bio 1st semester
1/285
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
286 Terms
Big Bang
13.7 billion years ago - formed Universe
Nebula Theory
5 billion years ago - formed Sun and solar system
Accretion
4.6 billion years ago - formed Earth
Cooling of the Earth
4 billion years ago - formed oceans
First living thing on our planet (bacteria)
3.8 billion years ago (simple cell prokaryotes)
Photosynthetic Bacteria (cyanobacteria)
3 billion years ago
The Endosymbiotic Theory
1.5 billion years ago (multicellular)
Making of Eukaryotic cells
1.5-2 billion years ago
Multicellular life
1 billion years ago
Mammals
200 million years ago (Mesozoic)
Death of Dinosaurs
65 million years ago (KT extinction)
Neanderthal dies
25,000 years ago
Humans
200,000 years ago (Cenozoic)
The #1 evidence for the Big Bang
Cosmic Background Microwave Radiation
Accretion
The process of growth or increase, typically by the gradual accumulation of additional layers or matter
The compound of water came to the Earth in two ways
Meteorites and comets
Early atmosphere was toxic, some compounds present were
Carbon monoxide, Hydrogen sulfide, and Hydrogen Cyanide
Denser elements are lower in the Earth
Crust > Mantle > Core
Plate Tectonics
The Earth's crust is broken into pieces we call plates and they move.
Convergent
Plates moving towards each other
Divergent
Plates pulling apart
Transform
Plates sliding past each other
Unicellular
Single cell
Anaerobic respiration
Respiration without oxygen
Aerobic respiration
Respiration with oxygen
Prokaryotic
Cells without nucleus; bacteria
Eukaryotic
Cell with a nucleus and small organs called organelles; Animals, plants, fungi, protista
Prokaryotic
Always unicellular
Eukaryotic
Often multi-celled organisms
The Endosymbiotic Theory
Proposes that eukaryotic cells arose from living communities formed by prokaryotic organism communities
Earth's history is broken into 2 geological categories
Eras 2. Periods
4 Eras
Pre-Cambrian (oldest) 2. Paleozoic 3. Mesozoic (age of reptiles and dinosaurs) 4. Cenozoic (youngest and age of mammals)
Mammals
Warm-blooded, give live birth, homeostasis, and have body hair
Extinction toward the end of Pre-cambrian time caused by excessive oxygen in the atmosphere
Killed off most prokaryotes: Cyanobacteria/Oxidation crisis
Greatest extinction in the history of our planet due to the formation of Pangea End of Paleozoic Era
Permian extinction
Complex Cells/Eukaryotes
1.5-2 billion years ago
Extinction caused by meteorite impact at the end of the Mesozoic era
K-T extinction
Why is mass extinction good and what % of living things have gone extinct?
Mass extinction is good because it provides ecological opportunities for weaker species. More than 99% of living things have gone extinct
Oldest era
Pre-Cambrian
2nd era
Paleozoic
3rd era
Mesozoic
Youngest Era
Cenozoic
3 gases in today’s atmosphere
Nitrogen, Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide
Fossil
The remains of a once living thing
Fossil record
All information about past life
What are the steps to becoming a fossil?
Organism Dies
Covered quickly
Becomes fossilized
What type of rock?
sedimentary
Fossil Record cont.
The fossil record provides evidence about the history of life on Earth. It also shows how different groups of organisms, including species, have changed over time. (Over 99% of all species that have lived on Earth have gone extinct)
Dating fossils (determining the age of fossils) using:
Relative dating
Radioactive dating
Relative dating
The age of a fossil is determined by comparing its placement with that of fossils in other layers of the rock. (index fossil)
Radioactive dating
Scientists use radioactive decay to assign an absolute age to rocks. Some elements are radioactive and steadily break down into non radioactive elements.
Radioactive dating is the use of?
half-lives to determine the age of a sample
Half-life
the length of time required for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay into daughter atoms and parent atoms.
Isotope
an atom of an element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
What do protons define?
