Botany Final: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Practical 4/Final Exam
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Complete flowers are composed of 4 parts:
Sepals: protect flower buds
Petals: entice pollinator
Stamens: male reproductive structure
Carpel/Pistil: female reproductive structure


Which letter(s) show a perfect flower?
A, D

Which letter shows an incomplete flower?
A, B, C

Which letter points to the androecium?
A


Which letter points to the corolla?
B


Which letter points to the calyx?
C

Raspberries are (simple/complex) fruit because they come from one flower, while pineapples are a multiple fruit because they come from an ___.
simple; inflorescence (cluster of flowers)

Label all parts.
A: Pedicle
B: Sepal
C: Style
D: Stigma
E: Petal
F: Anther
G: Filament
H: Ovary
I: Ovule

Dicot and Monocot
Dicots: two cotyledons in the seed; flower parts are usually in multiples of 4 or 5
Monocot: one cotyledon in the seed; flower parts are typically in multiples of 3
Complete vs Incomplete Flowers
Complete: have pistil/carpel, stamens, petals, and sepals
Incomplete: if any one of these parts is missing

Perfect vs Imperfect Flowers
Perfect: has pistil/carpel, stamens, - may lack petals and sepals
Imperfect: either pistil or stamen absent

Imperfect Monoecious Flowers
male and female flowers on the same plant
Imperfect Dioecious Flowers
male and female flowers on different plants
Embryo Sac Formation Steps

Double Fertilization Steps
the fusion of the egg and sperm and the simultaneous fusion of a second sperm and two polar nuclei that ultimately results in the formation of the endosperm (the food-storage tissue) of the seed


Label the Parts of a Developing Ovule
Micropyle
Ovary Wall
Style
Megasporocyte
Funiculus
Integuments
Ovary
Nucellus


Male Gametophyte Development

Define Fruit
a ripened ovary containing seeds, together with any adjacent floral parts that may be fused with it at maturity
What are the three types of fruits?
Simple: derived from a single pistil of one flower
Aggregate: derived from more than one pistil on one flower
Multiple: derived from pistils form several flowers
Dry vs Fleshy Fruits
Dry: fruit that becomes hard and dry when the seeds are ready to shed (mature)
Fleshy: soft, sweet, odiferous, brightly colored
Berry
entire pericarp is fleshy, although skin is sometimes tough; may have one or many seeds
EX) tomatoes, bananas, grapes, amur honeysuckle
Drupe
fleshy fruit with hard inner layer surrounding the seed
EX) peach, plum, black cherry, hackberry, sassafras, flowering dogwood

Pepo
berry with a hard, thick rind
EX) watermelon, cucumber, squash
Hesperidium
berry with a leathery rind and parchment-like partitions between sections
EX) orange, lemon
Legume
elongated “bean pod“ splitting along two seams
EX) honey locust, black locust, redbud
Samara
small, winged, one-seeded fruit, usually produced in clusters
EX) maples, ash, elm

