AP PSYCH Vocab Unit 0
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms

Hindsight bias
The tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that one would have foreseen it.
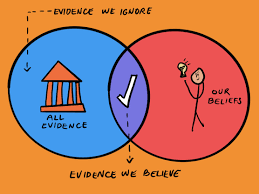
Confirmation bias
a tendency to search for info that supports our preconceptions and to ignore or distort contradictory evidence.

Overconfidence
The tendency to be more confident than correct- to overestimate the accuracy of our beliefs and judgements.
Peer review
The process where an authors research paper is evaluated by peers in the same field before it’s published.
Theory
An explanation using an integrated set of principles that organizes observations and predicts behaviors or events.
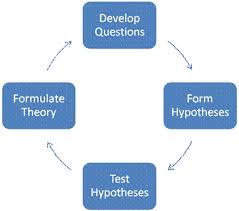
Hypothesis
A testable prediction, often implied by a theory.

Falsifiable
The principle that a scientific hypothesis or theory must be testable and potentially disproven by evidence or experiment.
Operational definition
A carefully worded statement of the exact procedures used in a research study.

Replication
Repeating the essence of a research study, usually with different participants in different situations, to see whether the basic finding can be reproduced.
Case study
A descriptive technique in which one individual or group is studied in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles.
Meta-analysis
A procedure for statistically combining the results of many different research studies.

Naturalistic observation
A descriptive technique of observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without trying to manipulate or control the situation.

Survey
A descriptive technique for obtaining the self-reported attitudes and behaviors of a particular group, usually by questioning a representative, random sample of the group.

Social desirability
Tendency for individuals to answer survey questions in a way that presents themselves favorably, aligns with social norms, or meets the researchers perceived expectations, rather than truthfully or accurately reflecting their actual behaviors, beliefs, or feelings.

Self-report bias
The tendency for the individuals to inaccurately or untruthfully report their own behaviors, thoughts, or feelings, often due to a desire to appear more favorable or socially acceptable.
Population
All those in a group being studied, from which samples may be drawn.
Sample
A group of individuals selected from a large population that a researcher plans to study.
Sampling bias
A flawed sampling process that produces an unrepresentative sample.
Random sample
A subset of a larger population chosen for a study where every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected, increasing the likelihood that the sample is representative of the population.
Convenience sampling
A non-probability sampling method where a researcher selects participants for a study based on their easily accessibly and convenient availability, rather than a random selection process.

Representative sample
A subset of a larger population that mirrors the characteristics and demographics of that entire population.
Methodology
The systematic principles and procedures used to conduct psychological research, encompassing the overall theoretical framework, specific techniques for data collection and analysis, and the overall design of a study to address a research question.
Non-experimental
A study that lacks the manipulation of an independent variable, random assignment of participants, or both.

