Seutics 2 - Manickam
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Define: Nanoparticles
tiny particles that carry drug to where they need to go to be delivered for drug target
NPs are a typoe of colloidal drug delivery system. What is the size range that is pharmaceutically relevant?
10-100 nm
NPs consist of drug entity and polymers/lipids that assemble them into nanosized particles. What are the drug entities that it could be?
small molecule drug
peptide
protein
nucleic acid
What are the two major types of NPs?
liposomes
micelles
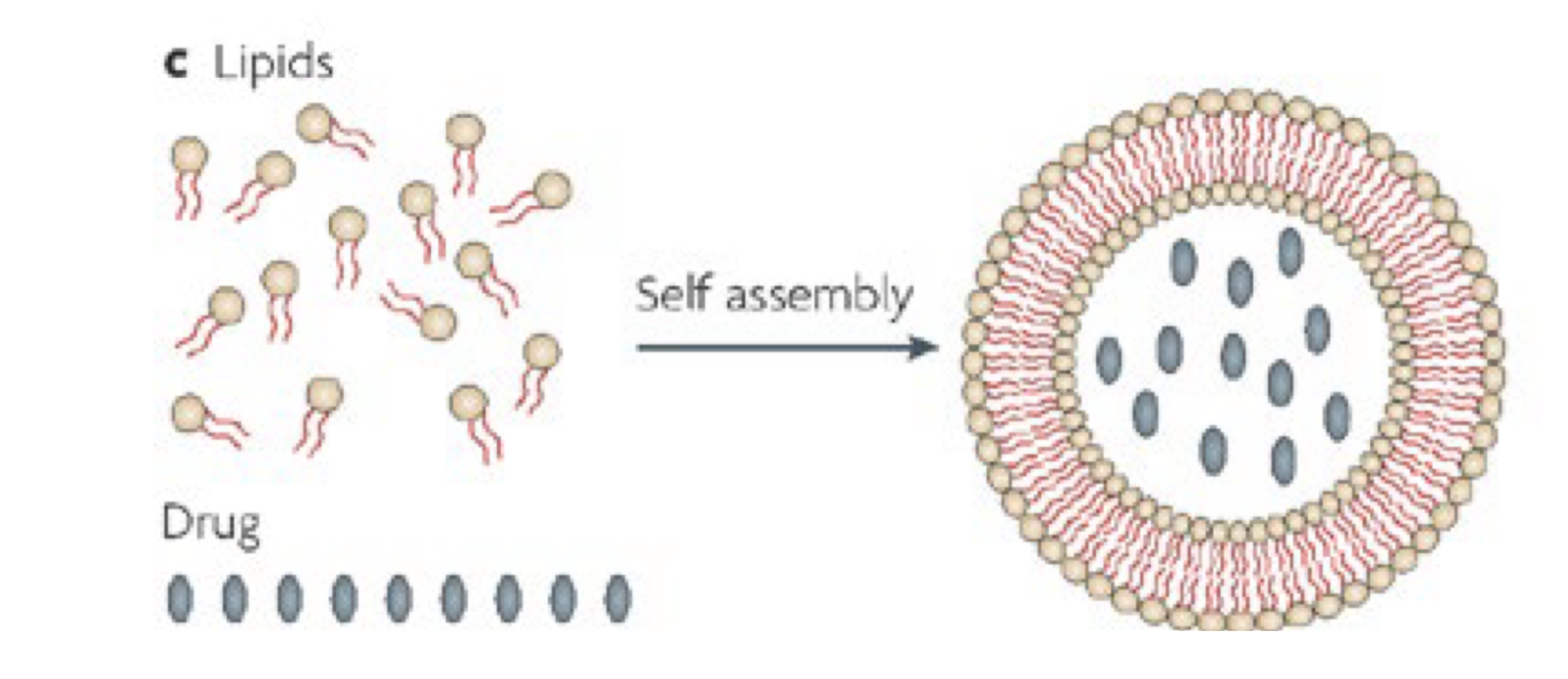
What structure is this?
