Unit 1 - Business Management SL
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
Private Sector
Part of economy owned and controlled by private individuals and business. Profit based.
Public Sector
Part of economy under the ownership of the government. Traditionally provide essential goods and services that would be under-provided or inefficiently provided by the private sector.
State-owned Enterprise
Organizations owned wholly by the government.
Sole trader
A self-employed individual who runs and controls the business and is held responsible for its success and failure.
Benefits of Sole Trader
Easier control and decision making.
Quick and easy to set up.
Financial privacy
Close customer relationship, competitive advantage.
Flexibility.
Drawbacks of Sole Trader
Compete against established business
Stress
Owners do all roles in the business
Limited capital
Limited expansion opportunities
Unlimited liability
Lack of continuity (no investments)
Unlimited Liability
Feature for sole traders and ordinary partnerships who are legally bound/liable for all the money owed to their creditor.
Limited Liability
Restriction on the amount of money that owners can lose if their business goes bankrupt. Which essentially means owner can only lose what they have put in, and they don’t have to compensate with their own private property.
Partnership
Are a type of private sector business owned by 2-20 people.
Some has more share than others.
Deed of Partnership
Is a legal contract signed by the owners of a partnership.
Advantages of Partnership
Different skills → allocate to different roles.
More expertise
Greater stability, low risk
Partner can help when on is unavailable.
Disadvantage of Partnerships
Unlimited liability
Less access to loans than corporation.
1 partner doesn’t have complete control
Profit have to be shared
Disagreement
Company/Corporation
A business that is owned by shareholders. Issued a certificate of incorporation, separate legal identity from its owner.
Incorporated
Legal difference between the owners of a company and business itself
Two Documents Must Be Produced and Submitted to Authority
Memorandum of association - brief document outlining fundamental details
Articles of Association - a longer document, stipulating the internal regulations and procedures of the company.
Advantages of Companies/ Corporations
Limited liability
Easier access to finance
Expansion possibilities
Established organizational structure
Disadvantages of Companies/Corporations
Takes time and money to set up
Selling shares
Loss of control (shareholders taking control)
Privacy loss
A company has no control over the stock market
No control over share ownership
Private Limited Company
Is a business owned by shareholders with limited liability but shares cannot be bought by or sold to the general public.
Public Limited Company
Incorporated business that allows the general public to buy and shares in the company via the stock exchange.
Initial Public Offering (IPO)
Occurs when a business sells or part of its business to shareholders on the stock exchange for the first time.
Stock Exchange
Marketplace for trading stocks and shares of public limited companies.
Business vs Company
Companies are owned by shareholders, which can be private or public companies.
Business covers other form of ownership such as sole traders and partnerships.
For Profit Social Enterprise
Social enterprise
Social purpose
Improve human, social, or environmental well-being.
Social Enterprise
Revenue generation business with social goals at the core of their operations. They are organizations that engage in business activities but set goals important goals in terms of improving a social cause. Can be organized as for-profit business, non-profit organizations, cooperatives.
Private For-Profit Social Enterprises
Aim for surplus (profit) instead of relying on donations to achieve social aims
Triple bottom line framework for ethical business practices
Public For-Profit Social Enterprises
State-owned enterprises to operate in a commercial way
Help in raising government revenues to provide services to society that might be inefficient or undesirable if left to the private sector to deal with.
Cooperatives
A form of partnership with more than than 20 people. Each member participates in running the business and have equal say. A for-profit social enterprise that is set up, owned and run by members who can be employees or customers.
Advantages of For-Profit Social Enterprises
Favorable Legal Status
Strong Community Identity
Benefits to the stakeholder community
Disadvantages of For-Profit Social Enterprises
Complex decision making
Insufficient capital for growth and financial strength
Non-Profit Social Enterprises
Aim to fund a social purpose using surplus.
Non-Governmental Organizations
Private sector not-for-profit enterprises that operate for the benefit of others rather than aimed at making profit however still using business strategies to generate revenue and achieve financial stability.
Vision Statement
A written expression of an organization’s long-term ambitions that it hopes to achieve in the future. It is often an optimistic view of what the organization want to accomplish.
Mission Statement
A declaration of the organization’s overall purpose, forming the foundation for setting the business’ objectives. The mission can be seen as ways of accomplishing the organization’s vision.
Steps to Set Mission Statement
Define the organization e.g what it is
Outline the what the organization aspire to be (vision statement)
Limited enough to exclude risky goals
Broad enough to allow innovative and creative growth
Distinguish organization from others.
