Art Final Style Guide Practice
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
Pre-Historic (before writing)
Cave paintings of animals, loosely done, great vitality and movement. Small, portable sculpture. Paleolithic(Nomadic)Neolithic (Agricultural)
Ancient Near East
Bronze. Small Statues, Ziggurats, carved reliefs. Some violent, some calm and humble. Narrative. Beginnings of civilization.
Egyptian
Great monuments (Pyramid tombs) painted tombs, huge statues and small delicate works. Stiff body conventions (twisted torso). Very ordered and strict, lots of symbolism. Hierarchical scale. Burial goods.
Greek
Beauty, Harmony, Order. The Idealized view of man. Temples to the gods, cities, theatres, etc. The true beginning of "Western Culture." Art for Art's sake.
Roman
Similar to Greek but more realistic, shows people as they really look. Very narrative. Innovators in architecture.
Christian
Themes from the Bible. Few nudes. Teaching art. Move away from realism toward symbolic form.
Byzantine (East)
Retains Greek harmony. Themes from Bible. Mosaics. Not very realistic. (No illusion of depth.)
Medieval (Romanesque)
Early medieval--heavy architecture, stiff and often twisted figures, nervous, excited style. Use of round "Roman" arches.
Medieval (Gothic)
The great cathedrals (Notre Dame) Flying buttresses, pointed arches. Stained glass. French style, which spreads all over Europe. Move toward realism in both figures and decoration.
Italian Renaissance
Return to the ideals of Greek and Roman period. (Re-birth of Greco-Roman style). Man as a noble, perfect creature combined with Biblical themes. Mostly religious art. Humanism
Northern Renaissance
Dutch, Flemish, and German Renaissance. Move towards greater realism and more emotion. Influenced by the Reformation (Protestant).
Baroque
Takes realism from Renaissance and adds more movement, drama, energy, light, passion.
Rococo
Highly ornamental, busy, light-hearted, rich. (Pink, fluffy, clouds and cherubs.)Style of the aristocracy.
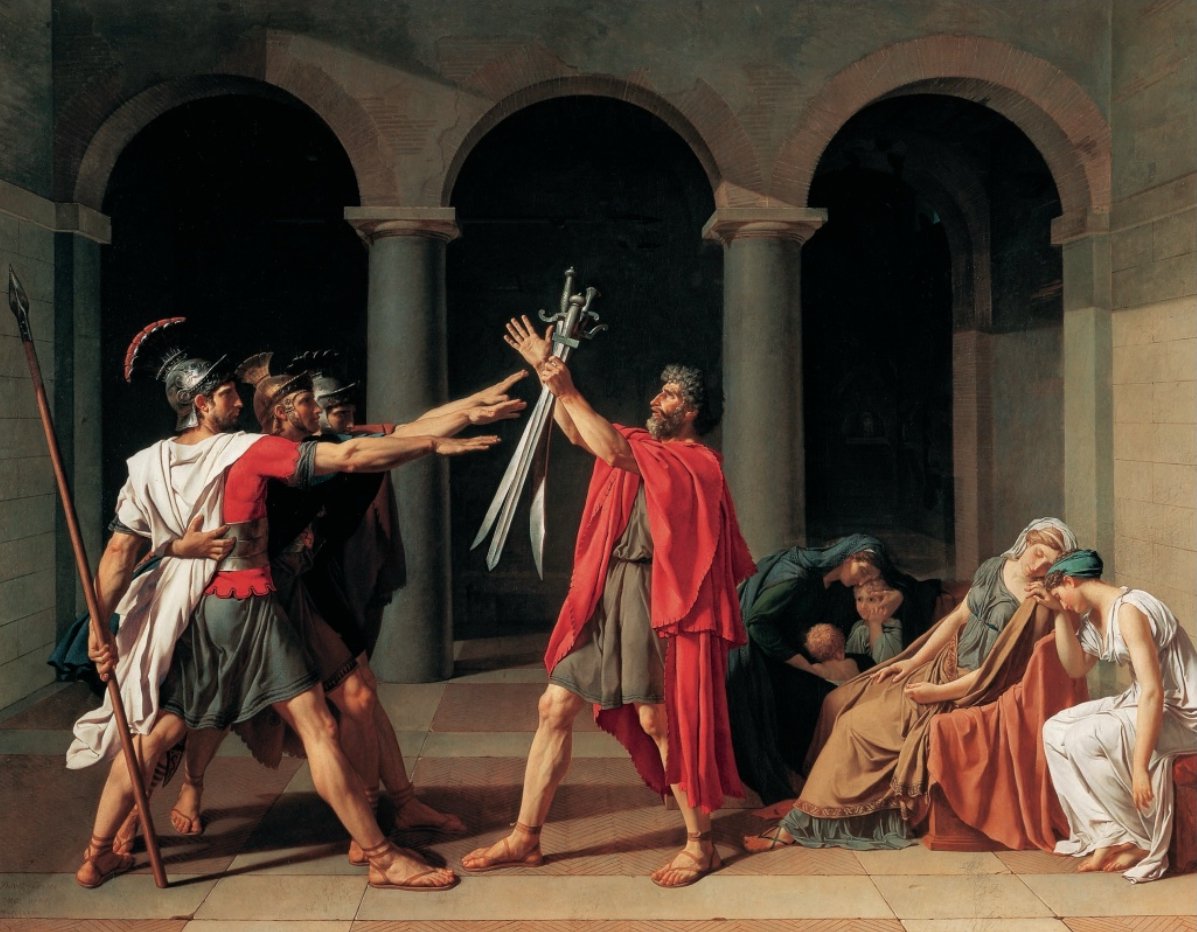
Neo-Classicism
Severely linear style- precise line. Cool, calm, classical.(Style of the French and American Revolutions.)
Romanticism
Highly emotive, sometimes horrific or sublime imagery. Images from the mind or psyche - often a literary connection. Nature over man.
Realism
New subject matter: current events and the modern world. Landscapes, still lifes, genre scenes.
Impressionism
Capturing the effects of light on surfaces, especially in landscape motifs. Brushwork more loose, painterly effects giving a sensation or "impression" of the image. Subject matter: Nature and the newly created middle-class
Post-Impressionism
Inspired by Impressionism. Two wings: One interested more in form and structure, the other interested more in emotion and symbolism. 1.Cezanne, Seurat. 2.Gauguin, van Gogh.
Art Nouveau
Decorative, floral, delicate designs - sensual rhythms and arabesque line.
Expressionism Fauvism
French form of Expressionism, intense color. Flattened space, little or no linear perspective. Leader: Matisse.
German Expressionism
fauve-like color, more acerbic in mood, angst-filled emotions. Die Brucke and Der Blaue Reiter groups. Kirchner, Nolde, Kandinsky, Marc, Beckmann, Kollwitz
Cubism
Faceted, broken forms, showing many sides at once. Some African and Oceanic influences. Leader: Picasso.
International Architectural Style
Clean, sleek, architecturewith no decoration.
Dada
Anti-art, anti-rationalism. An art focused on ideas and statements. Leaders: Tristan Tzara and Marcel Duchamp.
Surrealism
Focus on the subconscious and the world of dreams and visions. Utilized elements of chance and the accidental. Influenced by modern psychology: Freud and Jung. Leaders: Andre Breton, Dali, Miro.
Action Painting
Part of Abstract Expressionism. Very personal, expressive imagery and brushwork. Usually completely abstract(no recognizable forms). A very process-oriented art. Also influenced by modern psychology - More Jung though than Freud. Gorky, de Kooning, Pollock.
Color-Field Painting
Part of Abstract Expressionism. Saturated color applied either flatly or using a staining technique. Rothko, Frankenthaler.
Pop Art
Using commercial art elements as fine art. Warhol, Johns, Oldenburg.
Op Art
Focusing on optical effects
Minimalism
Totally abstract....very few forms. Sometimes associated with Gestalt Psychology
Performance Art
Art through actions. Beuts, Anderson.
Earthworks
Large projects often involving large spatial areas of an actual landscape and many people. Christo, Smithson, Holt.
Conceptual Art
Idea-oriented art. Kosuth.
Perceptual Art
Art that changes the way you "see" a space or form. Irwin, Turrell.
Post-Modernism
Eclectic use of past styles.
Post-Impressionism (people)
Cezanne, Seurat, Gauguin, Van Gogh
Expressionism (people
Matisse
German expressionism (people)
Die Brucke and Dee Blaue Reiter groups. Kierchener, Nolde, Kadinsky, Mare, Beckmann, Kollwitz
Cubism (people)
PIcasso
Dada (people)
Tristan Tzara, Marcel Duchamp
Surrealism (people)
Andre Breton, Dali, Miro
Action painting (people)
Gorky, de Kooning, Pollock
Color-Field Painting (people)
Rothko, Frankenthaler
Pop art (people)
Warhol, Johns, Oldenburg
Performance art (people)
Beuys, Anderson
Earthworks (people)
Christo, Smithson, Holt
Conceptual art (people)
Kosuth
Perceptual Art (people)
Irwin, Turrell
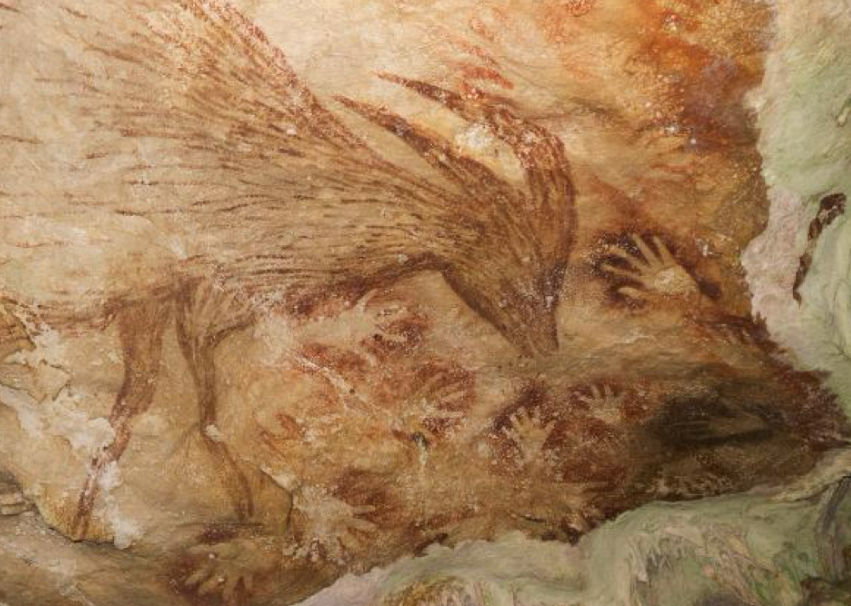

Paleolithic
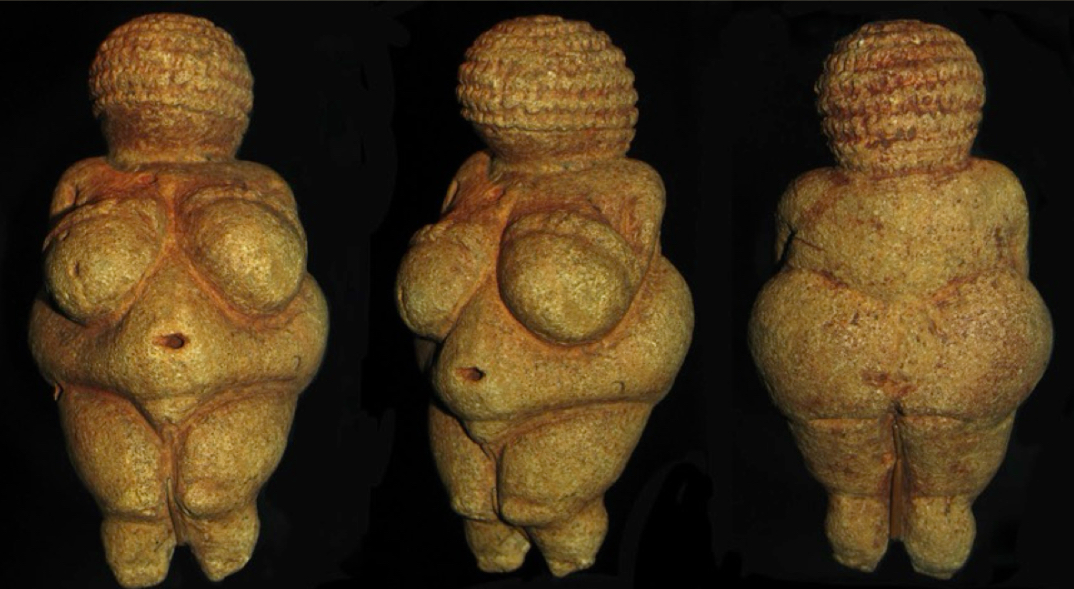
Paleolithic
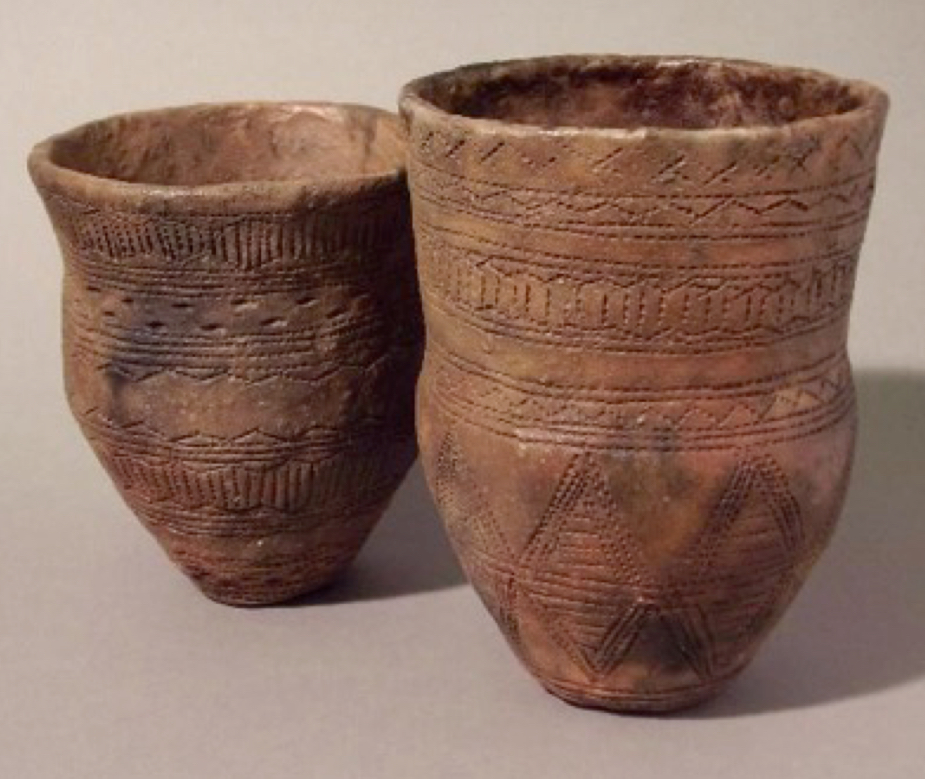

