IPS1- Classification of Amino acid Based on Structure
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
300 amino acids
Over _____ amino acids exist in nature
20
Over 300 amino acids exist in nature, but proteins are made mainly from ____special ones called L-α-amino acids
L-α-amino acids
Over 300 amino acids exist in nature, but proteins are made mainly from 20 special ones called_____
True
[Amino Acid]
[T/F]
Out of these 20 amino acids ,
10 are essential (we must get them from food)
10 are nonessential (our bodies can make them).
7 types
Amino acids are grouped into ____ types based on their structure
3-letter code and a 1-letter code
These amino acids are grouped into 7 types based on their structure. Each one has a _____ and ____ to represent it.
Selenocysteine
The 21st protein L-α-amino acid
Selenocysteine
____- is a special amino acid found in many living things
Selenocysteine
It’s like cysteine, but it has selenium instead of sulfur
Selenocysteine
_____-
Is added directly to proteins during translation (when RNA is turned into protein), not after the protein is made.
Is only in translation not in transcription
Selenocysteine
Unlike the other 20 amino acids, it doesn't use a regular 3-letter codon in the genetic code.
Amino acids with nonpolar side chains
[CLASSIFICATION OF AMINO ACID ACCORDING TO SIDE CHAIN]
These amino acids don’t give or take protons and don’t form hydrogen or ionic bonds
hydrophobic (don’t mix with water).
[CLASSIFICATION OF AMINO ACID ACCORDING TO SIDE CHAIN]
Amino acids with nonpolar side chains are like oil or fat, so they are____ [hydrophillic /hydrophobic]
Glycine
Alanine
Valine
Leucine
Isoleucine
Methionine
Phenylalanine
Tryptophan
Proline
Examples of Amino acids with nonpolar side chains [9]
Phenylalanine
Tryptophan
Proline
[CLASSIFICATION OF AMINO ACID ACCORDING TO SIDE CHAIN]
Most Amino acids with nonpolar side chains are ALIPATHIC HYDROCARBON except ___ [3] which are CLOSED RING HC STRUCTURE
Amino acids with uncharged POLAR side groups
[CLASSIFICATION OF AMINO ACID ACCORDING TO SIDE CHAIN]
These amino acids are having zero net charge at neutral pH.
Serine
Threonine
Cysteine
Aspargine
Glutamine
Example of Amino acids with uncharged POLAR side groups [5]
True
[CLASSIFICATION OF AMINO ACID ACCORDING TO SIDE CHAIN]
[T/F]
Amino acids with uncharged POLAR side groups
In the case of Cysteine and Tyrosine , they can lose proton at alkaline pH.
Amino acids with acidic side chains
[CLASSIFICATION OF AMINO ACID ACCORDING TO SIDE CHAIN]
____-
These amino acids are proton donors
They are fully ionized in neutral pH forming a negatively charged carboxylate group (-COO- )
Aspartic acid
Glutamic acid
Example of Amino acids with acidic side chains [2]
UNDERSTAND
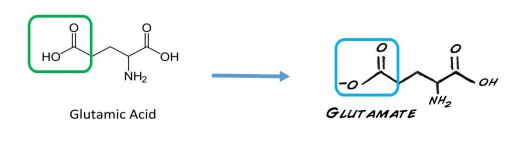
Ionization of aspartic and glutamic acid
The acid group (shown in the green box) loses a proton, which is typical acid behavior.
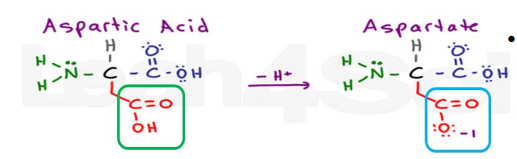
UNDERSTAND
This turns it into a carboxylate group (COO⁻),
Amino acids with basic side chains
[CLASSIFICATION OF AMINO ACID ACCORDING TO SIDE CHAIN]
These amino acids accept protons, based on the Bronsted-Lowry theory.
Lysine
Arginine
Histidine
Example of Amino acids with basic side chains [3]
True
[T/F]
Lysine (Lys) and Arginine (Arg) are fully charged and positive.
Histidine (His)
_____- is a weak base. By itself, it’s not charged, but in proteins, its side chain can be positive or neutral.
Arginine
Asparagine
Aspartic acid
Cysteine
Glutamic acid
Glutamine
Glycine
Histidine
Lysine
Serine
Threonine
🧬 Hydrophilic Amino Acids [11]
Alanine
Isoleucine
Leucine
Methionine
Phenylalanine
Proline
Tryptophan
Tyrosine
Valine
💧 Hydrophobic Amino Acids [9]
R-groups (side chains)
The _____of amino acids help enzymes do their jobs.
imidazole ring
The______ ring in histidine can give or take protons at normal body pH. This makes it important for enzyme reactions and for balancing H⁺ ions in red blood cells.
alcohol groups
nucleophiles
The ____groups in serine and threonine, and the -SH group in cysteine, let these amino acids act as____ during enzyme reactions
nucleophiles
____- attack other molecules during enzyme reactions
–SH group
disulfide bonds
The______ groups in cysteine can form _____ with another cysteine, helping shape and stabilize proteins
–OH groups
The ___ groups in serine, tyrosine, and threonine help control enzyme activity.
300 natural amino acids
20
There are over _____ natural amino acids, but only____make up proteins.
True
[T/F]
Humans and animals can’t make 10 of these 20 amino acids in enough amounts for growth and health.
essential
non-essential
Amino acids are called :
[essential / non-essential] ______- if we must get them from food
[essential / non-essential] _____ - if our body can make them
True
[T/F]
We can’t make essential amino acids because our DNA doesn’t have the instructions for them.
Aspartic acid
Amide of Asparagine (Asn)
Glutamic acid
Amide of Glutamine