Kinesiology Test 2
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Muscle is responsible for all of the following EXCEPT:
Temperature Regulation
Support/ Protection
Receiving and transmitting signals from the senses
Body Movement and Posture
Receiving and transmitting signals from the senses
True or False: Pennate fibers are longer, so the muscle’s range of motion is longer.
False
What type of muscle contraction occurs when a muscle is elongating?
Eccentric
Myometric
Isometric
Concentric
Eccentric
The _______ executes the action opposite of the agonist
Antagonist
Synergist
Protagonist
Neutralizer
Antagonist
Which type of parallel muscle has a wide belly, narrow at the ends and parallel fibers that taper to strong tendons
Flat
Sequential
Pennate
Fusiform
Fusiform
Most muscle attachments can be found on the more ______ bone
Stationary
Mobile
Stationary
What are the two main categories of muscle fiber arrangements?
Parallel and pennate
Pennate and bipennate
parallel and transverse
Diagonal and straight
Parallel and pennate
The deltoid is an example of which type of pennate arrangement?
Unipennate
Monopennate
Multipennate
Bipennate
Multipennate
Excessive joint motion that stems from joint laxity is also known as
Active Mobility
Range of Motion
Hypermobility
Hypomobility
Hypermobility
Which of the following joints is MOST mobile?
Hip joint
sacroiliac
Glenohumeral
Elbow joint
Glenohumeral joint
The main function of the ______ is to reduce friction between moving parts in joints of the body
Tendon sheath
articular capsule
bursa
synovial membrane
bursa
Which of the following is an example of an open Kinetic Chain Movement ?
Biceps curl
push up
pull up
dead lift
Biceps curl
the hip joint is an example of a/an ______ joint.
diaxial
multiaxial
biaxial
uniaxial
multiaxial
Which of the following does NOT impact range of motion?
Muscle strength and tightness
Diet
Elasticity of connective tissues
Age
Diet
Which of the following is not the movement that a convex/ concave joints can make ?
Flex
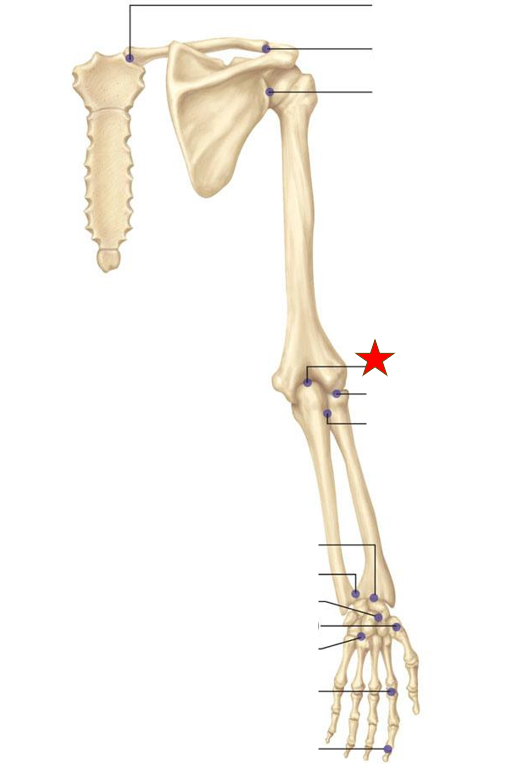
Which joint is this ?
Humeroradial
Ulnaradial
Radioulnar
Humeroulnar
Humeroulnar
True or False: An injury involving the stretching or tearing of a muscle or tendon is a sprain
False
When classifying joints by structure this type of joint holds bones together with dense regular connective tissue
synovial
connective
fiburous
cartilaginous
Fiburous
True or false: tendons connect bone to bone
False
Which property allows connective tissue to be both flexible and virtually in-comprehensive
Elasticity
Thixotrpic
Plasticity
Colloid
Colloid
From a functional standpoint, connective tissues can be _____ or ______ tissue
compressive; plastic
active; passive
compressive; tension
pension; pliable
Compressive; tension
_______ is a type of loose connective tissue located just under the skin and covering the entire body
Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue
Superficial fascia
Interosseous Membrane
Periousteium
Superficial fascia
When a tendon stretches and then returns to its original length this is an example of
Tensile strength
Plasticity
Creep
Elasticity
Elasticity
______ is/are the most abundant protein in the body
Elastin
Ground Substance
Collagen
Reticular Fibers
Collagen
Whats the bones correct shape: femur
Long bone
What the bones correct shape: Patella
Short bone
Whats the bones correct shape: Rib
Flat bone
Match the bone with the correct shape: vertebrae
Irregular bone