Dental Terminology
1/239
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
240 Terms
Dentistry
profession dealing with the diagnosis, prevention and treatment of diseases, disorders and conditions of the teeth, oral tissues and adjacent structures.
Careers in dentistry offer job security, satisfaction and opportunities, such as using advanced technology.
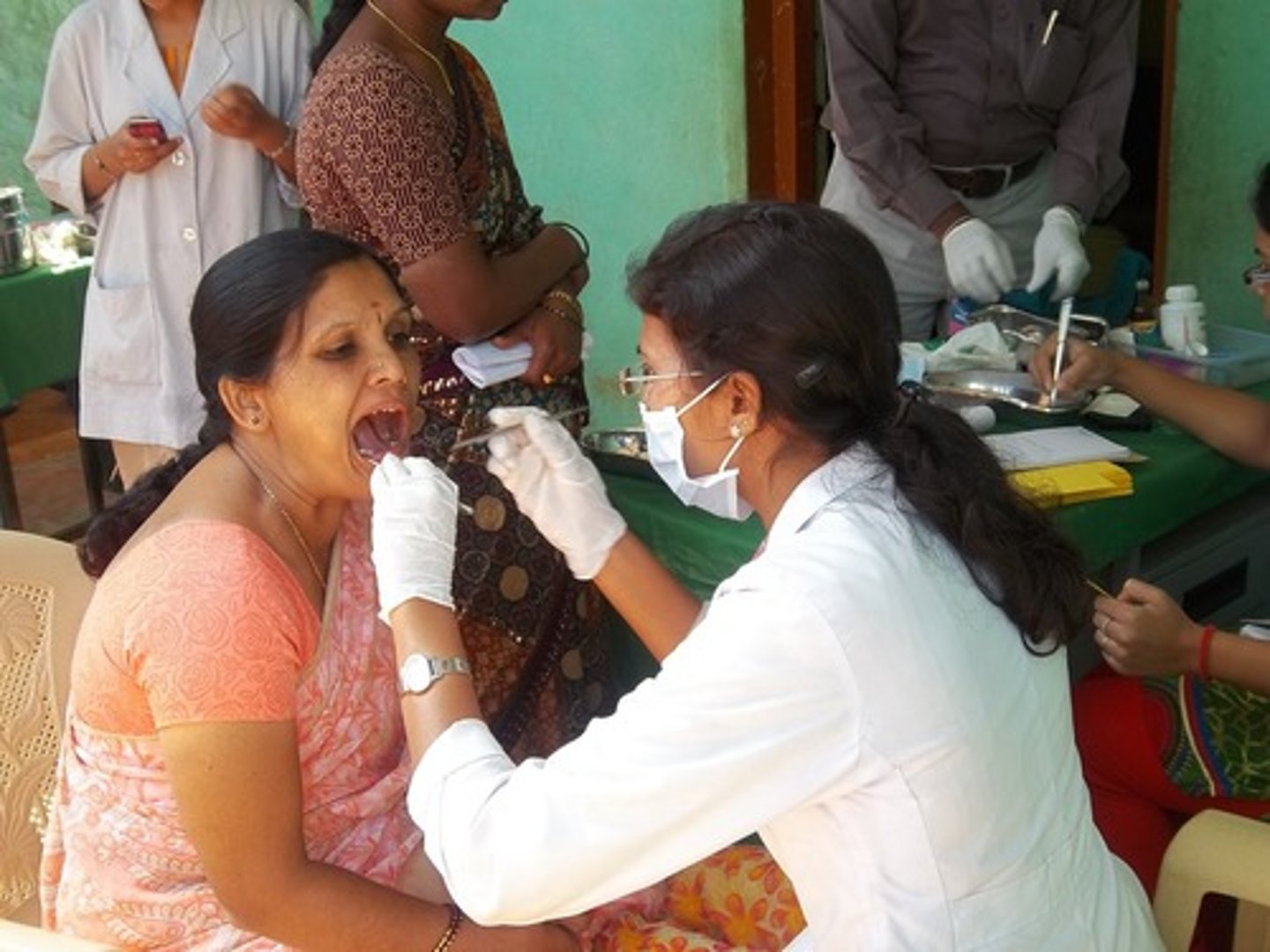
Dental Assistant
person working directly with the dentist and increasing their efficiency; a diverse job requiring dental knowledge, clinical skills and interpersonal skills.
May expose/process radiographs, provide instructions on oral care for clients, make impressions of clients' teeth for study models, assist the dentist in procedures, control dental materials, make dental appliances, develop infection control protocol, prepare equipment, record client information and treatment and perform office management tasks.
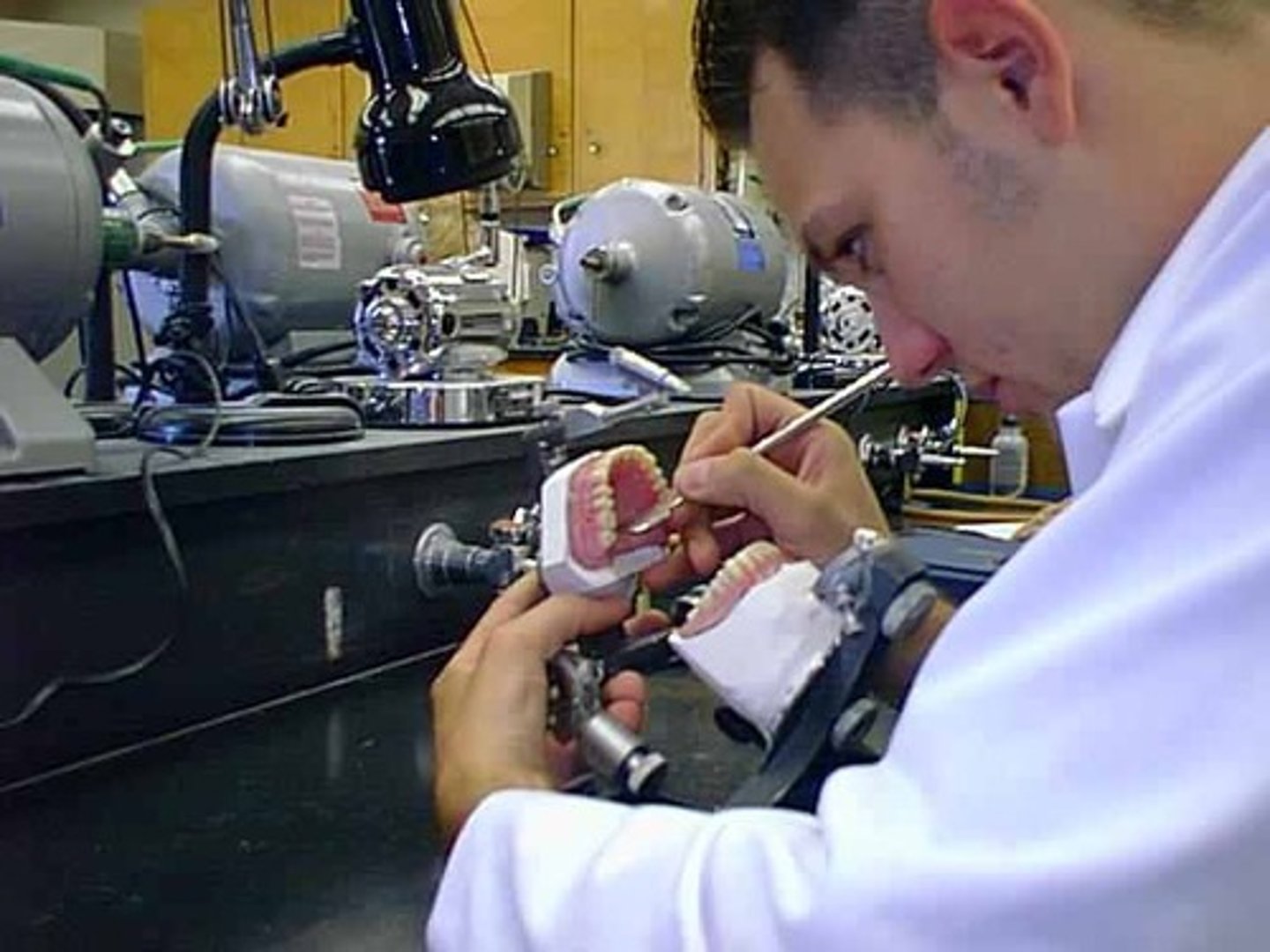
Dental Laboratory Technician
seldom work with clients, but creates dental prostheses (replace missing teeth) and dental appliances.
Needs artistic, hand and vision skills.
Fabricates using waxes, plastics, metals, porcelains and composites (made of many materials).
May create dentures, crowns, bridges, veneers, and appliances/splints.
