Ideologies - Social Studies 30-2
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Beliefs
what an individual accepts as being true
capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit.
collectivism
An ideology based on the primacy of collective welfare. The government controls the economy by owning properties and directing economic activities in the interest of the collective benefit, rather than individual benefit. Best for all.
communism
a political theory derived from Karl Marx, advocating class differences and leading to a society in which all property is publicly owned and each person works and is paid according to their abilities and needs.
Charter of Rights and Freedoms
a Canadian government document that lists the rights and freedoms of Canadian citizens. This addresses free speech, freedom of the press, legal rights, language rights, mobility rights, and much more.

classical liberalism
an ideology based on increased rights and freedoms for all individuals
culture
beliefs, customs, practices, and social behaviours of a particular group of people

economic individualism
an economic theory based on the idea that each person in society is responsible for meeting her or his own needs
economic value
the importance placed on money and possessions
economic collectivism
an economic theory based on the idea that a country's resources should be government-owned and divided equally among the people
Great Law of Peace
the oral constitution of the Haudenosaunee Confederacy. Some historians believe the American Constitution is based on the Great Law of Peace.
Humanitarian
to act in ways that benefit society. Humanitarians care for the underprivileged and find ways to help people in need.

Industrial Revolution
a time of change that began in Great Britain in approximately 1750. This period was marked by a great transformation in the way goods were made.

Intervention
the act of getting involved in another person's affairs. In a market economy, government will intervene when there are unfair business practices.
invisible hand
a term coined by Adam Smith to describe the self-regulating nature of the economic marketplace. The pursuit of profits guides entrepreneurs to determine what consumers want.
identity
an expression of who an individual is and what is important to that individual

individualism
an ideology based on the primacy of individual freedom. Property is owned by private individuals and economic activity is the result of competition by individuals in the marketplace.

ideology
a system of thought that includes beliefs and values
issue
a question about the direction society should take

language
a body of words that is common to a people of the same community, nation, or cultural group
labour union
an organization of workers who join together to improve working conditions, salaries, and rules about hiring, firing, and employment benefit