Neolithic
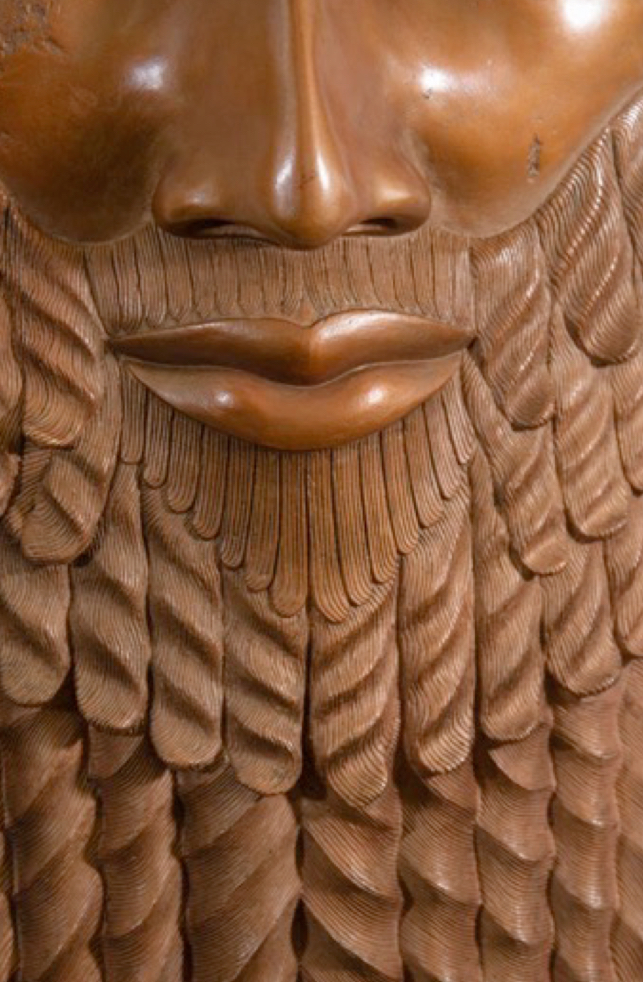

Ancient Near East
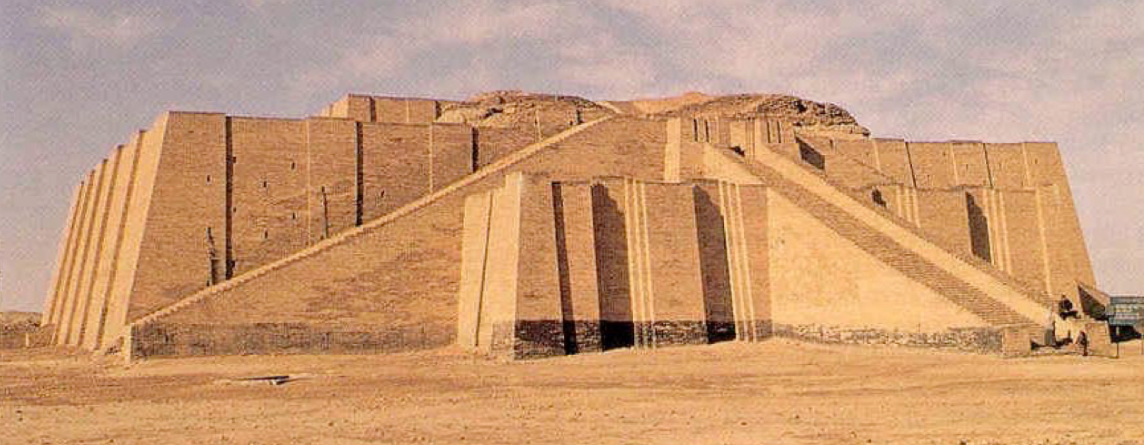

Ancient near east

Egyptian
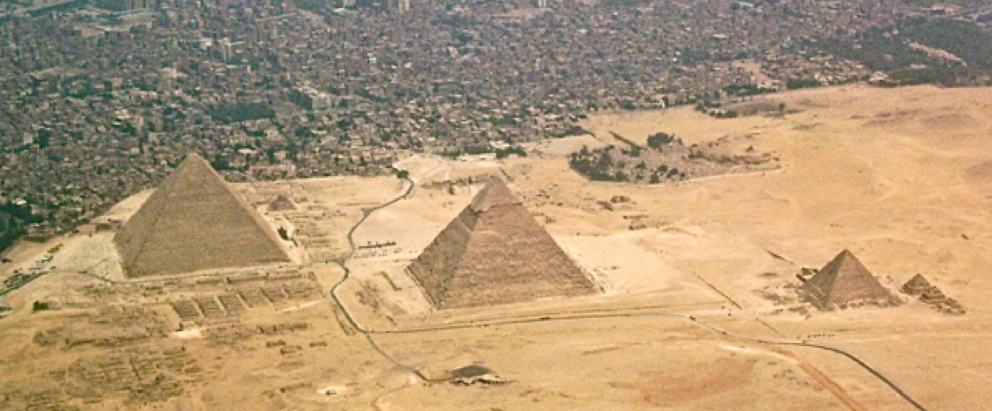

Egyptian
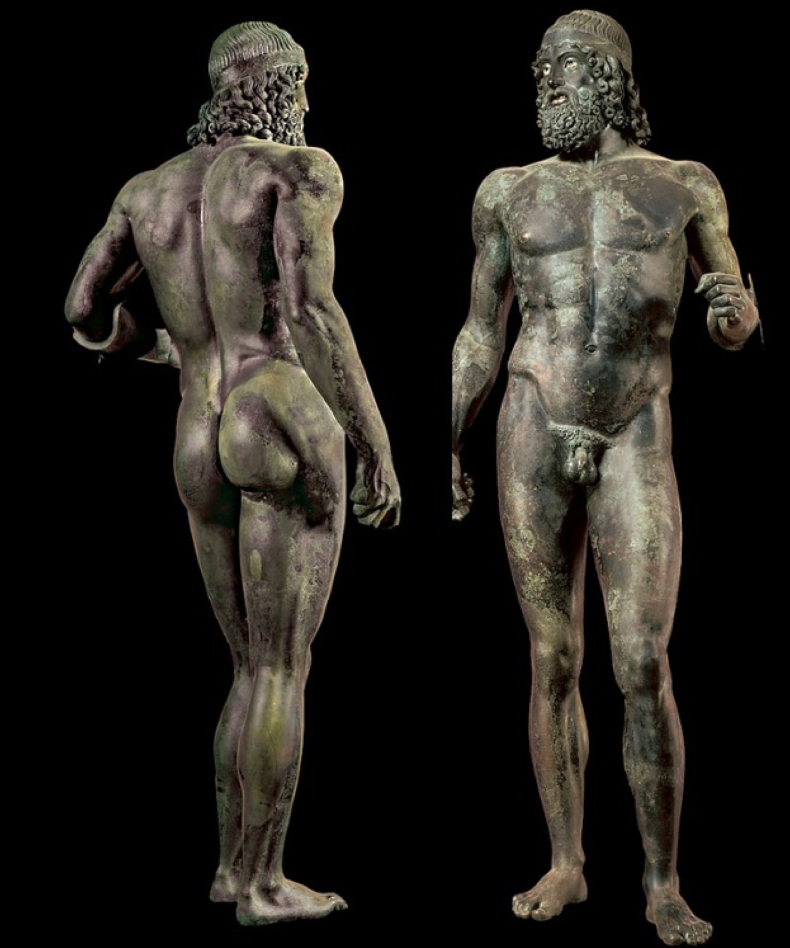

Greek (specifically classical)
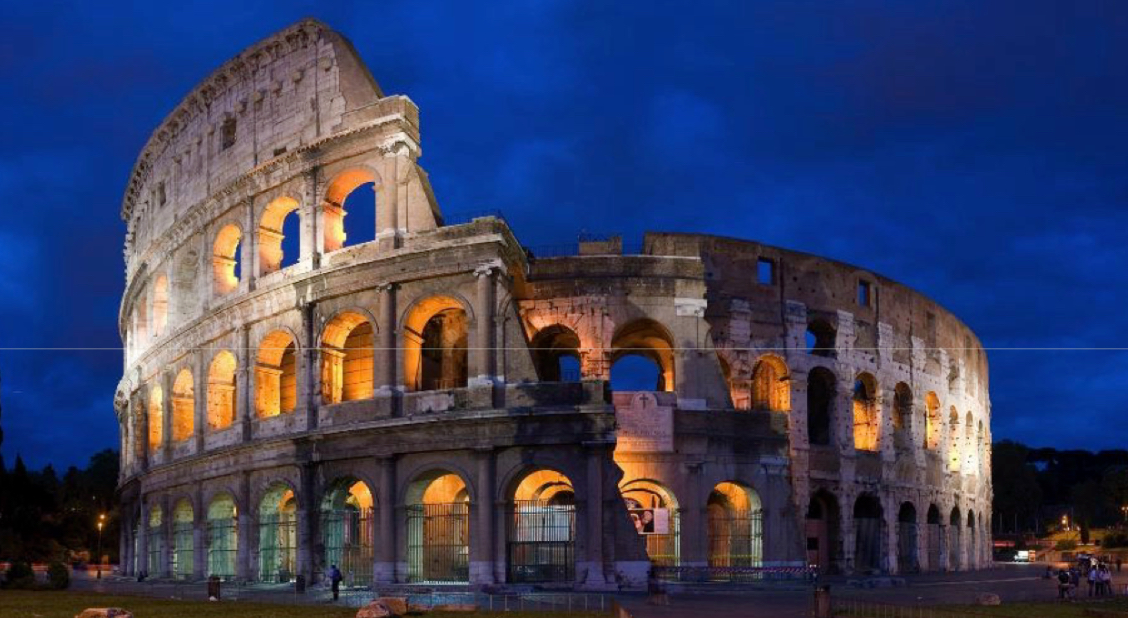

Roman