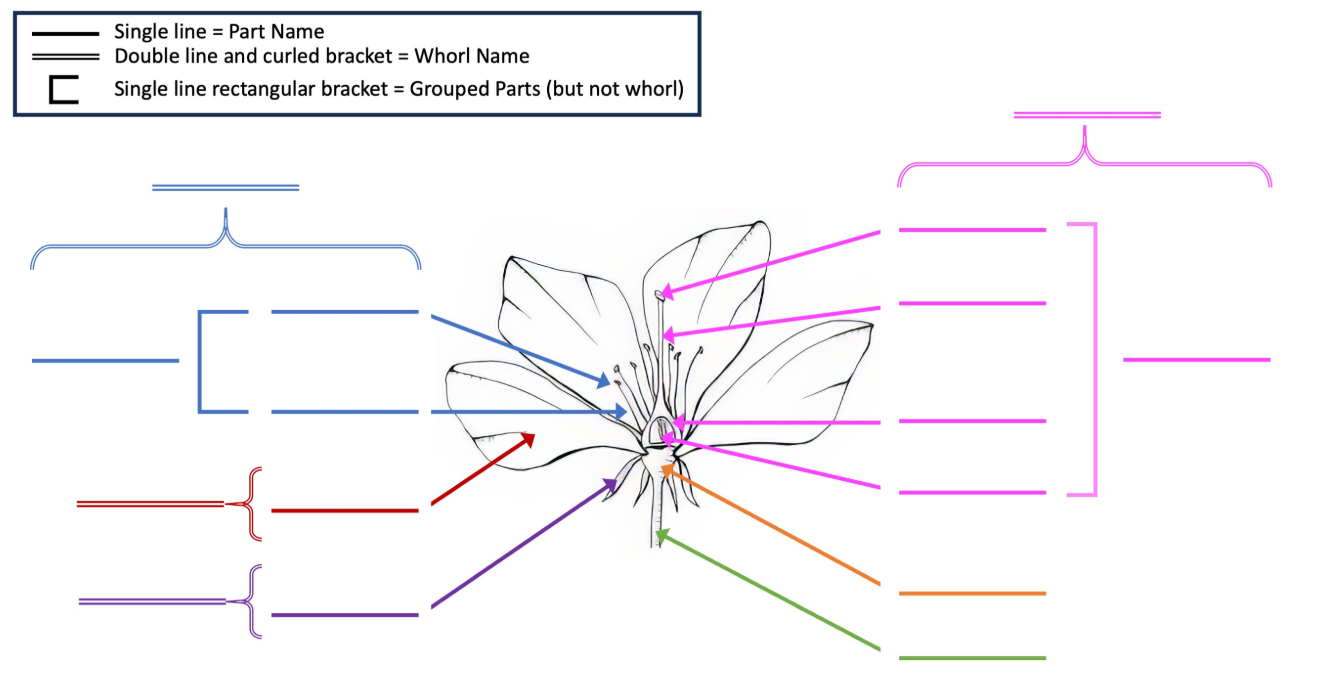
Label the diagram.
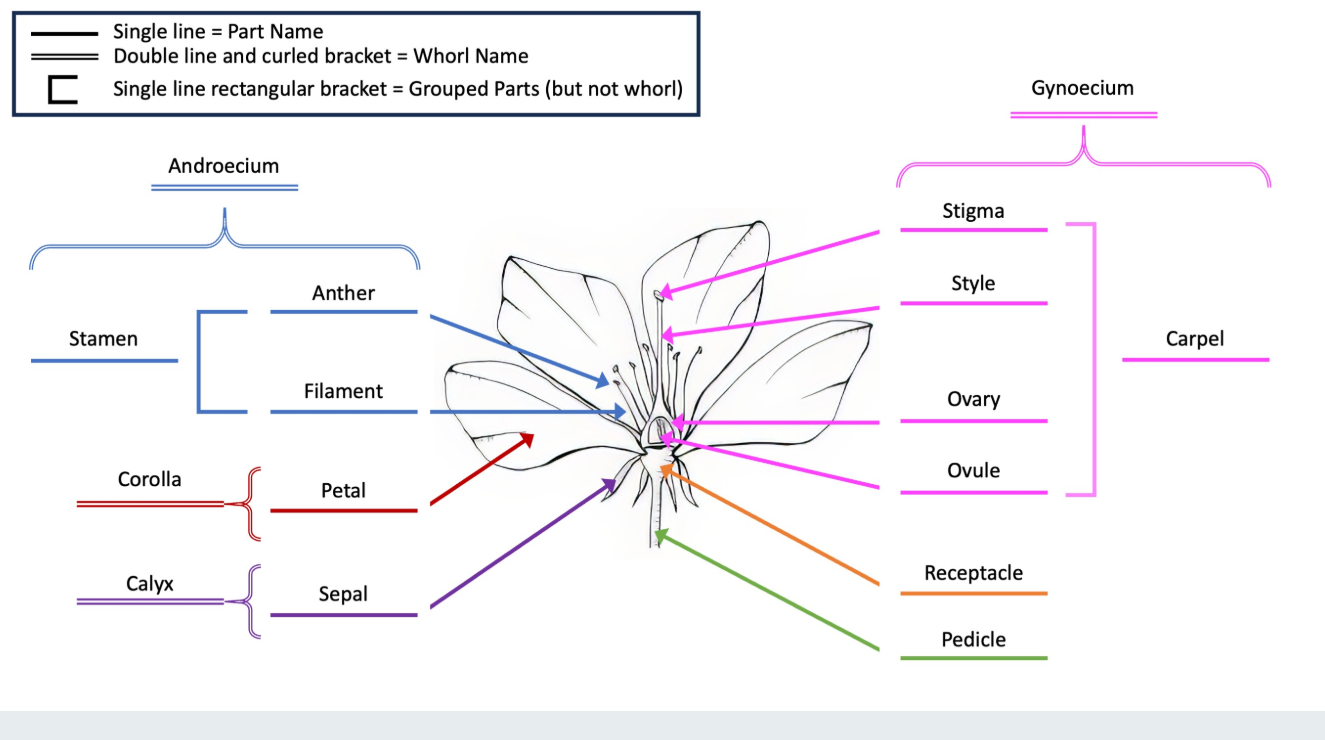
Floral Symmetry
Know all three terms for both types.
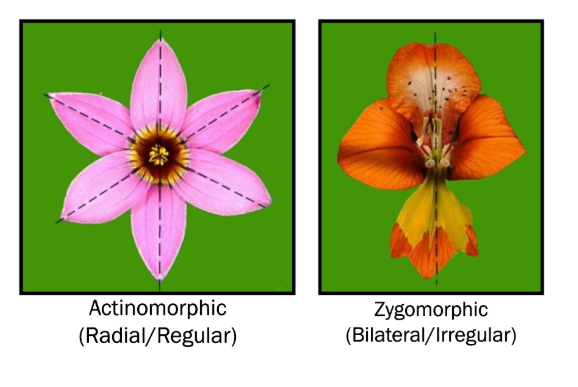
5 main differences between monocots and dicots
Monocot: ONE cotyledon
Seeds have one cotyledon
Flowers have 3 floral parts (or multiples thereof)
Leaves are narrow, with parallel veins
Vascular bundles small, and spread throughout stem
Fibrous roots
Dicot: TWO cotyledons
Seeds have two cotyledons
Flowers have 4 or 5 floral parts (or multiples thereof)
Leaves are oval or palmate, with net-like veins
Vascular bundles arranged in a ring around stem
Tap roots
Gymnosperm and Angiosperm: What is meant by 3 generations in a seed?
Seed coat (2n) - Origin: parent sporophyte integuments + remains of the megasporangium
Endosperm (3n) - Origin: parent gametophyte nutritive tissue for embryo when it germinates
Embryonic Sporophyte (2n): radicle (embryonic root), plumule (embryonic shoot apical meristem), and cotyledo
What is a seed and what does it contain?
A seed contains three main parts:
Embryo: The tiny plant that includes a root, stem, and leaves.
Endosperm: The nutritive tissue that provides food for the developing plant, often made up of starch, oil, and protein.
Seed Coat: The protective outer covering that safeguards the seed.
These components work together to support the seed's growth and development into a new plant.