Luddites
a group of workers in England who, from 1811-1816, organized themselves to destroy machinery because they believed the machinery created unemployment
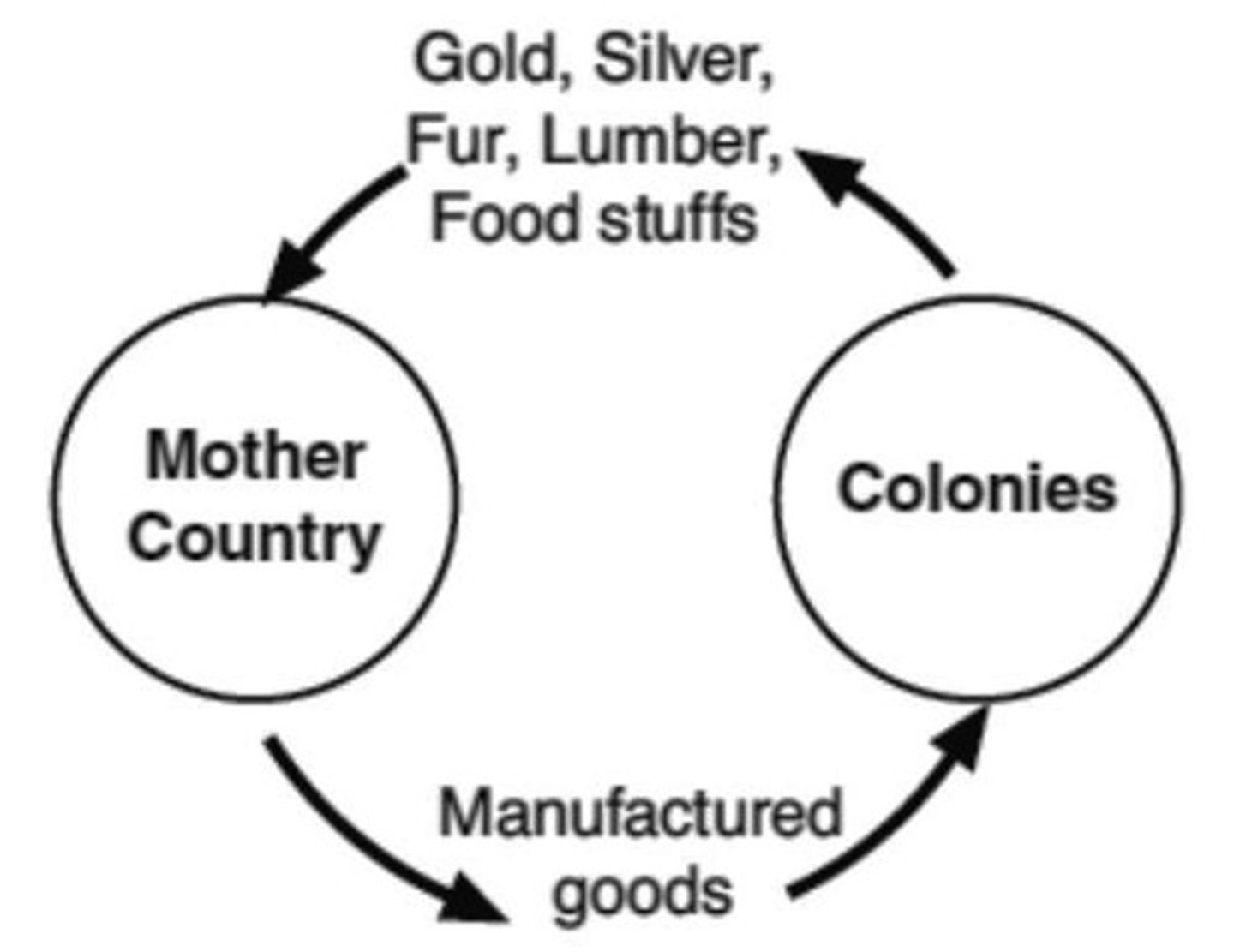
Mercantilism
an economic system based on the beliefs that a country should export more goods than it imports. Entrepreneurs/countries benefit from exporting & trading goods to new markets.
minority rights
government's consideration of the needs of individuals with different thoughts and beliefs than the majority. Democratic governments must consider the needs of all individuals in society, not just the needs of the majority of people.

Needs
products/items essential to the well-being of an individual

Pluralism
the belief that all groups have the right to exist alongside one another. Pluralists recognize that there are different social groups and that all groups have rights.

political spectrum
a continuum that allows governments to be compared to other governments. The amount of government control a government exercises on its people determines where the government is on the political spectrum. Political systems on the left side of the spectrum typically have more government control. Political systems on the right side of the spectrum typically have less government control.

political value
the importance government places on issues like taking care of the people, taking care of the environment, and treating people equally

rule of law
the idea that all individuals are equal before the law; laws, not individuals, rule the land

social value
the importance placed on concern for others and how others are treated
social contract
a written or oral contract that says individuals agree to follow established laws

socialist
a person who believes in equal ownership of all land and means of production
suffragette
a person who supported women's voting rights

values
ideas and beliefs that are important to an individual
worldview
a collection of beliefs held by an individual or group
wants
products desired by consumers that are not a necessity of life

welfare state
an economic system that places great importance on the health and security of its citizens
radical
An extremist of the political left, one committed to making fundamental changes in society and government. - Radicals believe violence is justified in order to create the society of the future.
Reactionary
An extremist of the political right who favors a return to traditional institutions and values of the past.
Thomas Hobbes
believed that people are born selfish and need a strong central government. Give up freedom for security.

John Locke
17th century English philosopher who opposed the Divine Right of Kings and who asserted that people have a natural right to life, liberty, and property. Less government interference, and it should protect rights & freedoms.

Charles Montesquieu
18th century French philosopher that argued for separation of powers into legislative, executive, and judicial realms. People need to be involved in government, in order for it to work.

Jean Jacques Rousseau
A French philosopher who believed that human beings are naturally good & free & can rely on their instincts. The government should exist to protect common good, and be a democracy. Social Contract.

John Stuart Mill
A philosopher who argued liberty and free speech (also for women which was radical at the time) over unlimited state control. Questioned unregulated capitalism. The government should take action, when necessary, to protect the workers.