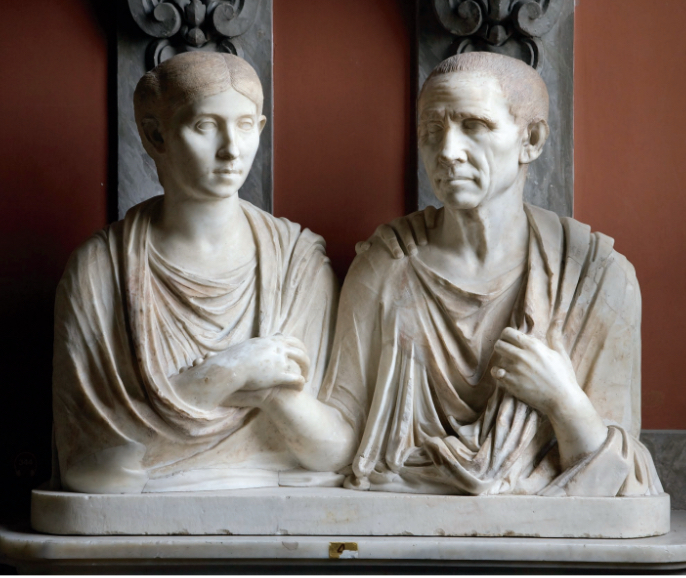

Roman
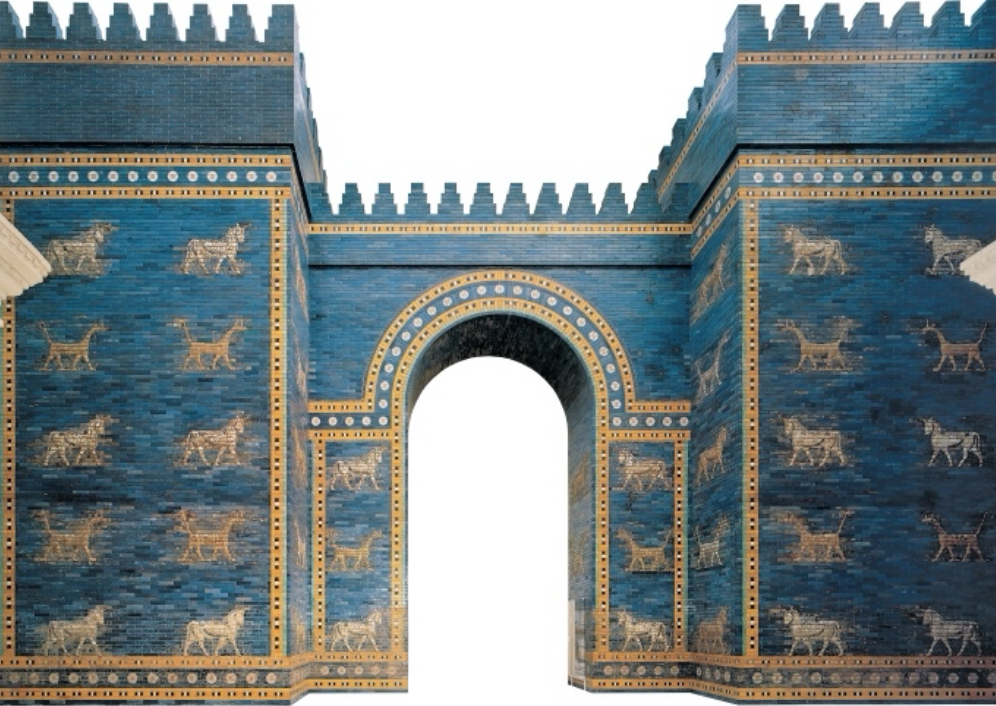

Ancient near east
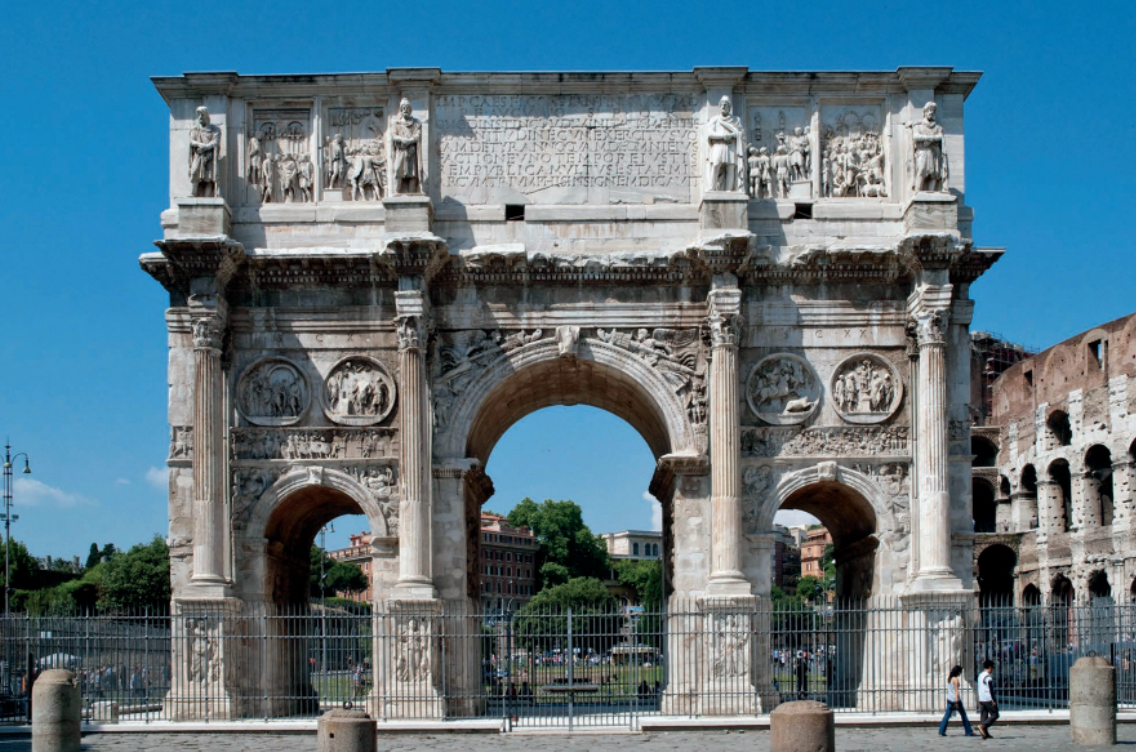

Christian (west)
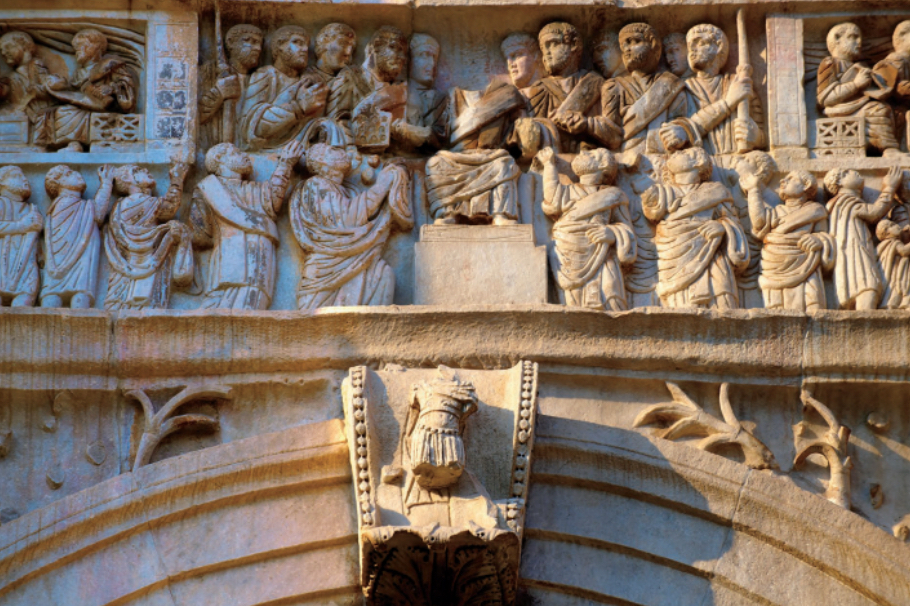

Christian (west)
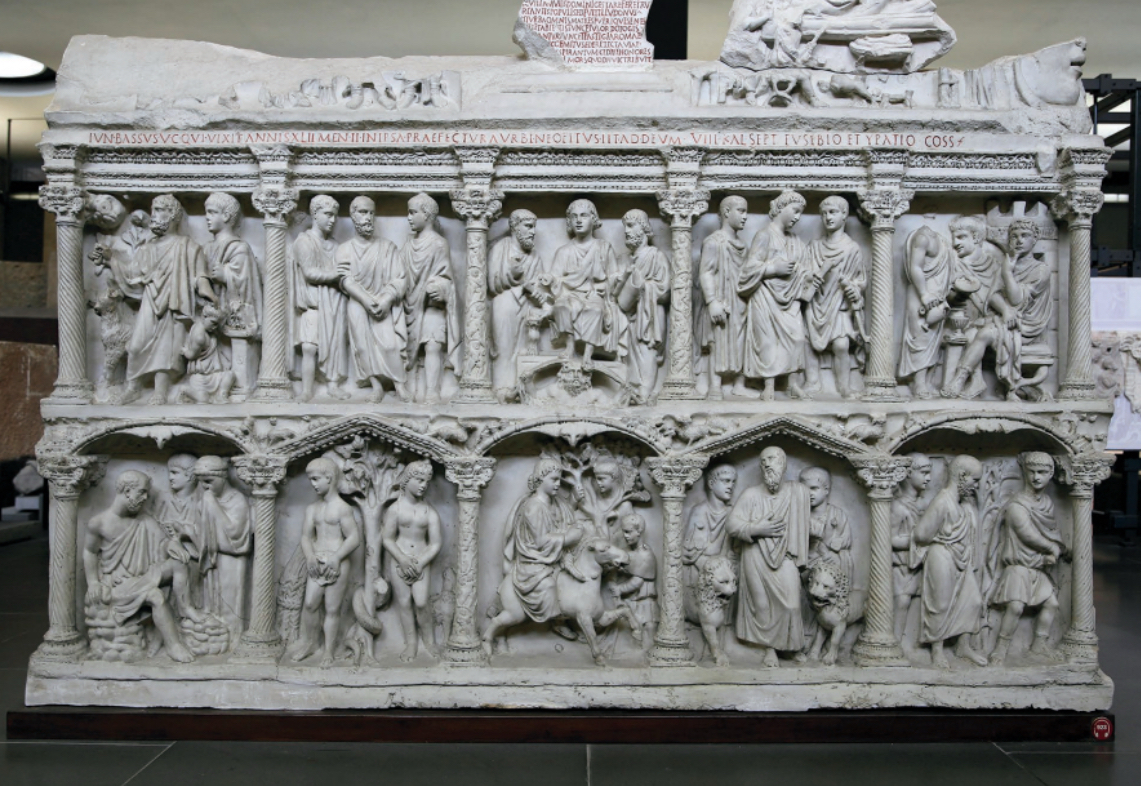

Christian (west)
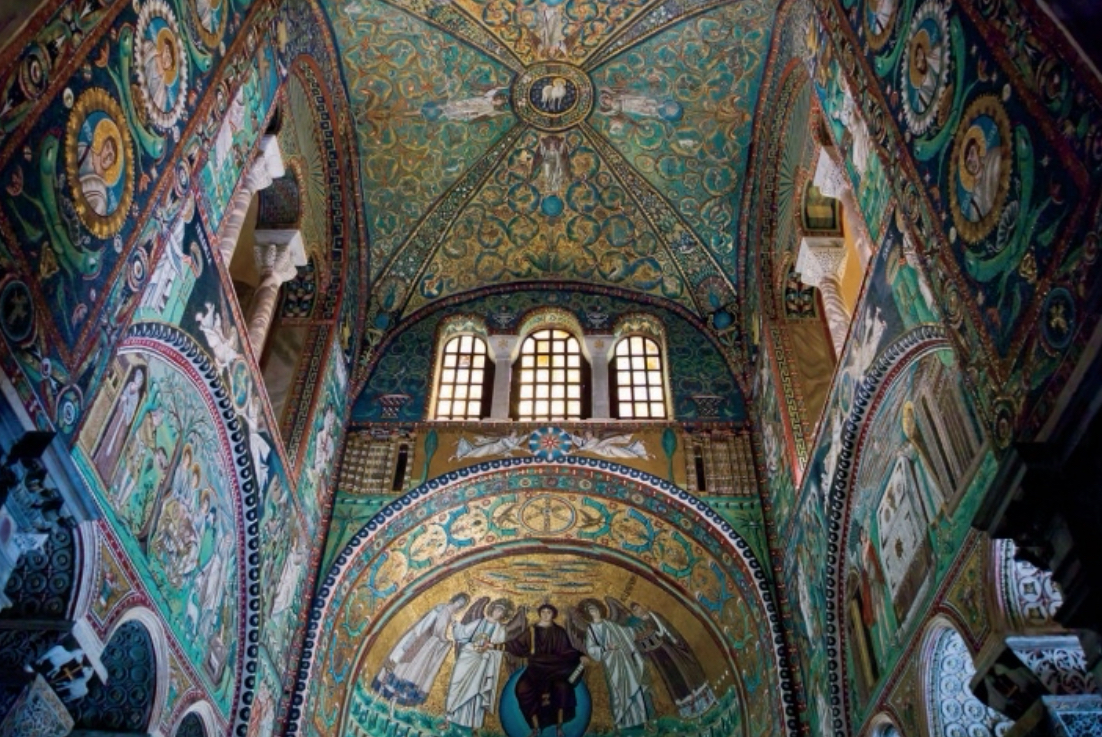

