3. Cellular Neuroscience Neurons, their organelles, and glia
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What glial cells myelinate the axons in the central nervous system?
oligodendrocytes
What glial cells myelinate the axons in the peripheral nervous system?
schawnn cells
What are the 3 functions of myelin?
Provide multilayered, membranous sheath
Insulates axon as plastic on electrical wire
Allows electrical impulses to travel quickly down axon
Synapses require additional metabolic support by _____ which make close contact with synapses.
Astrocytes
Transmission electron microscopy has electron a resolution limit of ___ A
2.5
What kind of things do electron microscopes observe?
fine details, smaller organs and vesicles
Light microscopy has electron a wavelength of ___ A
350-700 nm
Transmitted light microscopy uses white(___ wavelength) light
mixed
In transmitted light microscopy, contrast derives from interaction of light through specimen: ___.
Diffraction
T/F Contrast of most cells is low without help
True
Collection of diffracted light may be enhanced by __ in microscope
optics
Visible light + cells = _____
change in amplitude or phase
The goal of _____ is to separate out phase-shifted light from unaffected light
phase microscopy
____ uses specific wavelength of light for illumination.
Fluorescence microscopy
T/F Fluorescence microscopy collects higher energy, smaller wavelength, light
False - lower energy, longer wavelength
Fluorescence Microscopy relies on special properties of ___.
Fluorosphores
Fluorescence Microscopy is used to to look at what? (4)
(1) Visualize cell morphology and (2) organelles (3) identify cell types and (4) organelles by markers
Excitation of flurorphores VS emission of flurorphores
Excitation- absorb light at a wavelength
Emission- emit light at a longer wavelength
Exictation and emission spectra of fluorphores are different and can be separated by _____.
optic filters
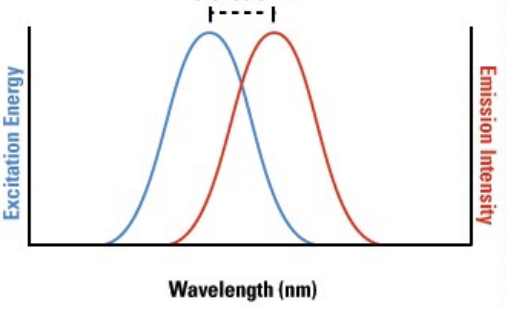
The difference between the excitation and emission of wavelengths is called the _____
Stokes Shif
What are the 3 advantages of fluorescence microscopy?
Low background
High signal
Can visualize specific cells, cell types, organelles, presence of proteins/macromolecules
Can you look at individual macromolecules by fluorescence microscopy?
No - light microscopy
What is an example of fluorescence microscopy?
Dye filled neuron
What are 2 kinds of organelle specific fluorescent dyes
DAPI Stain
MitoTracker Stain
What does DAPI stain bind to and what does it help us visualize?
Binds to dna, used to visualize the nucleus
Where does MitoTracker dye accumulate
Mitochondria
What kind of technique uses dye stained antibodies.
Immunofluorescence
Antibodies recognize specific dyed molecules that end up dying the whole antibody. These molecules are called ___.
Antigens
What is added to an antibody to dye it?
A fluorophore
What are the 2 types of immunofluorescence?
Direct
Indirect
What is the process of direct immunofluorescence?
A single primary antibody is directly conjugated to a fluorophore
What is the process of indirect immunofluroescence?
An unlabeled primary antibody binds to a target protein. A fluorophore-conjugated secondary antibody then binds to the primary antibody.
When is direct immunofluorescence needed?
It is needed when high specificity and low background are needed
When is indirect immunofluorescence needed?
When trying to detect low abundance proteins
Does direct or indirect immunofluorescence have higher amplification?
Indirect because multiple secondary antibodies bind to one primary.
What is immunofluorescence used for?
Identifying specific cells, specific organelles, and subcellular structures
With immunofluorescence astrocytes are labeled with what protein
GFAP
With immunofluorescence neurons are labeled with what protein
MAP2
Is DNA(nuclei), dyed blue also observed with immunofluorescence?
No, it’s dyed by fluorescent dye.
With immunofluorescence golgi apparatus are labeled with what protein
GM130
With immunofluorescence neurons are labeled with what protein?
MAP2
With immunofluorescence postsynaptic density are labeled with what protein?
PSD-95
With immunofluorescence presynaptic terminals are labeled with what protein?
synapsin
When you combine per and post synaptic markers(dye) you can identify what?
a synapse
Our ability to manipulate and introduce modified genes into organisms allows researchers to introduce fluorescence into living specimens, this is called _____.
Florescent tagging
What dye is used to look at the specimen: Aequoria Victoria (jellyfish)
GFP
What dye is used to look at the specimen: Discosoma (coral)
dsRed
What are the 2 steps to fluorescent tagging?
Create a ____ of a fluorescent protein and promoter, targeting sequence, and/or protein of interest.
Introduce ____ into cultured cells or whole organisms
fusion gene
modified gene
Using cell type specific ____ to label neuron subpopulations in mice
promoters
What are the 5 advantages/uses of fluorescent tagging?
Many colors of fluorescent proteins (FPs) exist now, from blue to far red
High levels of brightness and specificity
Observing cell/organelle morphology, protein distribution in living cells
Labeling cells based on genetic identity (using cell type specific promoters to drive FP expression)
Modified FPs can report on enzyme activity, protein-protein interactions, calcium dynamics, and much more.
Modified fluorescent proteins can report on what 4 things?
Enzyme activity
Protein-protein interactions
Calcium dynamics