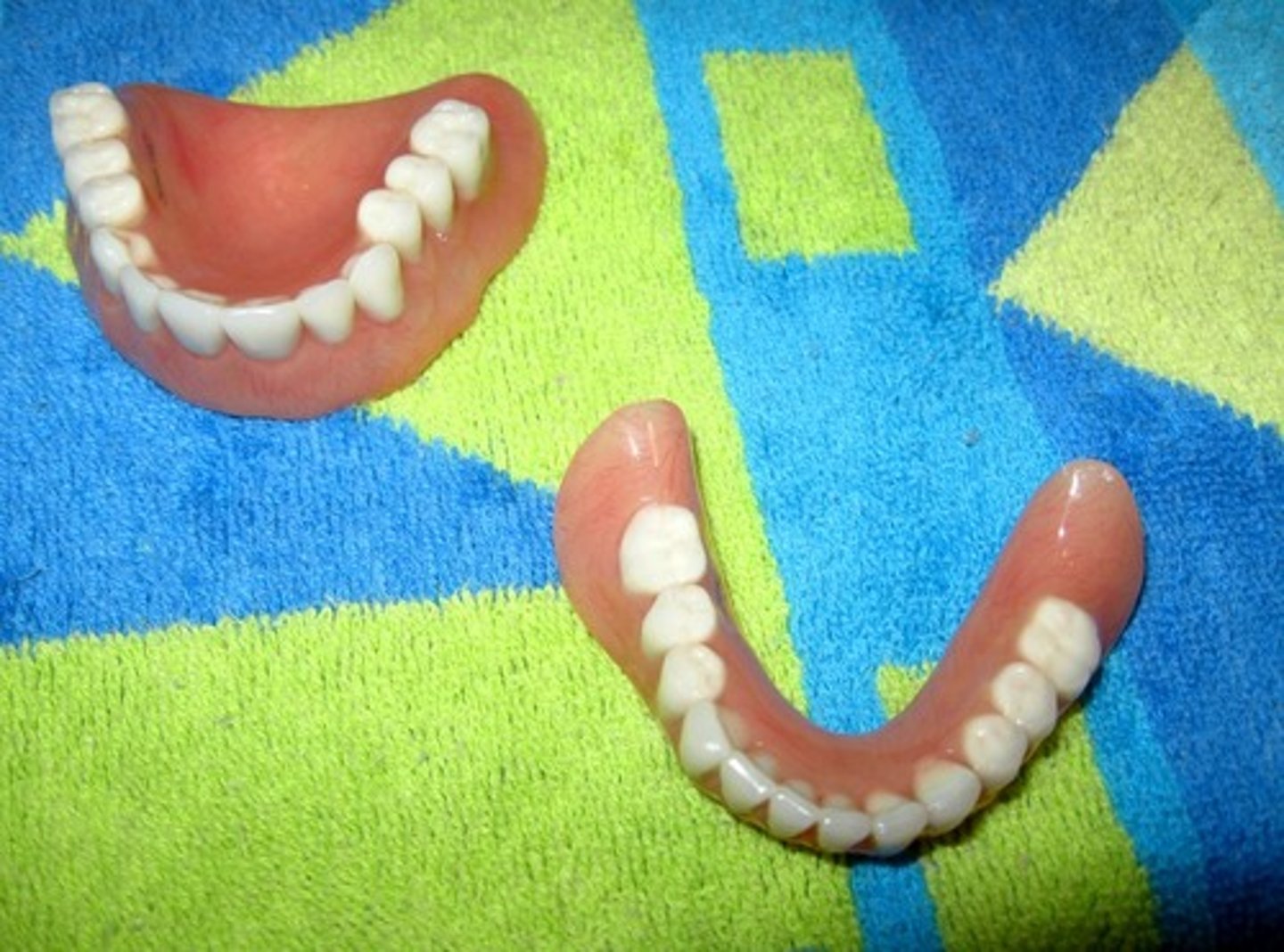
Dentures
a removable plate holding one or more artificial teeth.
Veneers
layer of material over a tooth to improve the appearance or protect the tooth from damage.
The two main types of material used to fabricate a veneer: composite and porcelain.
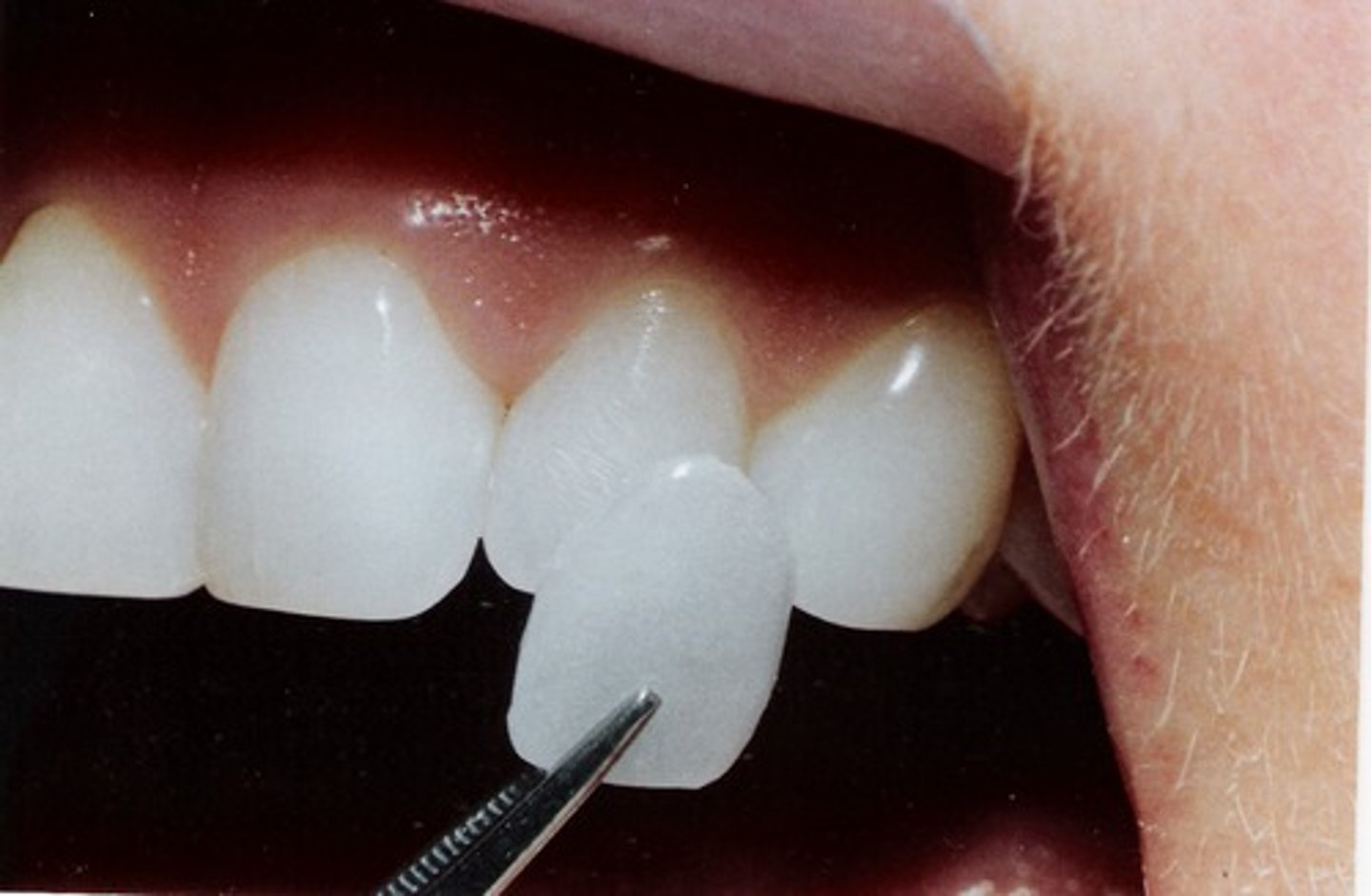
Splint
device fastening teeth in the same dental arch for support and immobilizing movement. May connect natural teeth to a prosthesis (artificial crown...)
Crown (Cr)
a prosthesis restoring the function of the natural crown of the tooth.
The natural crown of the tooth is the portion of the tooth normally visible in the oral cavity.
Bridge
fixed prosthesis replacing a missing tooth/teeth.
Dental Hygienist
provide oral hygiene care and dental health education to the client.
Need good communication skills, dental knowledge and clinical skills.
May access and chart oral conditions, review the client's health history, expose/process dental radiographs, instruct clients in hygiene techniques, provide nutritional dental counseling, remove calculus and plaque and apply preventive materials (fluoride, sealants)
Calculus
rough, hardened dental plaque combined with minerals in saliva.
Cannot be removed with regular brushing and flossing; must be removed by dentist.
Plaque
soft, sticky deposit on tooth's surface; consists of saliva, bacteria, food, tooth paste deposit...
Dentist
must have scientific ability, work well with others and enjoy helping others.
After completing dental schools, dentists receive a doctor of dental surgery (DDS) degree or doctor of dental medicine (DMD) degree.
May diagnose/treat diseases of the teeth and its tissues, tongue, lips and jaws, restore decayed teeth, replace missing teeth with artificial materials, provide cosmetic procedures, perform corrective surgery on the jaws and tissues, straighten teeth and perform oral hygiene procedures with instructions.
Dental Public Health
a specialty area; dental health prevention, education and treatment programs at the community level.
Endodontics
a specialty area; treatment of diseases of the pulp and periapical tissues.
Pulp
tooth tissue; the innermost tissue of the tooth; composed of blood vessels, nerves, lymphatics and connective tissue.
Is very large in newly erupted teeth, so it is more sensitive to thermal changes.
As the tooth ages, the amount of dentin increases and the pulp becomes smaller.
Pulp Chamber
the pulp within the crown of the tooth.