Byzantine (east)
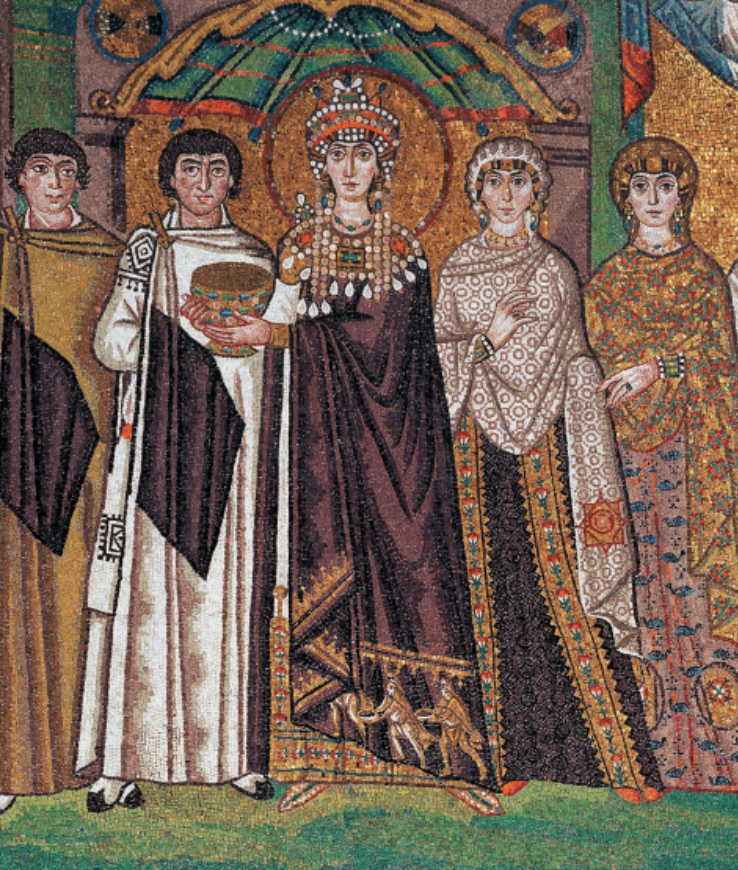

Byzantine (east)
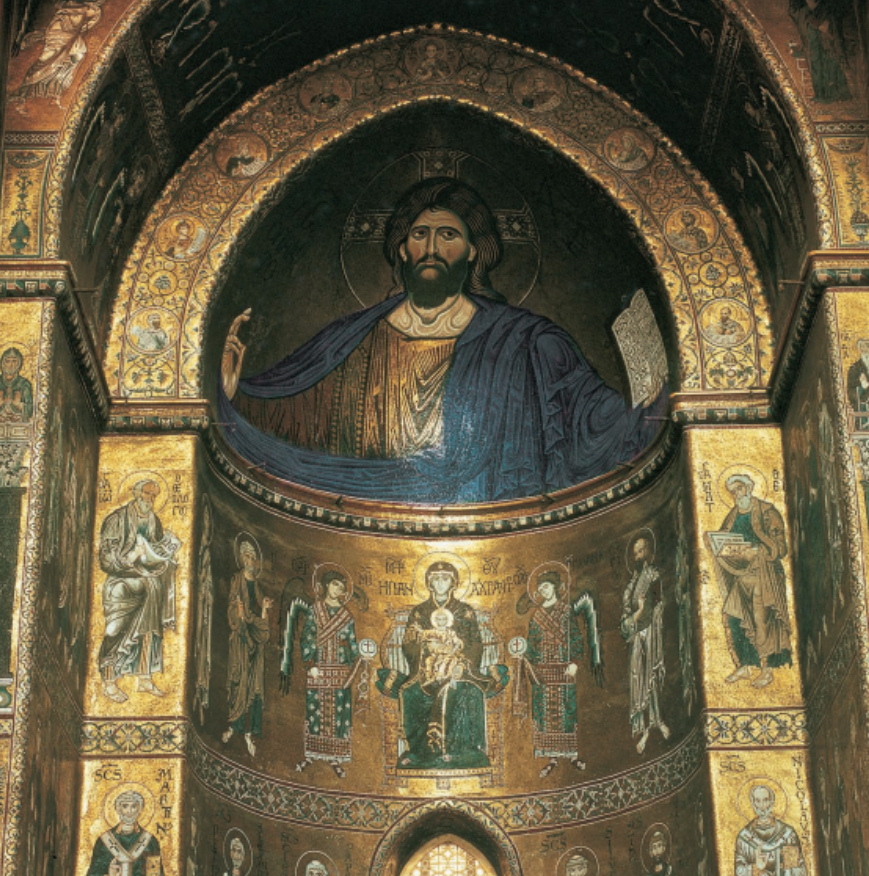

Byzantine (east)
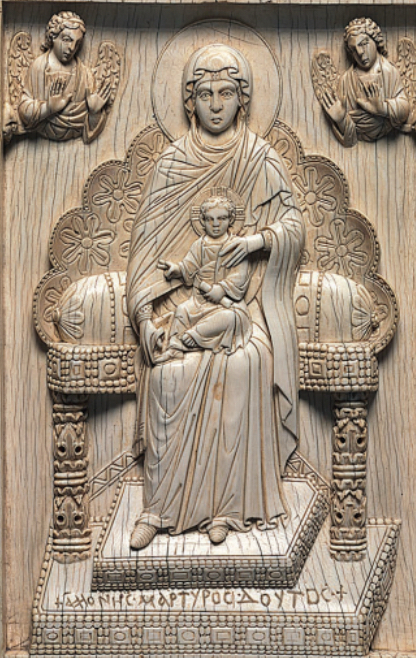

Byzantine (east)
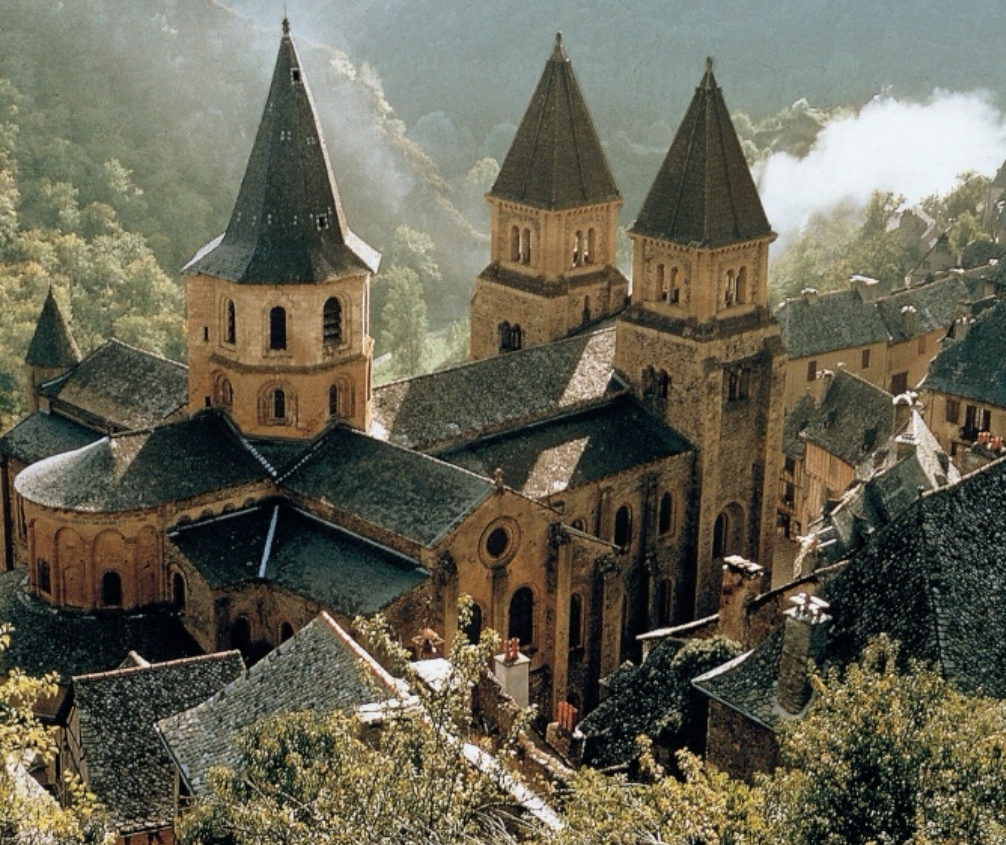

Medieval (Romanesque)
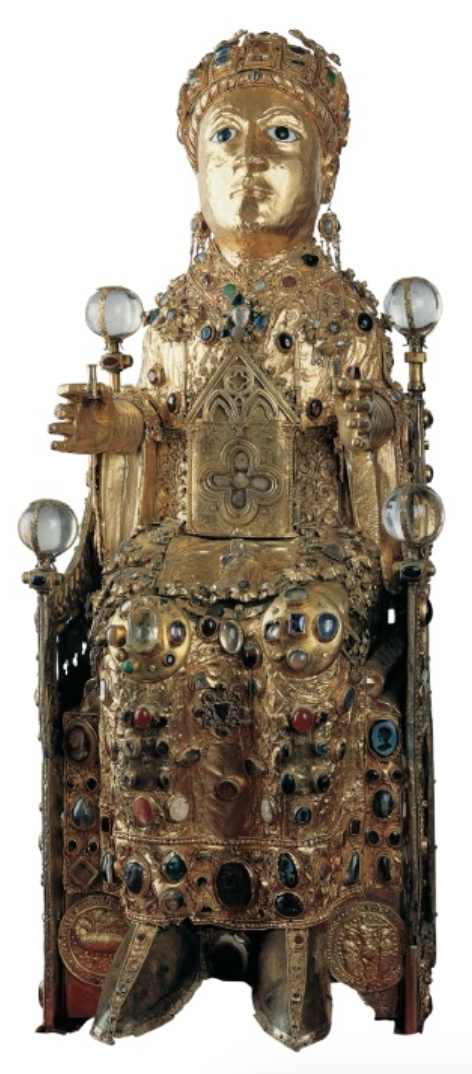

Medieval (Romanesque)
