Fungal Infections
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What are the treatment options for tinea corporis? What is the duration of therapy of
each? When should oral therapy be preferred?
Tina Corpis | Ringworm | Usually responds well to topical treatment
Oral- Alternative for pts with extensive involvement and patients who fail topical therapy
|
What are the treatment options for tinea cruris? What is the duration of therapy of
each?
Tinea cruris | Groin- Jock itch | Topical
Oral- Alternative for pts with extensive involvement and patients who fail topical therapy
|
What are the treatment options for tinea pedis ? What is the duration of therapy of
each?
Tinea Pedis | feet | Topica- 4 weeks Terbinifine cream 1 week Oral- Fluconazole 150mf q week x 1-4wks |
When should patients be referred for T. corporis, T. pedis, T. cruris?
What are the treatment options for tinea capitus and duration for each?
Tinea capitus | fungal infection of the scalp | Systemic treatment is the standard of care for children 1)Oral terbinifine x 4-6 wks 2) Oral griseofulvin x6-8 wks |
Risk factros for Tinea unguium
Age, DM, PAD, Smoking, History of trauma
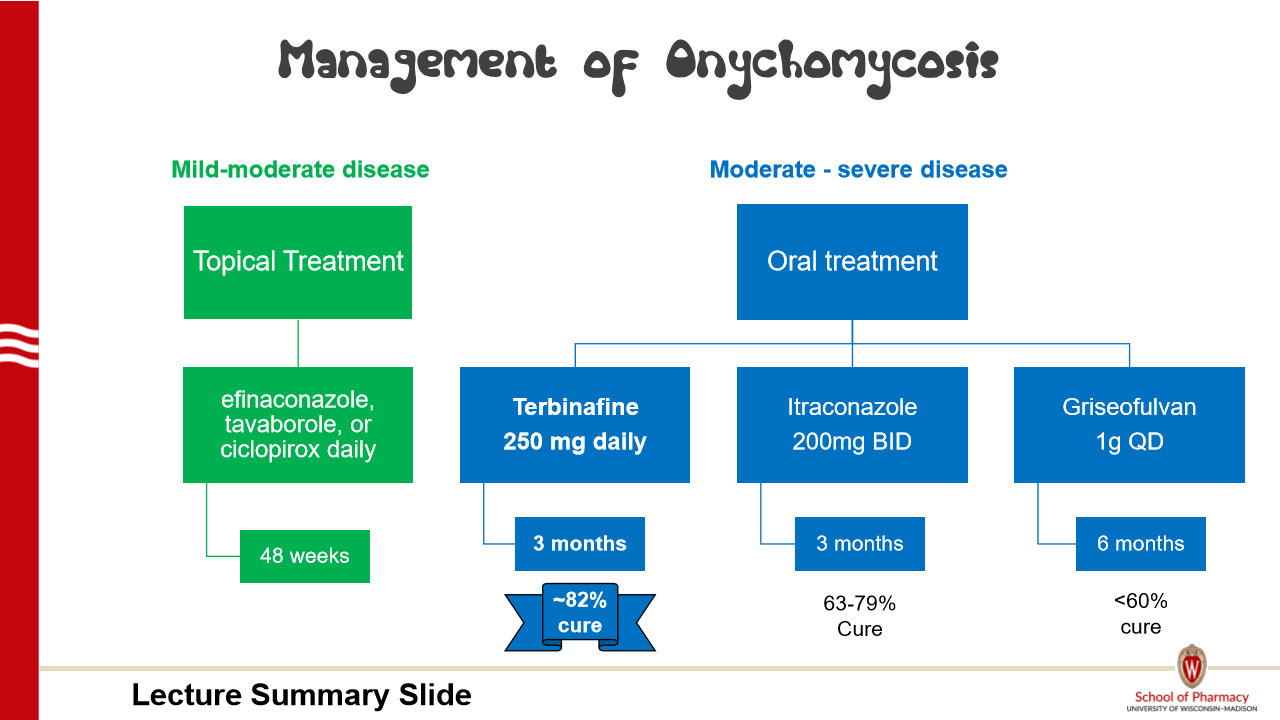
What is the preferred therapy (and duration) for mild-moderate and moderate-to-
severe Onychomycosis?
Treatment is not mandatory in all pts
Terbinafine counseling pearls
Take tablets (can crush) without regard to meals; granules with food (non-acidic food, no fruit-based food)
Contraindicated in chronic or active hepatic disease
Adverse effects: headache, GI, taste disturbances
Drug interactions: moderate inhibitor of CYP2D6
Griseofulvin counseling pearls
Tablet (can crush) and liquid (shake well)
Take with fatty meal
Contraindicated in hepatic failure
Pregnancy category X. Avoid in breastfeeding. Men should avoid fathering a child for at least 6 months after therapy
Adverse effects: GI, photosensitivity, hepatotoxicity
Drug interactions: contraceptives, warfarin (decrease effectiveness)
What is the causative organism of Vaginal cutaneous candidiasis (VCC)?
Mostly candida albicans
What are the treatment options for uncomplicated VCC, severe-acute VCC
Uncomplicated (Sporadic, infrequent, non-pregnant, mild-mod) | Fluconazole 150mg oral single dose more preferred for convenience Topical agents |
Severe acute (mod-severe) | Fluconazole 150 mg PO Q72 hours for 2-3 doses |
Treatment options for recurrent VCC
Defined as > 4 episodes of vulvovaginal candidiasis (VCC) within one year
Usually caused by azole-susceptible Candida albicans
Treatment:
Induction
Fluconazole 150 mg every 72 hours × 3 doses
Topical azole daily for 10 to 14 days
Maintenance
Fluconazole 150 mg once weekly × 6 months
Topical azole twice/week × 6 months
Pregnancy: Use topical azoles for symptom relief
What factors make a patient with VCC complicated?
Recurrent, Pregnant, Immunocompromised, non-albicans
(refer to MD)
What is the treatment of choice including duration for candiduria?
Candiduria | Asymptomatic:
Symptomatic:
|
How do you treat a non-neutropenic patient with candidemia?
Echinocandin: Caspofungin, micafungin, anidulafungin
Transition to fluconazole or voriconazole if:
clinicall stable, negative repeat blood cultures following initiation of antifungal
Vori if not susceptible to flucon
Treamt for 2 weeks beyond clearance, consider removing IV catheter
Pref drug in preg with Candidemia
1)Lipid formulation amphotericin
NO AZOLES!
Echinocandins AEs
Nausea, Abnormal liver function, histamine related symptoms
Amphotericin B deoxycolate AEs

Which azoles are notable 3A4 inhibitors
Fluconazole (moderate)
Isavuconazole (moderate)
Itraconazole (strong)
Posaconazole (strong)
Voriconazole (strong)
lol thats all of them
Which azoles are notable 2C19 inhibitors
Fluconzaole
Voriconazole
Which azole is a prodrug
Isavuconzaole
Which azole should be taken with food
Itraconazole tab
Posaconazole tab and suspension (fatty)
Which azoles cause vision changes (3)
Itraconzaole
Posaconazole
Voriconazole
Which azoles cause neuropathy (1)
Voriconazole
Flucystosine
AEs: Leukopenia, Thrombocytopenia, Hepatic, GI