2. krebs cycle
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
KREBS CYCLE- DIAGRAM
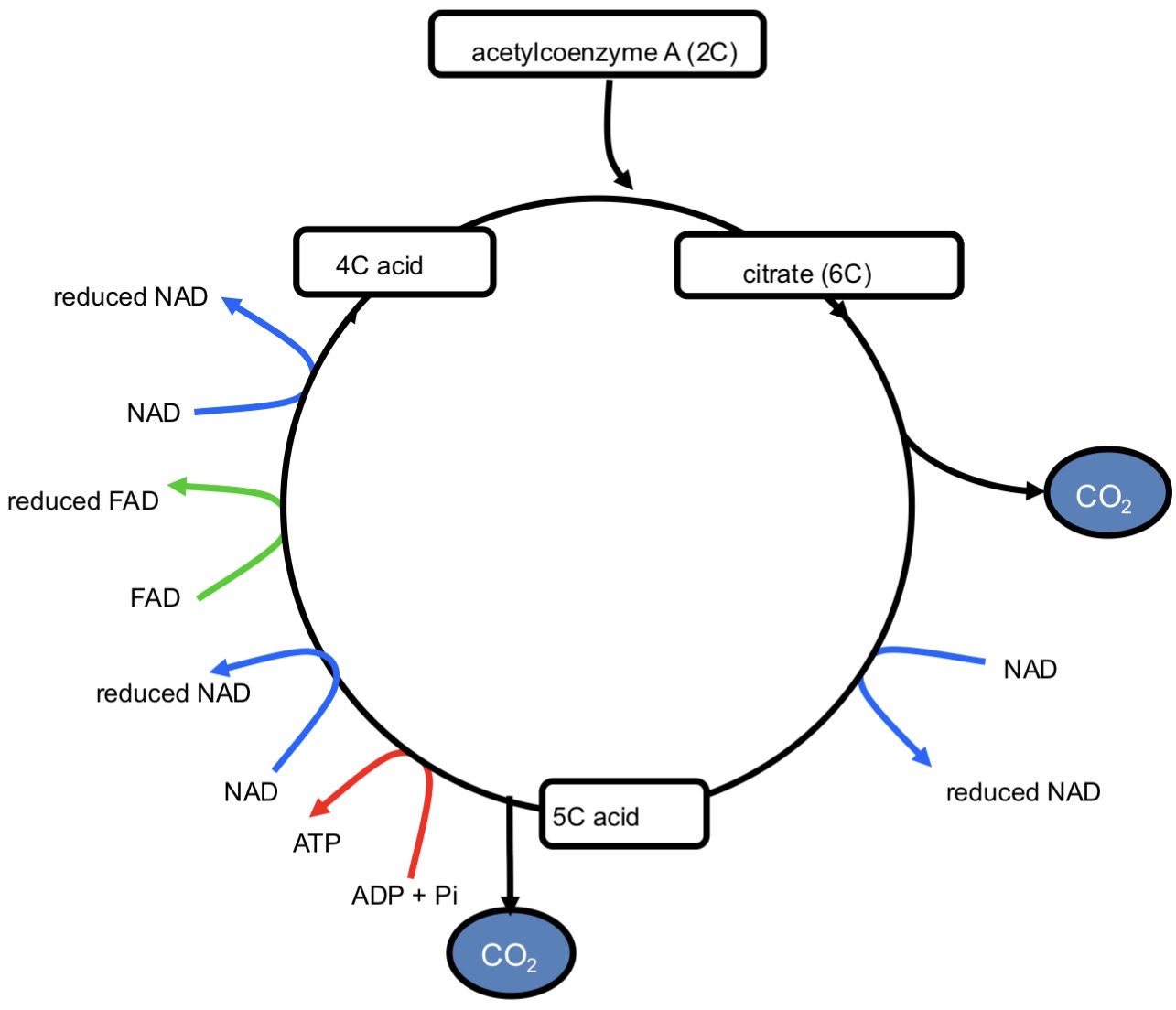
KREBS CYCLE- 1
acetylcoenzyme A (2C) combines w/ a 4C compound in mitochondrial matrix
6C compound called citrate is formed
KREBS CYCLE- 2
citrate is decarboxylated by removal of CO2
KREBS CYCLE- 3
citrate is oxidised by removal of hydrogen
hydrogen is accepted by NAD to form reduced NAD
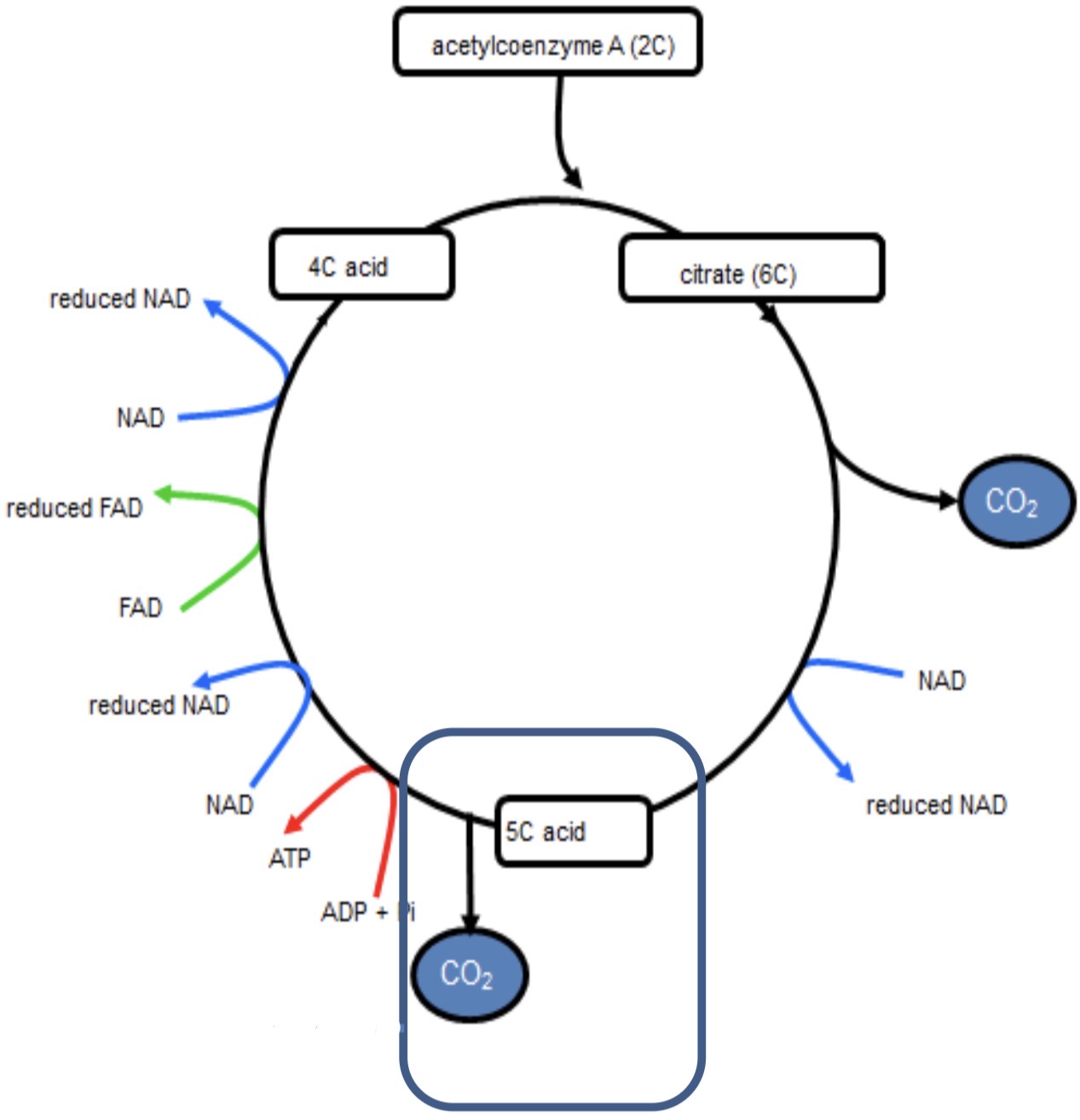
KREBS CYCLE- 4
5C compound (acid) is formed