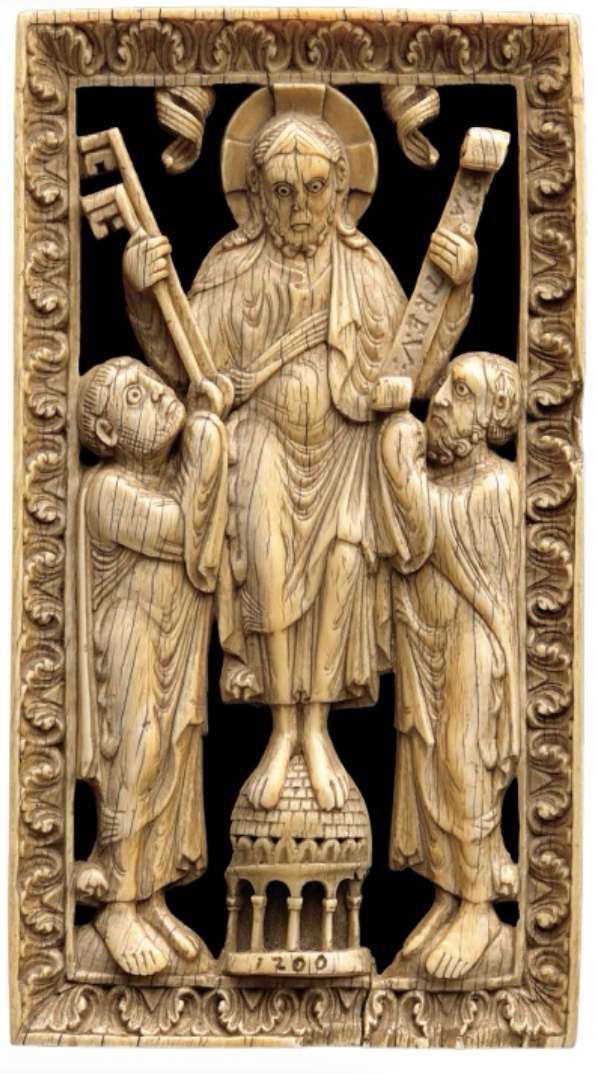

Medieval (Romanesque)
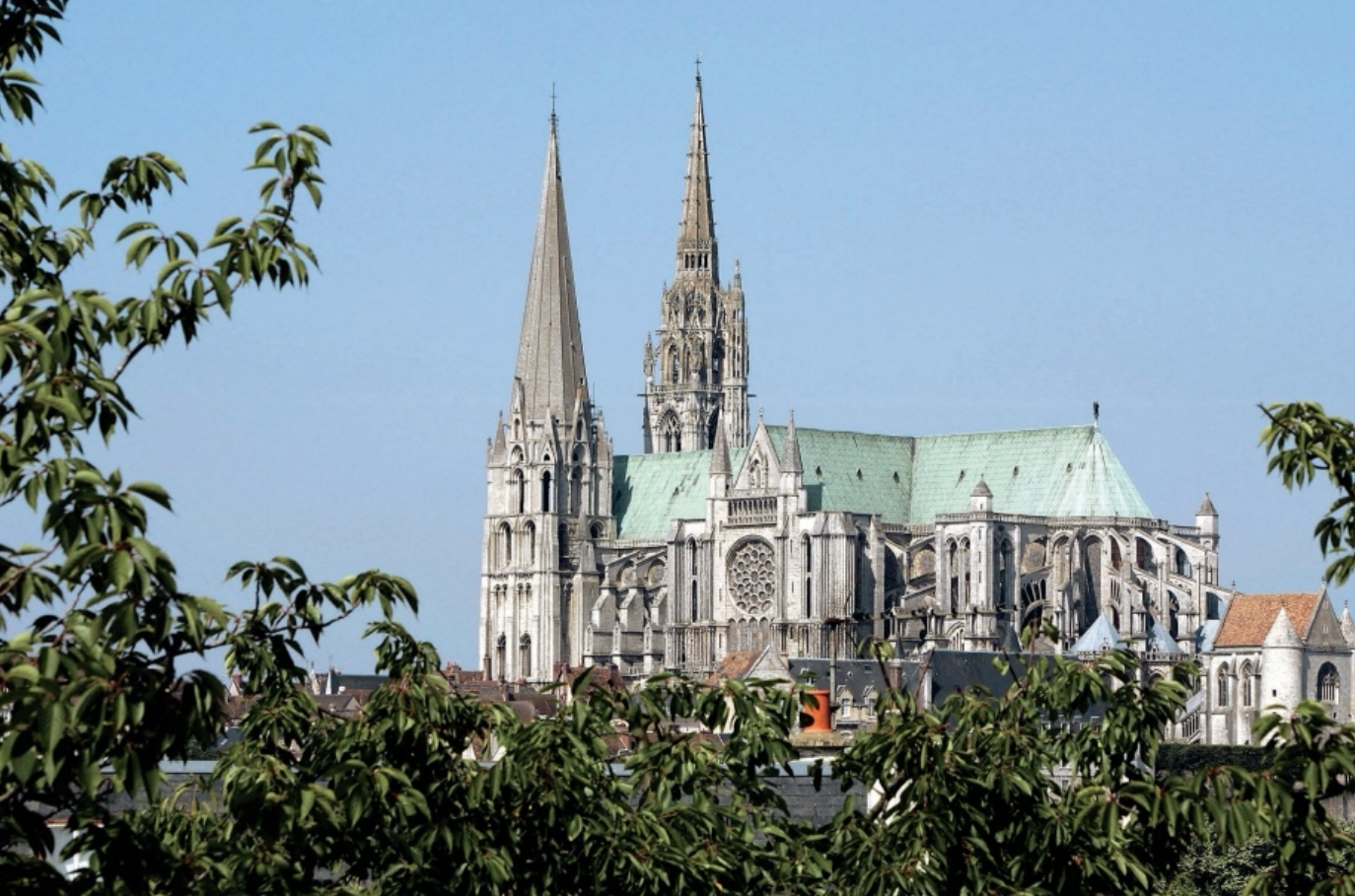

Medieval (gothic)
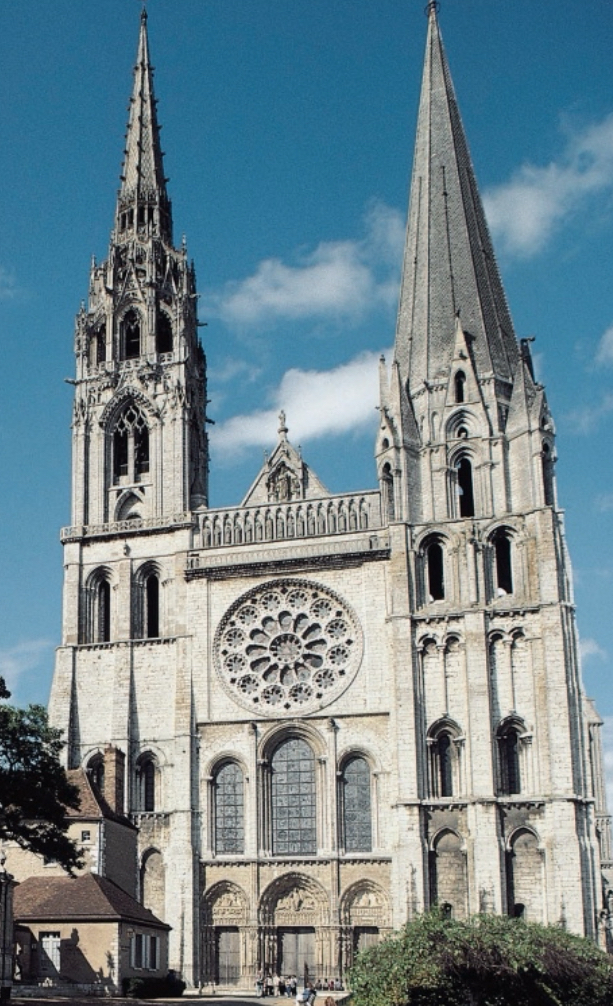

Medieval (gothic)
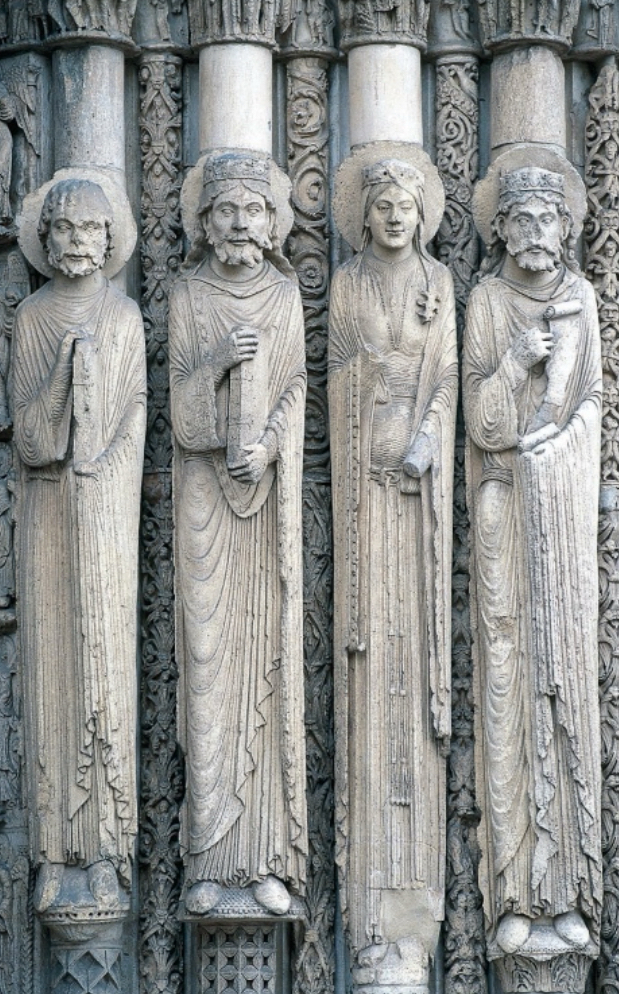

Medieval (gothic)
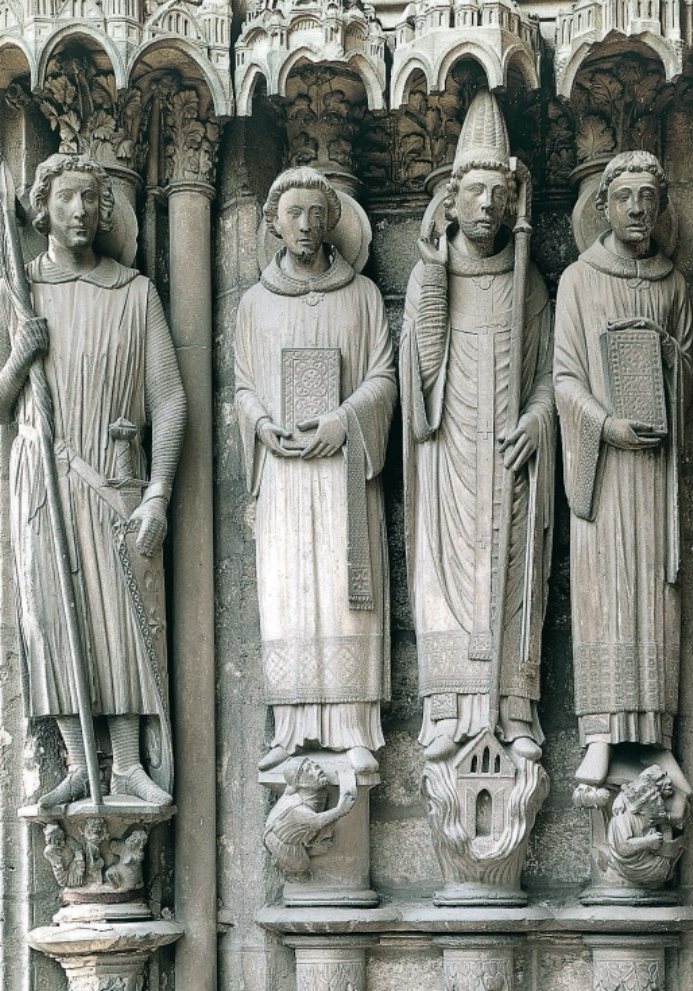

Medieval (gothic)

Medieval (gothic)