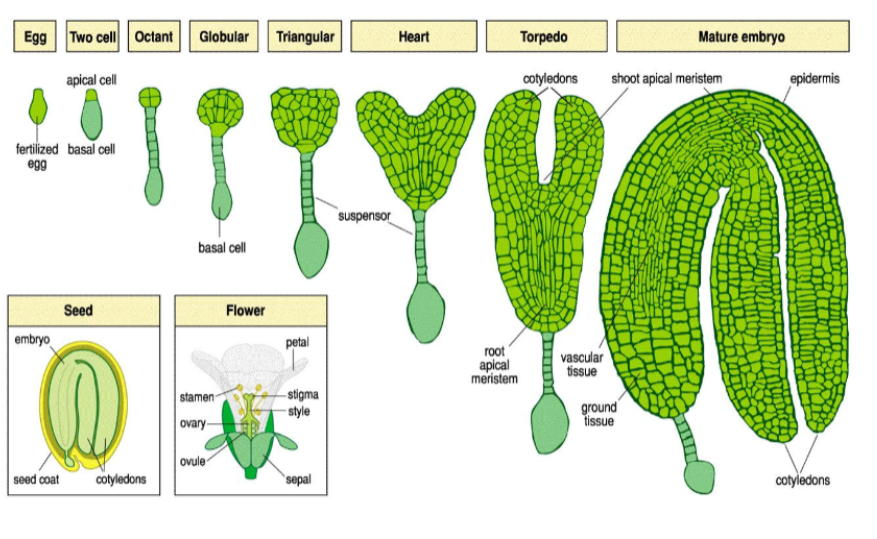
Stages of Embrogenesis
Two-Cell Stage:
After fertilization, the zygote undergoes asymmetric cell division, resulting in an upper apical cell and a lower basal cell. The basal cell develops into the suspensor, which connects the embryo to the maternal tissue and facilitates nutrient transfer.
Globular Stage:
The apical cell divides further, forming a spherical structure known as the globular stage. This is the first stage where the structure is recognized as an embryo proper
Torpedo Stage:
The cotyledons elongate, and the embryo takes on a torpedo shape. This stage is characterized by the differentiation of the shoot and root meristems, which will give rise to the plant's above-ground and below-ground structures.
Mature Stage:
The final stage of embryogenesis results in a fully developed embryo, which includes the shoot apical meristem, hypocotyl, root meristem, cotyledons, and root cap. At this point, the embryo is ready for dormancy and eventual germination when conditions are favorable.

