narrow market focus is to a differentiation-based strategy as a
False
(T/F) To generate above average returns, a firm following an overall cost leadership position should not be concerned with attaining parity or proximity on the basis of differentiation relative to its peers