Correlation
A measure of the extent to which two factors vary together, and thus of how well either factor predicts the other.
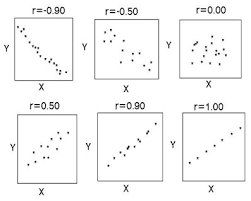
Correlation coefficient
A statistical index of the relationship between two things.
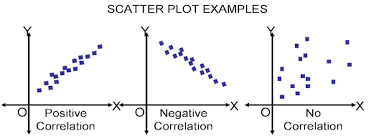
Scatterplot
A graphed cluster of dots, each of which represents the values of two variables.
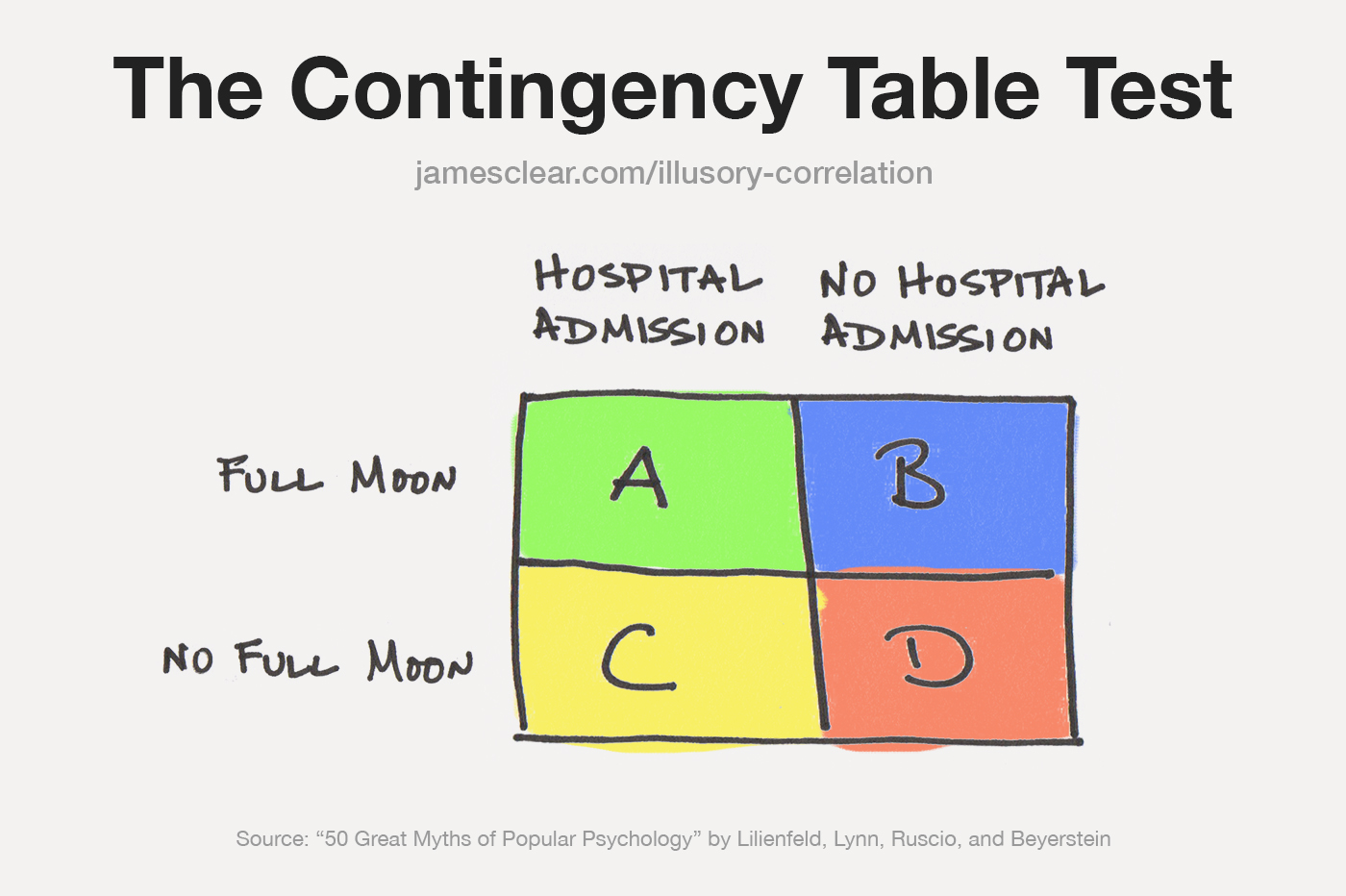
Illusory correlation
Perceiving a relationship where none exists, or perceiving a stronger-than-actual relationship.
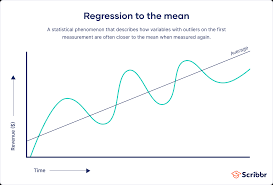
Regression towards the mean
The tendency for extreme or unusual scores or events to fall back toward the average.

Experiment
A research method in which an investigator manipulates one or more factors to observe the effect on some behavior or mental process.

Experimental group
In an experiment, the group exposed to the treatment, that is, to one version of the independent variable.

Control group
In an experiment, the group not exposed to the treatment.
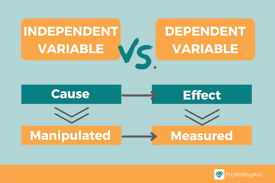
Independent variable
In an experiment, the factor that’s manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied.
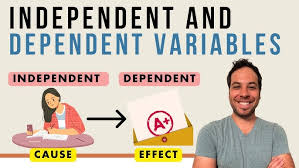
Dependent variable
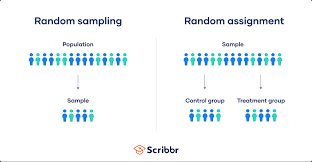
Random assignment
Assigning participants to experimental and control groups by chance, thus minimizing preexisting differences between different groups.
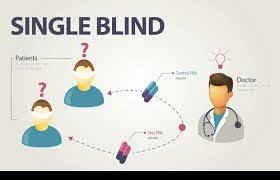
Single-blind procedure
Participants are unaware of which experimental group they belong to, while the researchers and experimenters who interact with them are fully aware of the group assignments.

Double-blind procedure
An experimental procedure in which both the research participants and the research staff are ignorant about whether the research participants have received the treatment or a placebo.

Placebo
An inactive substance or treatment designed to resemble the actual treatment being tested but lacking any real therapeutic effect.
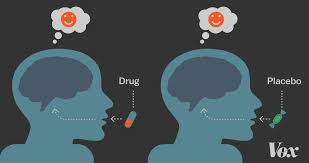
Placebo effect
Experimental results caused by expectations alone; any effect on behavior caused by the administration of an inert substance or condition, which the recipient assumes in an active agent.
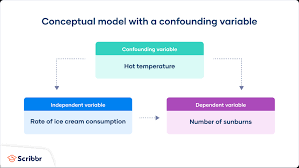
Confounding variable
A factor other than the factor being studied that might influence a study’s results.