Medieval (gothic)
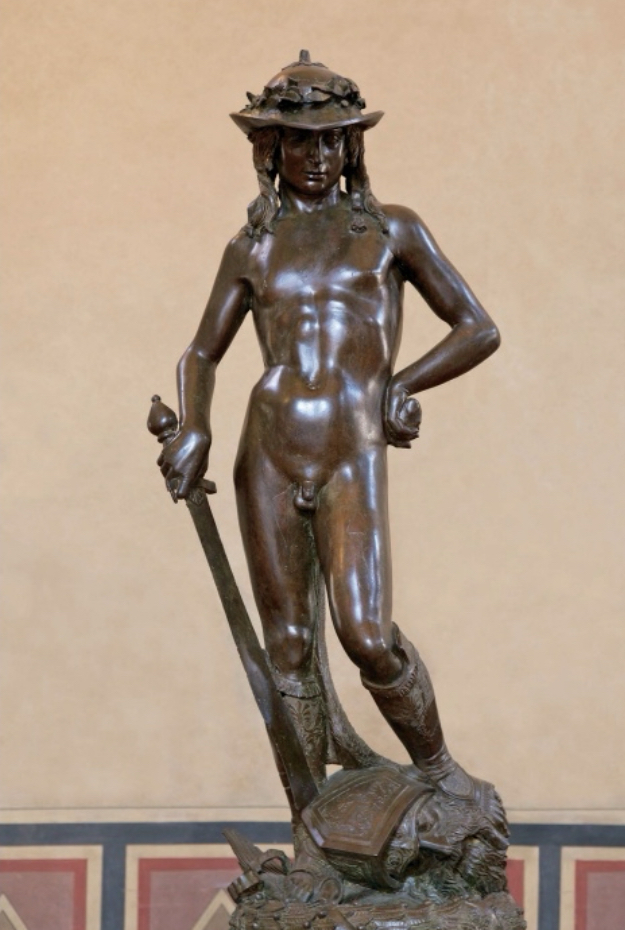

Italian Renaissance

Italian Renaissance
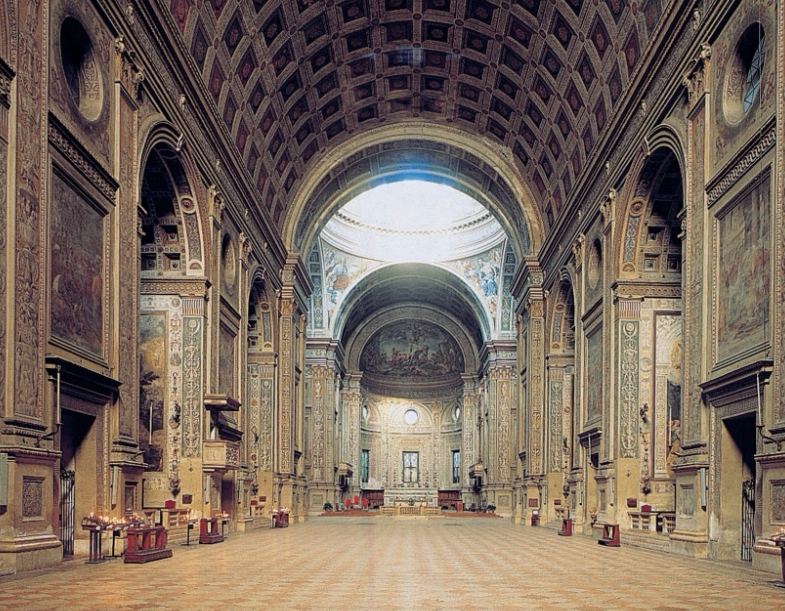

Italian Renaissance
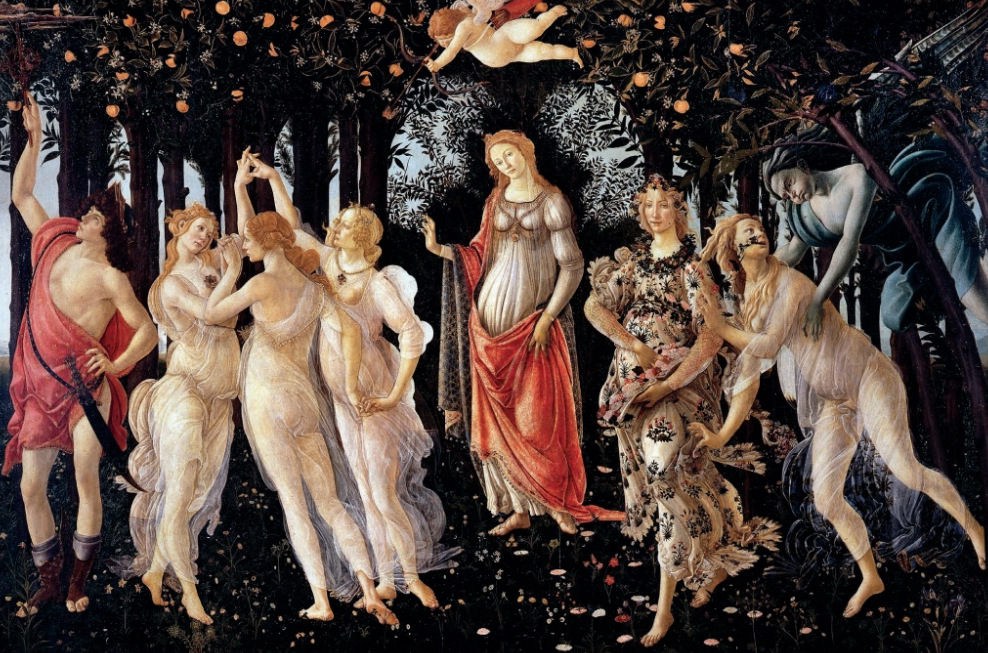

Italian Renaissance
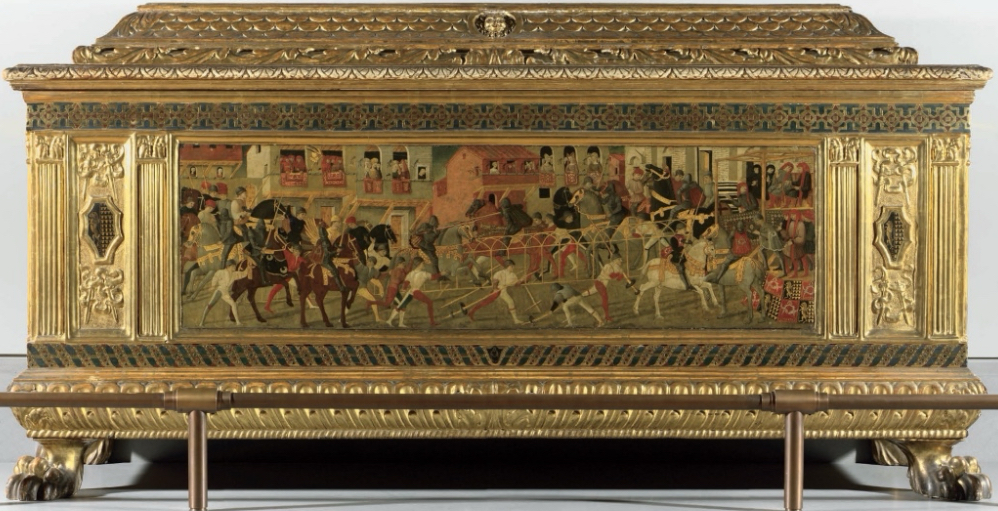

Italian Renaissance
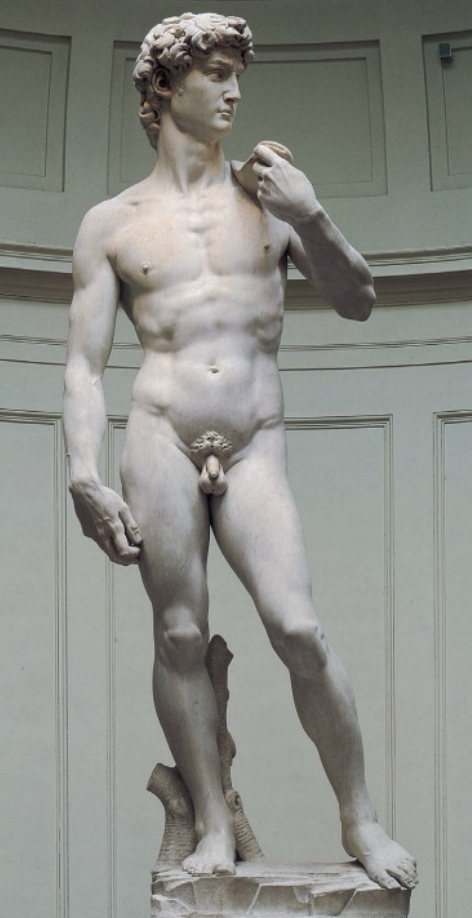

Italian Renaissance
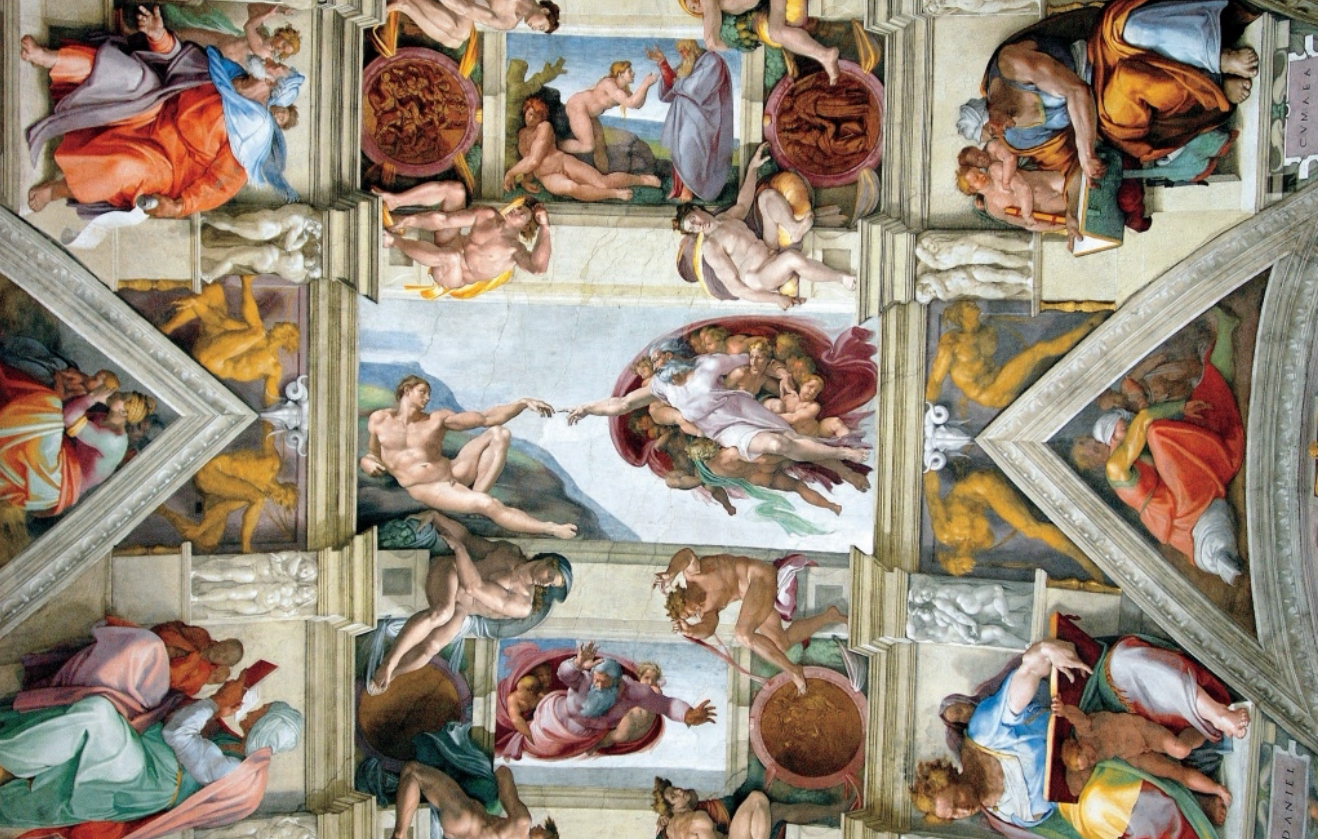
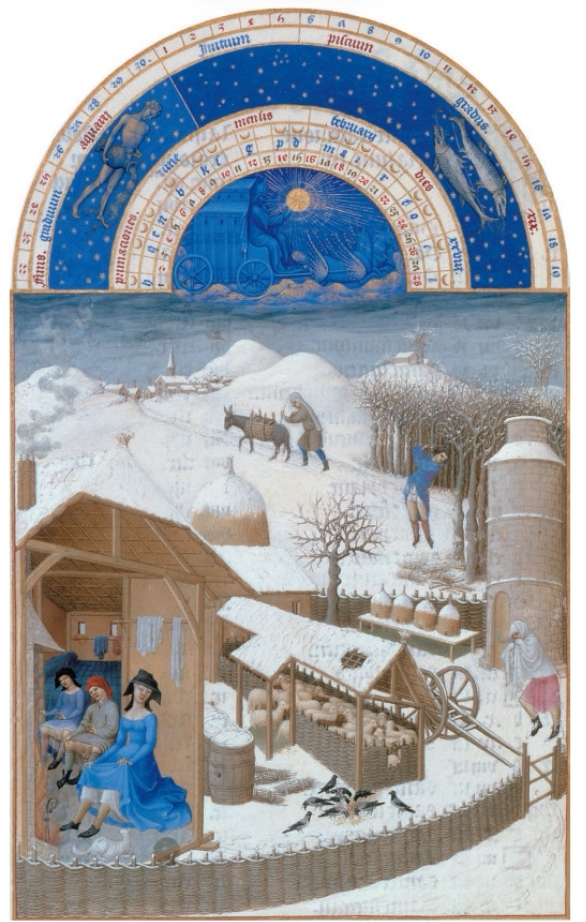