What is this?
Ginkophyta/Ginko Biloba
Fan-shaped leaves
Dioecious reproductive system
The fruit resembles a fleshy, brownish-orange seed, which is actually a naked seed with a foul odor. Not a true fruit.
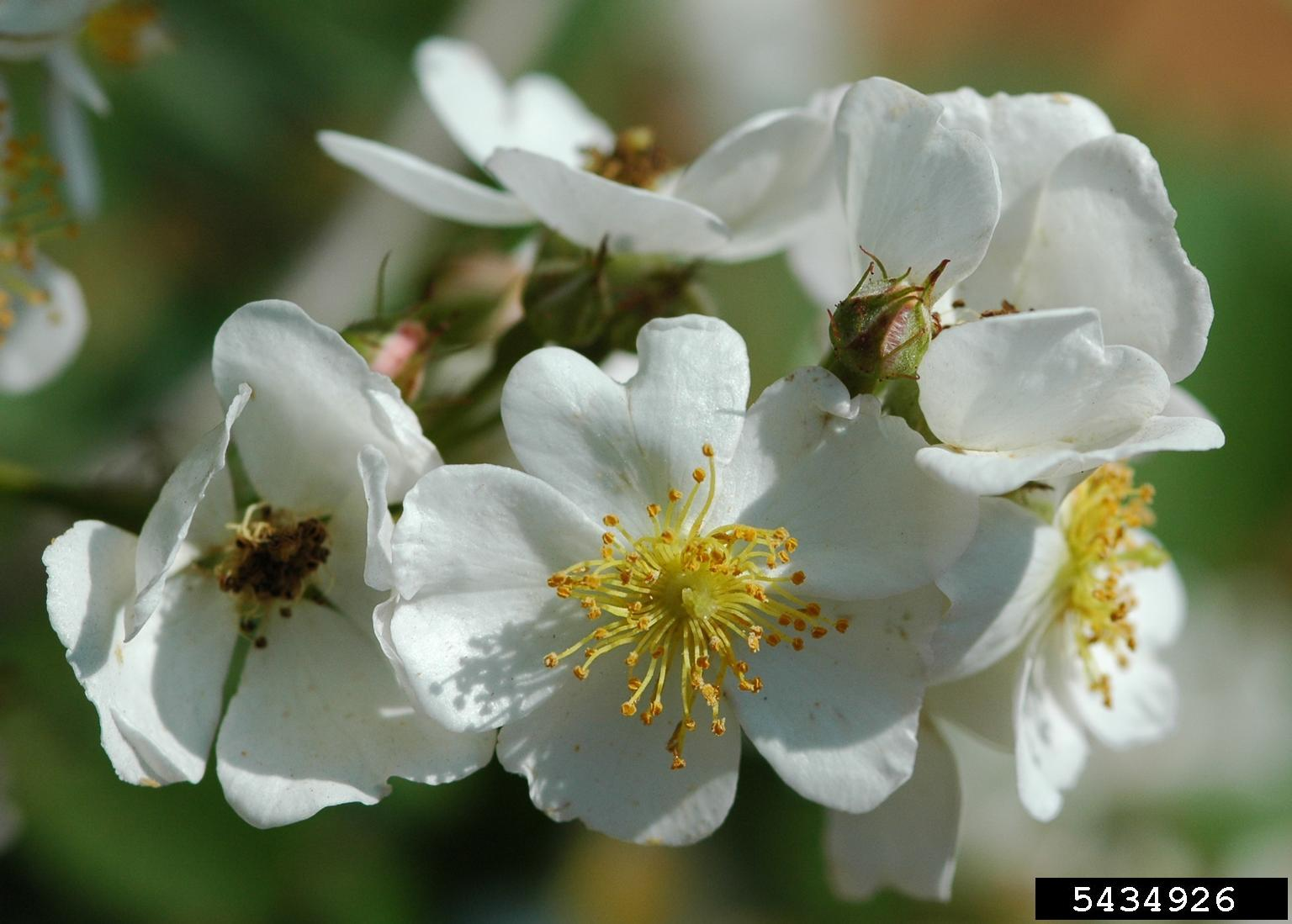

