Bodily Fluids Comp. Exam :0
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
Normal Urine Sediment
–0-2 RBCs/hpf
–0-5 RBCs/hpf
–0-2 Hyaline or Fine Granular Casts/lpf
–Few epithelial cells
–Slight presence of mucus (especially in female patients)
RBC in Urine
Abnormal
indicates glomerular damage or menstrual contamination
ghost cells seen in alkaline urine
can be confused with yeast or oil droplets / to differentiate add 2% acetic acid all rbc will be lysed
WBC in urine
indicate infection or inflammation (pyuria)
can be present in clumps
Tamm Horsfall Protein ( uromodulin)
main component of casts that is secreted by renal tubule epithelial cells
Factors that cause cast formation
Decreased pH
- Decreased urine output
- Increased solute concentration (increased SG)
- Increased protein in urine
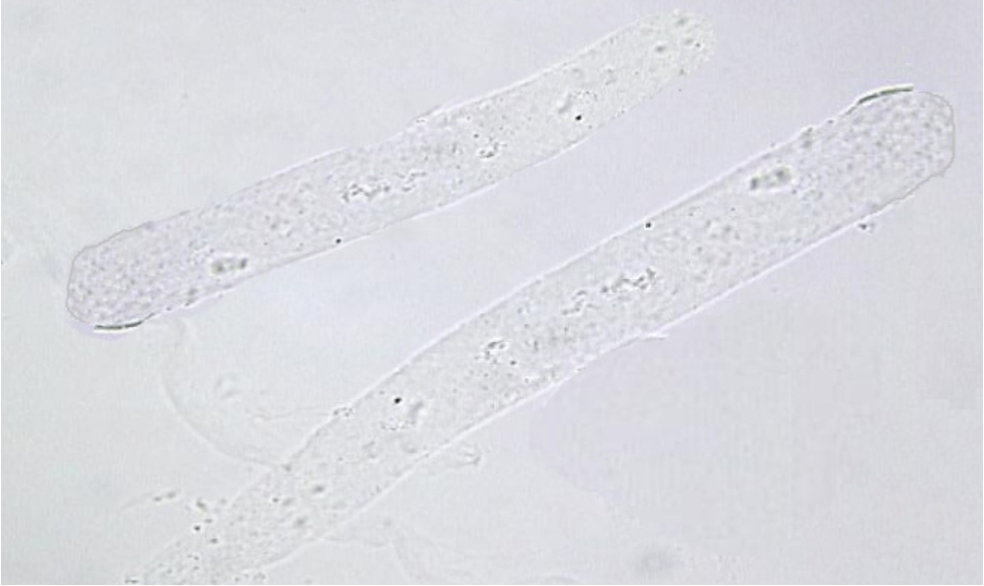
Hyaline Cast
most commonly seen