Use to evaluate current business activities
Phrase clearly to be understood
Aims
General and long-term goal of a business, often vague and unquantifiable statements. Often expressed in the firm’s mission statement
Objectives
Short-to-medium and specific targets an organization sets in order to achieve its aims. Often expressed as SMART objectives.

SMART
Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic and Time Constrained
Types of Objectives
Strategic, Tactical, Operational
Strategic (global) Objectives
Medium to long term objectives made by senior management.
Tactical Objectives
Medium to short term objectives set by middle managers.
Operational Objectives
Daily objectives set by floor managers.
Issues to meet Objectives
Culture clash - difference in culture
Financial constraints - money
Conflict
Business Strategy
Plans/approachs/scheme of action that businesses use to achieve their targets. Generally, strategies involve important decisions that may be risky and are done by senior mana
Business Tactic
Short-term plans of action that firms use to achieve their objectives. A tactic is an approach or scheme to achieve aim or objective. Tactic, compare to strategies, involve less resources and risk. They may not require senior management because they can be easily modified or reverse.
Internal Environment Factors Affecting Objectives
Leadership
HR
Organization (merger/acquisition)
Product
Finance
Operations
External Environmental Factor Affecting Objective
Technological
Social
Economic
Ethical
Political
Legal
Ecological
Why organizations set ethical objectives?
Build customer loyalty
Create a positive image
Develop positive work environment
Reduce risk of legal redness
Satisfying customers’ higher expectation
Increase profit
Impacts from Implementing Ethical Objectives
The business itself
Competitors
Suppliers
Customers
Local community
Government
Ethical Objectives Vs Corporate Social Responsibility
Ethical objectives are just 1 element of CSR
CSR is the concept that a business is obligated to operate in a way that have a positive impact on society.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
The conscientious considerations of ethical and environmental practices related to business activity.
Ethics
Moral principles that guide decision-making and strategy.
Ethical code of Practice
Documented beliefs and philosophies of an enterprise.
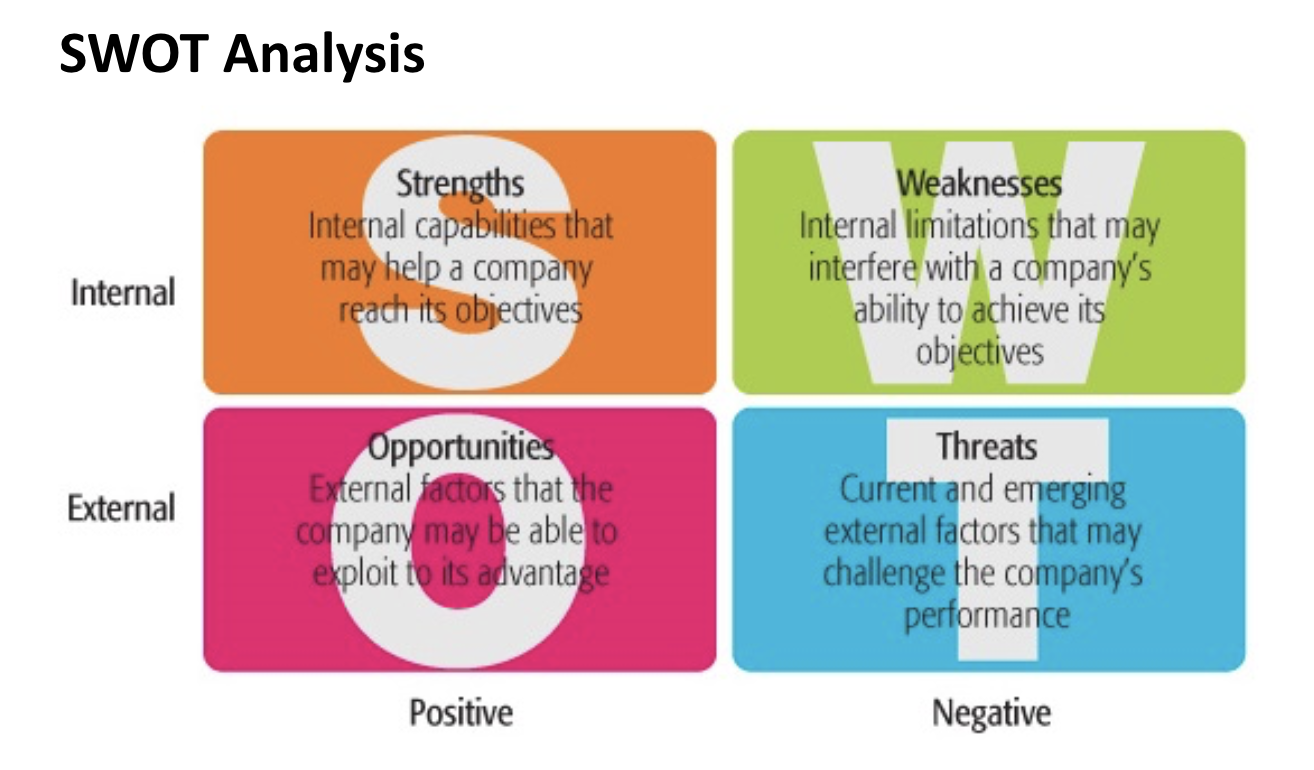
SWOT Analysis
An analytical tool used to assess the internal strengths and weaknesses, external opportunities and threads of a business decision, issue or problem.