5C compound is decarboxylated by removal of CO2
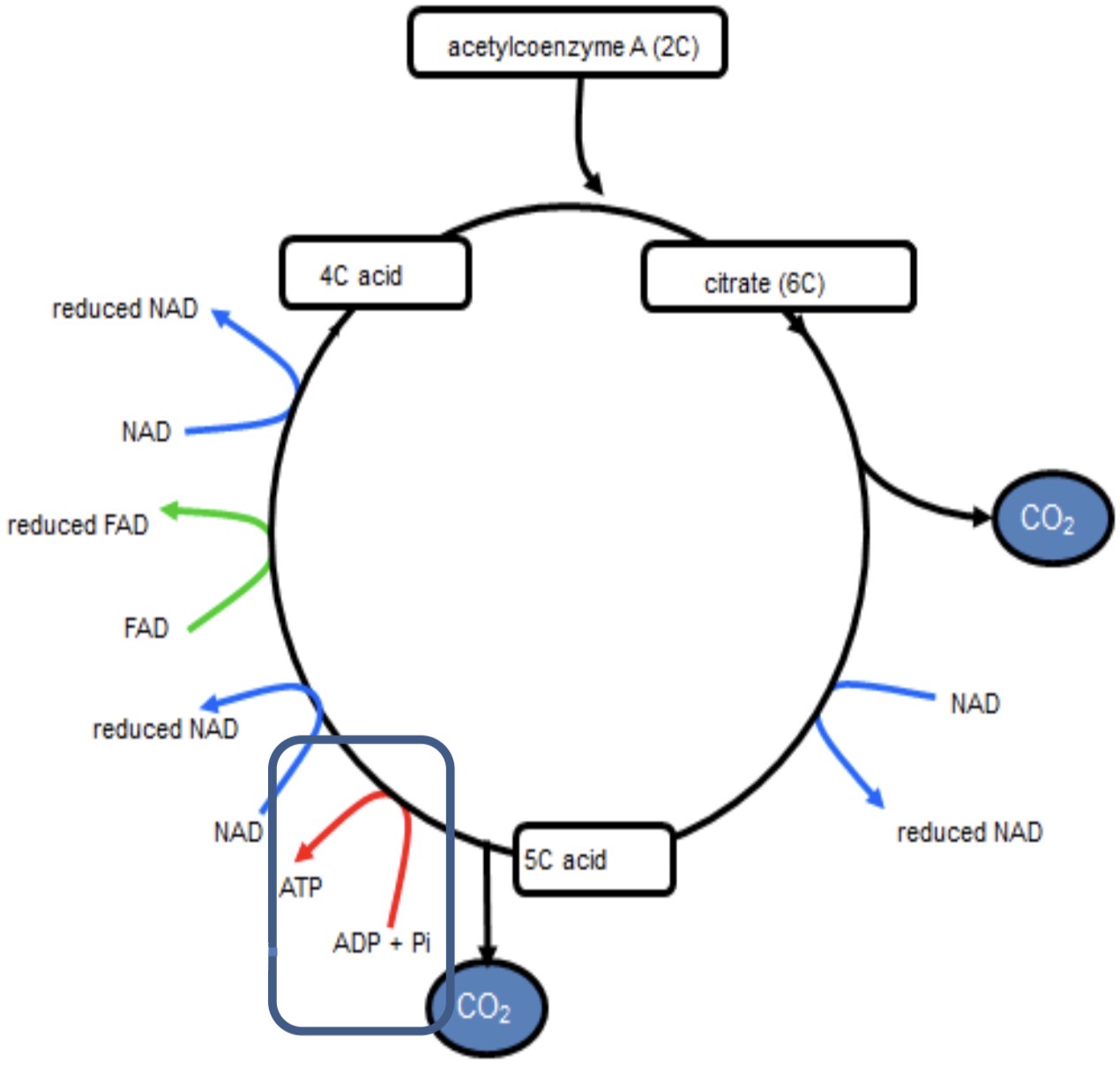
KREBS CYCLE- 5
during conversion of 5C compound into 4C compound, 1 molecule of ATP is synthesized by combining ADP + Pi- substrate level phosphorylation
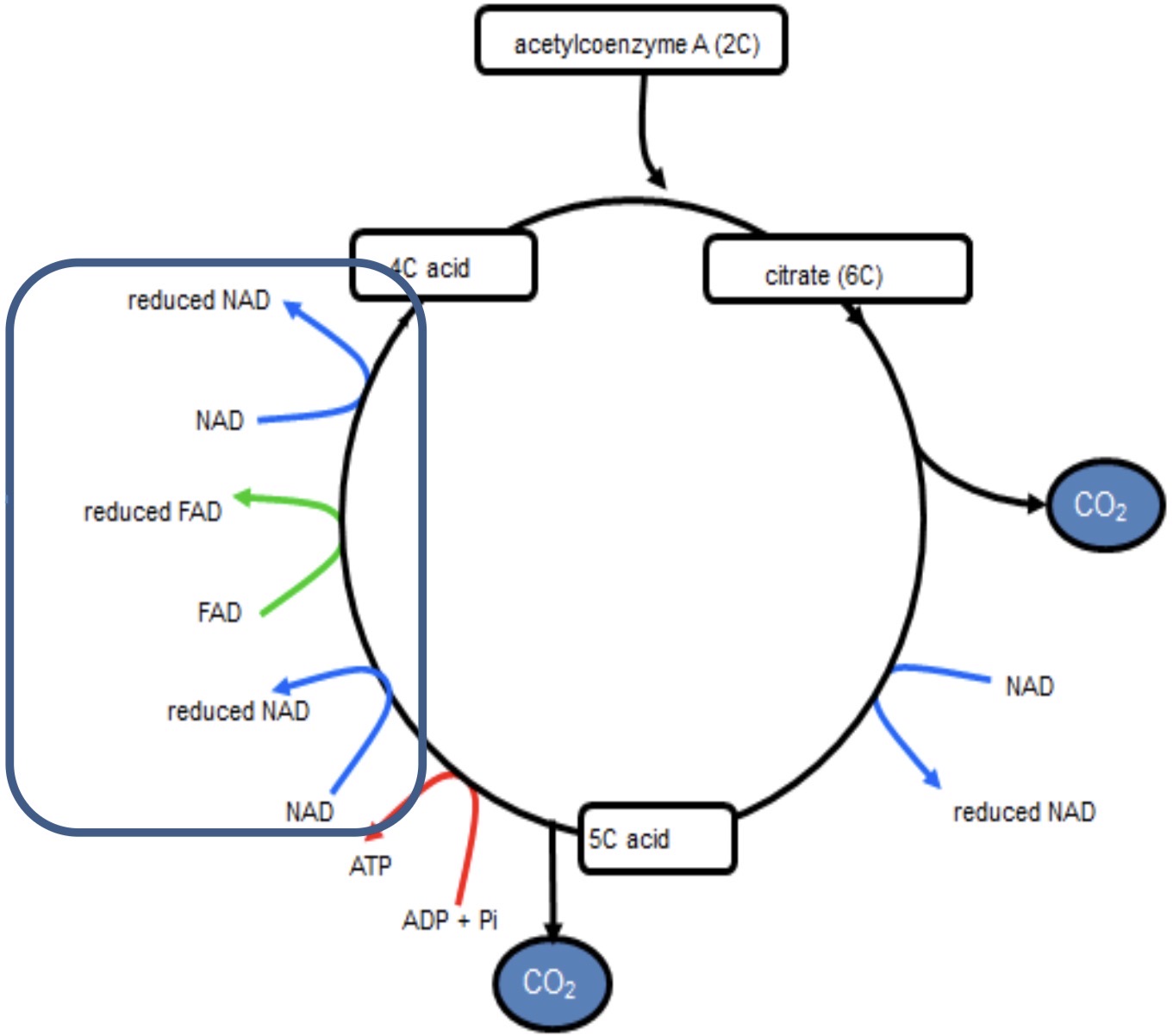
KREBS CYCLE- 6
5C compound is oxidised by removal of hydrogen
hydrogen accepted by coenzymes NAD and FAD and are reduced
4C compound regenerated and cycle restarts
KREBS CYCLE- PRODUCTS
2 turns of cycle for every glucose molecule broken down in glycolysis
so for every glucose molecule, Krebs cycle produces:
2 ATP
4 CO2
6 reduced NAD
2 reduced FAD
DEVELOPING KREBS CYCLE-1
before Krebs discovery, experiments by Thunberg, Batelli and Stern showed that minced animal tissues contained substances transfered H atoms from specific intracellular organic acids (including citrate) to methylene blue dye, reducing it to a colourless form
now know these substances are dehydrogenases
DEVELOPING KREBS CYCLE-2
Albert Szent-Gyorgyi extended studies by describing sequence of enzymic reactions involving oxidation of organic acids which are part of cycle
krebs then worked out cyclic nature of reactions by realising the 2C molecule combined with 4C to form citrate (6C)
used different inhibitors that brought about halt of specific reactions to work out which compounds were involved
also realised that series of reactions he proposed could take place at a fast enough rate to account for the known pyruvate and O2 use of tissues