534: Cardio Wk 7 PII
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What are the major causes of thrombophlebitis?
short-term venous catheterization of superficial arm veins
Long term peripheral inserted central catheter (PICC)
What is the MC pathogen associated with superficial thrombophlebitis?
S.aureus
Which systemic system causes secondary hypercoagulability tothta leads to superficial thrombophlebitis?
Abdominal cancer; pancreas carcinoma
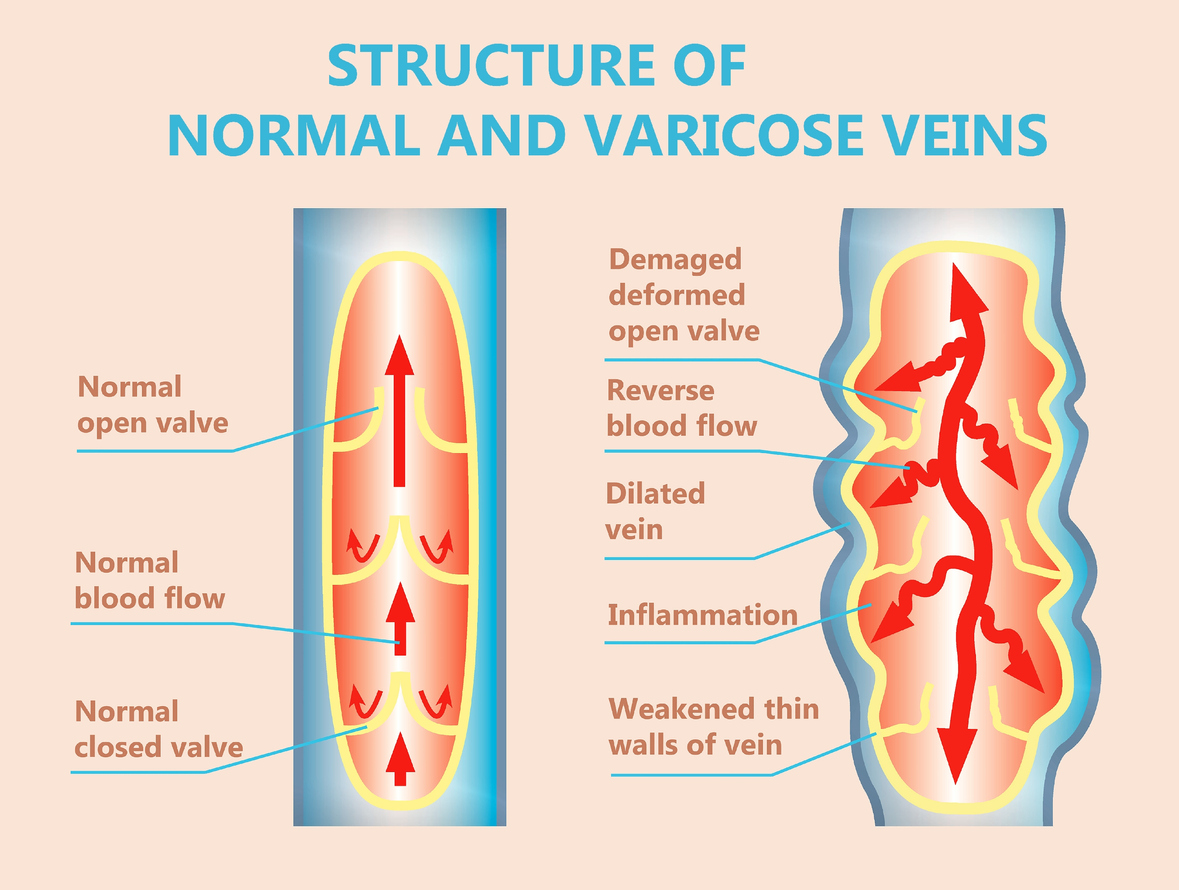
What is the pathology behind varicose veins?