Experimenter bias
The subconscious or conscious tendency for a researcher to influence the results of a study, often by treating participants or recording data in ways that confirm their own hypothesis.
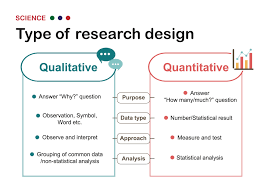
Quantitative research
The systematic collection and analysis of numerical data to identify patterns, make predictions, test hypothesis, and generalize findings to a larger population.

Qualitative research
A method that gathers and analyzes non-numerical, descriptive data, such as in-depth interviews, case studies, and naturalistic observations, to explore subjective experiences, behaviors, beliefs, and meanings rather than quantify them with numbers.
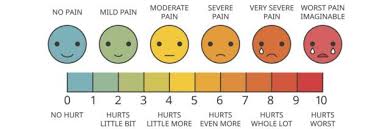
Likert scale
A numerical rating scale used to measure attitudes, opinions, or degrees of agreement with a statement, often
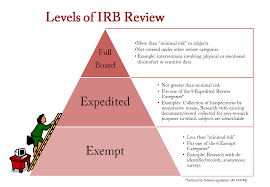
Institutional review
A committee at a research institution that reviews and approves research involving human subjects to ensure ethical standards and participants welfare are protected.

Informed consent
Giving potential participants enough info about a study to enable them to choose whether they wish to participate.
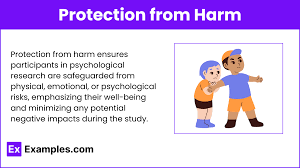
Protect from harm
A core ethical principle requiring researchers to prevent participants from experiencing significant physical or psychological distress, such as embarrassment, stress, or pain, throughout a study.

Confidentiality
Ethical principle that ensures info provided by research participants or therapy clients is kept private and secure, with the researcher or professional taking steps to prevent it’s disclosure to others without the participants or clients consent.
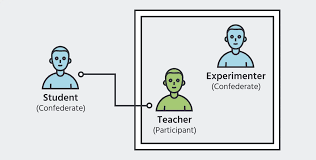
Research confederates
An individual who acts as a participant in a psych experiment but is actually working for the researchers, not the true subject being studied.

Debriefing
The post-experimental explanation of a study, including it’s purpose and any deceptions, to it’s participants.
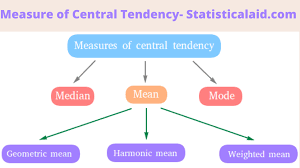
Measure of central tendency
A single value that attempts to describe the center or typical value of a data set, indicating where the data points tend to congregate.

Mode
The most frequently occurring score(s) in a distribution.
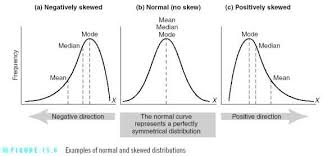
Mean
The arithmetic average of a distribution, obtained by adding the scores and then dividing by the number of scores.

Median
The middle score in a distribution.
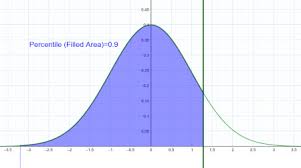
Percentile rank
Indicates the percent of scores in a distribution that fall at or below a specific score.
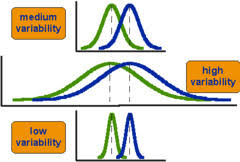
Measures of variation
Describe the dispersion or spread of data points in a dataset.

Range
The difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution.
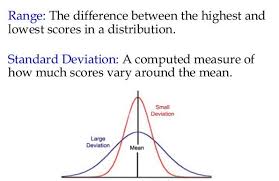
Standard deviation
A computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean.
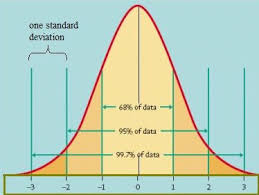
Normal curve
Bell-shaped curve that describes the distribution of many types of data.
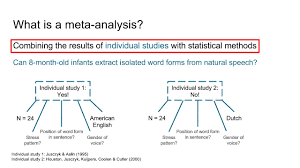
Meta-analysis
A procedure for statistically combining the results of many different research studies.

Statistical significance
A statistical statement of how likely it is that an obtained result occurred by chance.
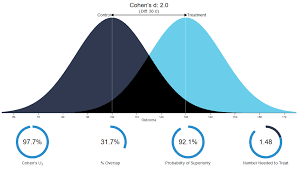
Effect size
Quantifies the magnitude or strength of a relationship between variables or the difference between groups, indicating how significant the finding is in real-world terms.