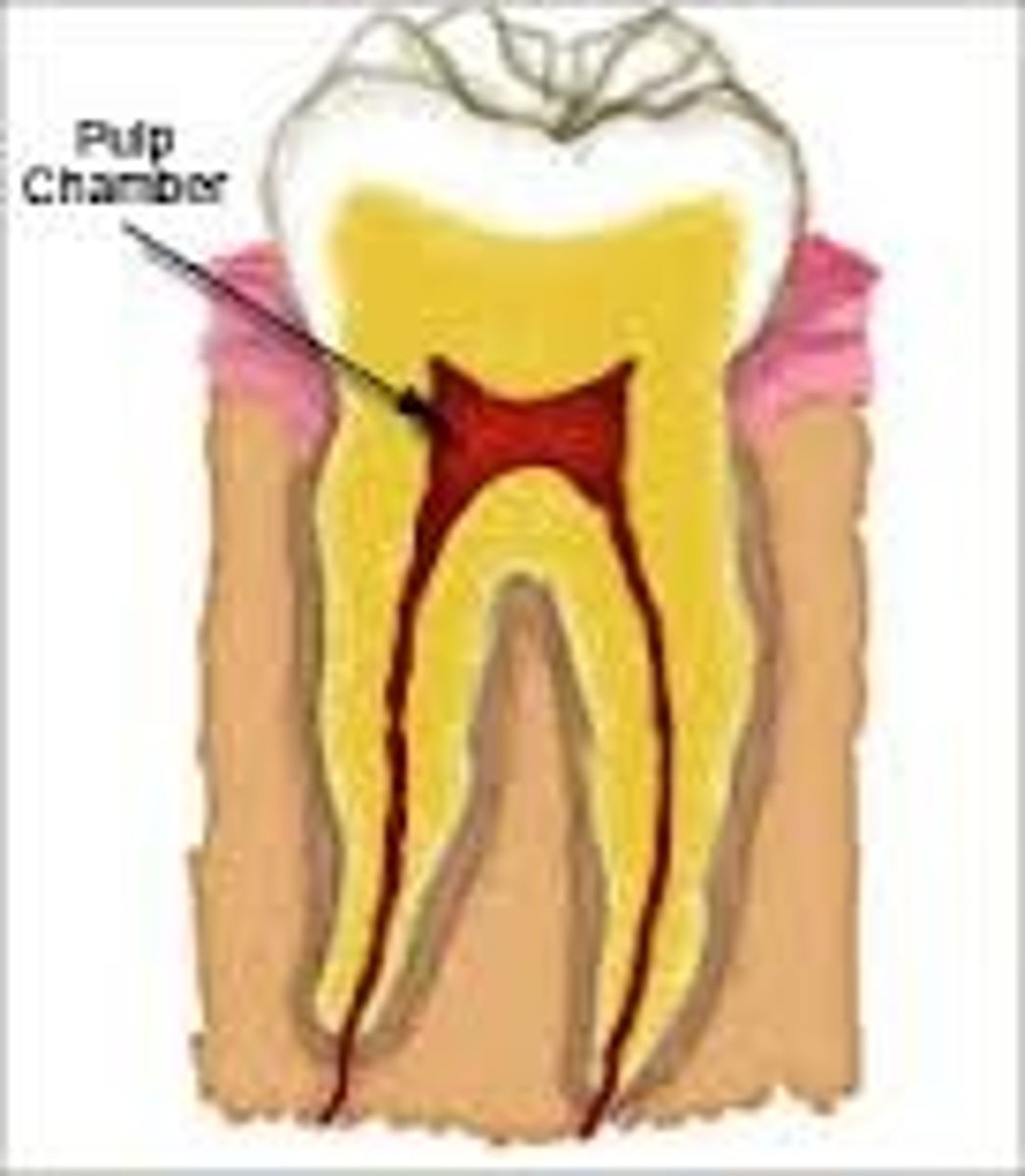
Pulp Canal
pulp in the roots of the tooth.
Usually corresponds with the number of roots of the tooth.
Periapical Tissues
surrounds the apex of the root of the tooth.
Apex
at the end of the root located farthest away from the crown.
Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology
a specialty area; research, identification and management of diseases affecting the oral structures.
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
a specialty area; surgical treatment of diseases, injuries and defects of the oral and maxillofacial region.
Maxillofacial Region
area around the jaws and face.
Periodontal Diseases
diseases of the supporting and surrounding tissues of the teeth; gingiva, periodontal ligament and alveolar bone.
It's first stage is gingivitis, than periodontitis.
Signs include; gingival swelling, redness, bleeding, recession, loss of teeth and bad breath/taste
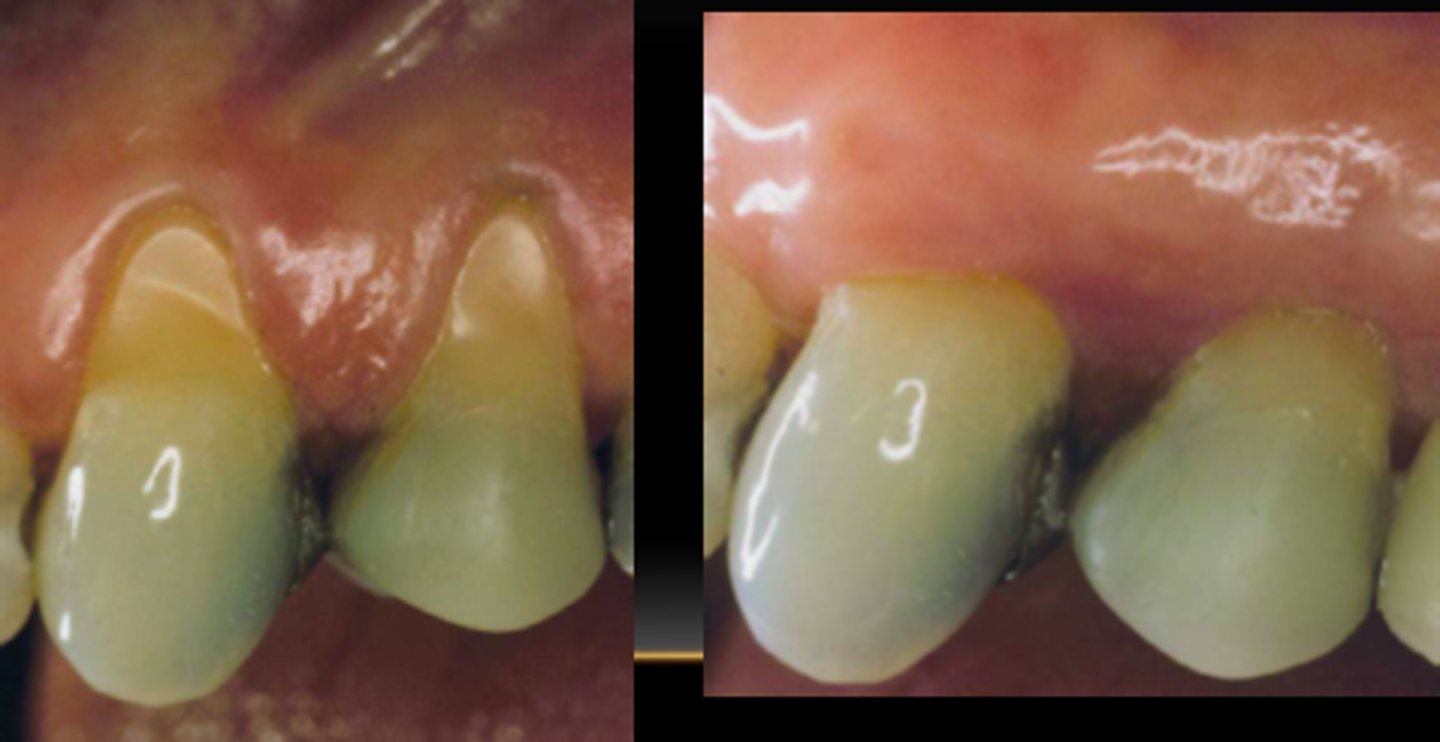
Gingival Recession
the drawing back of the gingiva from the neck of the teeth, exposing the root surfaces.