Is this an angiosperm or gymnosperm? Dicot or monocot?
Angiosperm, Dicot
image: multiflora rose
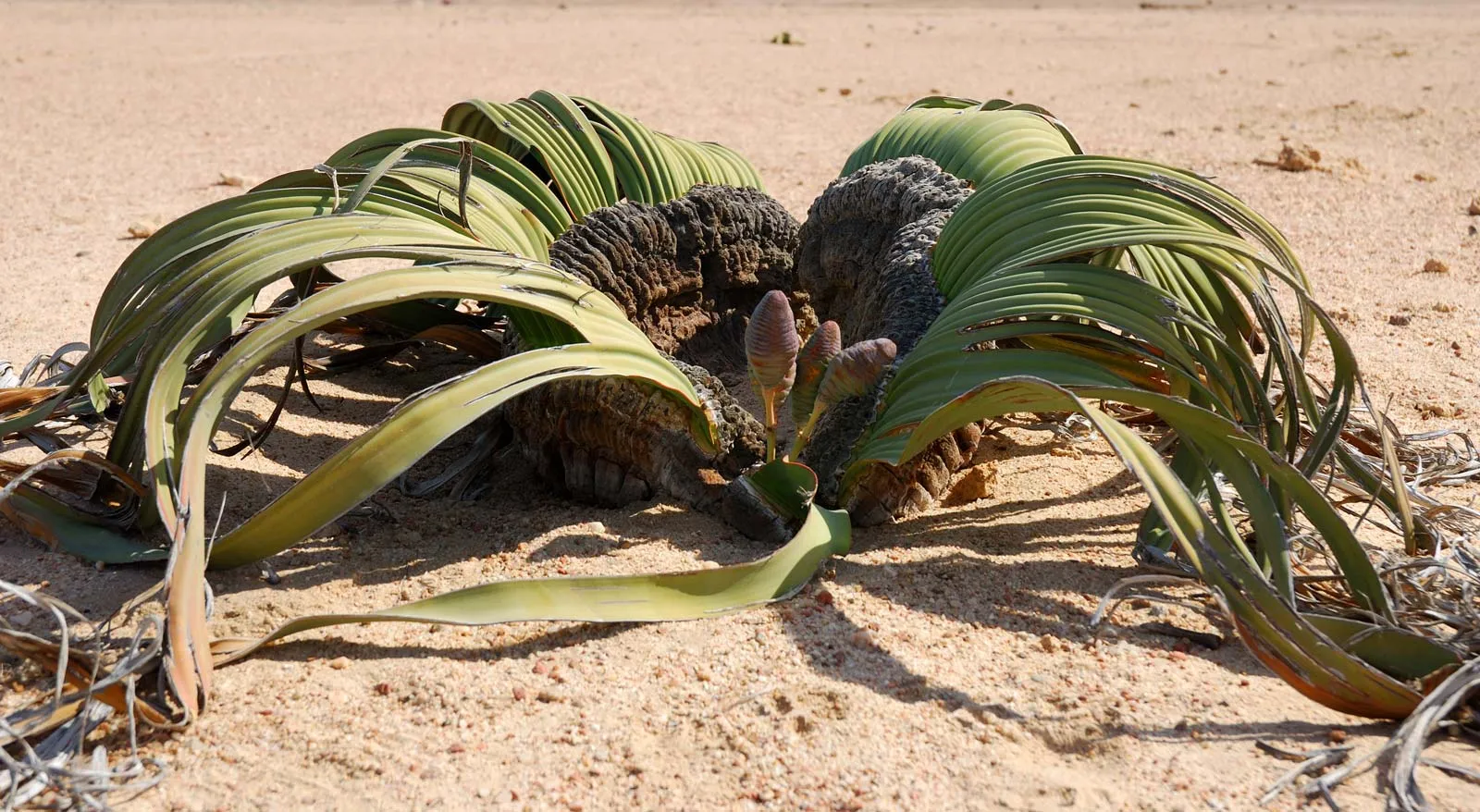