Liposome
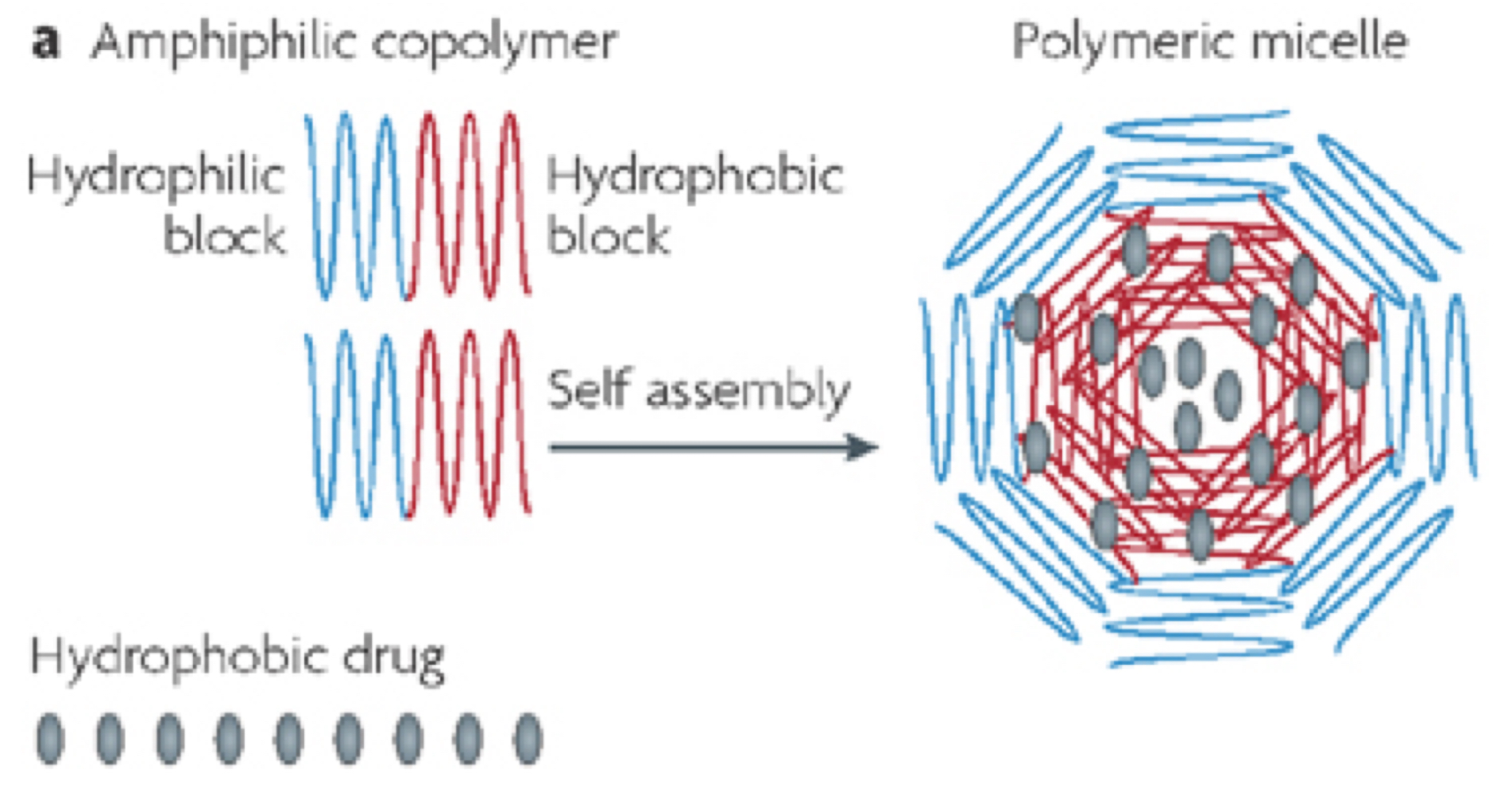
What structure is this?
Micelle
Define: Liposome
bilater lipid assemblies with hydrophilic center/core
contains amphilphilic molecules that make liposomes good for hydrophilic drug delivery
Core/center: hydrophilic
Middle bilayer: hydrophobic
Amphiphilic molecules
head = hydrophilic
tail = lipophilic/hydrophobic
Define: Micelle
aggregates of amphiphilic copolymers with hydrophobic core
hydrophobic core with hydrophilic shell (hydrophobic drug loaded in center)
What is the key advantage of micelles and liposomes as applied to drug solubility
incr. amt of drug loading and it increases overall drug solubility in carriers
What are the three key messages regarding nanoparticles and their characteristics
NPs are not rapidly cleared via kidneys
NPs circulate longer and accumulate better in tumors
NPs are internalized by cells via endocytosis
Advantage of drug in nano particle
greater probability for drug to get to target site
8 characteristics that make nanoparticles useful for anticancer drug delivery
greater drug loading capacity
can load multiple drug molecules for drug drug combinations
allow for modifying drug release rate
circulate longer, lesser elimination by kidneys
can be modified with PEG → decreases non specific uptake into liver and spleen and increase circulation times (PEGylation)
Multivalency/Drug targeting
Enhanced permeability and retention effect for anti cancer drug delivery
can overcome drug resistance and still deliver drug to cells
Advantage of PEGylation
PEGylated particles are not rapidly cleared via liver therefore pegylated particles circulate for longer times
How are NPs affected by PEGylation?
normally opsonin on NPS will sent signals to machrophages and be cleared; however PEGylation adds PEG chains to NP and it reduces opsonin association
opsonin are negatively charged particles
Define: Multivalency
refers to NP surface mods using multiple copies of targeting ligand → leads to greater uptake and therefore more drug enters cell
What is meant by enhanced permeability and retention of NPs?