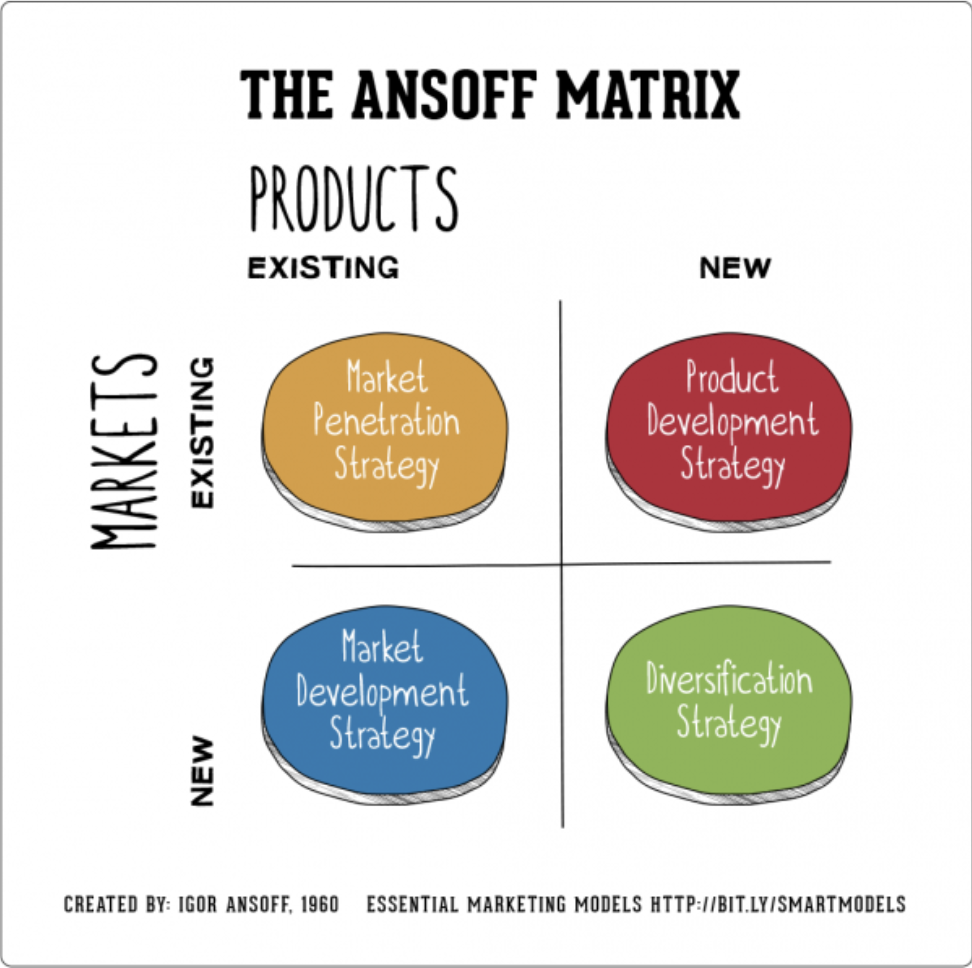
Ansoff Matrix
An analytical tool to devise various products and market growth strategies, depending on whether the business want to market new or existing products in either new or existing markets.
Advantages of using the Ansoff matrix
Provides analytical framework for strategic marketing decisions
Highlights the various risk degrees associated with strategic direction of marketing
An identified quadrant points to the marketing tactic that can be used.
Disadvantages of using Ansoff Matrix
It is only a tool and can be misused.
It simplifies a complex problem, can be too much.
Cannot predict actual events and thus, can be misleading.
Stakeholders
Individuals and organizations with a direct interest in the activities and performance of the business. It is a group that affects an organization or is affected by it.
Shareholders
Owners of a limited liability company.
Internal Stakeholders
Members of an organization but have a direct interest in its activities and performance.