Dilated, bulging, tortuous superficial veins
>3mm diameter
What is the difference between dilated intradermal veins and telangiectasias?
dilated intradermal veins
blue-green
measure 1-3 mm in diameter
No protrusion
Telangiectasias
Small at <1 mm in diameter
Dilated
spider-web pattern
What is the difference between primary and secondary varicose veins?
Primary
Origin in superficial system and 50% has + FMHX
Defective structure/function of valves of saphenous veins
Intrinsic weakness of vein wall
High intraluminal pressure
Secondary
2nd to HTN, deep-venous insufficiency or deep-venous obstruction
→ incompetent perforating veins → enlarged superficial veins
Ex: arteriovenous fistulas - varicose veins in limbs
Define chronic venous insufficiency
Consequence of incompetent veins →:
venous HTN
extravasation of fluid
blood in tissues of limb
What are some causes to chronic venous insufficiency?
varicose veins
disease in deep veins
What is the difference between primary and secondary chronic venous insufficiency
Primary
consequence intrinsic structural/functional abnl in vein wall or venous valves → valvular reflux/regurg.
Secondary
obstruction and/or valvular incompetence from previous deep-vein thrombosis.
What is the physiological changes seen in deep-vein insufficiency due to DVT?
Valves become:
Thickened
Contracted
Can’t prevent retrograde flow of blood
→ Vein becomes rigid and thick walled
How does DVT relate to 2nd causes of deep-vein insufficiency?
Due to the high pressures in distal valves →
distends the veins
separate leaflets
What else can cause 2nd varicosities?
R-sided heart disease
What are the primary forms of venous thrombosis?
DVT in extremities
PE in lungs
How does tissue factor contribute to the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin?
TF combines with VIIa → VIIa/TF which is then added to X → Xa
What is the purpose of antithrombins like TFIPI, heparin, protein C/S?
Limit production of thrombin to prevent prolongation of coagulation and thrombus formation
What is the difference between activation between venous thrombosis and arterial thrombosis?
Venous
Initiated of coagulation by exposure of TF → formation of thrombus + conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin
Arterial
Promoted by adhesion of platelets to injured vessel + stimulated by exposed extracellular matrix
What are some heritable causes of arterial and venous thrombosis?
Prothrombin: 202010G → A
Protein C Anticoagulant Pathway: Factor V Leiden: 1691G → A (Arg506Gln)
What are some genetic variation and pharm responses to platelet inhibitors?
Clopidogrel/Prasugrel
CYP2C19
CYP3A4
CYP3A5
ASA
COX1
COX2
Abciximab/Eptifibatide/Tirofiban
PIA1/A2
Define atrial septic defect (ASD)
Left-to-right shunt
Intracardiac holes that allows blood to transmit between chambers or spaces
Size determines R sided dilation
What is the difference between secundum ASD and primum ASD?
Secundum
MC
Occurs at fossa ovalis
Primum
Deficiency of AV canal portion of atrial septum
Always ass w/ abnl development of AV valves w
MC: cleft in mitral valve
both fixed by sx
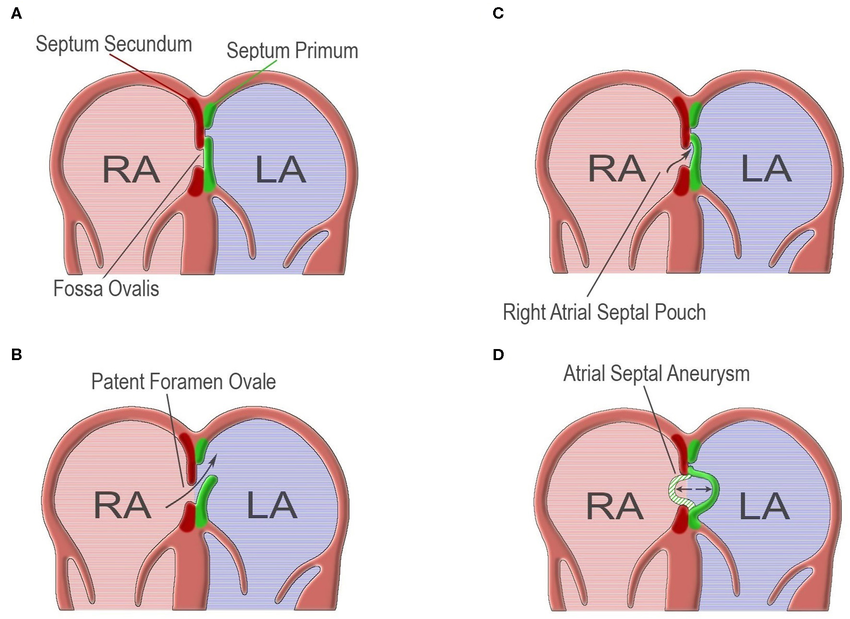
What is patent foramen ovale (PFO)?