Sign of periodontal diseases
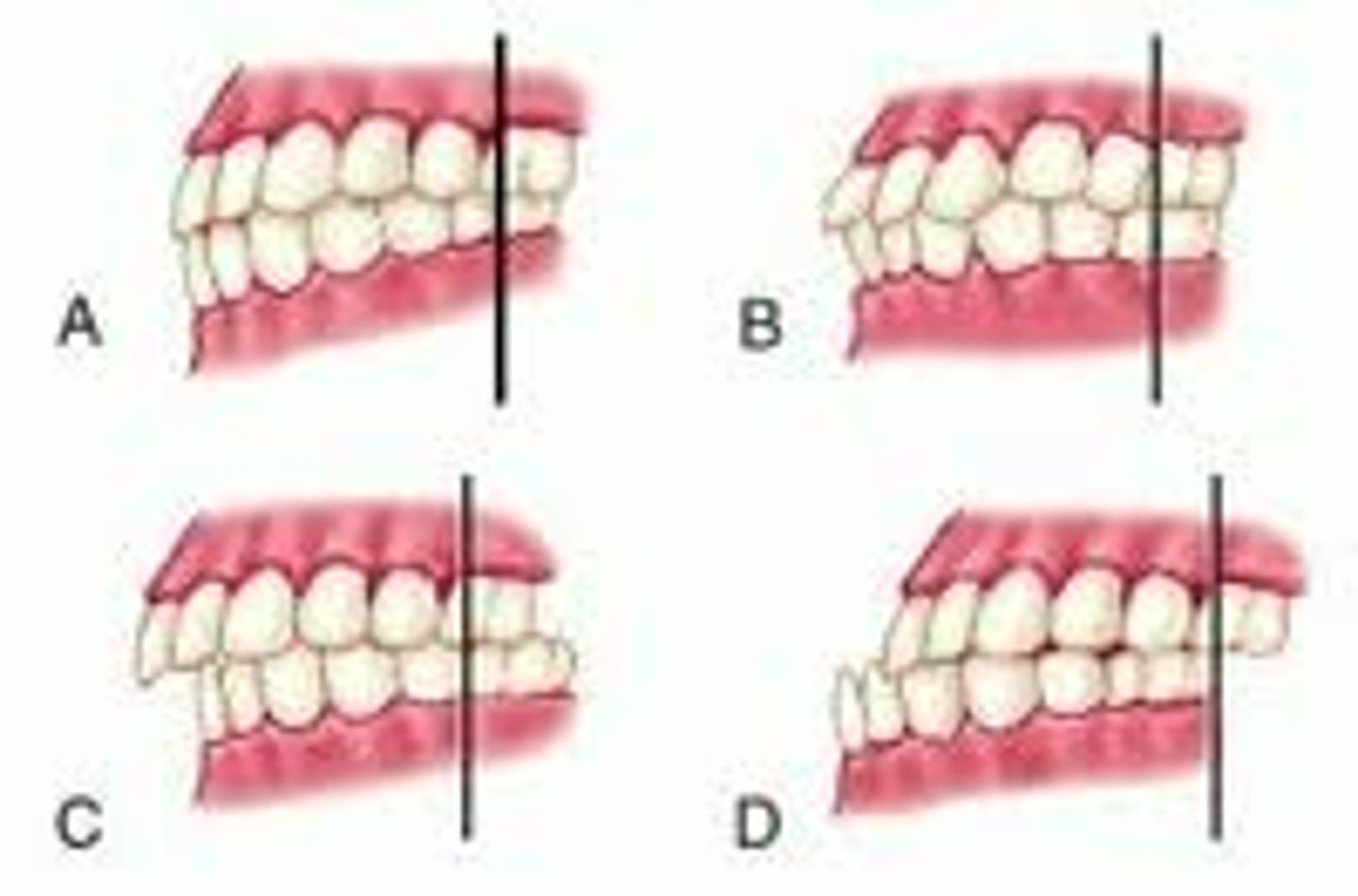
Malocclusions
abnormal relationship of the teeth when biting or closing.
Pediatric Dentistry
comprehensive dental care of infants and children through adolescence (puberty), including clients who have special needs.

Periodontics
prevention and treatment of periodontal diseases.
Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics
correction of tooth alignment and malocclusions.
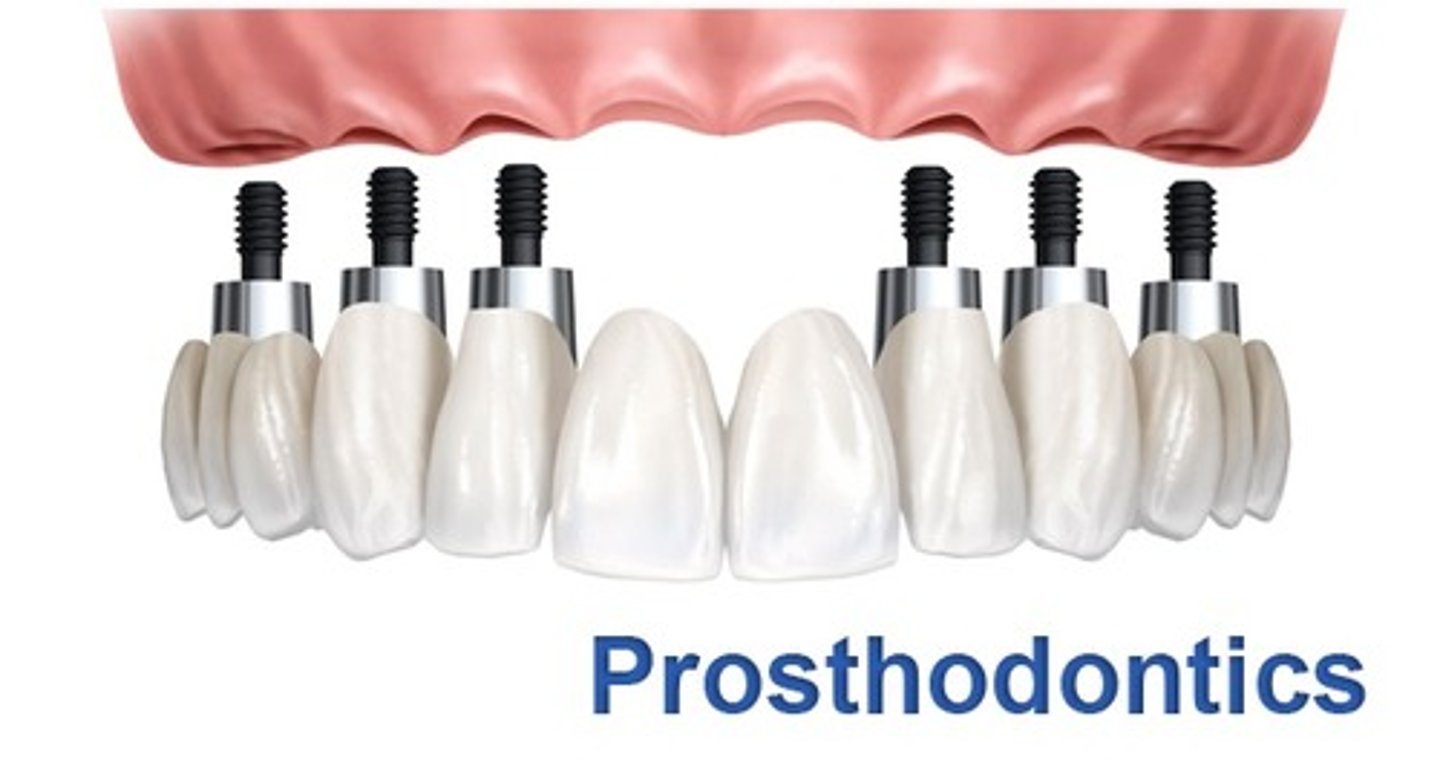
Prosthodontics
replacement of missing teeth and oral structures with artificial substitutes.