What is this?
Gnetophyte
Vascular plant
image: Welwitschia

What is this?
Pineophyta
Dicot
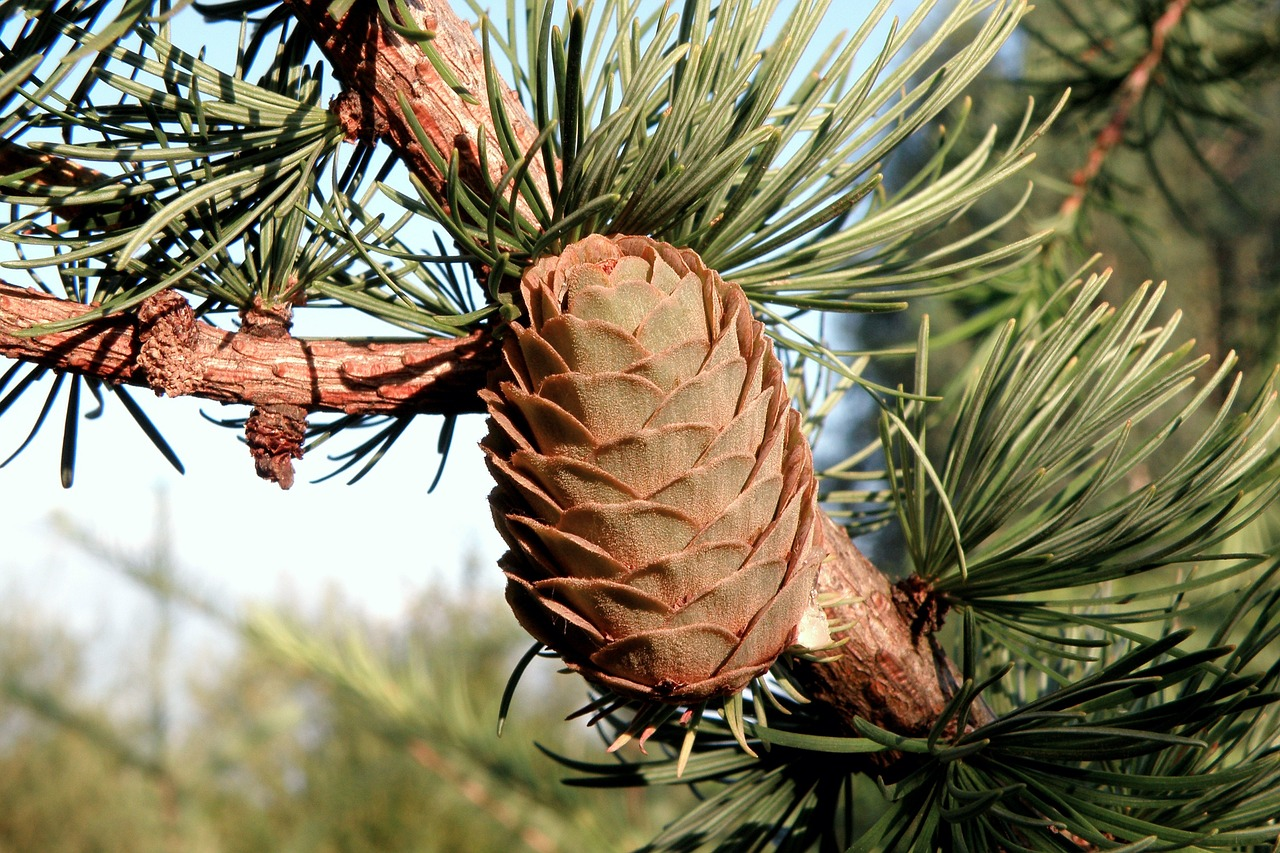

What is this?
Coniferophyta