made of mostly uromodulin ( transparent in appearance )
RBC Cast
indicates bleeding in the nephron caused by glomerular dysfunction
critical result of intrinsic renal disease (glomerulonephritis)
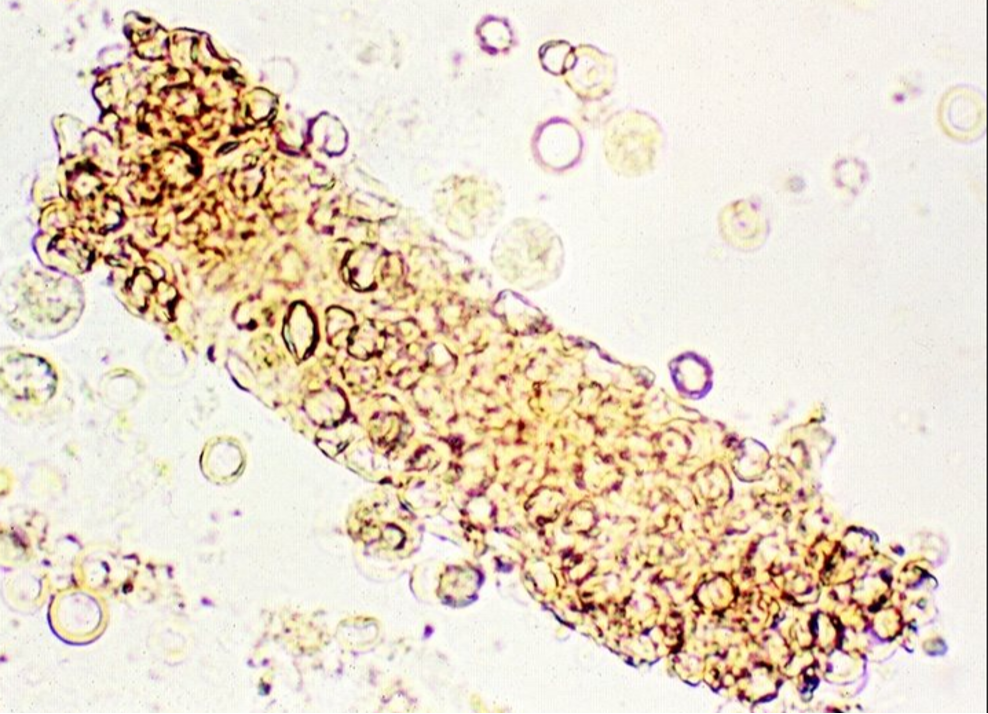
WBC Cast
associated with pyelonephritis
used to differentiate between cystitis and pyelonephritis
in pyelonephritis the casts will be seen
to differentiate between wbc clumps and casts look for a cast matrix
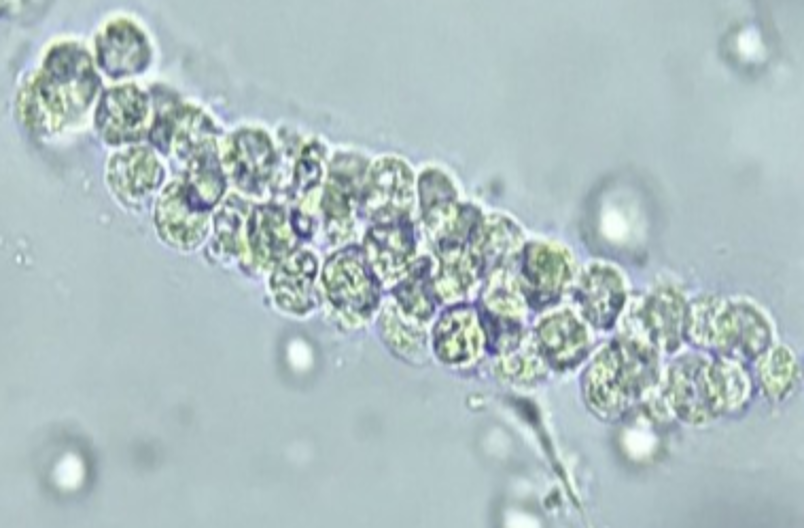
Granular Cast
–Disintegrated cellular casts
–Sometimes seen following strenuous exercise due to dehydration decreasing urine flow
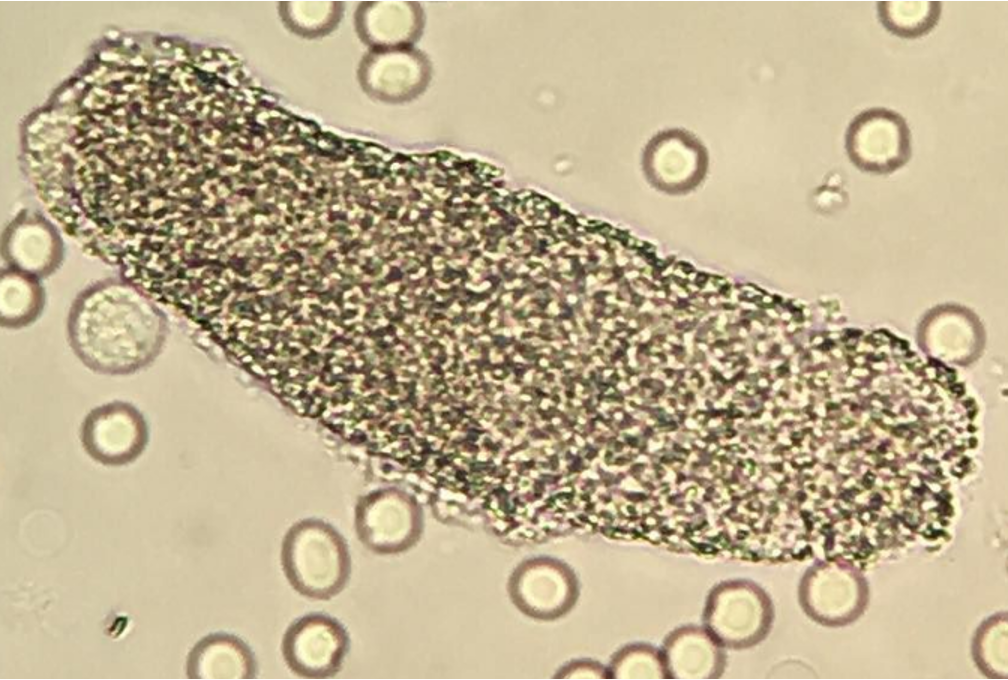
Broad Waxy Cast
–Advanced stage of Hyaline, Cellular, or Granular Cast
–Indicates prolonged urinary stasis (think…stagnant urine)
–Diagnostic of Chronic/End Stage Renal Disease
–Also called “Renal Failure Casts”
–Possesses distinct “notches”