Protons define the element
All life depends on 4 macromolecules which are:
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
Mono-
one
Di-
two
Poly-
3 or more (many)
Monomer
Basic unit
Polymer
3 or more monomers
Polymerization
The process by which monomers join together to form a polymer
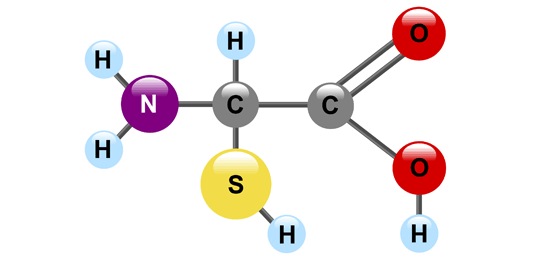
Protein’s monomer
monopeptide (1 amino acid)
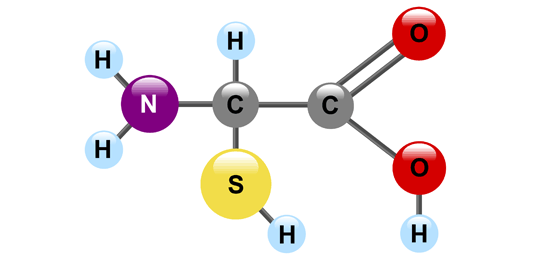
Protein’s polymer
polypeptide (many amino acid)
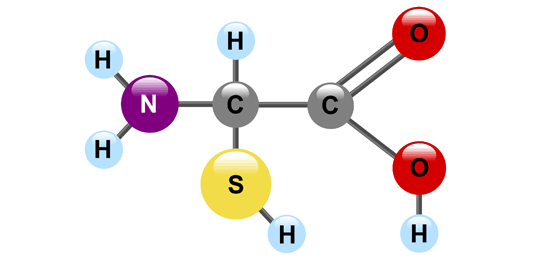
Protein’s job/purpose