gymnosperm
monoecious
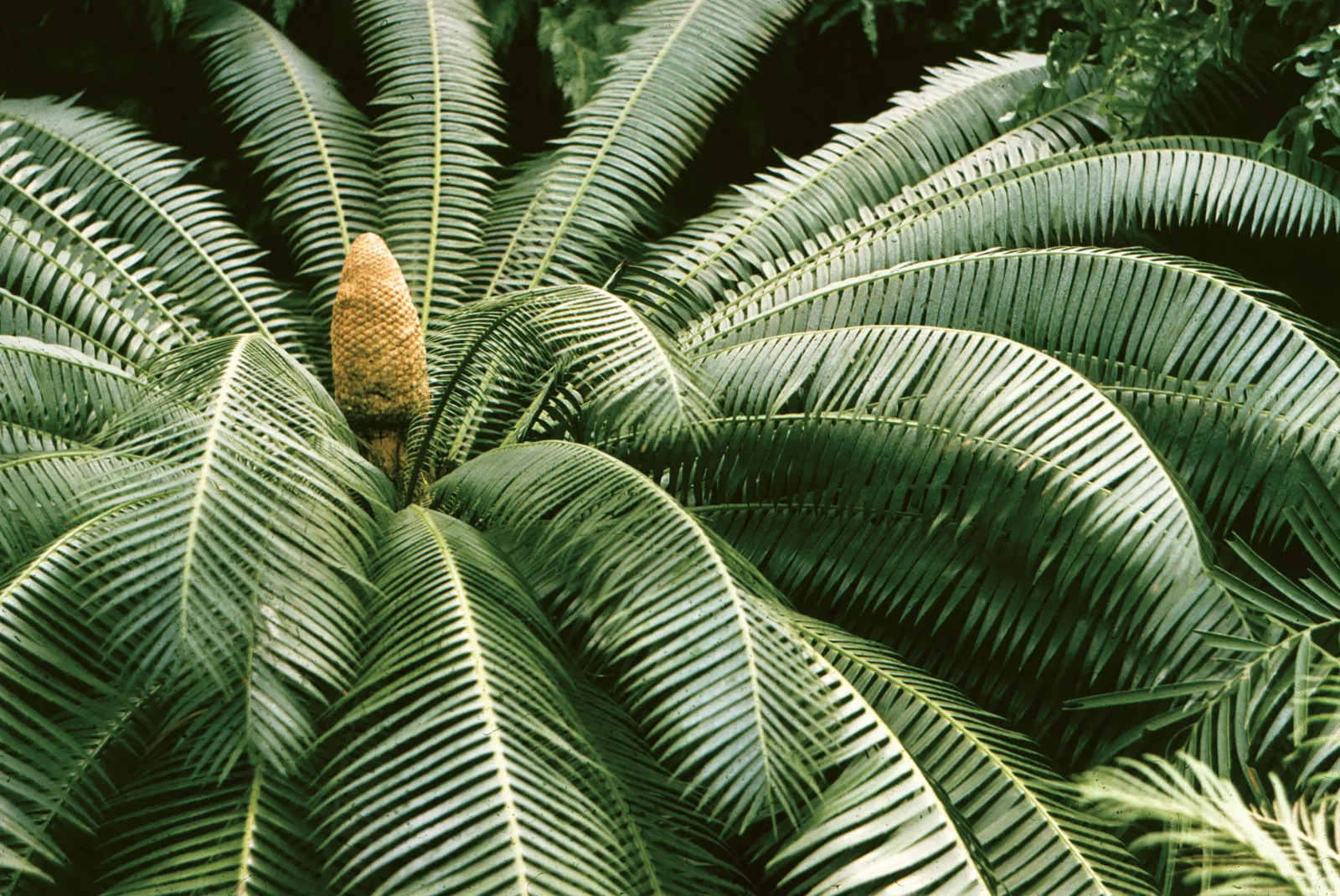

What is this?
Cycadophyta
gymnosperm
dioecious
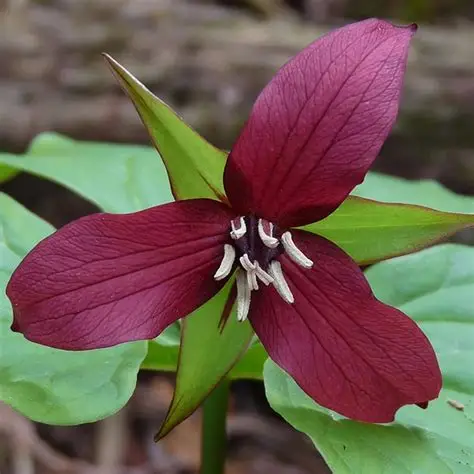