–Form in Collecting Ducts that have become dilated due to damage (BAD SIGN!!!)
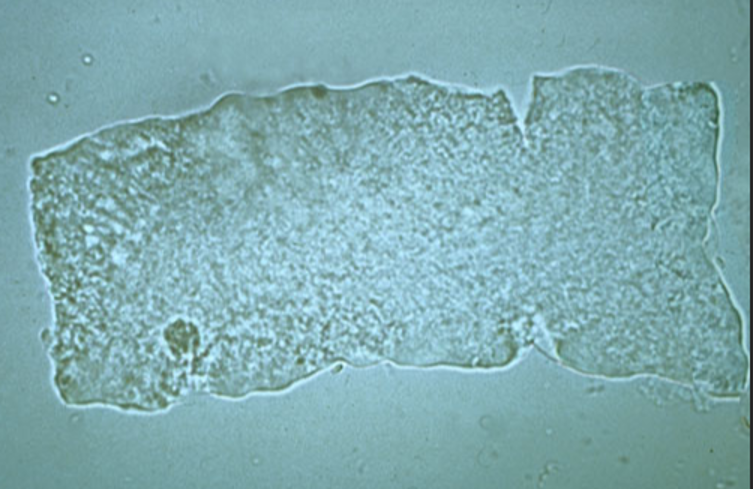
Fatty Cast
–Made from breakdown of epithelial cell casts that contain Oval Fat Bodies
–Seen in Nephrotic Syndrome
Squamous Epithelial Cell
•Largest cell, BUT LEAST significant (frequently seen, especially in urine specimen from females)
•Has abundant irregular cytoplasm
•Has a central nucleus (about the size of a RBC)
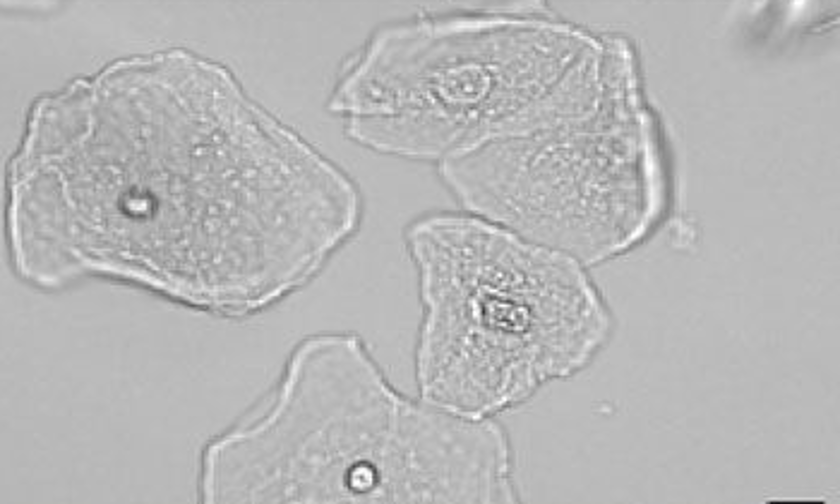
Transitional Epithelial Cell
•Round or pear shaped (Round can be confused with RTE)
•Has central nucleus
•Can absorb water and swell to 3X its normal size
•Present in Renal Carcinoma
•Lines bladder and upper urethra
•Increased presence in patients with catheters
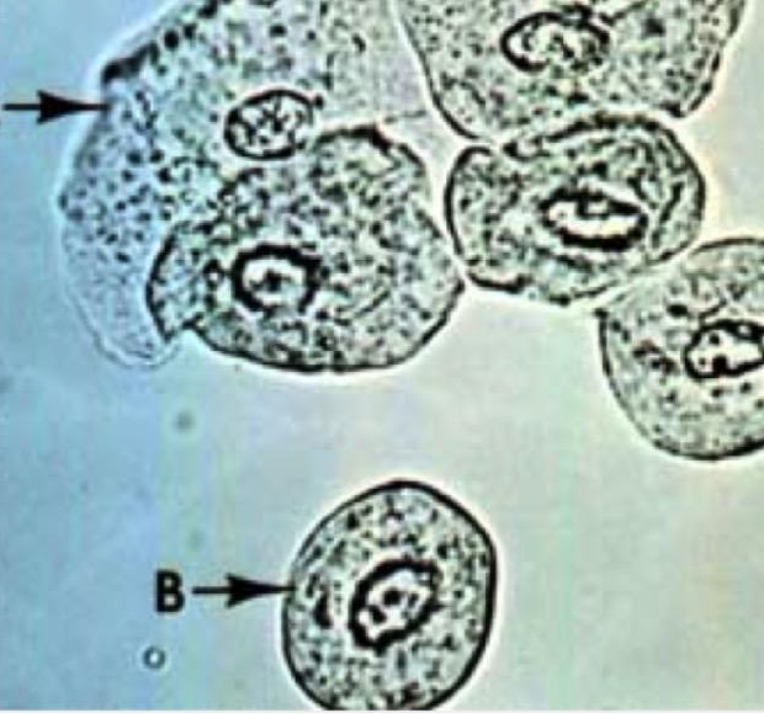
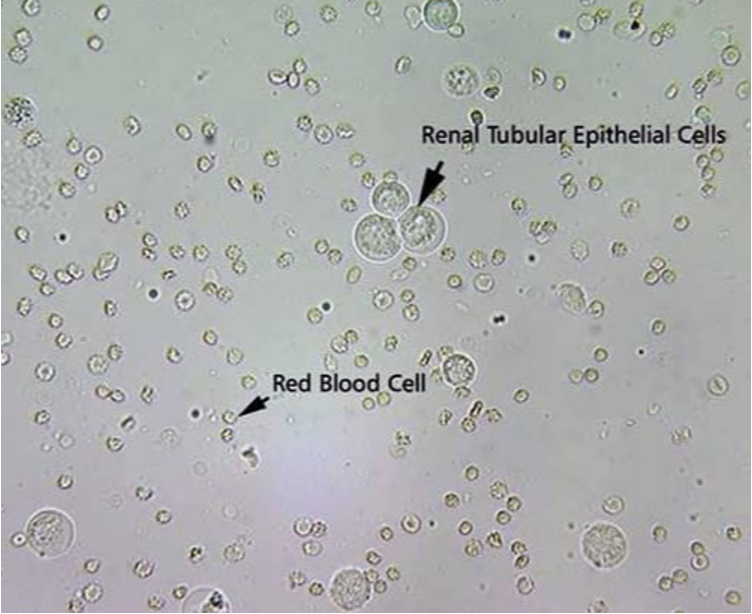
Renal Tubule Epithelial Cell
•MOST significant
•Round eccentric nucleus