NPs can extravasate/permeate into leaky capillaries and accumulate in greater amts in tumors
NPs are retained longer due to reduced lymphatic drainage in tumors.
NPs can overcome surface efflux pump mediated drug resistance. NPs enter cells via ____ and avoid recognition by efflux pumps
endocytosis
What does PEG modification to NPs do?
PEG modification decreases liver clearance of NPS and therefore ..
increase circulation times
increase t1/2 → decreases clearance
NPs clear ___ compared to free drug
slower
PEG chains increase circulation _ _ of liposomes
half life
Micelles circulate _ and have a slower clearance
longer
Micelles have improved therapeutic effacy compared to _ drug
free
Small molecules are considered _ than 1000 Da
less
Large/macromolecule drugs are considered _ than 500-1000 Da
more
What are biologics
class of drugs that are derived from biological sources
Proteins have a range of molecular masses and protein drugs act on specific __ __ / receptors in body
target sites
Biologics
New class of treatments made from living organisms
have capability to more effectively treat diseases
Why are biologics more capable to more effectively treat diseases?
action specificity
require lower/smaller doses compared to traditional small molecule APIs (INCREASED POTENCY)
5 challenges to delivery of polypeptide drugs
large molecular mass proteins have a lower permeability across cell membranes
charged proteins (anionic vs cationic) will have a difficult time passing through membrane
enzymatic degradation by digestive proteases
immunogenicity against recombinant proteins
large molecular mass /cationic → will be hydrophilic
What are the advantages of oral protein and peptide delivery systems
protect drug from enzymatic degradation and decrease their systemic clearance
increase cargo solubility
controlled release and minimize undesirable side effects
improve biodistribution - decrease non specific uptake (by liver and spleen) and increase amts available for selective uptake by target cell/organ
lower immunogenicity
PEGylation is process of ___ ___ of PEG to a protein/polypeptide
covalent attachment
3 characteristics of PEGylated proteins
increase particle size = lower kidney clearance
increased H2O solubility (hydrophilicity) → for IV injections
reduced proteolytic / enzymatic degradation
PEGINTRON (PEGylated interferon alpha 2b) is used to treat ..
hepatitis from HCV infection
How does Interferon Alpha 2a affect PK and PD effects
modify with PEG
stays in blood longer and therefore increased absorption and sustained absorption
clearance is longer
increased t1/2
How does PEGylation affect dosing interval?
decreases dosing interval and therefore increases pt compliance
What are nucleic acids
sugar
ribose (RNA)
Deoxyribose (DNA)
nucleotide bases
AUCG (RNA)
ATCG (DNA)
negatively charged phosphate backbone
What are the key characteristics of nucleic acids that are also the challenges for delivery?
anionic and hydrophilic biomacromolecules
Where should drug be delivered if delivering DNA
cell nucleus
Where should drug be delivered if delivering mRNA
cytoplasm
DNA and mRNA delivery allows expression of __ ___
encoded protein
What are the steps in NA delivery
extracellular
particle injected
circulation
accumulation
penetration
intracellular
enters cell via edocytosis
endo/lysosomal escape
DNA → nucleus
RNA → cytoplasm
_ function to carry NA to their sites of action
vectors
Define: _ _ is the clinical application of DNA molecules → involvesreplacement of mutated copy of gene with a healthy/normal DNA copy
Gene therapy
Strimvelis is a gene therapy for treatment of ___
ADA-SCID
Limited packaging capacity of viral vectors and ____ are key concerns that drive need for safer alternatives for gene delivery
immunogenicity
3 main extracellular barriers/challenges to NP delivery of NAs
renal filtration
non specific uptake by liver/spleen
nuclease degradation
What are 3 main intracellular barriers/challenges to NP delivery of NAs
cellular entry
endosomal escape
nuclear uptake for DNA delivery
Polymers and lipids, or __, are used for NP formulation
Carriers
In nucleic acids, what funtional group binds to Phosphate grps
amines
Why do Liposomes carry nucleic acids
because of hydrophilic interior
What are the types of cargo that can be loaded into Lipid nanoparticles
ionizable cationic lipid
cholesterol
helper lipid
lipid anchored PEG
what do the cargo in LNPs promote?
formulation of mRNA loaded particles
allows escape from endosomes
increases stability in circulation