Control the rate of reactions, effect development, help form muscles and bones, transport substances, and fight disease (enzymes are protein)
Food with protein
Animal products, nuts/seeds, beans, plants (minimally)
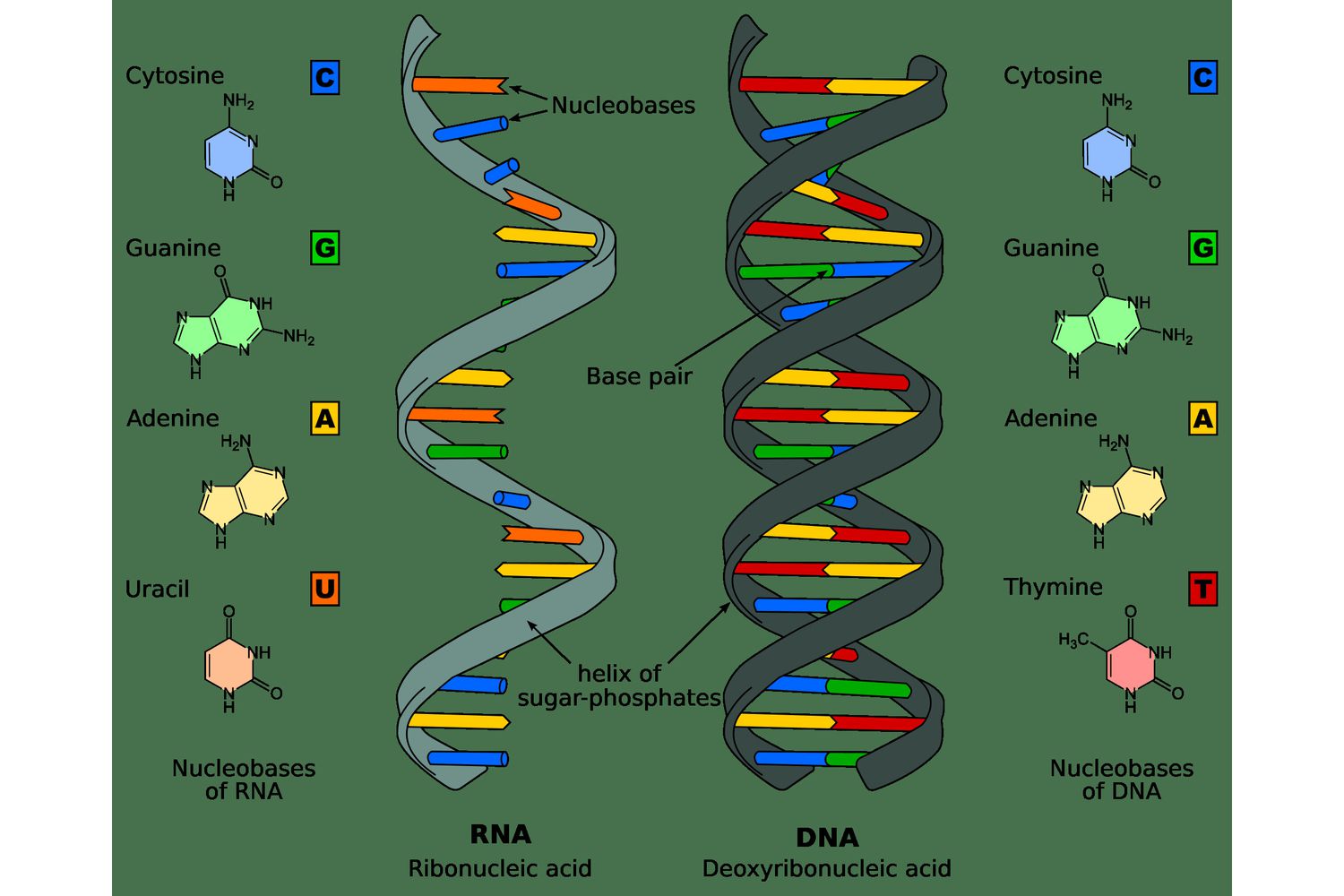
Nucleic acids monomer
Nucleotide
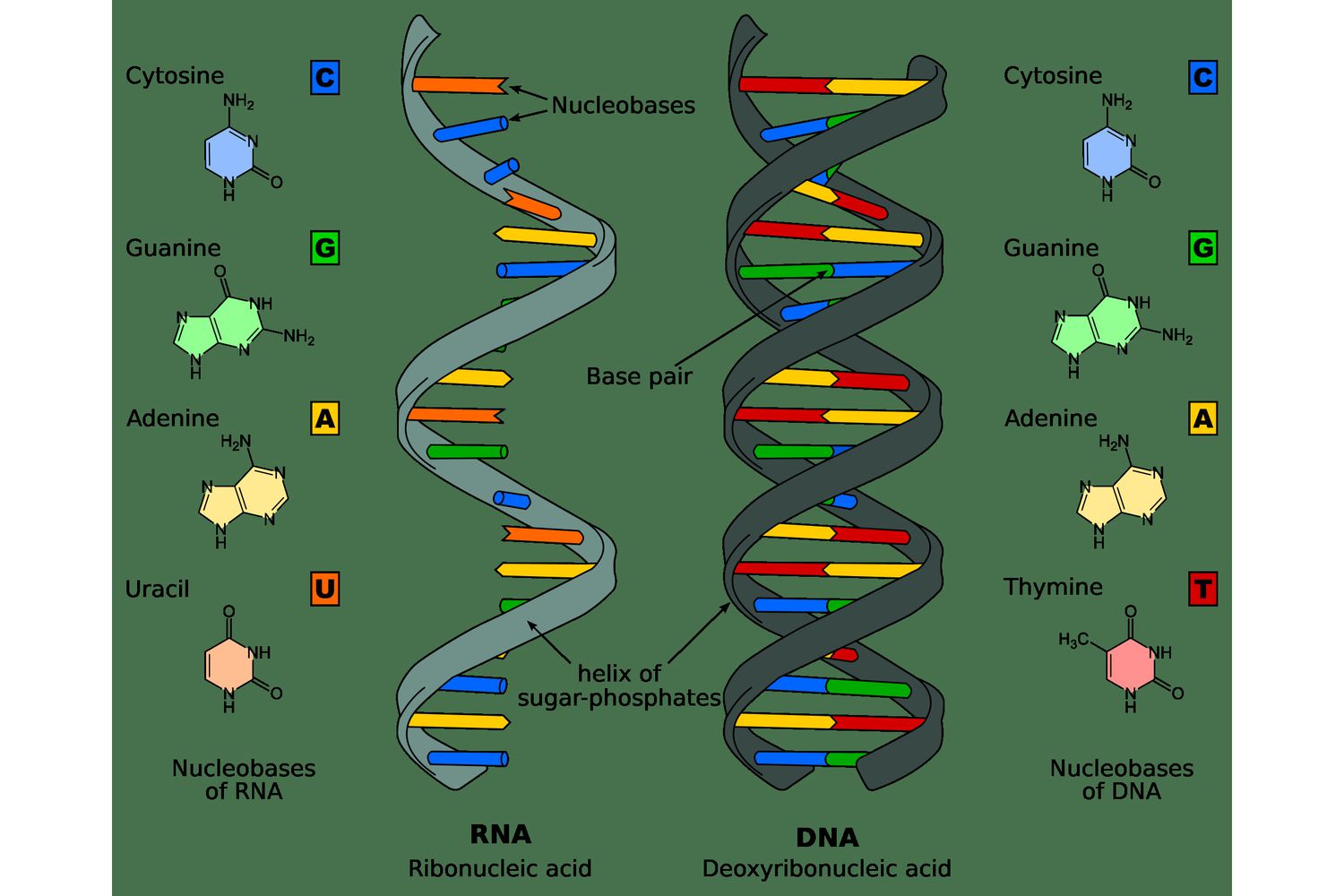
Nucleic acids polymer
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA), Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
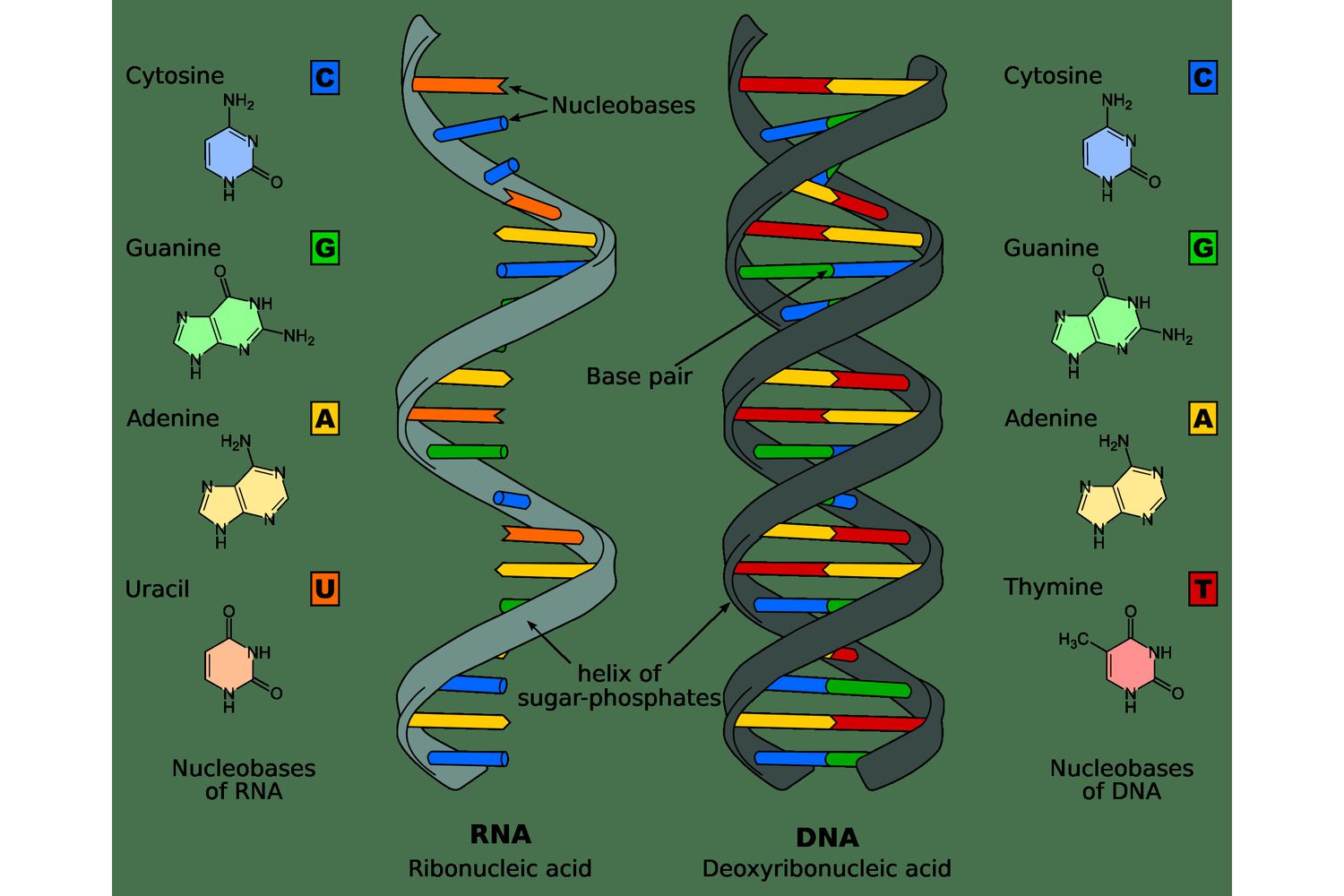
Nucleic acids job/purpose
Store and transmit genetic information
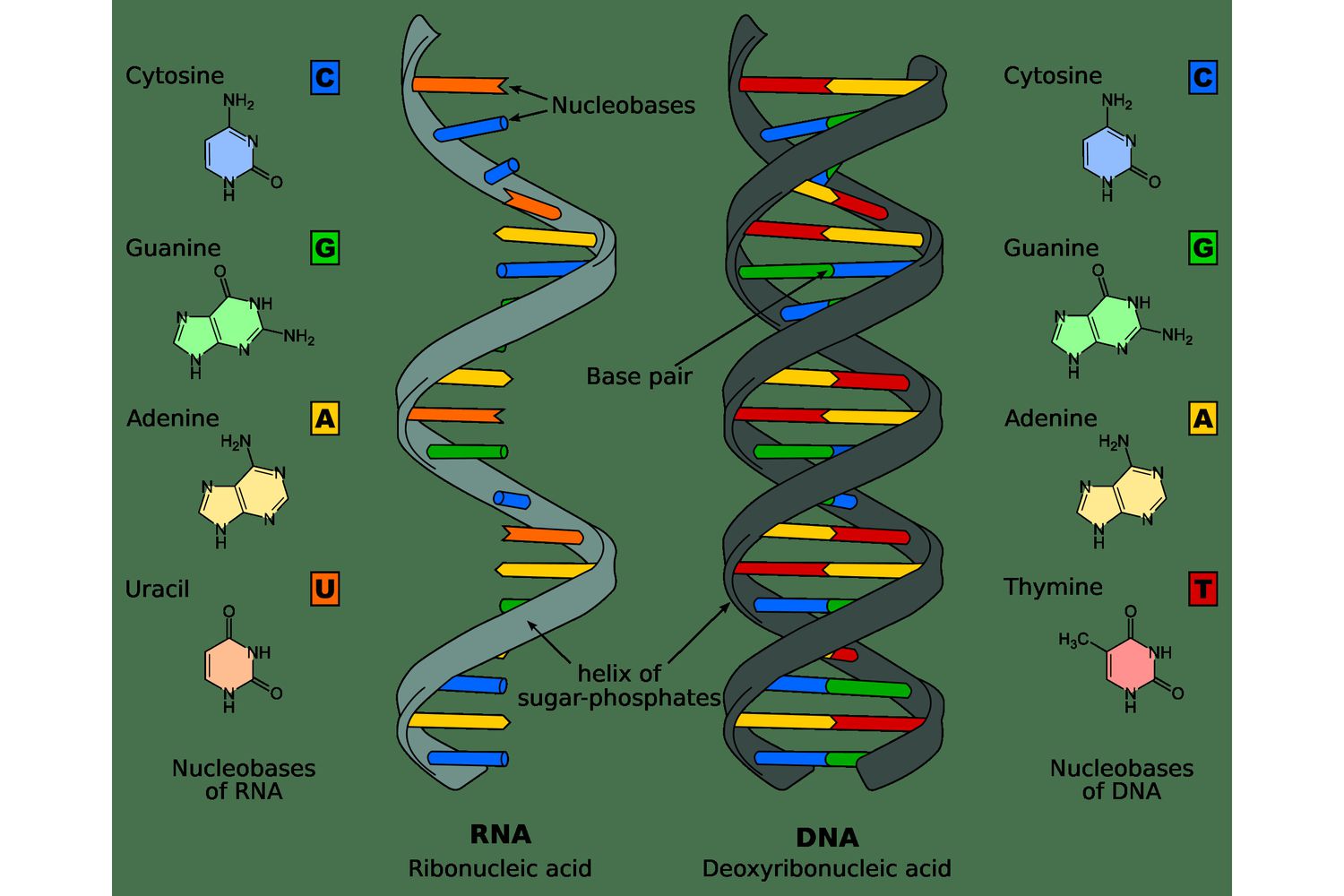