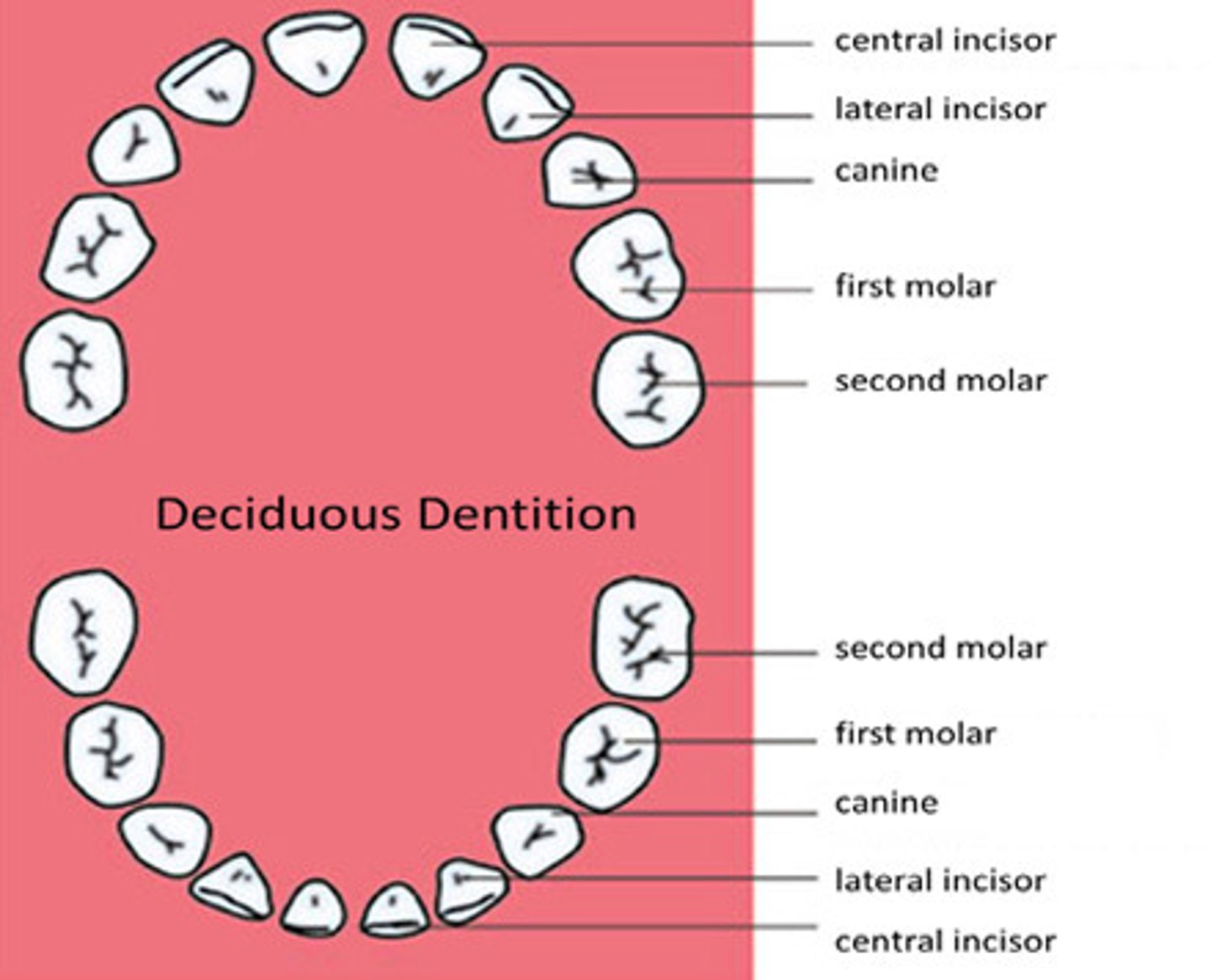
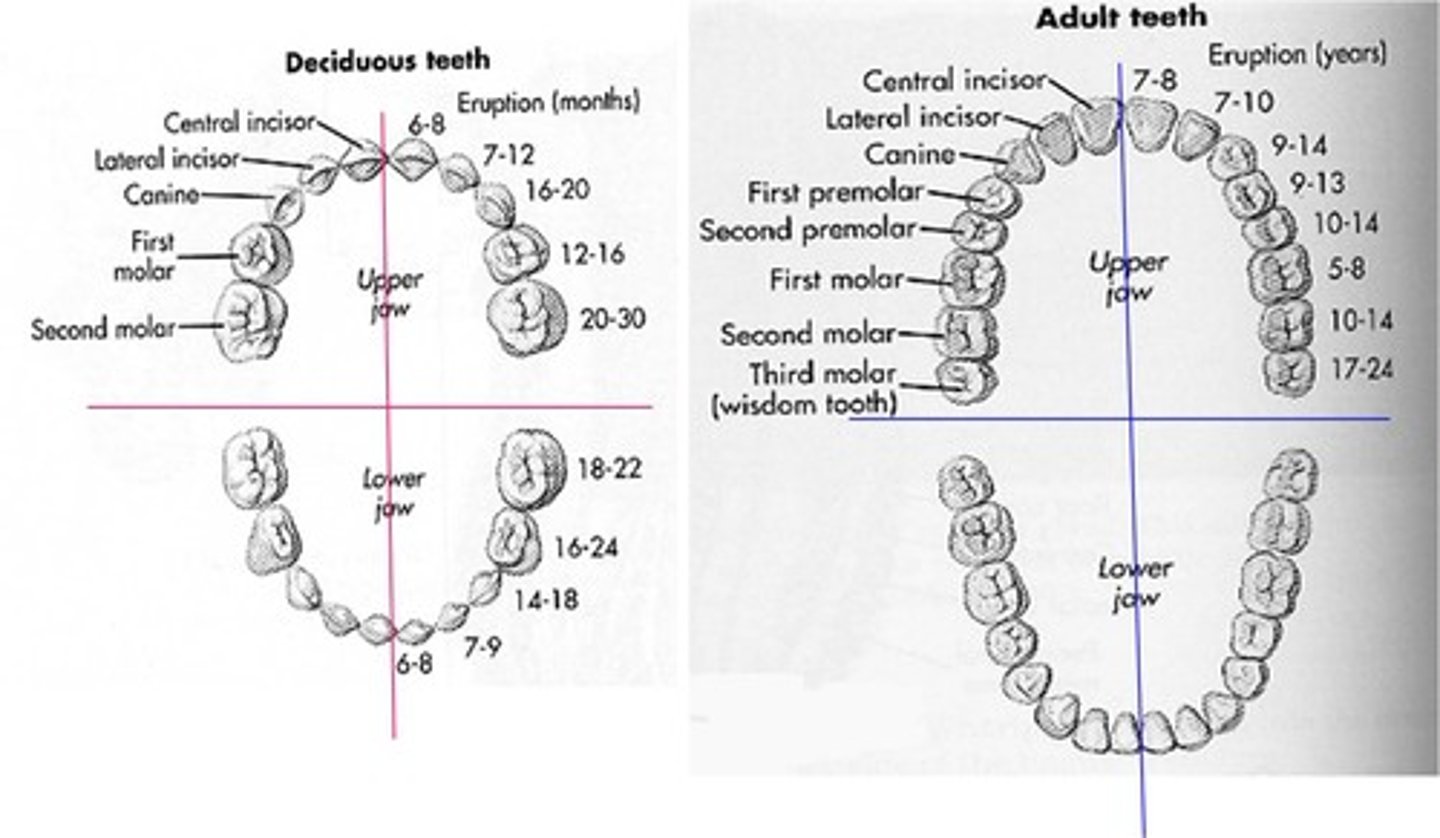
Deciduous Dentition
primary teeth; first set of teeth- 20.
First teeth erupt at about six months and all twenty teeth have erupted by about two and a half years of age.
Ten teeth in the maxilla, ten in the mandible
Maxillary Arch (Maxilla)
upper jawbone.
Mandibular Arch (Mandible)
lower jawbone.
Midsagittal Plane
midline dividing the arches and separating the oral cavity into quadrants.
Permanent Dentition
permanent teeth replacing the primary teeth that fall out from ages 6-12.
After the primary teeth resorb, the permanent molars erupt distal to the primary molars and therefore, do not replace the primary teeth. As the child grows, the jaws become longer and larger, creating more space for additional teeth.
Consists of 32 teeth; begins to erupt at age six. With the exception of third molars, all permanent teeth should have erupted by ages 12-14.
Resorb
dissolve. In this case, the primary teeth are resorbing from the pressure of the developing permanent teeth located directly below in the jawbone.
Mixed Dentition Period
when both primary and permanent teeth are present.
Distal Incisal (DI) Surface
surface of the tooth farthest from the midline.
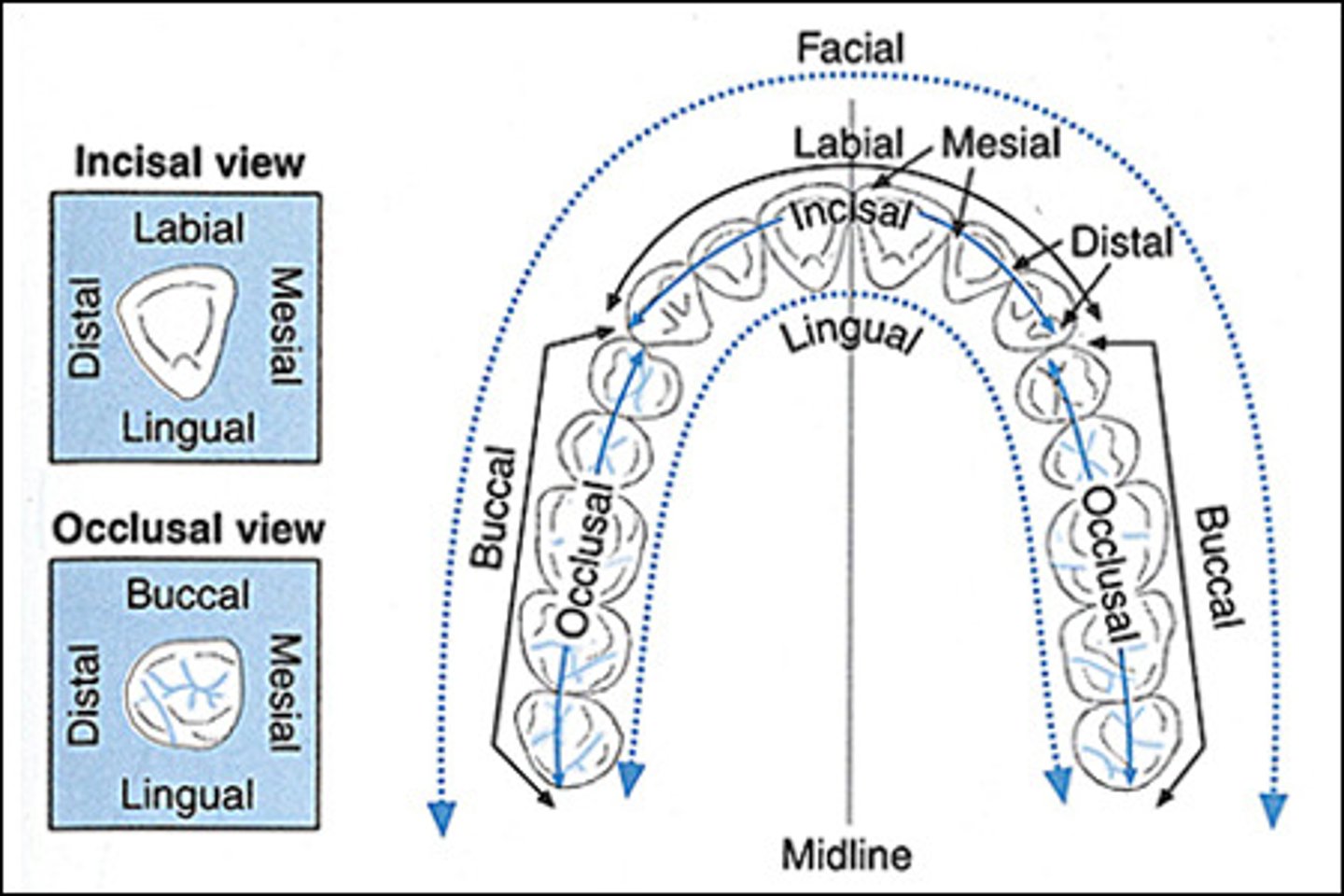
Anterior
teeth in the front portion of the mouth covered by the lips.