•Larger in size than a WBC
•Lines renal tubules
•Indicates Tubular Necrosis
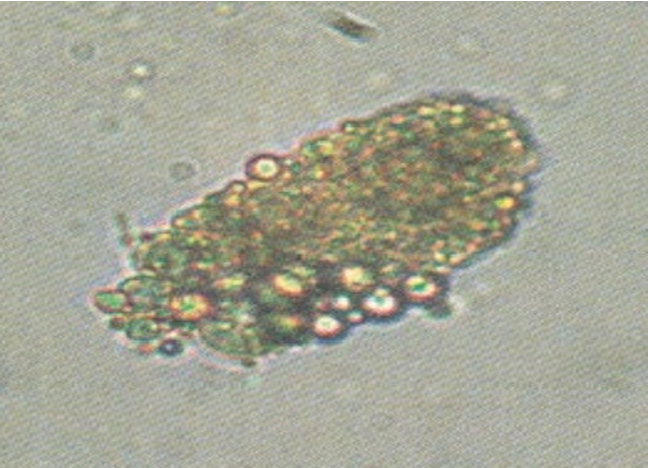
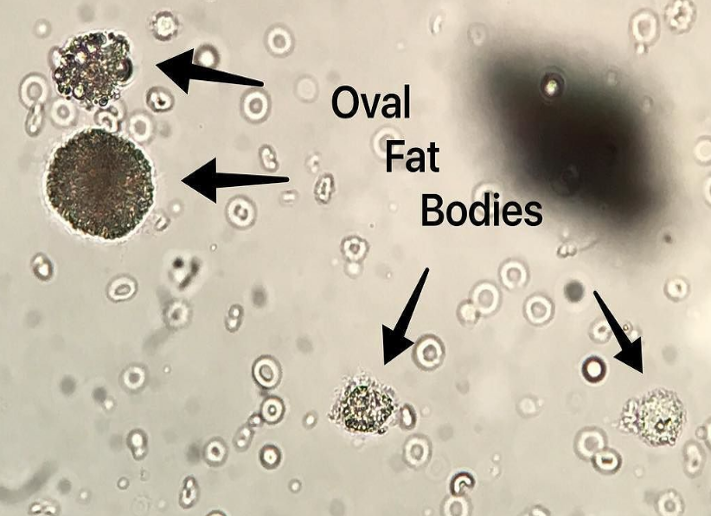
Oval Fat Body
•RTE cells that absorb fat deposits in certain fat-producing disorders
•Highly refractile
•Present in Nephrotic Syndrome
•Possesses distinct “Maltese Cross” when polarized
•Can stain with Sudan III or Oil Red O
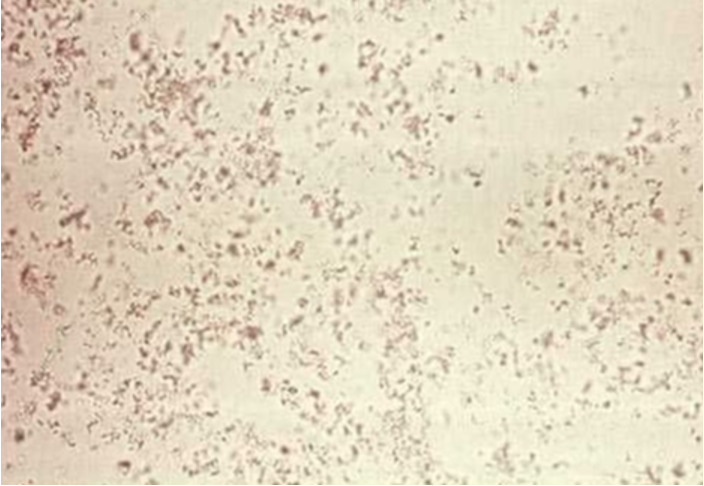
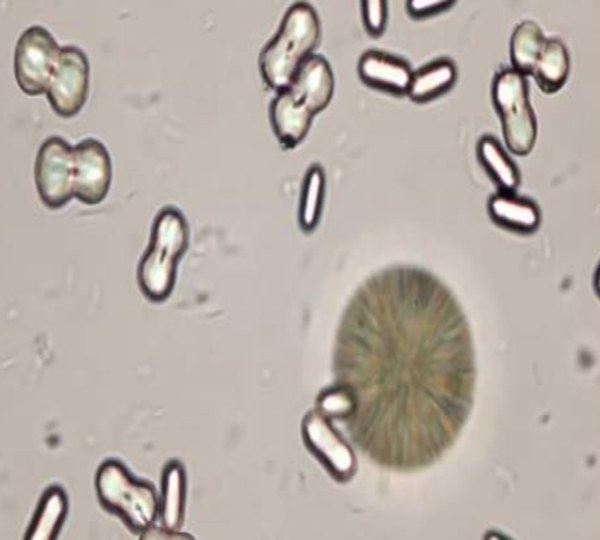
Amorphous Urates
pink sediment with yellow-brown granules
in normal urine
Uric Acid
typically in rhomboid shape
indicator of Lesh-Nyhan Syndrome
(Lesh-Nyhan :incomplete metabolism of dietary purines )
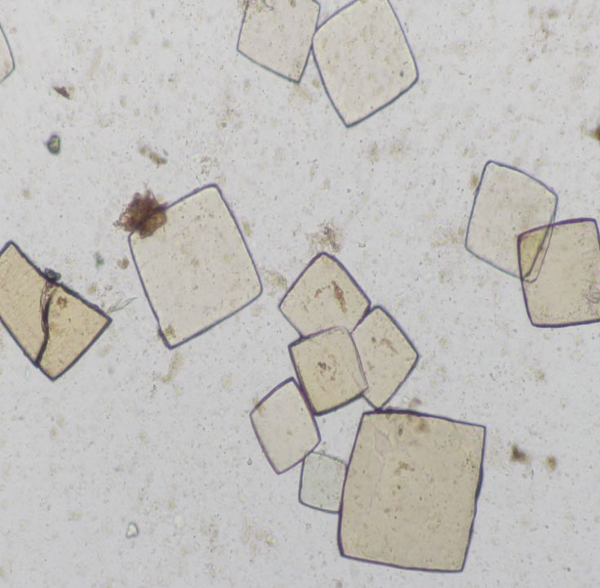
Calcium Oxalate
envelope shape or distinct “X”
seen in children with antifreeze poisoning
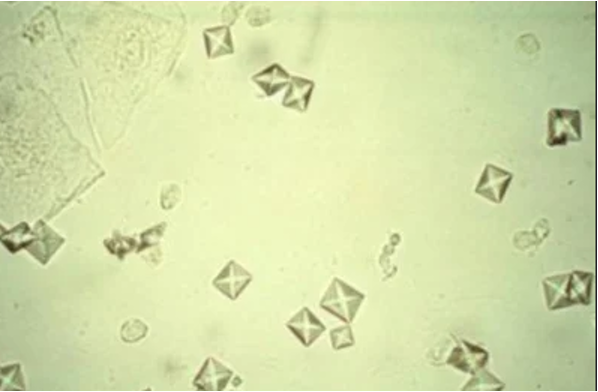
Normal crystals in alkaline urine