Nucleic acids food
Anytime you eat a once living thing, you are eating DNA
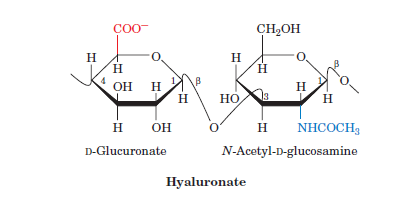
Carbohydrate monomer
monosaccharide (1 sugar)
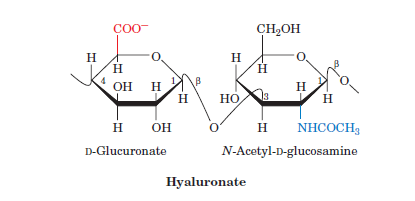
Carbohydrate polymer
polysaccharide (many sugars)
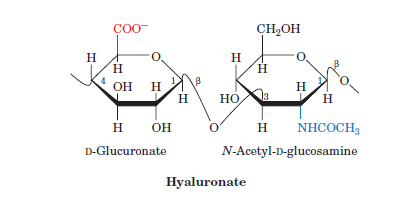
Carbohydrate jobs/purpose
provide the body with glucose, which is converted to energy used to support bodily functions and physical activity.
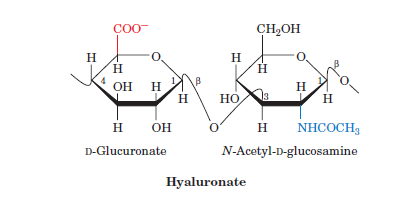
Carbohydrate food
fruit = fructose, milk = lactose, candy = sucrose, plant structure = cellulose