Posterior
teeth in the back portion of the mouth covered by the cheeks.
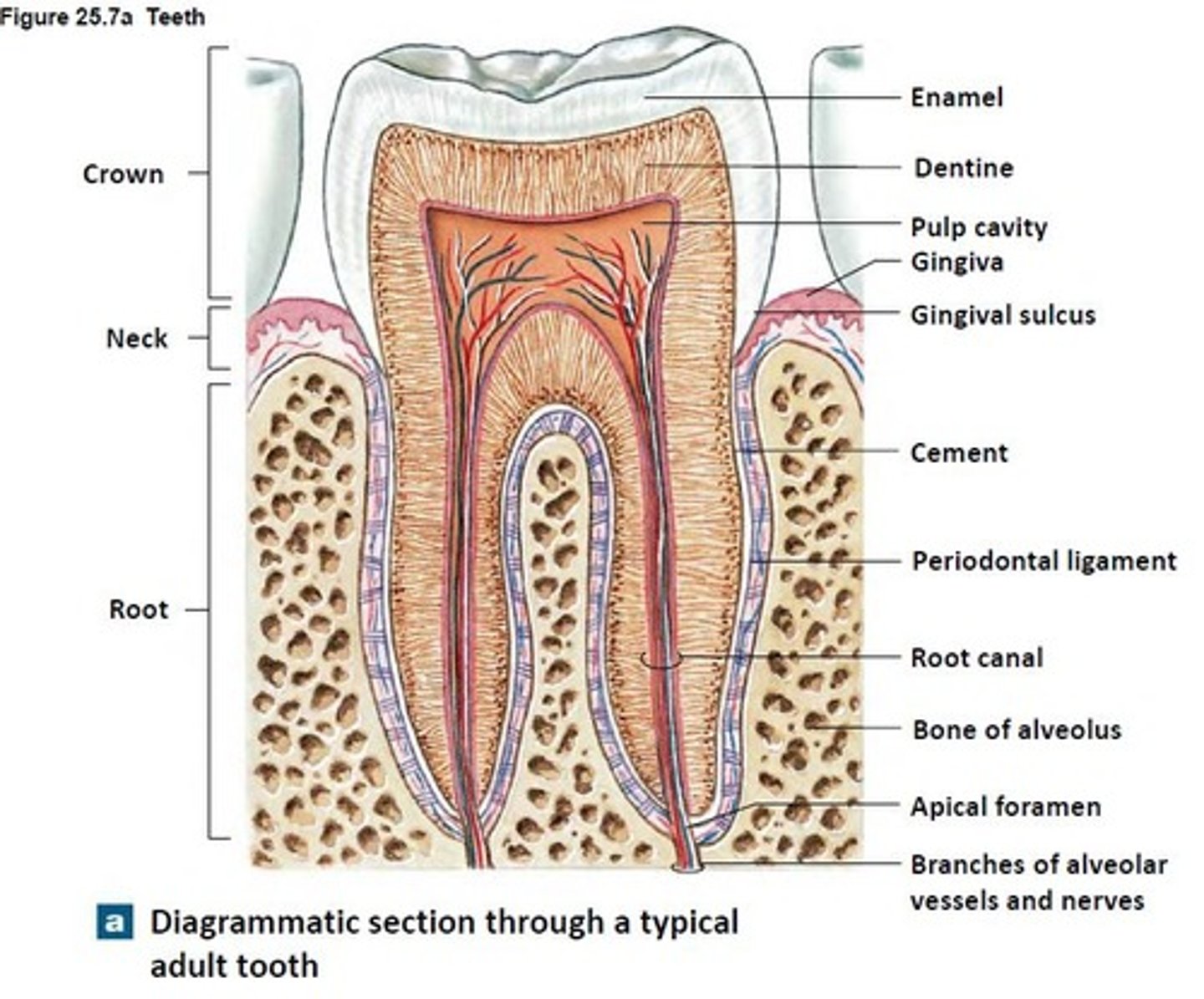
Root
portion of the tooth not visible in the oral cavity; embedded in the bone; keeps the tooth in its position.
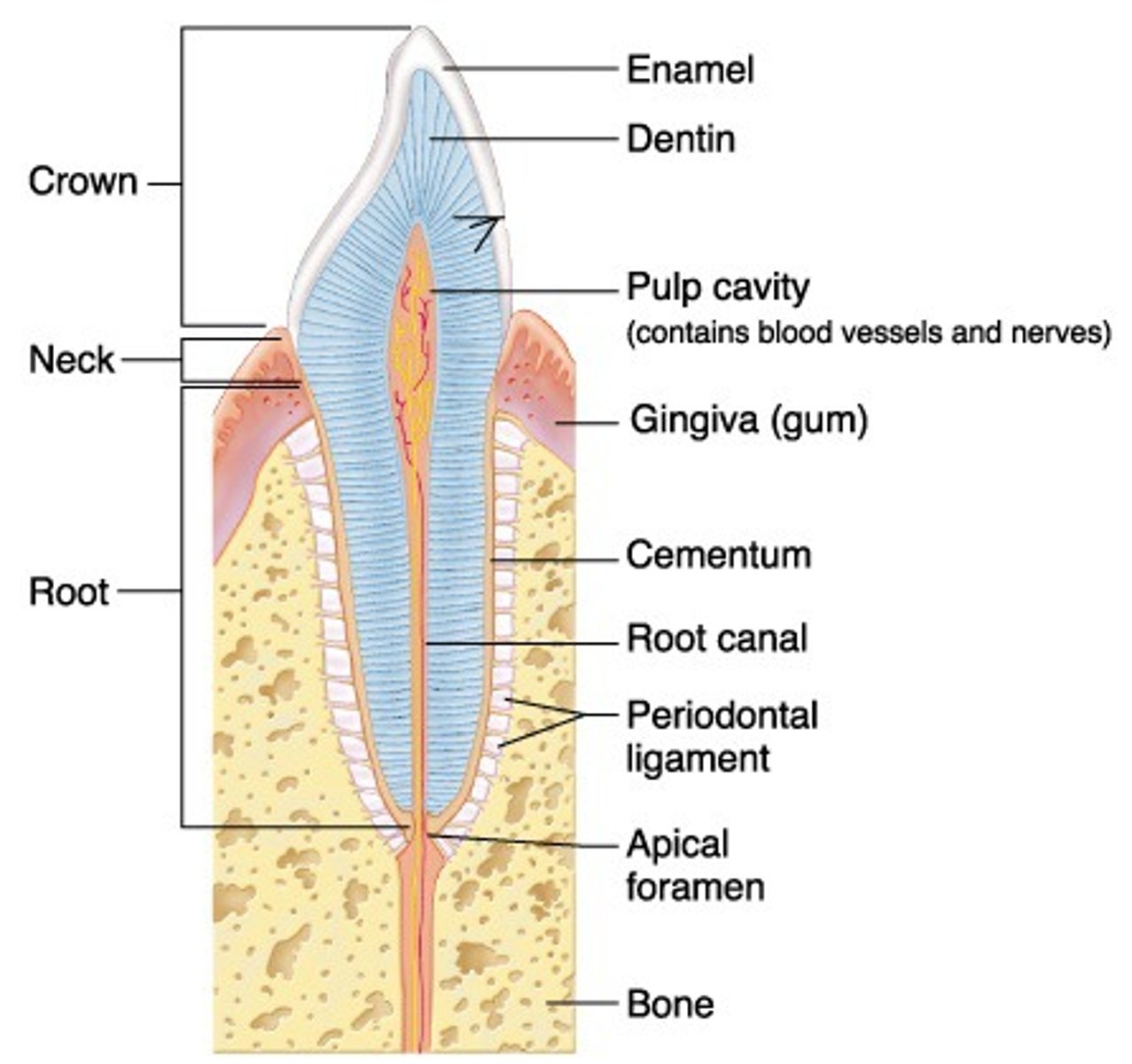
Cervical Line (Cementoenamel Junction)
line formed by the junction of the crown and the root.
"Neck' of the tooth
Mesial Occlusal Surface (MO)
surface of the tooth closest to the midline.
Facial Surface
surface of the tooth closest to the face; may be called the buccal or labial surface.