–Amorphous Phosphates: white sediment with yellow-brown granules
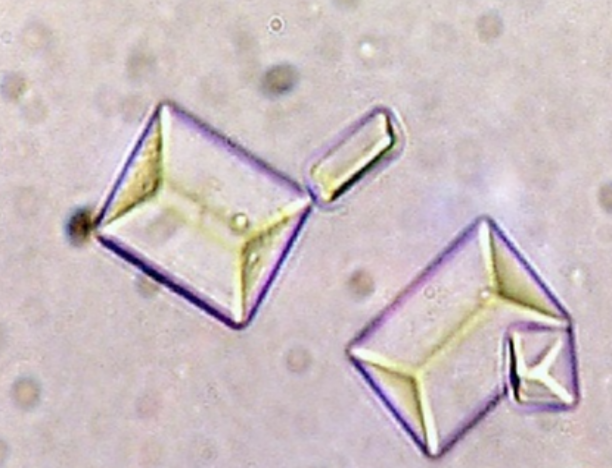
–Triple Phosphate: “coffin lid”
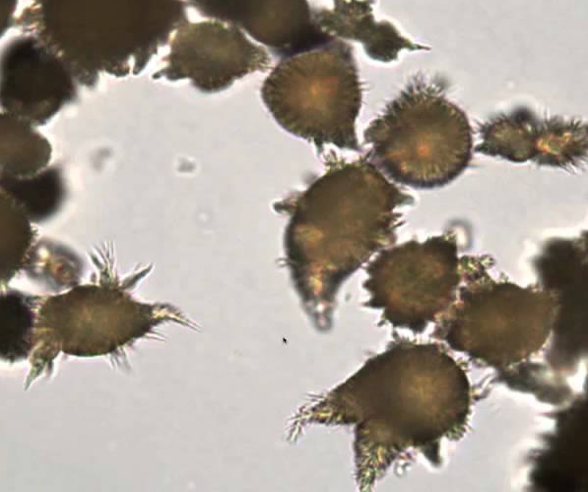
–Ammonium Biurate: “thorny apple”
–Calcium Carbonate: “dumbbell”
Amorphous Phosphate
Triple Phosphate
Ammonium Biurate
Calcium Carbonate
Bilirubin
small clusters of yellow-brown fine needles
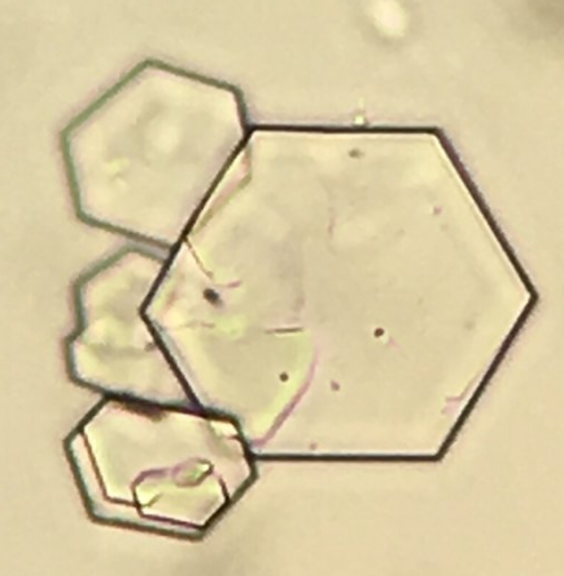
Cystine
colorless hexagonal plates
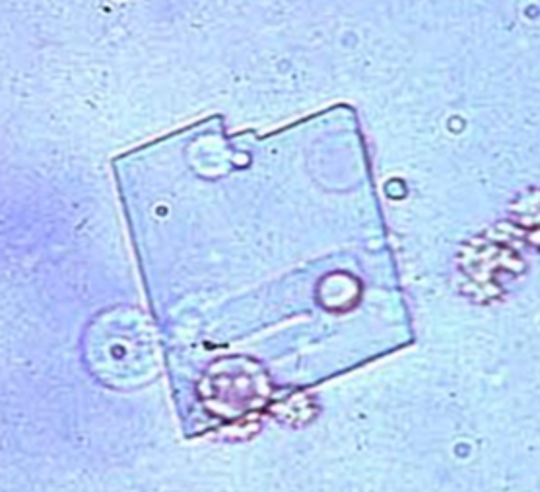
Cholesterol
rectangular plates with notched corners
•Birefringent: exhibits two colors under polarized light
•Commonly seen in urine with 4+ Protein (ex: Nephrotic Syndrome)
Leucine
yellow-brown spheres with concentric circles or radial striations
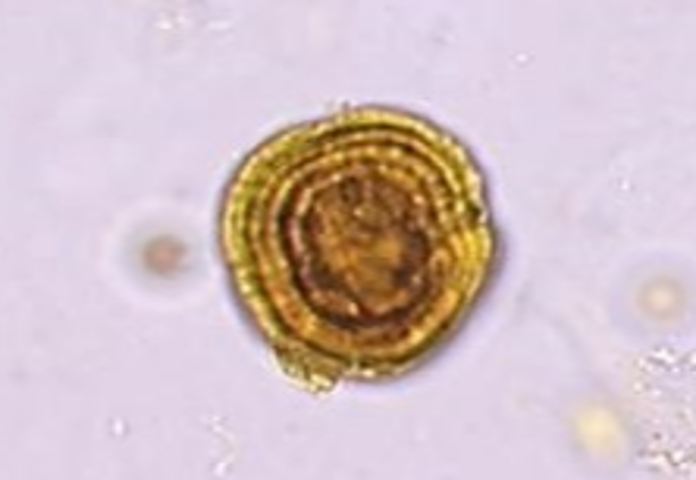
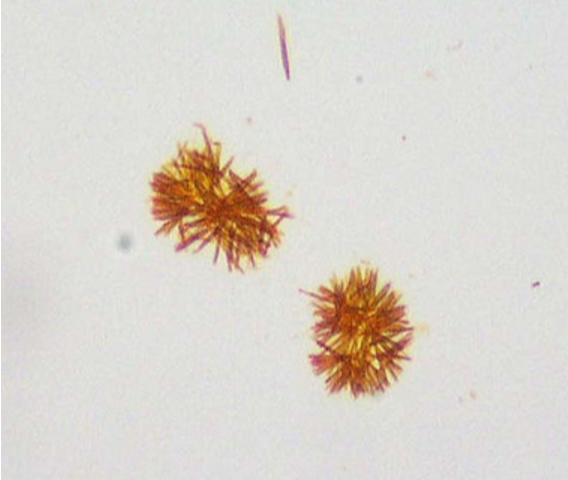
Tyrosine
–fine, delicate needles
•When found together with Leucine = Liver Disease!!!