External stakeholders
Individuals and organizations not part of the organization but have direct interest in its activities and performance.
Stakeholders includes (examples):
Owners/shareholders
Managers
Workers
Customers
Suppliers
Government
Local community
Financiers
Pressure groups
Media
Internal Stakeholder Interest
Shareholder - Return on investment
Workers - good pay and work conditions
Managers - meeting objectives, ensure job security
External Stakeholder Examples
Government - employ people, pay taxes
Suppliers - stable relationship
Customers/consumer - want the best product at the best price
Local community - effect of the business
Pressure groups
Pressure Groups
Consist of individuals with a common concern and seek to place demands on organizations to act a particular way.
Stakeholder Conflict
Refers to situations where stakeholders have disagreements on certain matters due to differences in their opinions and objectives.
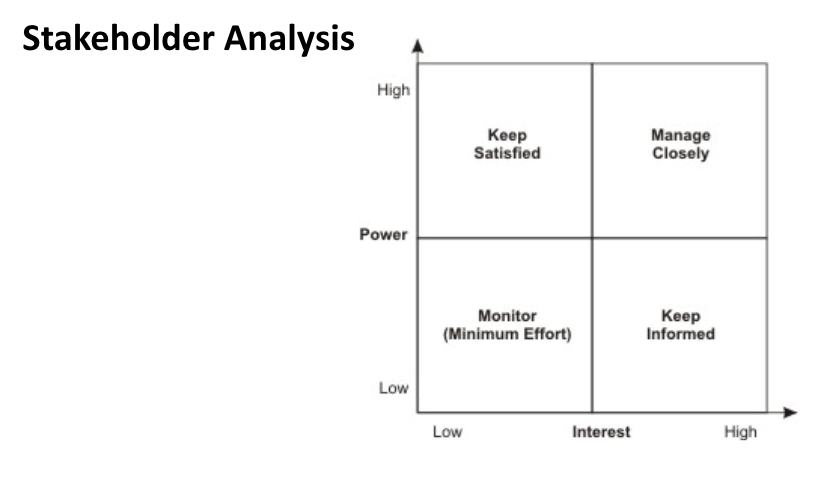
Stakeholder Analysis
A process used to asses and categorize stakeholders in a project, policy, or decision. This analysis helps organizations understand the various stakeholders' interests, influence, and participation levels, allowing for effective engagement strategies.
Variable Cost
Cost that vary with production
Fixed costs
Remain the same no matter how much or little you make.
Total Cost Formula
Fixed costs + Variable costs
Average Cost
Cost per unit of output (cost to make a product)
Average Cost = Total Cost/ Quantity of Output
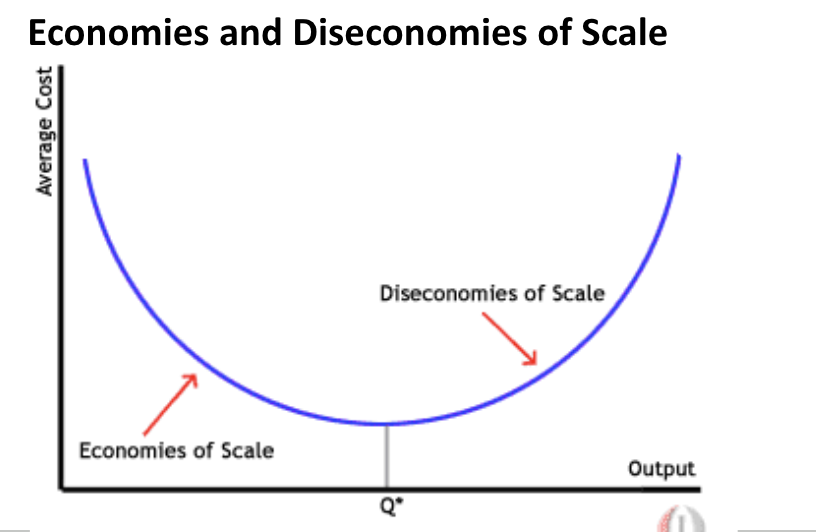
Economies of Scale (EOS)
Refers to lower average cost of production as a firm operates on a larger scale due to gains in productive efficiency.
Diseconomies of Scale
The cost disadvantages of growth. Unit costs are likely to eventually rise as a firm grows.