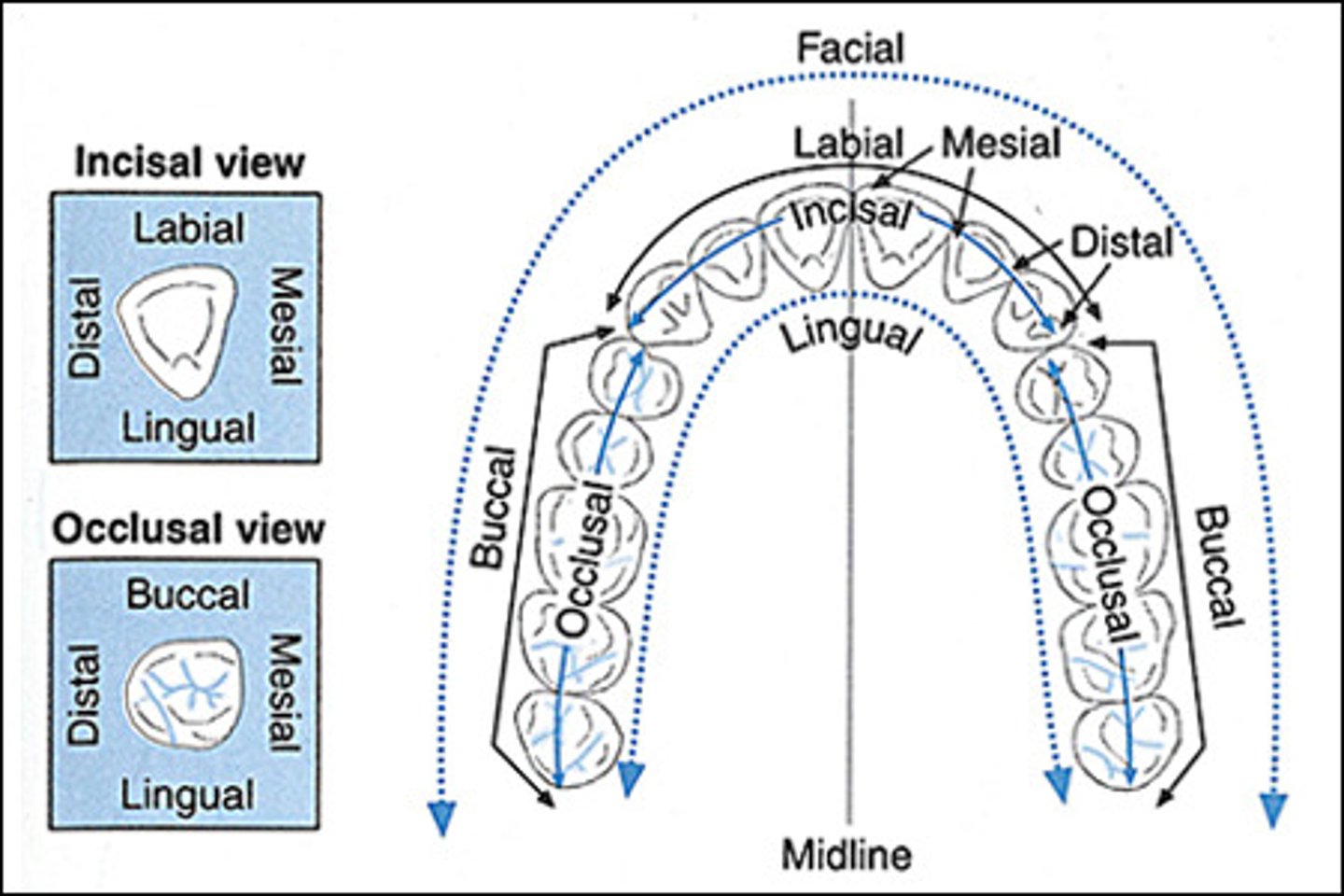
Buccal Surface
surface of a posterior tooth closest to the cheek.
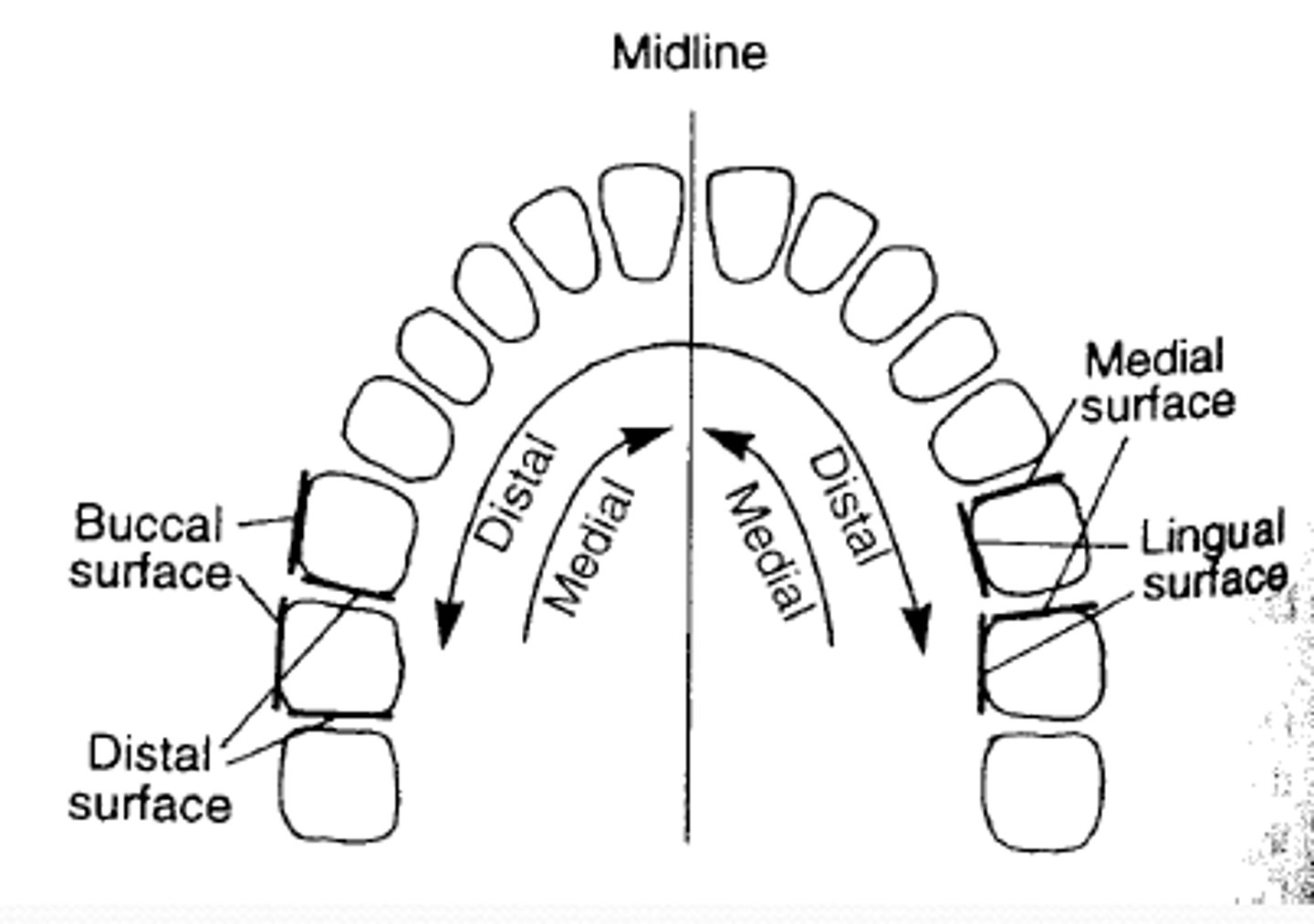
Labial Surface
surface of an anterior tooth closest to the lips.