•Commonly found in urine POS for Bilirubin
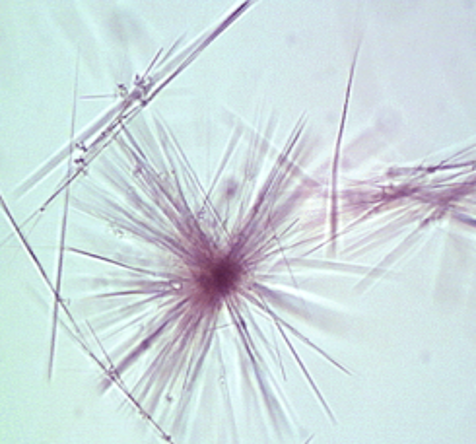
Sulfonamide
needles or brown spheres from sulfonamide drugs
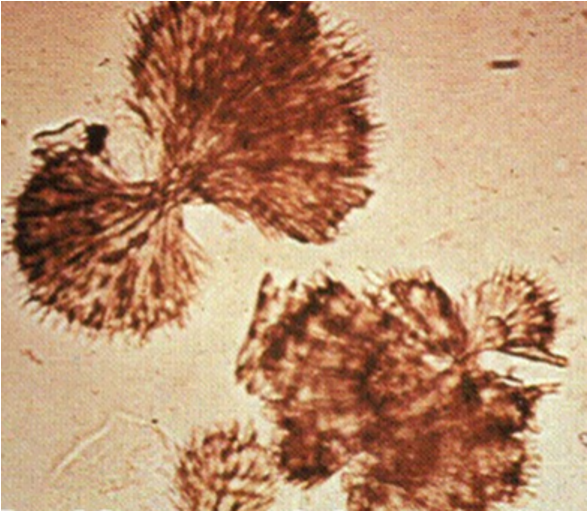
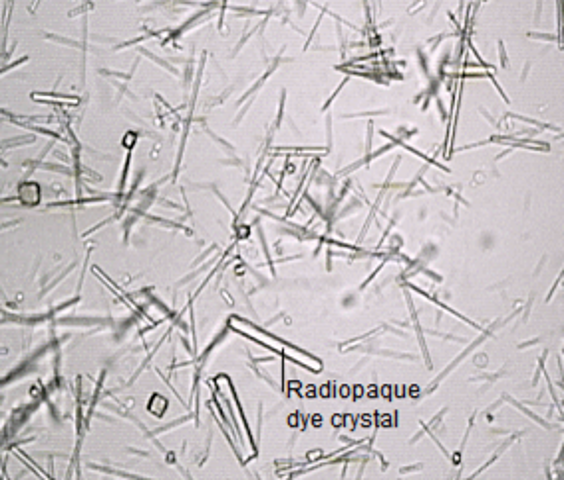
Radiographic dyes
plates or may appear as needles

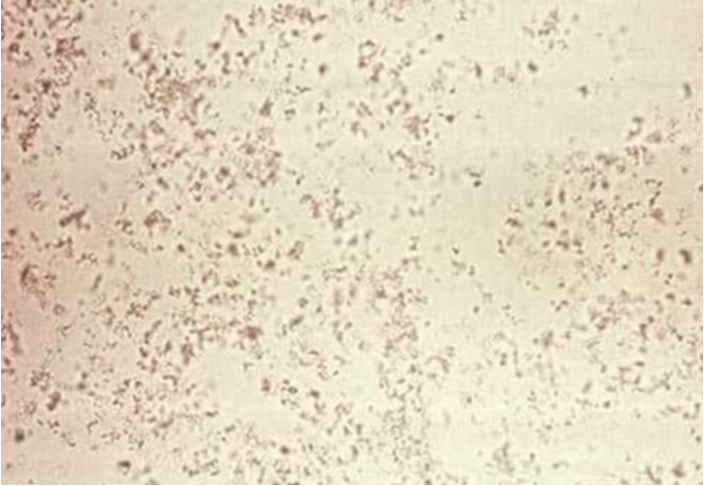
Bacteria
•“Rod Shaped” is most commonly found form
•MOST significant with POS Leukocyte Esterase result (WBC’s)
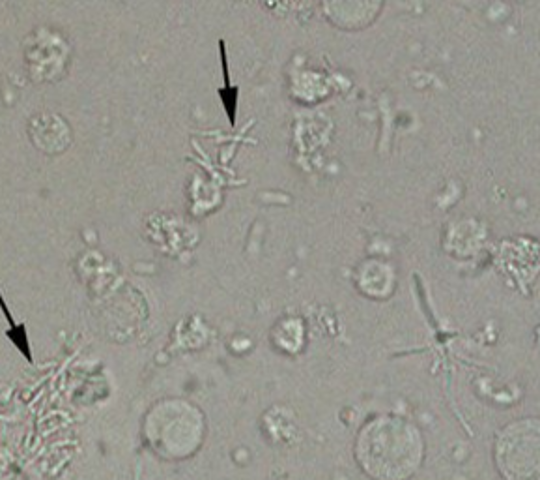
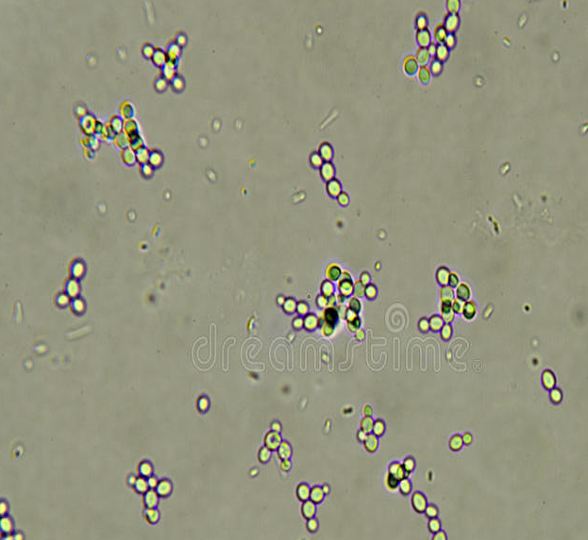
Yeast
•Often represent vaginal infection
•Simple “budding” or hyphae yeast can be present
Must correlate with clinical findings (ex: POS Glucose)
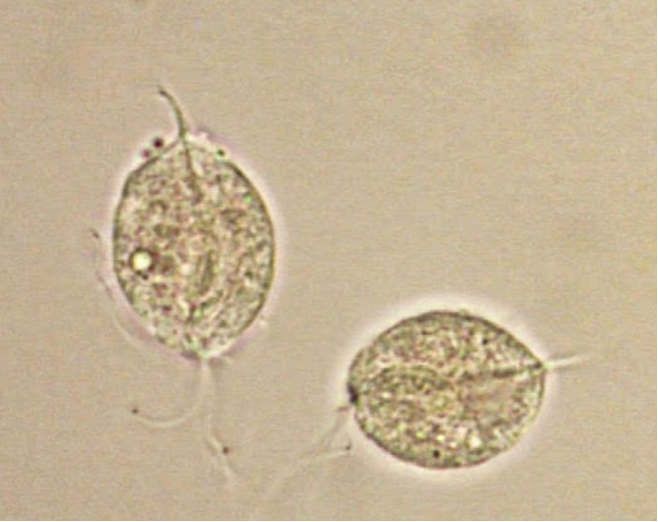
Paracites
•Trichomonas Vaginalis: parasite transmitted through sexual intercourse
–Look for “whipping” motility…moves in circles
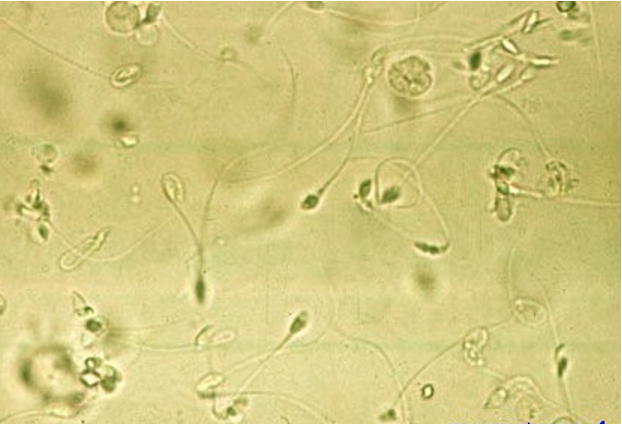
Sperm
may be seen in both male and female patients
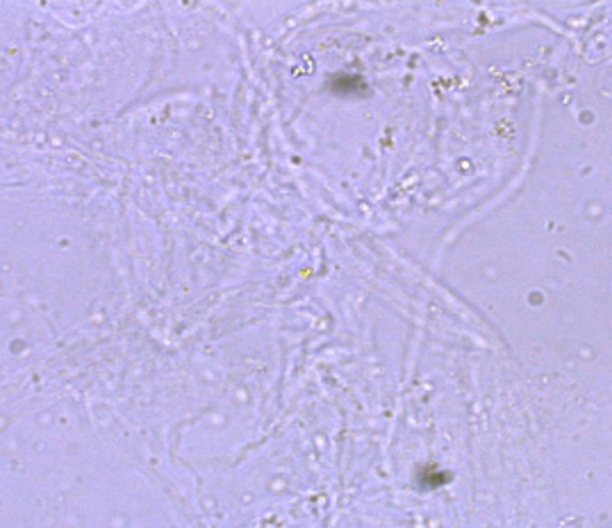
Mucous
•More common in female specimens, but can be seen in both
•Has no clinical significance
Clue cells
•Squamous epithelial cells with “rod shaped” bacteria clustered on borders