Northern Renaissance
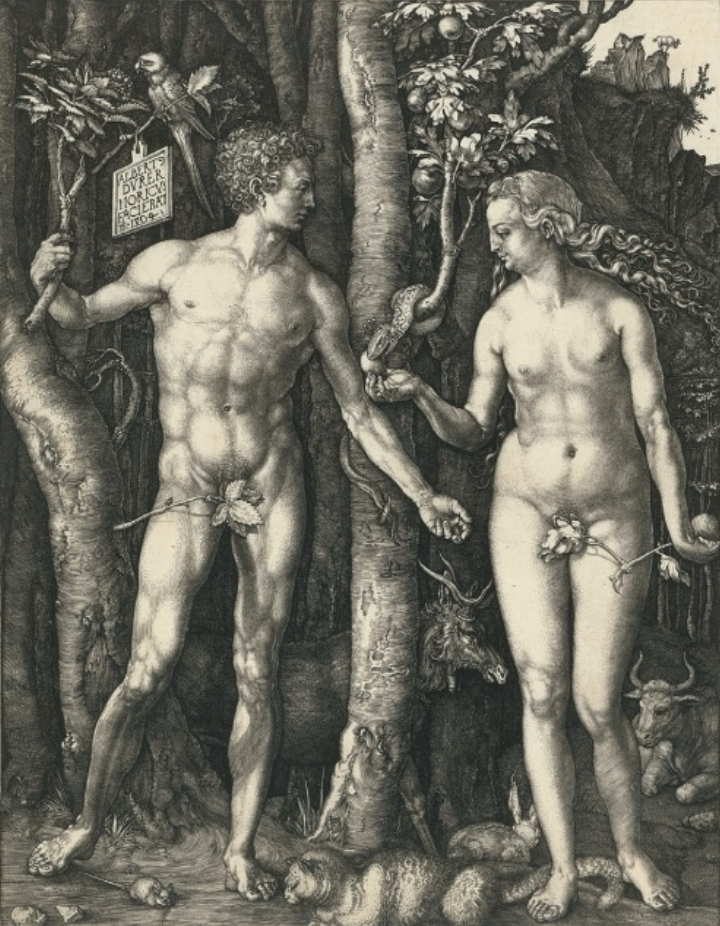

Northern Renaissance
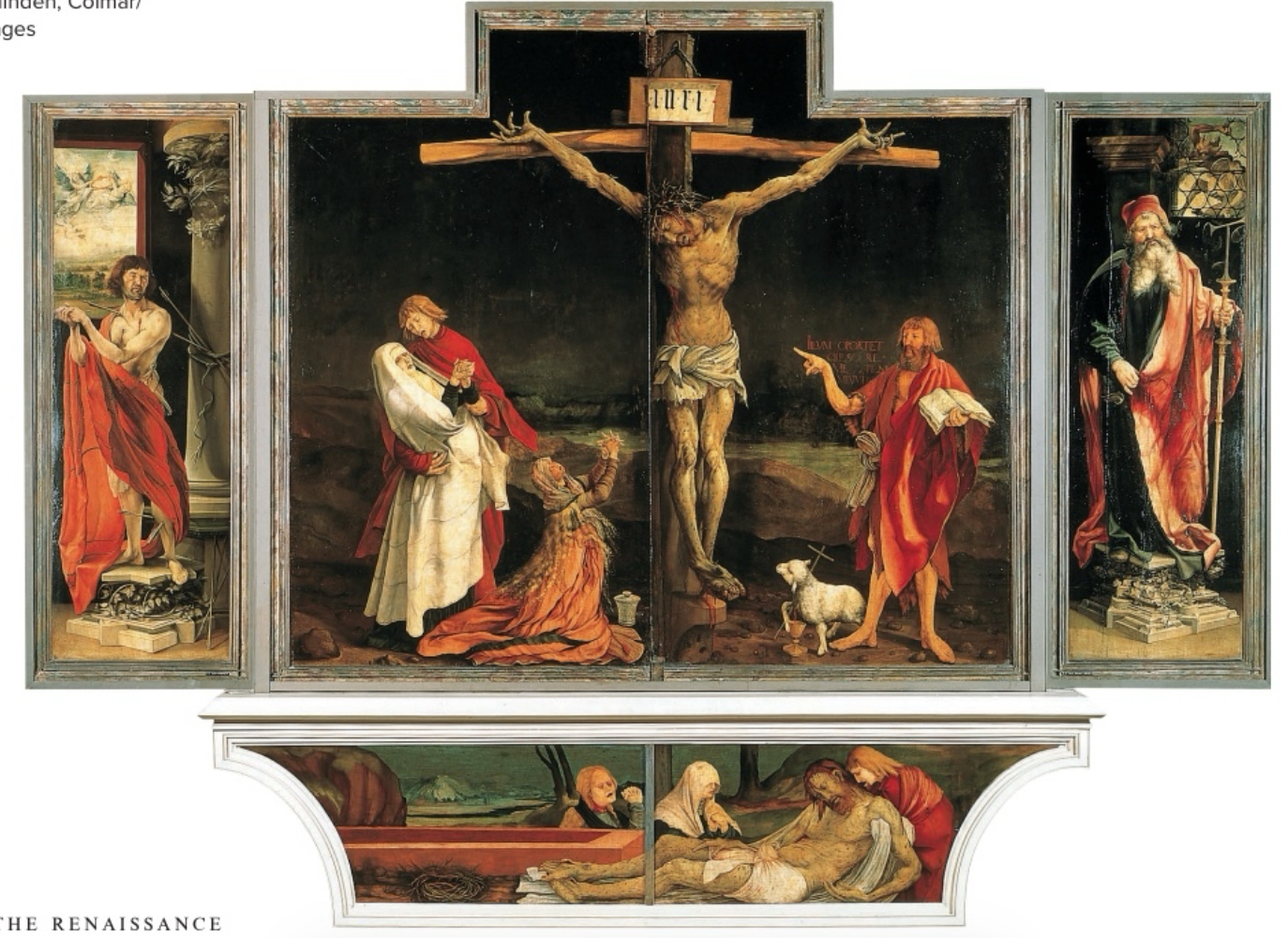
Northern Renaissance
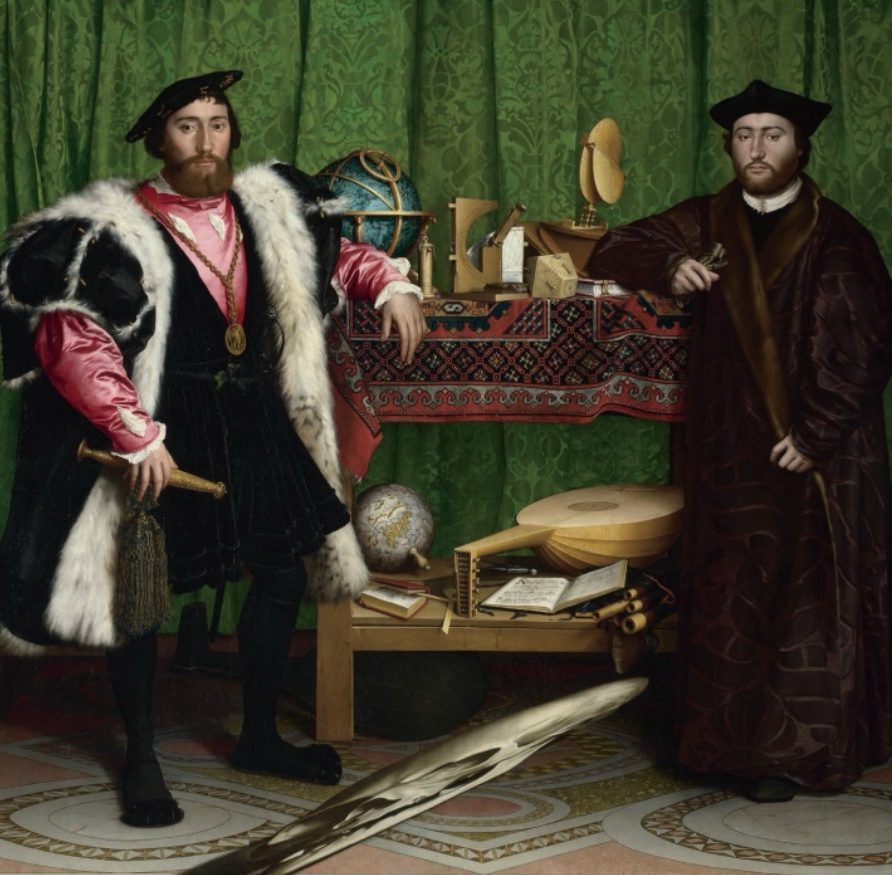

Northern Renaissance
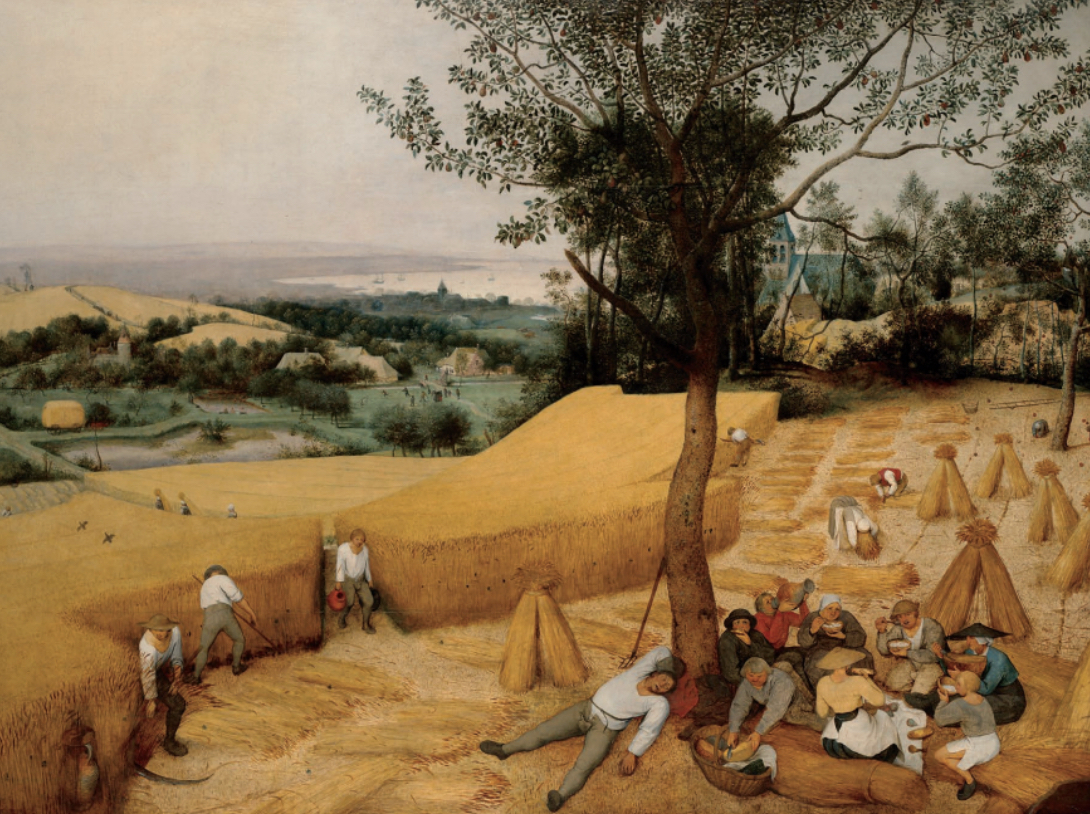

Northern Renaissance
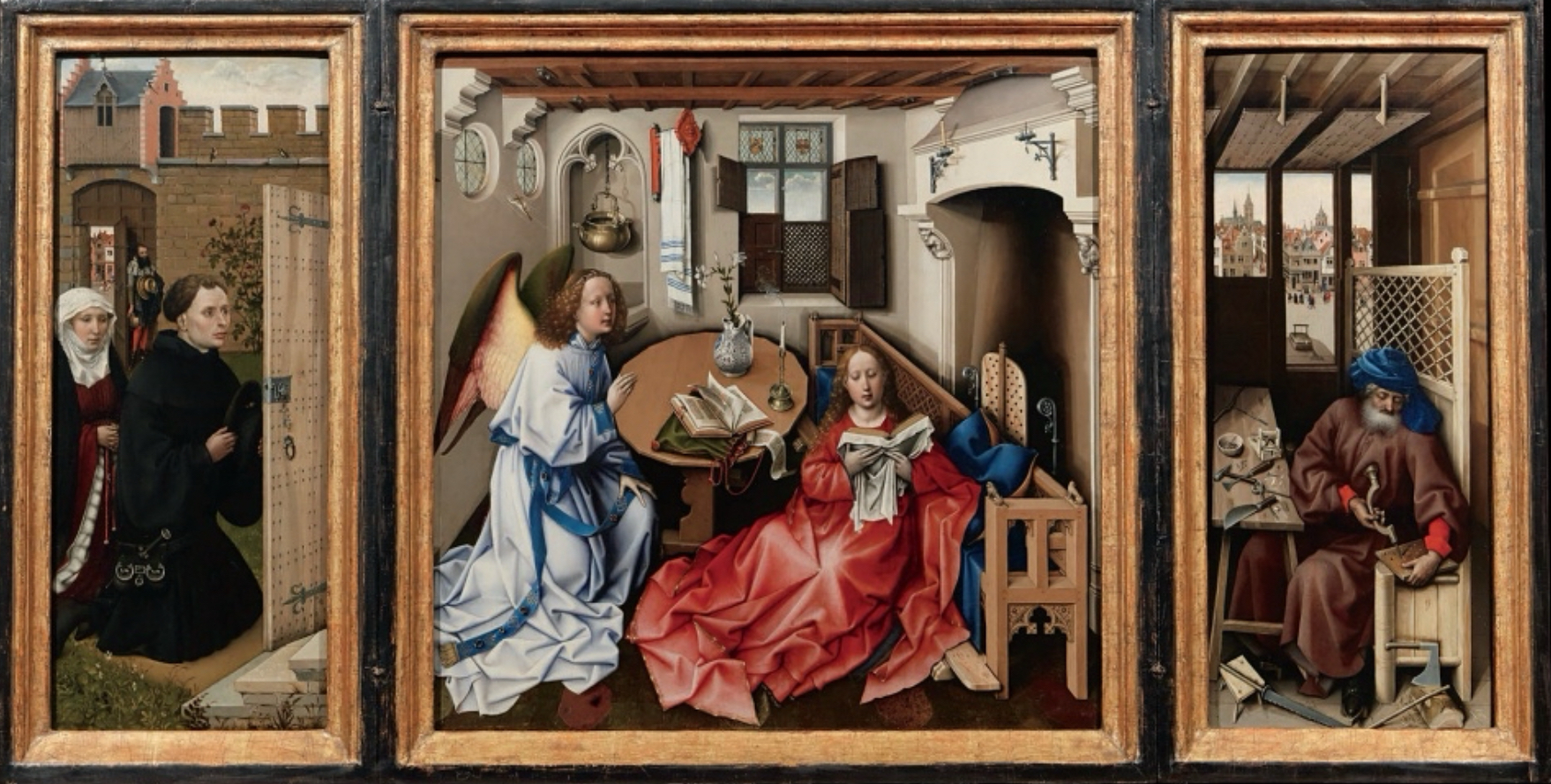
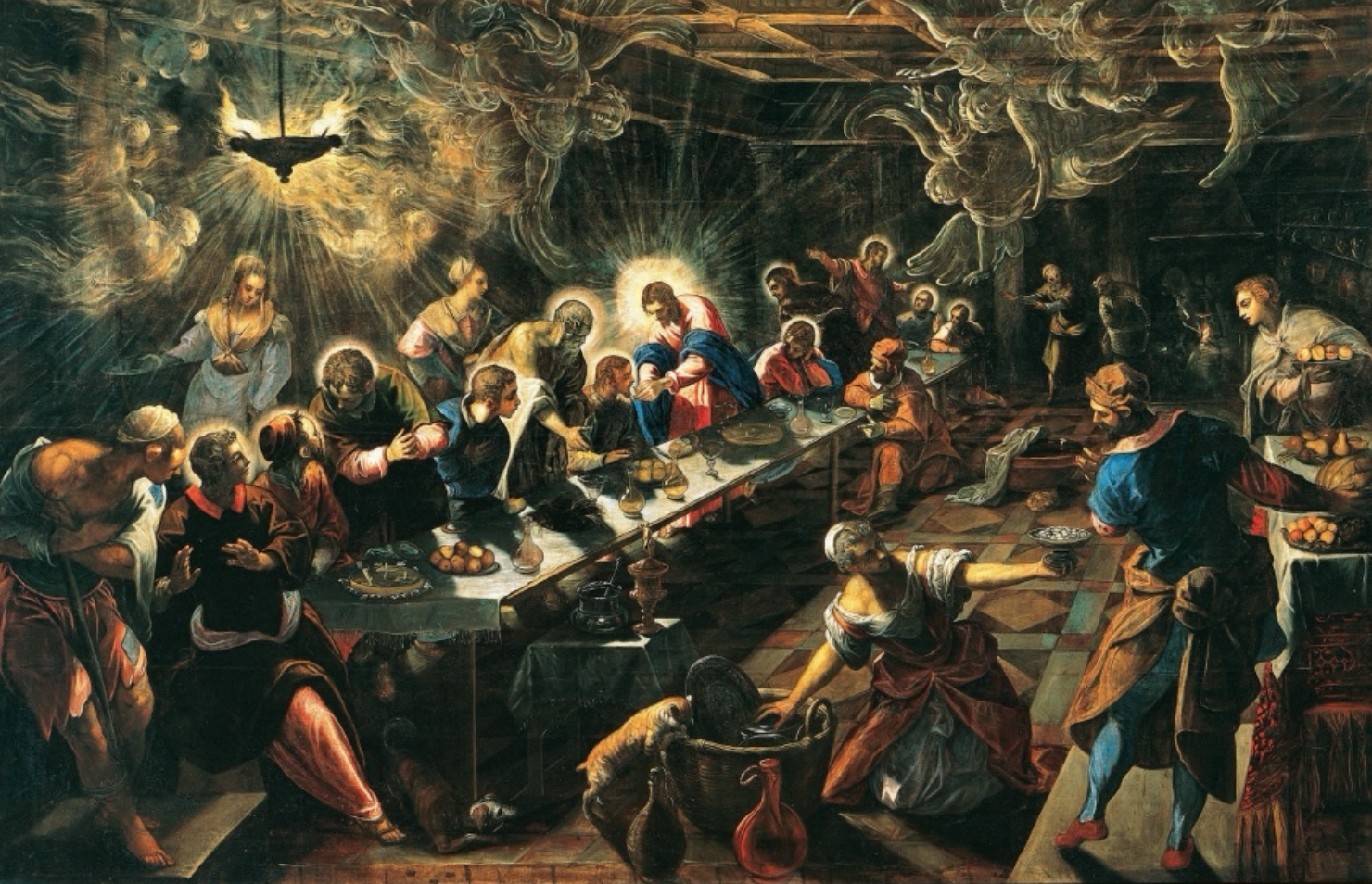