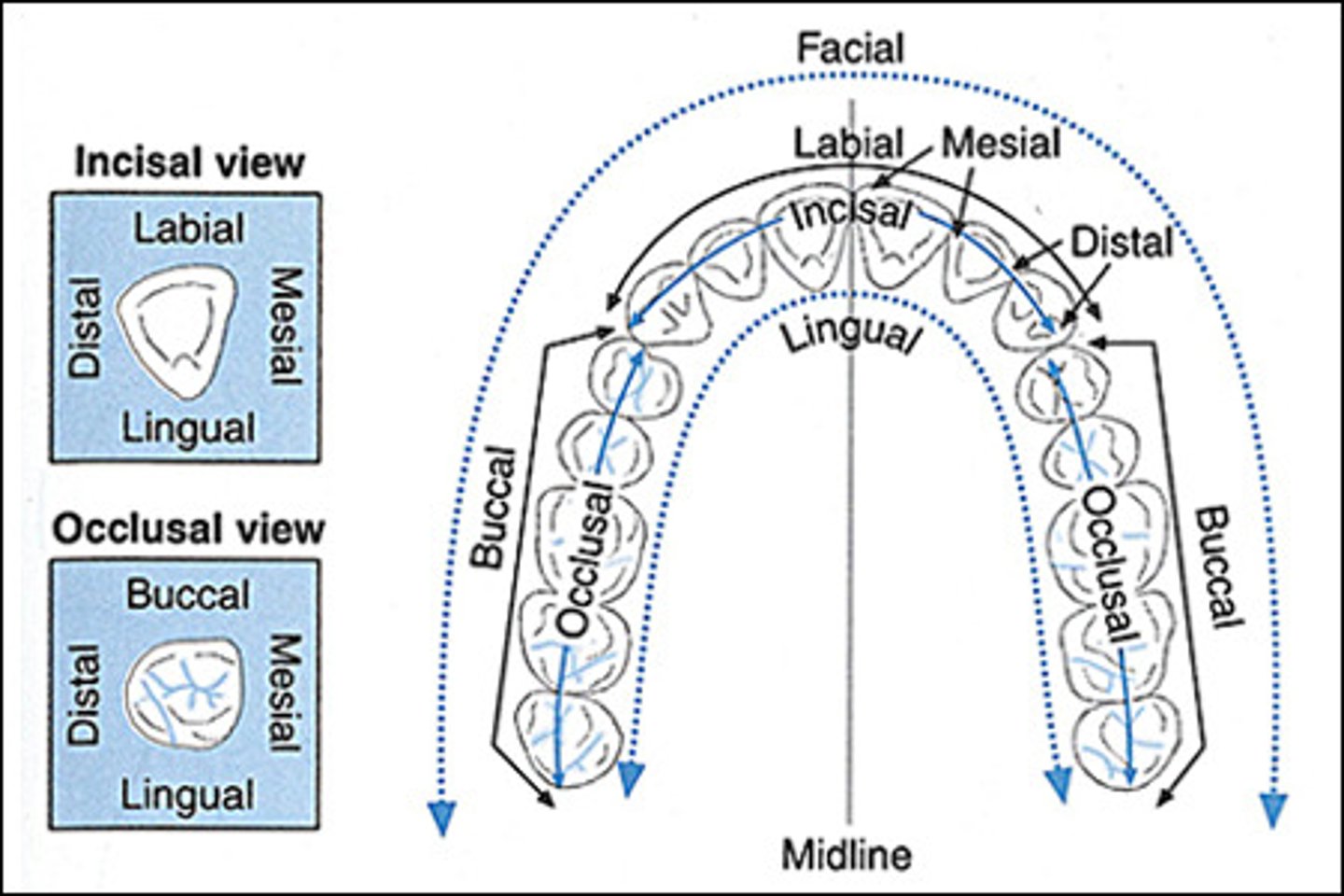
Occlusal
chewing surface of the posterior teeth (premolars and molars).
Cusp
on the occlusal surface; pointed elevation on the surface of the tooth.
Marginal Ridges
on the occlusal surface; boundaries or edges of the occlusal surface.
Development Grooves
on the occlusal surface; lines on the occlusal surface marking the junction of the development lobes.
Development Lobes
four or more special areas where the development of each tooth occurs.
Fissures
on the occlusal surface; deep development grooves resulting from incomplete fusion of the development lobes.
Incomplete Fusion
results in a large tooth crown.
Pit
on the occlusal surface; a small, deep depression on the surface of a tooth; usually found at the end of a development groove or at the junction of two or more grooves.
Fossa
on the occlusal surface; rounded depression on the surface of a tooth.
Lingual
surface of the tooth next to the tongue.
Proximal Surface
tooth surface next to an adjacent tooth; general term including mesial and distal surfaces.
Adjacent Tooth
teeth next to each other.
Contact Area
small area on the proximal surfaces where two adjacent teeth touch one another.
Interproximal Space
triangle-shaped space between adjacent teeth; normally filled with gingival tissue.
Gingiva
soft tissue surrounding the neck of the tooth; fills interproximal spaces; covers underlying alveolar bone.
Free Gingiva
immediately surrounds the neck of the tooth and is not actually attached to the tooth or underlying bone.
Gingival Sulcus
space between the free gingiva and the tooth.
A healthy mouth's space would be no deeper than 3 mm. It is an very accurate way of determining the periodontal health of the client.
Mucogingival Junction
merges with the attached gingiva and alveolar mucosa.
Alveolar Mucosa
covers the remaining alveolar bone, the interior of the cheek and the floor of the mouth.
Interdental Papilla
V-shaped gingiva that lies between teeth and fills the interproximal space.
Marginal Gingiva
the uppermost part of the free gingiva, overlapping the neck of the tooth.
Attached Gingiva
firmly bound to the underlying bone and extending apically (apex) from the base of the free gingiva.
This means the gingiva extends towards the root of the tooth.
Then merges with the alveolar mucosa.
Enamel
tooth tissue; outer layer of the crown of the tooth. It is the hardest tissue of the human body, white and cannot be repaired (from decay or worn away damage) or added to.
Cementum
tooth tissue; the thin, outer layer of the root of the tooth.
Similar in hardness of bone and is not as white as the enamel.
Dentin
tooth tissue; lies below and supports the enamel of the crown and cementum of the root.
Makes up the bulk of the tooth, is not as dense as enamel and is yellower than enamel and cementum.
Periodontal Ligament
fibrous membrane surrounding the cementum of the root and attached to the alveolar bone on the other side.
Suspends the tooth in the tooth socket.
A shock absorber for the pressure during cutting, grinding and chewing of food.
Alveolar Bone
the thin layer of bone making up the maxilla and mandible; is pierced by small blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves.
Mastication
the first stage in digestion when the teeth cut, chew and grind food.
Incisors
example of an incisal; (central incisors, lateral incisors and cuspid) have a relatively sharp edge used to cut (incise) food.
Have one root.
Maxillary incisors are larger than the mandibular incisors.
The mandibular central incisor is the smallest tooth in the mouth.
Canine (Cuspid)
example of an incisal; have one pointed cusp used for holding and tearing food.
Have one root.
Maxillary cuspid is the longest tooth in the mouth.
Premolar (Bicuspid)
example of an incisal and occlusal; generally have two cusps, one on the buccal surface and one on the lingual surface.
Have a broad occlusal surface used for chewing food.
Have one root except for the maxillary first premolar, which has two roots; one buccal and one lingual.
Molar
example of an occlusal; generally has four cusps and a broad occlusal surface used for chewing, crushing and grinding food.
Have four functional cusps, except for the mandibular first molar; has five.
Maxillary molars have three roots; mesiobuccal, distobuccal and lingual. Mandibular molars have two roots; mesial and distal.
The third molars (wisdom teeth) are the smallest of the molars; have fused roots and resemble either the first or the second molar in the same arch.
Mesiobuccal Root
maxillary molar root; found near the mesial portion of the tooth and the buccal side of the alveolar ridge; visible
Distobuccal Root
maxillary molar root; smaller than the lingual root; hidden behind the mesiobuccal root
Lingual Root
maxillary molar root; larger than the distobuccal root; visible; to the lingual side of the alveolar ridge.
Mesial Root
mandibular molar root; located toward the mesial side of the tooth.
Distal Root
mandibular molar root; located toward the distal side of the tooth.
Fused Root
roots of the third molars (wisdom teeth); root joined with another
Caries
dental decay; creates the need for a great number of dental procedures.
Major cause of tooth loss.
Decay Process
bacteria + sugar = acid
acid + tooth surface = decay
Acquired Pellicle
clear, sticky film formed within minutes on the teeth after brushing the teeth.
Forms usually near the cervical line and on the proximal surfaces.
First stage in plaque formation.
Provides a surface to which bacteria can easily attach, which is present in the oral cavity. Once attached, bacteria multiplies.
Bacteria combined with sugar in the food produces acids that decalcify tooth tissues, creating a cavity.
Decalcify
remove or dissolve minerals.
Cavity
the hole created due to the weakening of hard tooth tissue.
Gingivitis
gingival inflammation caused by the formation of toxins in plaque's bacteria.
Initial stage in periodontal disease.
With appropriate treatment and care, is reversible. If not treated, can progress to a more advanced stage of disease called periodontitis.
Periodontitis
affects the underlying supporting tissues and bone; occurs after gingivitis.
Fluoride
compound of fluorine; prevents tooth decay and cavities
Sealent
thin plastic coating the surface of the tooth to prevent decay and cavities.
Bass Technique
toothbrush begins with the facial of the maxillary molars.
Placed near the gingival margin at 45 degrees.
Light pressure, back and forth movement.
Bristles stroked towards occlusal surface.
Continued around maxillary arch.
Repeated for the mandibular teeth.
Repeated for the lingual surfaces of the maxillary and mandibular posterior teeth.
To clean the lingual surfaces, the head of the toothbrush is vertical and moves back and forth towards the incisal surface.
On occlusal surfaces, the bristles are flat against the surface and move in circular, scrubbing motions.
Tongue is brushed in a back to front sweeping motion.
Mandibular Right Quadrant
# l
Mandibular Left Quadrant
l #
Maxillary Left Quadrant
l _#_
Maxillary Right Quadrant
_#_ l
Universal System
approved by the American Dental Association; most common system in the United States.
Every permanent tooth is given a number from 1-32. Maxillary right; 1-8, maxillary left; 9-16, mandibular left; 17-24, mandibular right; 25-32 (clock-wise)
For deciduous teeth, letters A through T identify the primary teeth.
A right angle symbol identifies the quadrant and tooth number, which is written in the angle.
Palmer's System
used in some dental offices; mainly orthodontic and pediatric.
Permanent teeth are numbered from 1-8 in each quadrant beginning at the midline with the central incisor labeled number one and ending at the third molar labeled number eight.
Labeled from A to E in each quadrant's angle if using deciduous teeth.
Dental Treatment Area
equipped with a dental chair, dental assistant's chair, operator's chair, dental unit, operating light, fixed and mobile cabinets and an X-Ray unit.