Internal Economies of Scale (efficiencies)
Technical
Managerial
Financial
Marketing
Purchasing
Risk Bearing
External Economies of Scale
Technical progress
Improved transportation networks
Skilled labour force
Regional specialization
Economies and Diseconomies of Scale Graph
Internal DIS-economies of Scale (inefficiencies)
Managerial - Lack of control
Poor working relationships
Disadvantages of specialization
Bureaucracy
Complacency (too satisfied to notice risks or danger)
External Diseconomies of Ccale
Increased market rents
Higher wages and financial rewards - retain workers
Traffic congestion
Optimal level of output
The most efficient scale of operation for a business which occurs at the level of output where the average costs of production are minimized.
Ways to Measure a Firm’s Size
Market share - a firm’s sales revenue as a percentage of the industry’s total revenue.
Total revenue - the value of a firm’s annual sales turnover per time period.
Size of a workforce - the total number of employees hired by the business.
Profit - the value of a firm’s profit over a time period
Capital employed - the value of the firm’s capital investment for the business to work.
Larger Business Benefits
Brand recognition
Brand reputation
Value added services - more resources to provide a range of services.
Lower price - offer greater price due to economies of scale
Greater choice - more choice
Customer loyalty - customers remaining loyal due to perceived trust and value for money.
Smaller Business Benefits
Personalized services - more time to devote to individual customers.
Flexibility - more flexible and adaptive to change, large businesses have larger financial commitments
Small market size - no large firm will compete with it hence allowing it to thrive
Cost control - no dilution of control (shareholders), less chance to face diseconomies of scale
Financial risk - Smaller business have less finance hence better control.
Government aid - Grants and subsidies can be offered to small business by government.
Local monopoly power - Can enjoy being the only firm in a location.
Why firms want to grow
To have benefits of larger scale production (economies of scale)
Gain larger market share and power. Allow charging higher prices.
Growth for survival, grow to compete with rivals who are also growing.
To spread risks by diversifying. If one market is at risk, having operations in other markets help ensure firm’s survival.
Internal Growth (organic)
Using the business own capabilities and resources to increase scale of operation and revenue.
Ways Business and Grow Internally
Changing price
Good promotion
Producing better products
Sell through a better distribution network
Offer preferential credit
Increase capital expenditure (investment)
Improved training and development
Providing overall value for money
Advantages to Internal Growth
Better control and coordination
Easier to control internal factors
Inexpensive
No interest in paid on retained profit (reinvestment in the company)
Less risky
Builds on the strength of business.
Disadvantages of Internal Growth
Diseconomies of scale
Higher unit costs of production and result from internal growth.
Restructure need
Sole trader can control the business easily, if it grows into a multinational company then structure has to change.
Dilution of control and ownership
Firm grows can change from sole trader to a plc, which then owners have to share decision-making with shareholders.
Slow growth
Internal growth is slower than external growth
External Growth
Happens when a business grows by collaborating with, buying or merging with another firm.
Benefits of External Growth
Faster way to grow
Quick way to reduce competition
Greater market share and power
Sharing of ideas with other businesses
Help a firm evolve and spreading risks across different markets.
Disadvantages of External Growth
The main disadvantage of external growth is the huge costs which can be higher than internal growth.
Mergers
2 business merge to form a new business
Acquisition (takeover)
When one business buys a controlling interesting in another business.
Hostile takeover is when the acquisition is done without the consent of the target company’s management.
Why firms become targets for takeovers
Growth potential but lacks sufficient funding for growth
Seen as small rival with growth potential
Widely recognized branding but are facing financial crisis.
Vulnerability
Forward Vertical Integration
Growth strategy that occurs with the amalgamation of a firm operating at a later stage in the production process.
Backward Vertical Integration
Growth strategy that happens when a firm amalgamates with a firm operating at an earlier stage in the production process.
Conglomerates
Businesses that provide a diverse range of products and operate in multiple industries.
Advantages of M&As (Merger and Acquisitions)
Greater market share
Economies of scale
Synergy - access to other’s resources
Survival - a bigger company, more change of survival
Diversification
Disadvantages of M&As
Redundancies - when a role is no longer necessary in a company, hence the need to terminate employees
Conflict
Culture class - things need to adapt to the culture of a newly formed organization.
Loss of control - more people have the say in decision-making
Diseconomies of scale
Regulatory problems - governments are concerned with M&As, preventing them due to the risk of monopolies.
Joint Ventures
Growth strategy that combines the contributions and responsibilities of two different organization in a shared project by forming a separate legal enterprise (no rebranding or a new organization, just a project)
Strategic Alliances
Similar to join ventures but:
More than 2 businesses
No new businesses is created
Individual businesses in the alliance can stay independent
More fluid than Joint Ventures
Franchise
Right given by one business to another to sell goods and service using its name and branding. (this is a right, a franchise). An agreement where franchisor to sell the rights to another business, to sell products under its name.