Is this Anthophyta Monocot or Eudicot?
Anthophyta Monocot
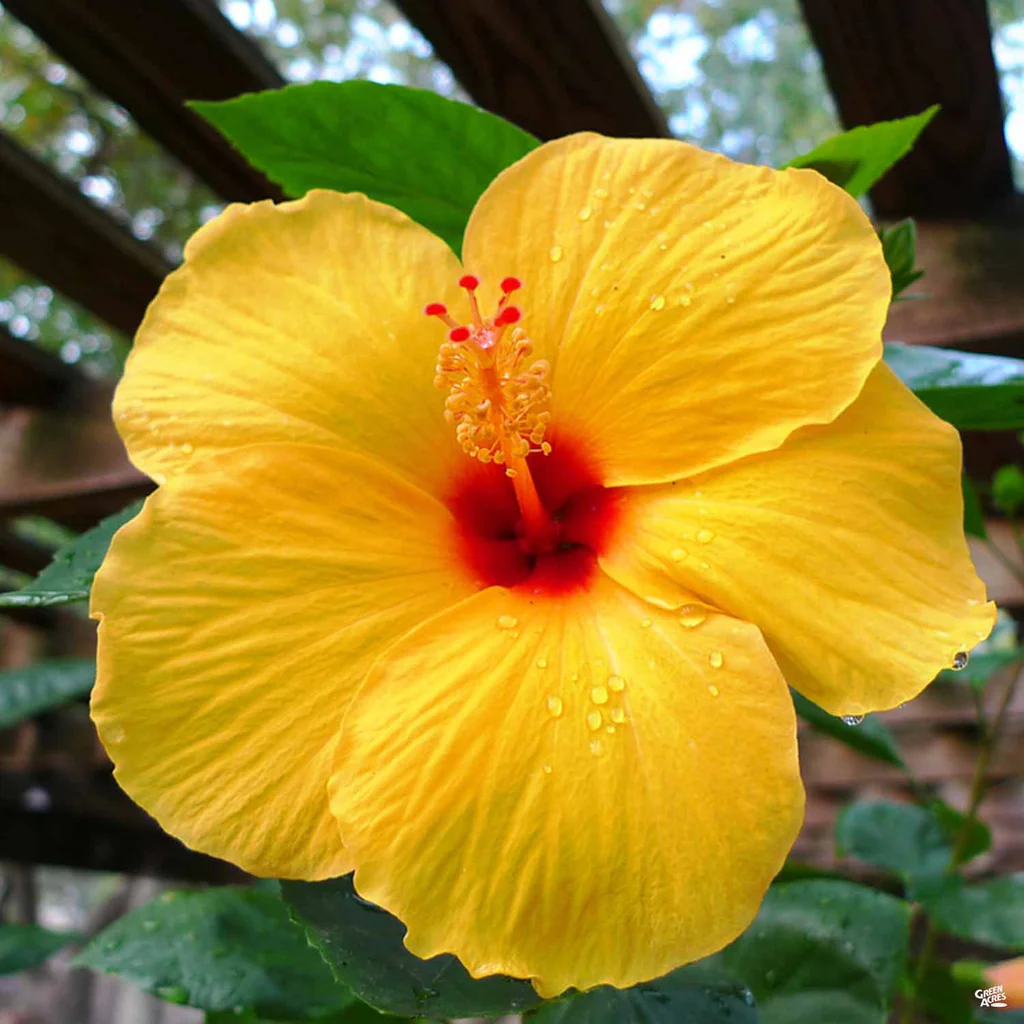

Is this Anthophyta Monocot or Eudicot?
Anthophyta Eudicot
What is the function of Petals (Corolla)?
Petals are usually the most noticeable part of a flower and serve a vital function in attracting pollinators, such as bees, butterflies, and birds.
What is the function of Sepals?
These are small, modified leaves that enclose and protect the flower bud before it opens. They are often green, but in some flowers, they are brightly colored and resemble the petals.
What is the Receptacle?
This is the part of the flower where the flower attaches to the pedicle/stalk.
What is the function of Anther?
This part of the stamen produces and contains pollen. The anther is usually at the end of a thin tube-like structure called the filament.
What is the function of Filament?
The filament is a stalk that holds up the anther, making the pollen accessible to pollinators or wind.
What is the function of Stigma?
This is the part of the pistil that receives pollen. It is often sticky or feathery for trapping and holding onto the pollen grains.
What is the function of Style?
This is the long tube-like structure that connects the stigma and the ovary. Once a pollen grain lands on the stigma, it grows a pollen tube down the style to reach the ovary and accomplish fertilization.
What is the function of the Ovary?
This is the part of the pistil that holds the ovule(s). It is within the ovary that fertilization occurs and seeds develop.
What is the function of the Ovule?
The ovule is the potential seed within the ovary. Each ovule contains an egg cell. When an ovule is fertilized by a sperm cell from a pollen grain, it develops into a seed.