•Presence indicates Bacterial Vaginosis (BV)
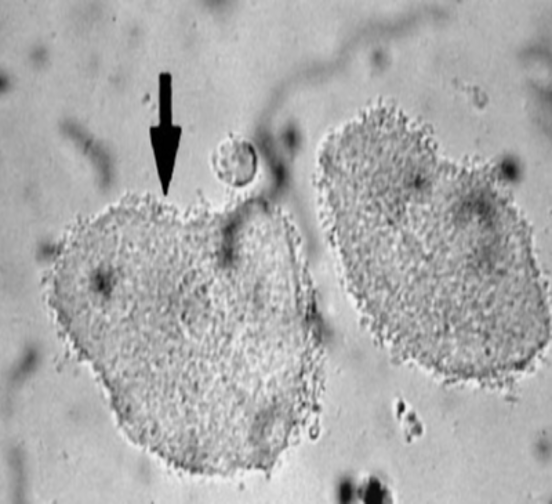
Glitter Cells
•In urine with LOW SG (Hypotonic), WBC’s absorb water and swell causing granules to exhibit Brownian Movement.
Artifacts
components that are not clinically significant, but can sometimes contaminate urine. Should be ignored during microscopic examination
Powder
•Can be confused with crystals
•“Maltese Cross” can be seen when viewed with polarized light, BUT NOT ROUND like Cholesterol. Has “dimpled center.”
Fat
•Triglycerides will stain positive with fat stains (Sudan III and Oil Red O)
•Cholesterol will NOT stain with fat stains
Hair
•May be confused with casts
Fiber
•Also may be confused with casts
•Polarizes light, while casts do NOT
Phenylketonuria
caused by failure to produce phenylalanine hydroxylase
mousy odor
guthrie test
Tyrosinuria
the accumulation of excess tyrosine
rancid odor
caused by 2 reactions p-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid and p-hydroxyphenyllactic acid
underdeveloped liver
metabolic disorder
alkaptonuria
failure to produce the enzyme homogentisic acid oxidase
build up in homogentisic acid
urine darkens at room temp.