Italian Renaissance
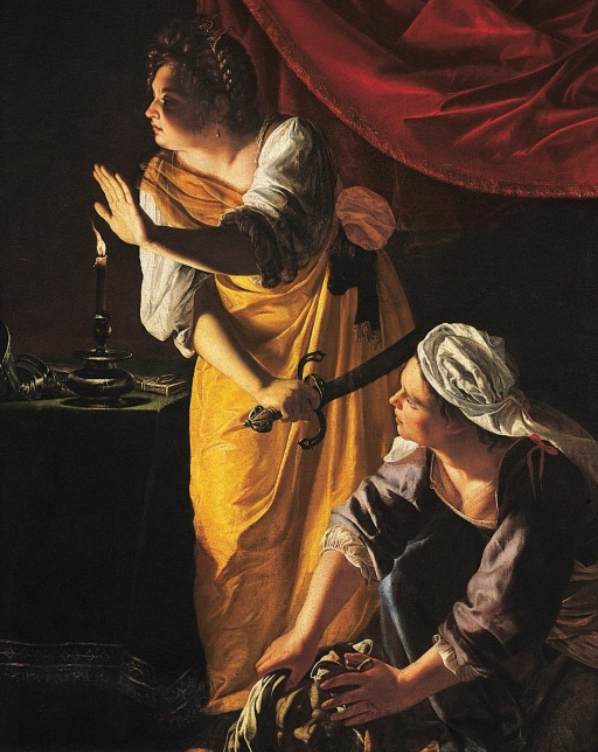


Baroque

Baroque
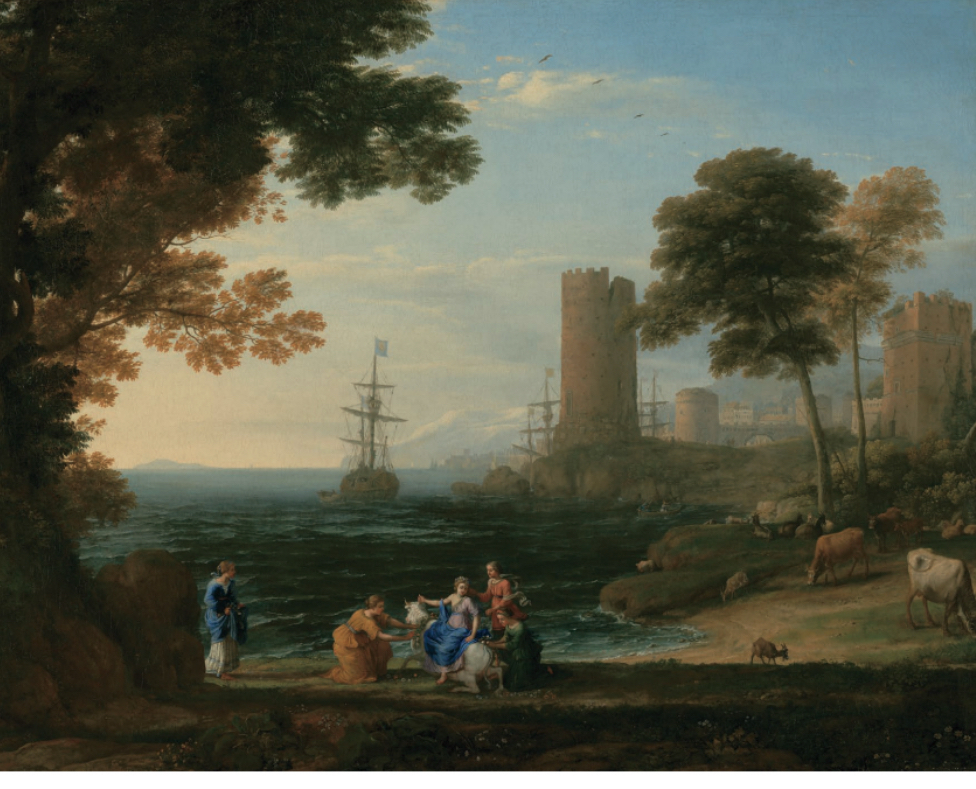

Baroque
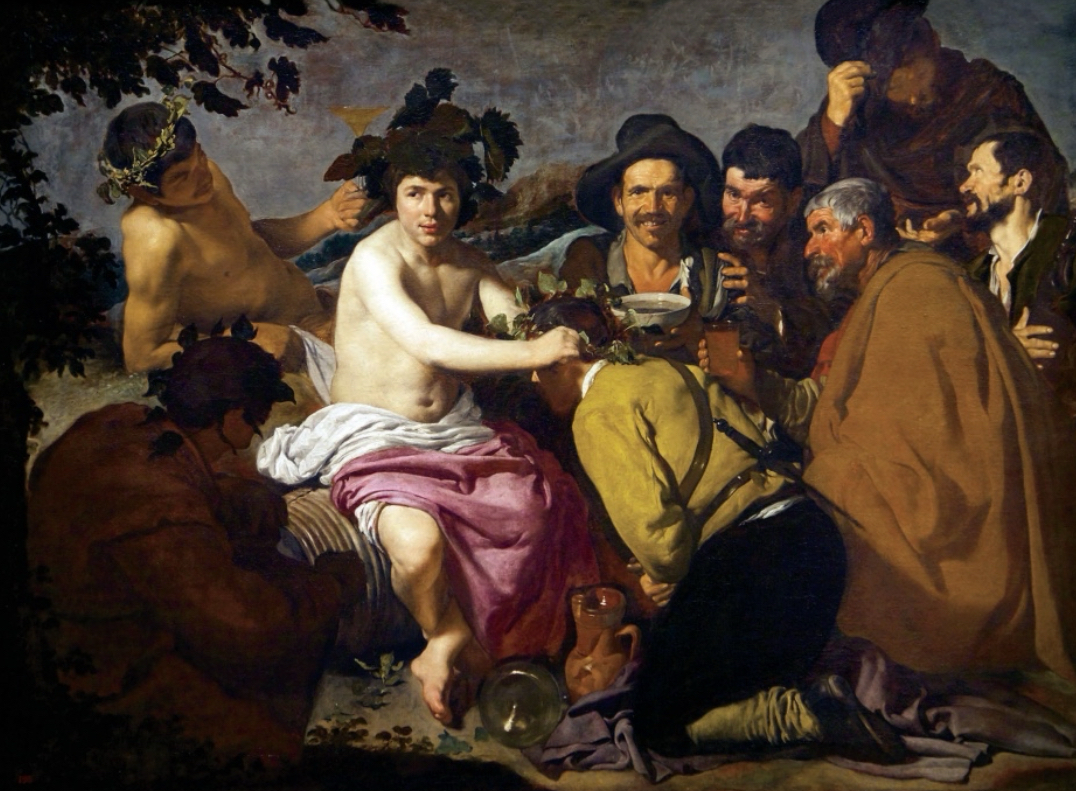

Baroque
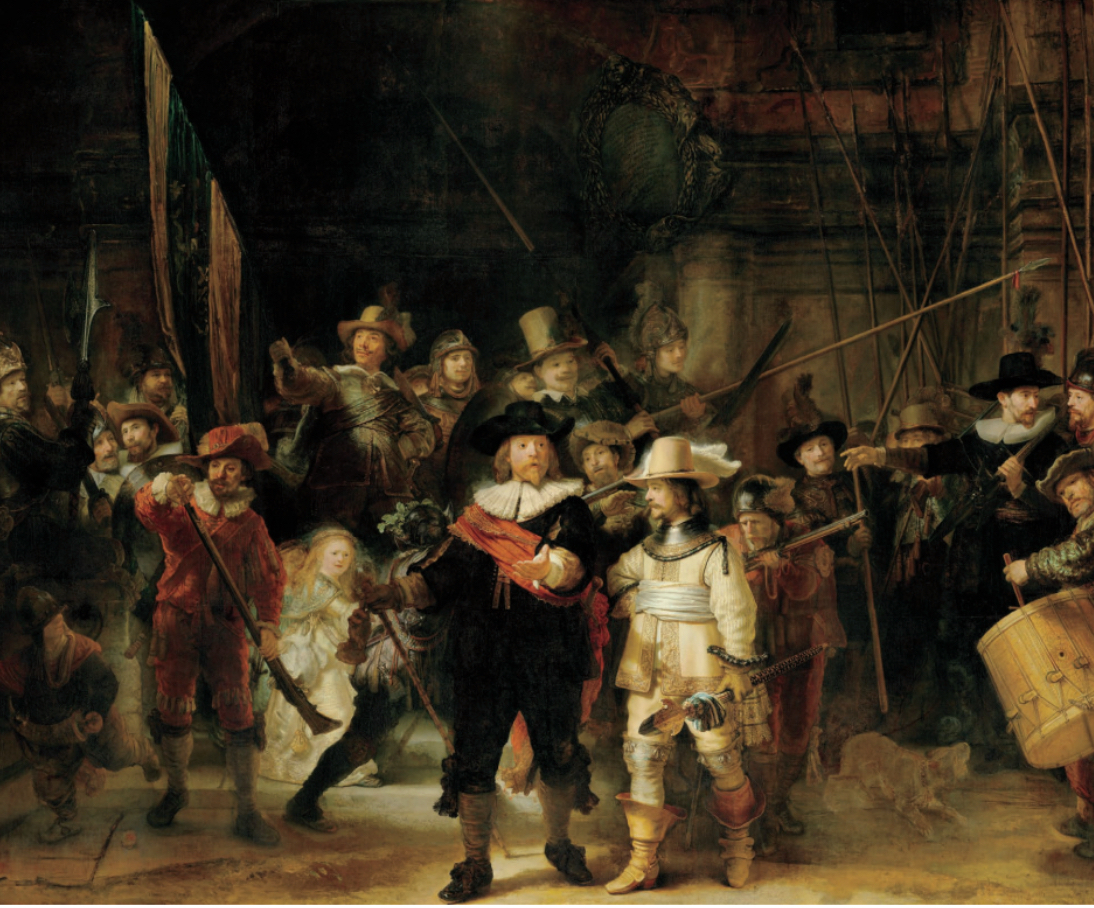

Baroque