Valve flap of fossa ovalis that did not close after birth and does NOT relate to R sided cardiac dilation
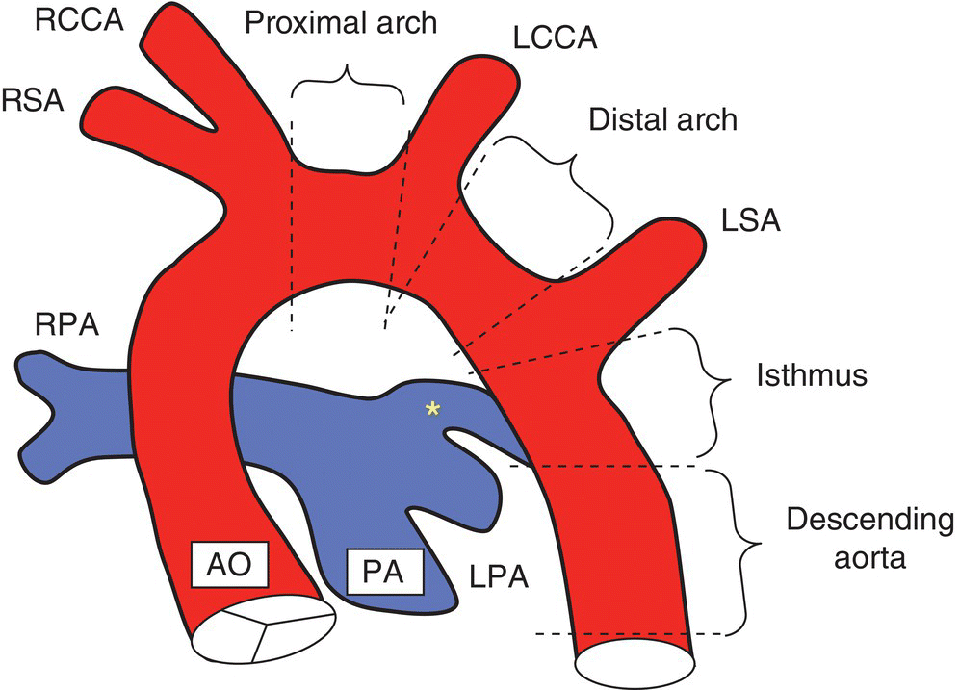
What is Coarctation of the Aorta?
Obstruction at the (MC) descending aorta that passes posterior to junction of main and left PA.
Less commonly at transverse aortic arch
What is patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)?
ductus arteriosus remains open
Located between aortic isthmus and origin of one of the branch pulmonary arteries
Brings oxygenated blood from aorta to lungs
What is the difference presentation between a small PDA and large PDA?
Small
Silent during auscultation
Does NOT cause hemodynamic changes
Large
Left heart dilation → chronic elevated pulmonary vascular resistance
eisenmenger syndrome
What is the most common congenital anomaly recognized at birth?
ventricular septal defect (VSD)
What presentation is associated with a large VSD?
HF and poor somatic growth
What is the MC location for VSD to occur?
Membranous septum
also known as perimembranous or outlet defects
What is the common form of cyanotic CHD
Tertralogy of fallot
What is the physical changes seen in tertalogy of fallot?
R ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) obstruction
VSD
R ventricular hypertrophy
override of aorta