metabolic disoder
melanuria
caused by malignant melanoma
build up of melanin
urine darkens on exposure to air
metabolic disorder
Maple Syrup Disease
autosomal recessive trait
build up of leucine, valine, and isoleucine
ketoacids in the blood and urine
urine will have maple syrup smell
metabolic disorder
indicanuria
causes by obstruction or abnormal bacteria
build up of indica
blue urine when exposed to air
hartnup disease
tryptophan disorder
5-Hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA)
Tryptophan disorder
Caused by tumor that involves argentaffin cells
build up of serotonin
5-HIAA in the urine
Cystinuria
inability of renal tubules to reabsorb cystine
cystine crystals in urine
sulfur odor
Cystinosis
incomplete metabolism of cystine
build up of cystine
cystine deposits throughout the body
polyuria
aminoacid uria
positive clinitest
lack of urinary concentration
sulfur odor
Uroporphyrin, Coproporphyrin, protophyrin
precursor is porphobilinogen
can be due to lead poisoning, excessive alcohol intake, iron deficiency, renal disease, and liver disease
Ehrlich Reaction tests for aminolevulinic acid (ALA) and porphobilinogen
urine has a portwine color
Lesh-Nyhan Disease
purine disorder
sex-linked recessive disorder
build up of uric acid
uric acid crystals in urine
crystals in joints, tendons, and organs
The 3 layers of meninges
Dura mater- outer
Arachnoid mater- middle web-like
Pia mater- soft inner
CSF Fluid
flows between the middle and inner layer
secreted from the choroid plexus
3 Functions of CSF Fluid
mechanical support or cushion to the brain against trauma
removes metabolic waste products from the brain
supplies nutrients to the tissues and nerves of the CNS
Blood-Brain Barrier
bi-directional active transport between the blood, CSF, and brain
lumbar puncture
done between the 3&4 or 4&5 lumbar vertebrae
tube collection
tube 1 : chemistry
tube 2: microbiology
tube 3: hematology
Traumatic tap
blood in all 4 tube
xanthochromic
supernatant with a yellow pink or orange color
indicates a subarachnoid hemorrhage
is always pathological
3 visual examination to determine traumatic tap
uneven distribution of blood
clot/ pellicle
clear supernatant
what causes cloudy CSF
bacterial or viral infection (meningitis)
traumatic tap (fibrinogen)
cell count in CSF
RBC and WBC must be counted within 1 hr of collection
may use saline or 3% acetic acid
hemocytometer is used to count
pleocytosis
increased cellularity in bodily fluids
Normal WBC in CSF
Adults: 0-5/ul
Babies: 0-30/ul
B-2 Micorglobulin
increased levels of B-2 microglobulin indicate reduced GFR
not specific for GFR
Blood Test Strip
detects RBC, hemoglobin, and myoglobin
rxn principle: 1. peroxide + O2 / 2. O2 + indicator = color change
aid in detection of hematuria, hemoglobinuria, myoglobinuria
bleach and other oxidizing agents cause a false positive
Protein Test Strip
tests for the presence of albumin( and globulin)
rxn principle: protein error of indicators
interfering substances: highly alkaline urine which causes a false positive
indicates presence of renal abnormalities with glomerular involvement
Glucose Test Strip
detects glucose ONLY
rxn principle: Glucose Oxidase Method glucose → gluconic acid & hydrogen peroxide → peroxidase catalyzes oxidation of chromagen
used for diagnosis of diabetes
interfering substances: oxidizing agents cause a false positive
Osmolality Gap
2x (sodium) + 1.5(glucose/18) + (urea/2.8)
Microalbumin Strip Test
used for early detection of diabetic nephropathy
indicated decreased glomerular function
rxn principle: immunochemical rxn
Yellow-Green Urine
bilirubin
Green Urine
pseudomonas infection
Brown Urine
melanin/ phenol derivatives
Pink Urine
blood, beets, rhubarb
What affects urine color?
urochorme,uroerythrin, porphyrins
food, drugs, disease
Abnormal Urine Appearance
Turbid, cloudy, opaque
pink, red, brown, black, green
Normal Urine Appearance
clear or hazy
colorless, pale yellow, amber
Pyelonephritis
Cause: advanced UTI
Microscope finding: WBC casts and bacteria
Cystitis
Cause: UTI
Microscope finding: WBC, bacteria, possible RBC
Acute Interstitial Nephritis
Cause: allergic reaction causing inflammation of renal tubules
Microscope findings: eosinophil count
Acute Pyelonephritis
Lab Findings
turbid specimen
nitrite positive
leukocyte esterase positive
WBC casts
bacteria
Nephrotic Syndrome
Lab Findings
fat droplets
oval fat bodies
fatty casts
Acute Glomerulonephritis
Lab Findings
gross hematuria
turbid specimen
RBC casts
dysmorphic RBC
proteinuria
possible cause: goodpasture’s syndrome
Non-immune causes of Glomerular Damage
exposure to chemicals/ toxins
disruption of electrical membrane changes
deposition of amyloid material from systematic disorders
basement membrane thickening associated with diabetic nephropathy
Type of Renal Disease
glomerular
tubular
interstitial
vascular
Acute Tubular Necrosis
Damage to the renal tubules
Causes: shock, trauma, crushing injury, surgical procedure
UA:
mild proteinuria
microscopic hematuria
RTE cells and casts
Tubular Disorders
disruption of tubular function
may be caused metabolic or hereditary
The Medulla Contains
loop of Henle
Collection tubules
The Cortex Contains
Glomerulus
Bowman’s capsule
Proximal portion of tubules
Function of the Kidneys
waste elimination
acid/base balance
regulate volume of body fluids
maintain BP and erythropoisis
Criteria for Glomerular Filtration Testing
Neither excreted or reabsorbed by tubules
Is produced at a constant rate and not influenced by the body’s state of hydration
(creatinine)
Ascending Loop of Henle
sodium
passive transport
GFR
measures the rate at which the kidneys are able to remove a filterable substance from the blood
Ultrafiltrate contains
water
glucose
electrolytes
amino acids
uria
creatinine
ammonia
Proximal Convoluted tubule and Ascending Loop of Henle
urea
passive transport
Loop of Henle (except ascending)
water
passive transport
Distal Convoluted Tubule
sodium
active transport
Ascending Loop of Henle
chloride
active transport