Lipid subunits
Glycerol, fatty acid
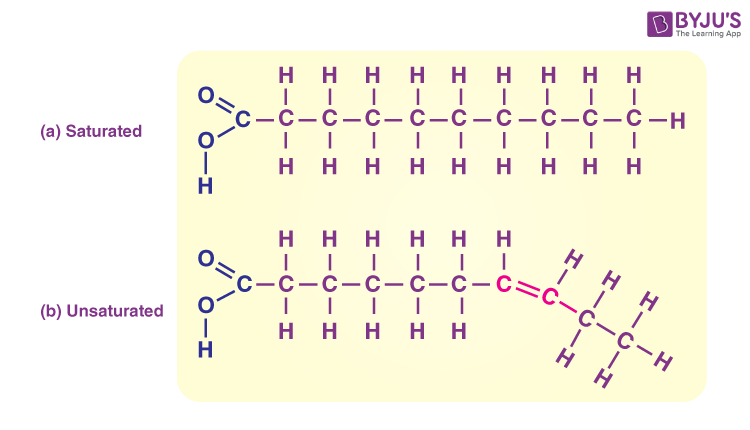
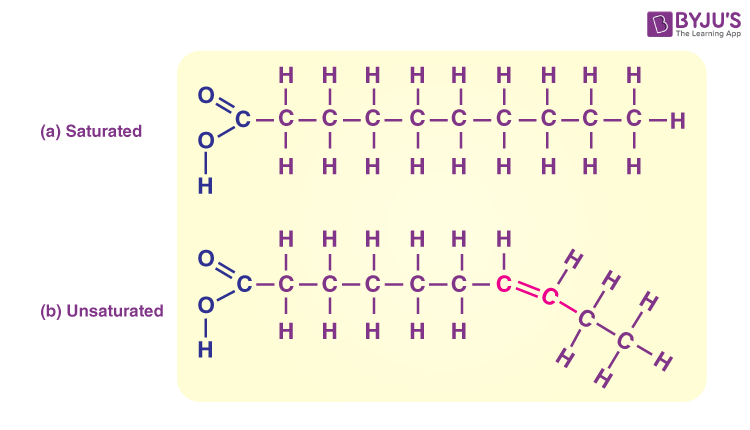
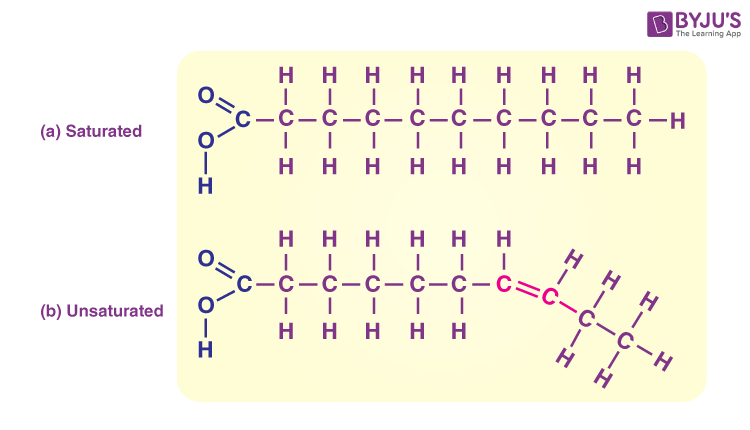
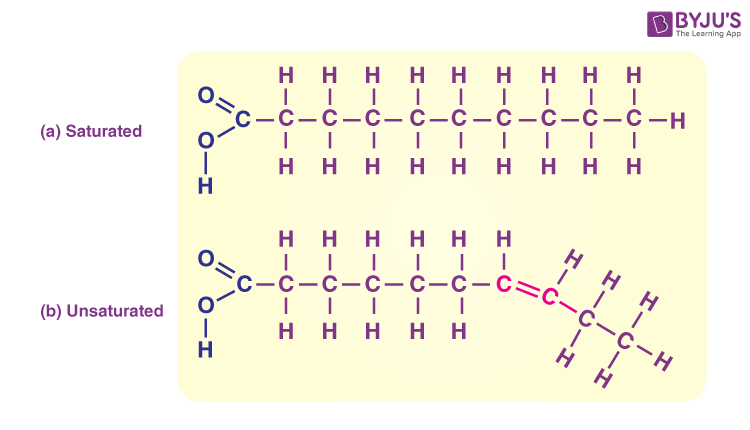
Lipid saturated
Saturated fat (from animals) solid at room temp
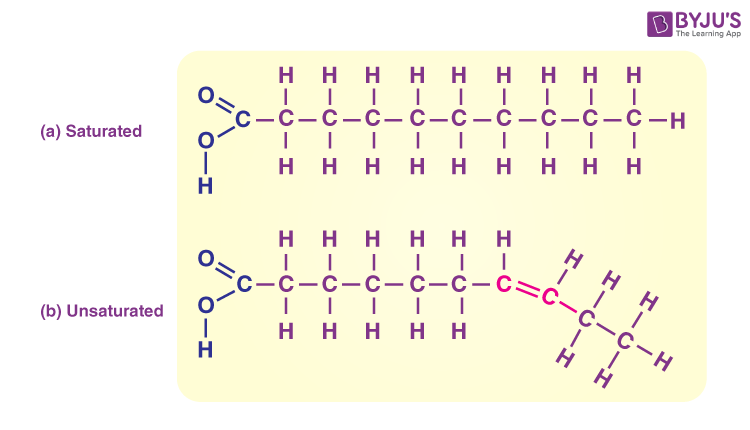
Lipids unsaturated
unsaturated fat (from plants) liquid at room temp
Lipids common categories
fats, oils, waxes, and steroids
Lipids job/purpose
store energy, chemical messengers, and biological membranes
Open system
moving in 1 direction
Closed system
recycle
Sunlight/energy is a _ system
open
Carbon cycle and nutrients are _ systems
closed
Why is carbon important for all living things?
Carbon is the backbone of all organic molecules
How does the Industrial Revolution deal with the Carbon Cycle?
During the Industrial Revolution, they burned a large amount of fossil fuels, putting Carbon into the atmosphere.
There are _ carbon stores
7
There are _ carbon processes
11
Atmosphere→
Air
Lithosphere→
Land
Hydrosphere→
Water
Biosphere→
Living things
Carbon Stores/Reservoirs
store carbon
Carbon processes
how carbon goes through the cycle
Source
puts out more carbon than it takes in (output)
Sink
takes in more carbon than it puts out (input)
How is carbon stored underground
in the form of coal, oil, and gas
When there is too much carbon in the atmosphere
the heat from the sun is trapped causing global warming/climate change
How are fossil fuels created
over thousands of years of being compressed underground
Burning fossil fuels produces carbon by..
the process of combustion
Carbon in the atmosphere mostly consists of
CO2 (carbon dioxide)